Economies and diseconomies of scale
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Economy of scale - definition
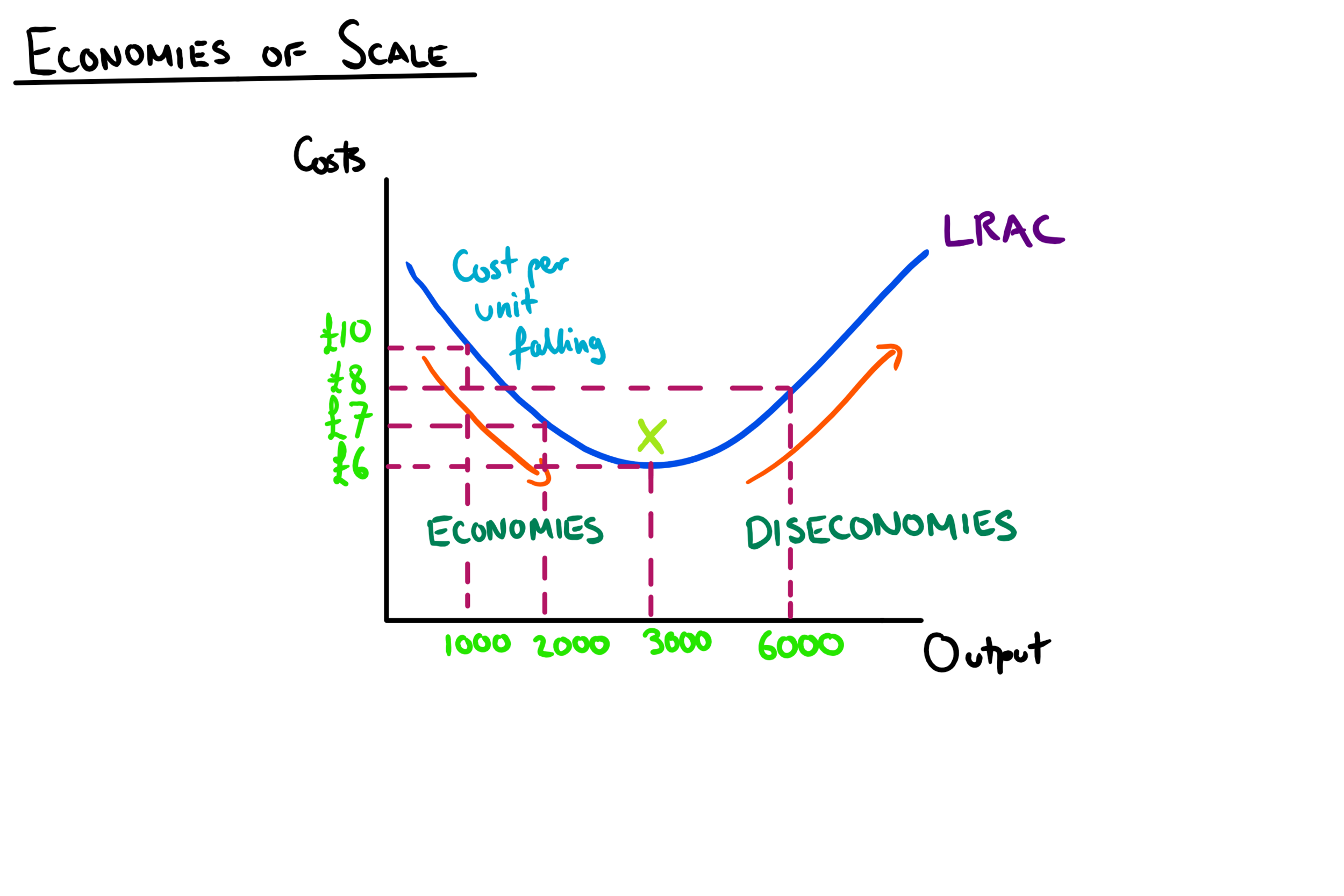
As a firm grows it is able to increase its scale of output, generating efficiencies which lower its average cost.
Diseconomy of scale - definition
After a certain point, average costs will start to increase as scale increases.
Long run avg. cost curve
Minimum point - minimum efficient scale, where avg costs are lowest - the optimum level of production
All internal economies of scale are fully exploited
Types of Internal economy of scale : Really Fun Mums Try Making Pies
Risk bearing
Financial
Managerial
Technological
Marketing
Purchasing
Risk bearing - definition
When a firm is larger they can expand their production range, therefore they can spread the cost of uncertainty as have other parts to fall back on if one fails.
Financial - definition
Banks are willing to lend loans more cheaply to larger firms, as less risky, so credit is cheaper
Managerial - definition
More able to specialise an employ supervisors, lowering their AC
Technological - definition
Larger firms can invest in more advanced and productive machinery and labour
Marketing - definition
Can divide marketing budget across larger outputs so avg marketing costs per unit is less than that of a smaller firm
Purchasing - definition
Larger firms can bulk buy which means each unit will cost them less, higher buying power
External economies of scale
Factors outside the firm, but on an industry scale:
geographic cluster
Transport links
Skilled labour
Favourable legislation
Types of diseconomies of scale
Control - it becomes harder to monitor how productive the workforce is as the firm becomes larger
Coordination - harder to coordinate every worker with 1000s of employees
Communication - workers may feel alienated and excluded as the firm grows, leading to fall in productivity.
