Reformation Quizlet
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
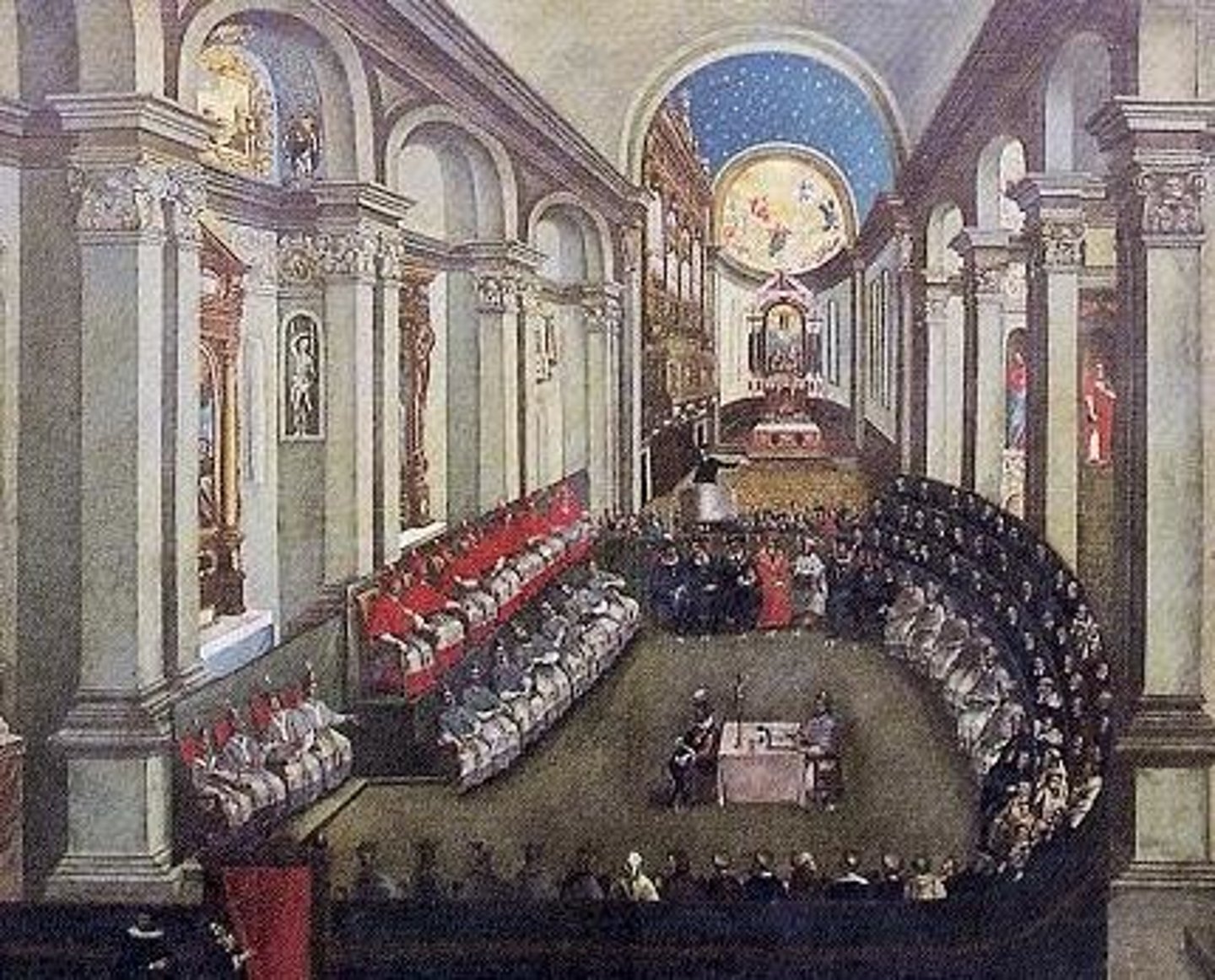
Council of Trent (1545-1563)
Reformed Catholic Church discipline and reaffirmed church doctrine. Preserved the papacy as the center of Christianity. Confirmed all seven existing sacraments. Reaffirmed Latin as the language of worship. Forbade clerical marriage.

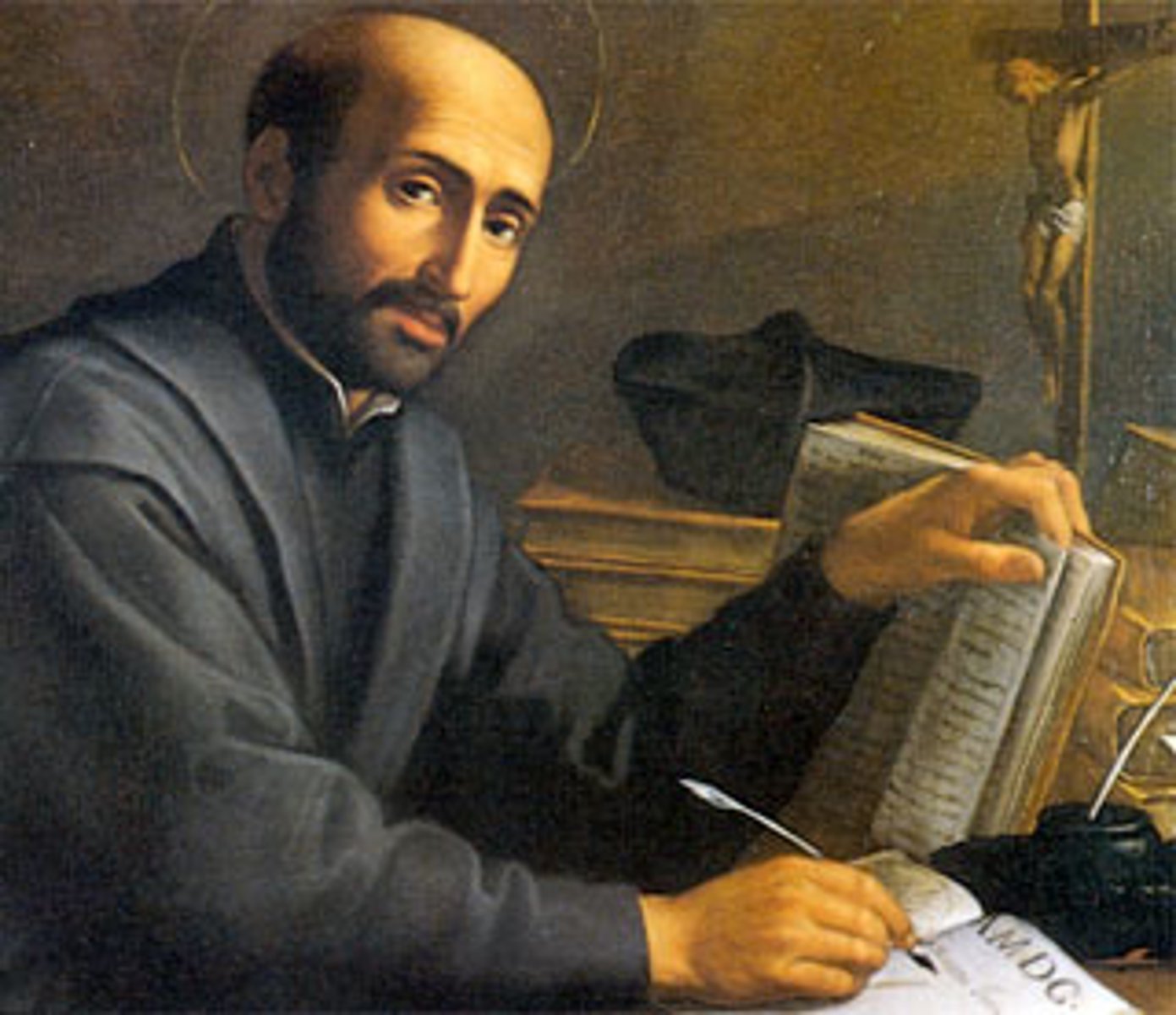
Ignatius of Loyola
Founder of the Jesuits