Short vs long run avg cost curves
Short run - day to day operations
Long run - firms can plan to increase the scale of production
What happens to firms’ cost curves when scale increases
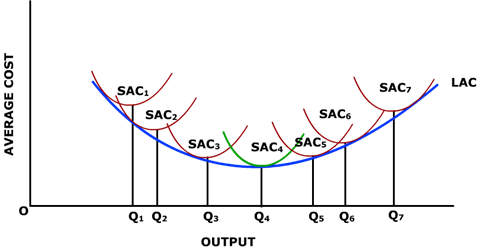
In economies of scale, firms move onto a new SRAC with lower unit costs
How are SRAC and LRACs related
The LRAC is the line of best fit between the lowest points of the SRAC curves
Where does LRAC meet the marginal cost curve
At the MES, as for each future unit produced average cost increases
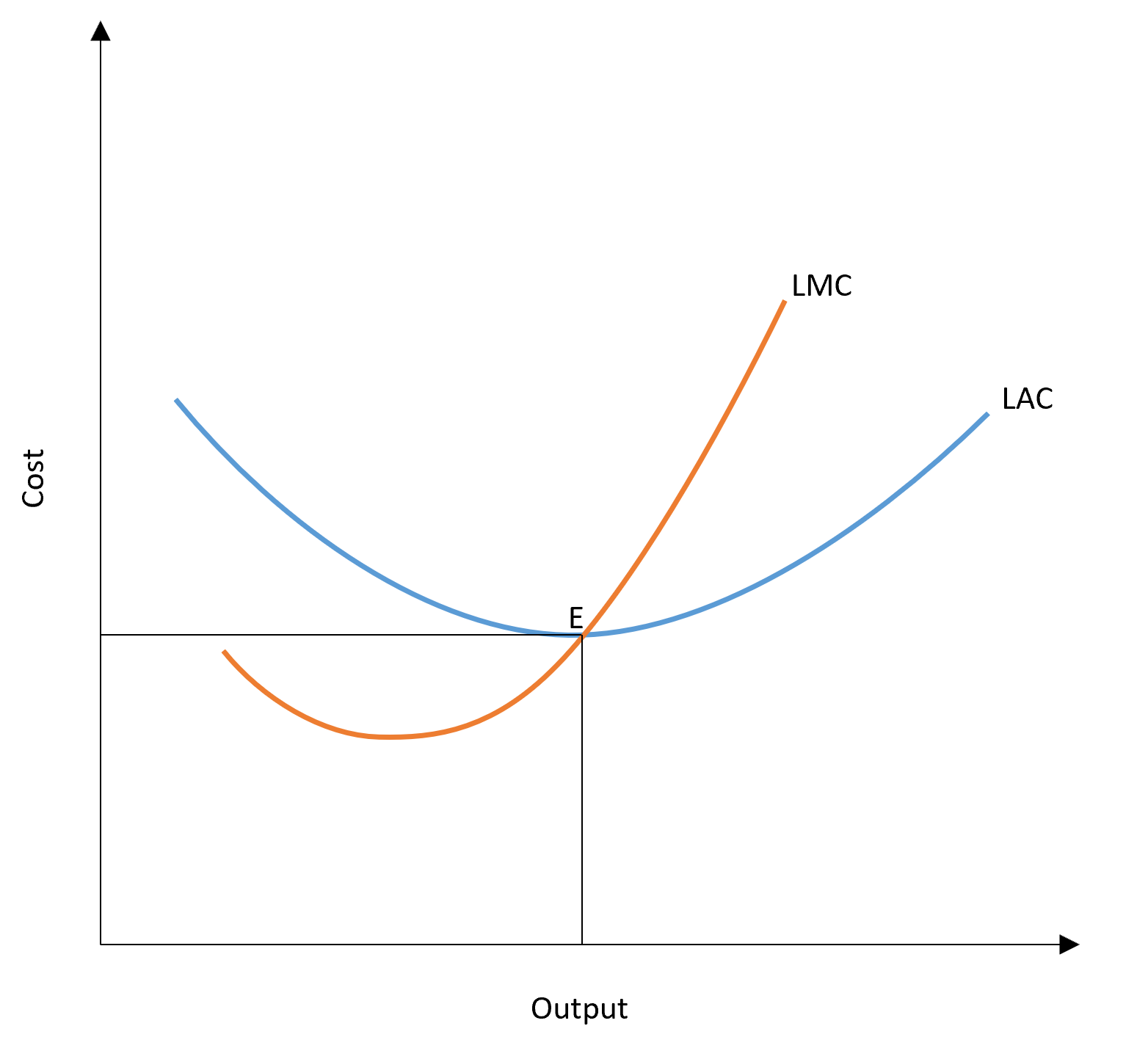
How are the LRAC curves different for small and large firms in market
MES is further right for large firms as a higher output is needed to reach it.
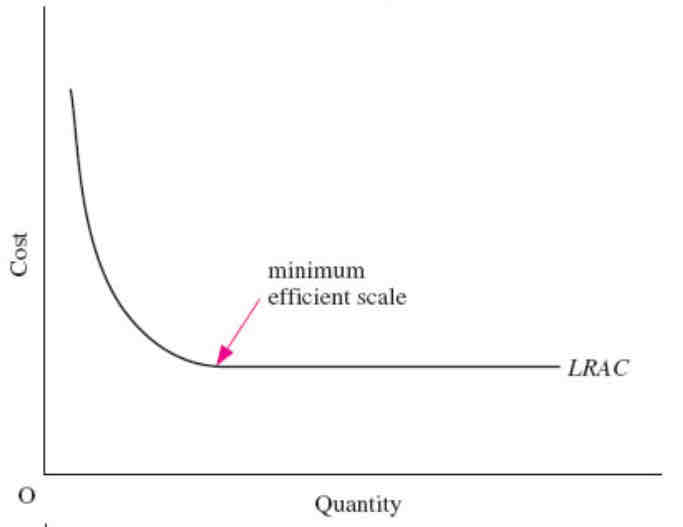
What does a flat LRAC curve show?
The whole flat part is the MES, no diseconomies of scale