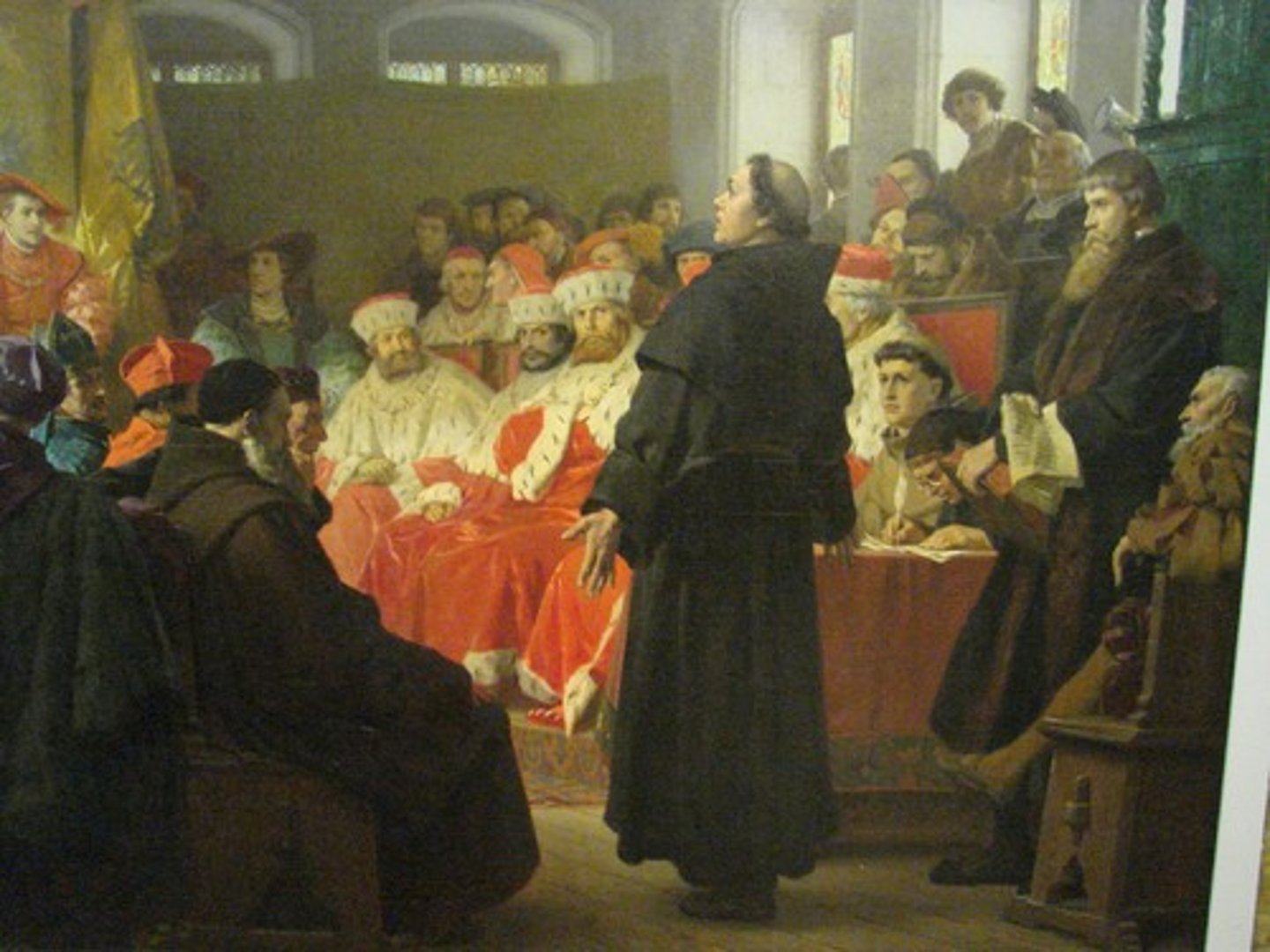
Martin Luther
a German monk who became one of the most famous critics of the Roman Catholic Church. In 1517, he wrote 95 theses, or statements of belief attacking the church practices.

Diet of Worms/Edict of Worms
1521, The meeting of leaders in the Holy Roman Empire at which Luther was formally condemned and excommunicated from the church. Luther stops being a Catholic and becomes Protestant, Edict of Worms is when he is formally kicked out(verdict)

Lutheranism
A Protestant denomination of Christian faith founded by Martin Luther

Predestination
Calvin's religious theory that God has already planned out a person's life.

Henry VIII of England
Tudor king who split the Church of England to divorce himself from Catherine of Aragon, 1509-1547

Church of England (Anglican Church)
The national church of England, founded by King Henry VIII. It included both Roman Catholic and Protestant ideas.

Counter Reformation (Catholic Reformation)
response and reforms by the Roman Catholic Church to the Protestant Reformation
Indulgence
a pardon releasing a person from punishments due for a sin

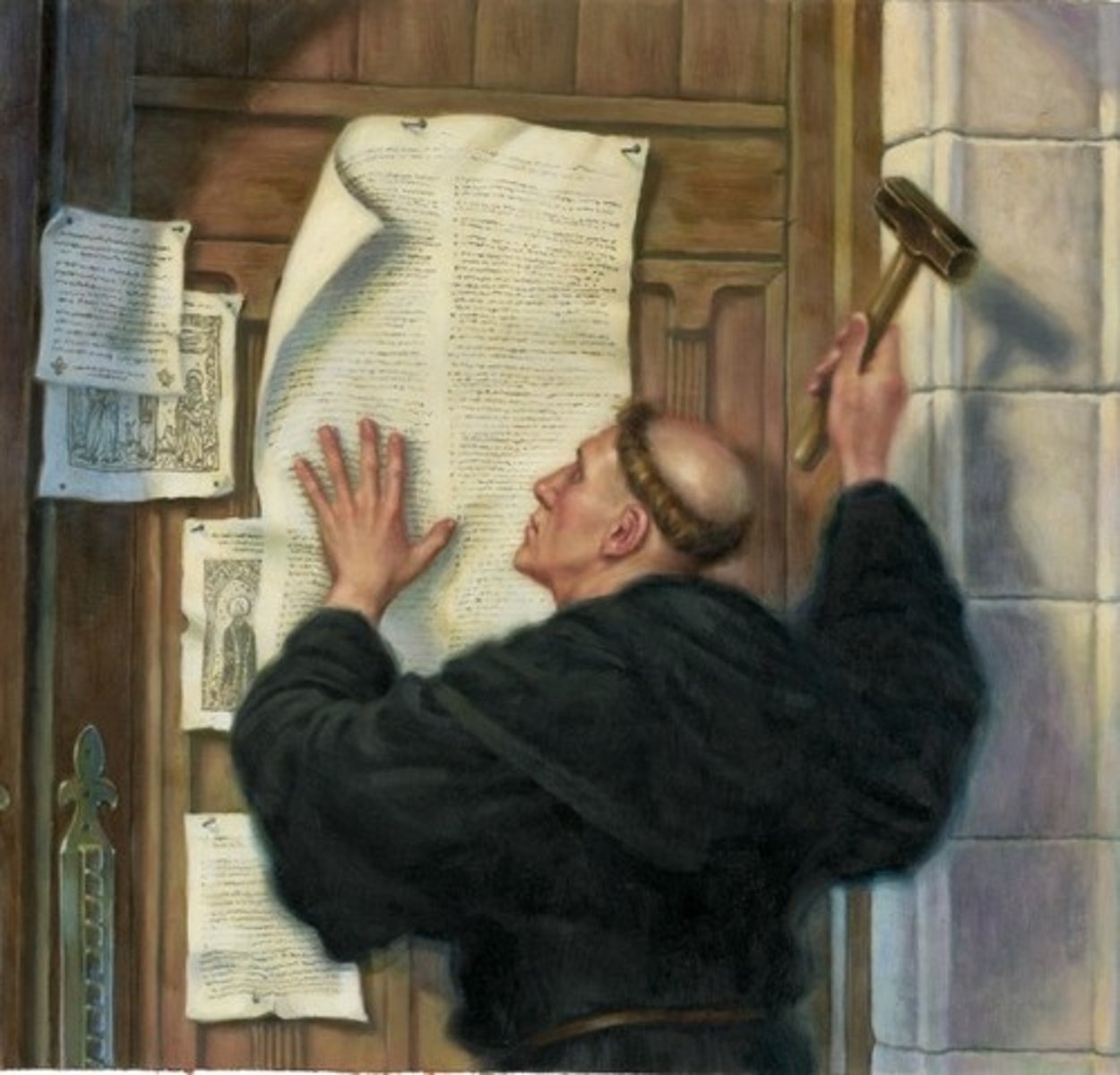
95 Theses (1517)
Martin Luther's ideas that he posted on the church door at Wittenberg which questioned the Roman Catholic Church. This act began the Reformation

Protestantism
a form of Christianity that was in opposition to the Catholic Church

John Calvin
1509-1564. French theologian. Developed the Christian theology known as Calvinism. Attracted Protestant followers with his teachings.

Jesuits
Also known as the Society of Jesus; founded by Ignatius Loyola (1491-1556) as a teaching and missionary order to resist the spread of Protestantism.

Inquisition
A Roman Catholic tribunal for investigating and prosecuting charges of heresy - especially the one active in Spain during the 1400s.

Scientific Revolution
A major change in European thought, starting in the mid-1500s, in which the study of the natural world began to be characterized by careful observation and the questioning of accepted beliefs.

Copernicus
Devised a model of the universe with the Sun at the center, and not earth.

Galileo Galilei
Italian astronomer and mathematician who was the first to use a telescope to study the stars

Heliocentric Theory
the idea that the earth and the other planets revolve around the sun.
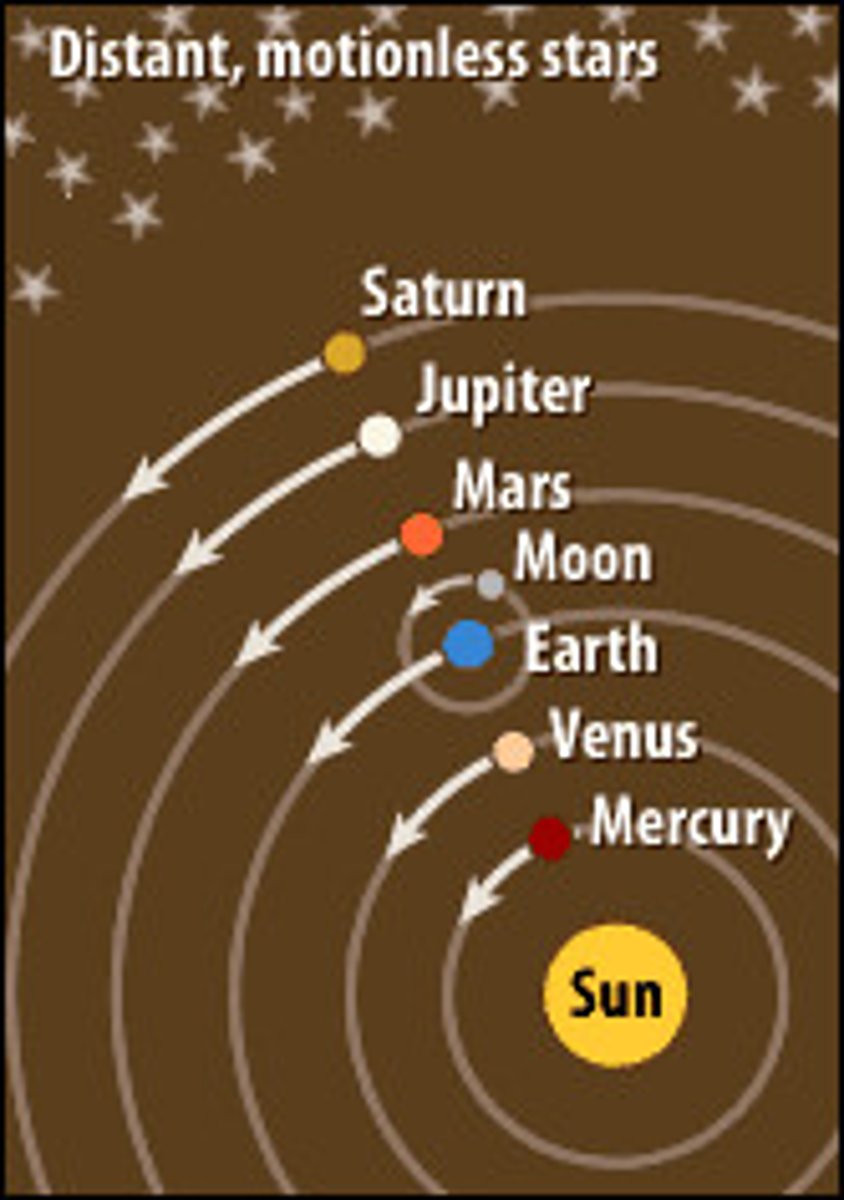
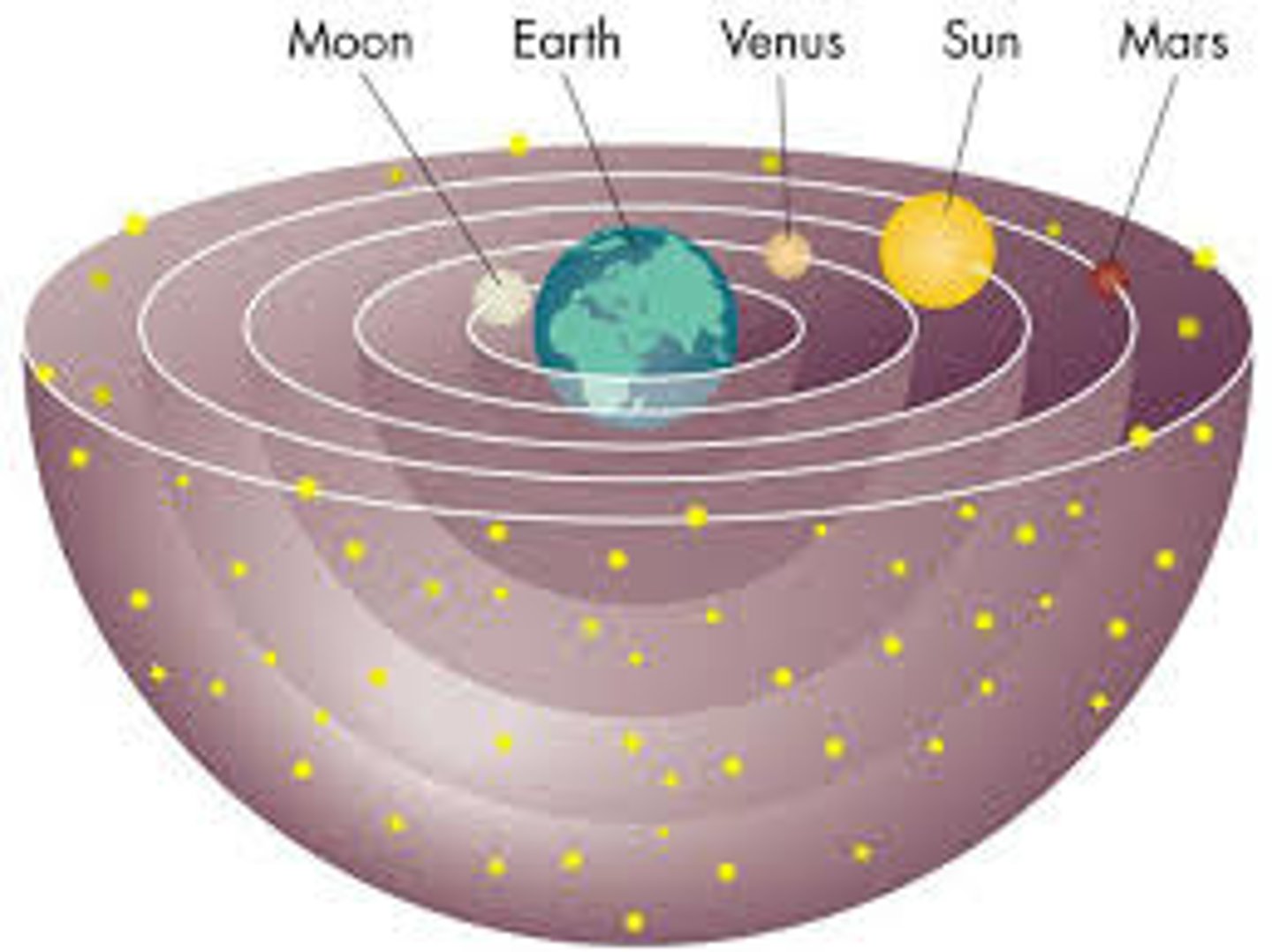
Geocentric Theory
Earth is the center of the Universe
Isaac Newton
Defined the laws of motion and gravity. Tried to explain motion of the universe.

Scientific Method
A series of steps followed to solve problems including collecting data, formulating a hypothesis, testing the hypothesis, and stating conclusions.
Protestant Refromation
the religious movement began as an effort to reform the catholic church and spread through German towns in the 1520s and then to other parts of Europe.

Printing Press
A mechanical device for transferring text or graphics from a woodblock or type to paper using ink. Presses using movable type first appeared in Europe in about 1450.
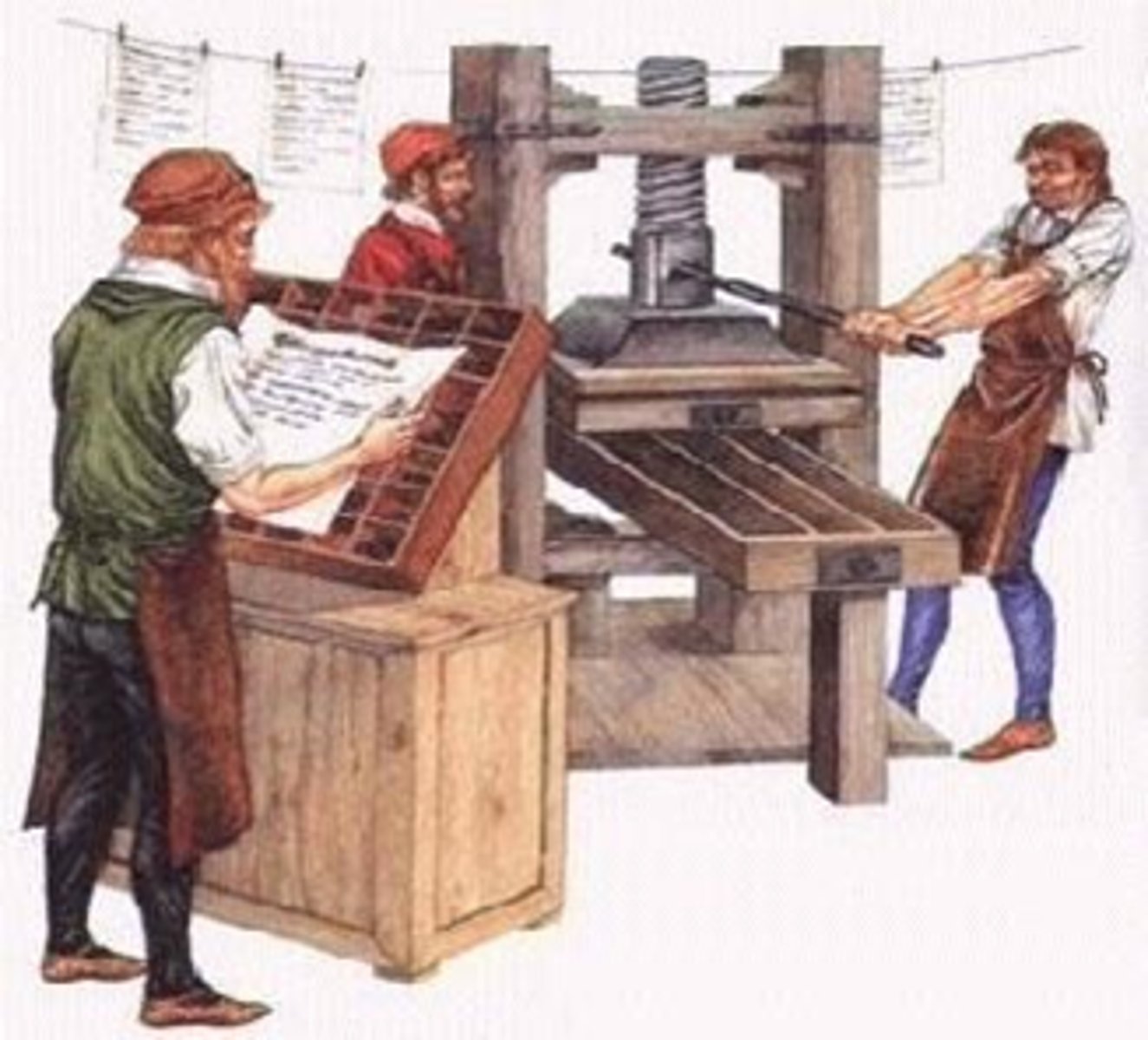
Johann Gutenberg
Invented the printing press

Still learning (9)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!