Institutions Ch 4 (Done)
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Major Duties and Responsibilities of the Federal Reserve System: Chapter Overview
Central banks determine, implement, and control the monetary policy in their home countries
The Federal Reserve (the Fed) is the central bank of the United States
Founded by Congress under Federal Reserve Act of 1913
Independent central bank
Duties incorporate four major functions:
Conducting monetary policy
Supervising and regulating depository institutions
Maintaining the stability of the financial system
Providing payment and other financial services to the U.S. government, the public, financial institutions, and foreign official institutions
Central banks
_____________ determine, implement, and control the monetary policy in their home countries
Federal Reserve (the Fed)
The ______________________ is the central bank of the United States
Founded by Congress under Federal Reserve Act of 1913
Independent central bank
Duties incorporate four major functions:
Conducting monetary policy
Supervising and regulating depository institutions
Maintaining the stability of the financial system
Providing payment and other financial services to the U.S. government, the public, financial institutions, and foreign official institutions
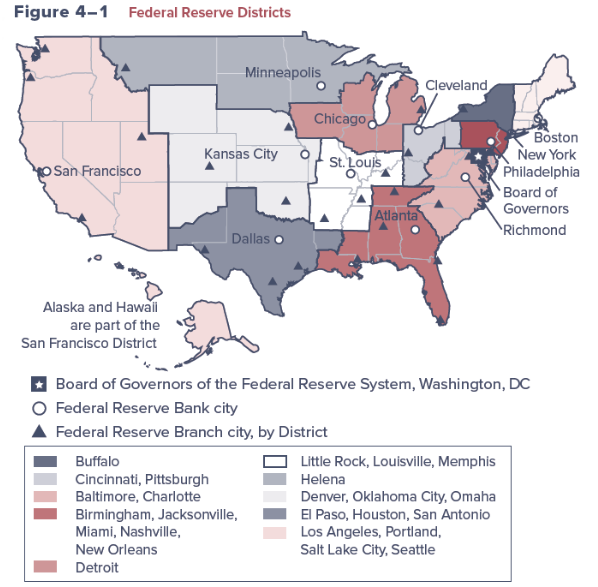
12 Federal Reserve Banks in cities throughout the U.S.
Each acts as a depository institution for the banks in its district
Operate under general supervision of the Board of Governors
Each has its own 9-member board of directors
Nationally chartered banks are required to become members of the FRS
7-member Board of Governors in Washington, D.C.
Each member appointed by the president of the U.S. and must be confirmed by the Senate
Members serve a nonrenewable, 14-year term
Primary responsibilities are the formulation and conduct of monetary policy and the supervision and regulation of banks
Federal Reserve Districts
Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC)
FOMC is the major monetary policy-making body of the Federal Reserve System
Required to meet at least four times each year in Washington, D.C., but typically meet more often
Main responsibilities are to formulate policies to promote full employment, economic growth, price stability, an da sustainable pattern of international trade
Set guidelines regarding open market operations, the purchase and sale of U.S. government and federal agency securities, as the main policy tool to achieve monetary targets
Beige Book summarizes information on current economic conditions by Federal Reserve district
FOMC
________ is the major monetary policy-making body of the Federal Reserve System
promote full employment, economic growth, price stability, an the sustainable pattern of international trade
(FOMC) - Main responsibilities are to formulate policies to ____________________________________________________________.
open market operations
Set guidelines regarding ____________________, the purchase and sale of U.S. government and federal agency securities, as the main policy tool to achieve monetary targets
Functions Performed by Federal Reserve Banks (FRBs)
Assistance in the conduct of monetary policy
Set and change the discount rate
Loans transacted through each FRBs discount window
Supervision and regulation
Each FRB has supervisory and regulatory authority over the activities of state-chartered member banks and bank holding companies located in their districts
Consumer protection and community affairs
Possess authority to implement federal laws intended to protect consumers in credit and other financial transactions
Government services
Serves as the commercial bank for the U.S. Treasury
Assistance in the conduct of monetary policy
Set and change the discount rate
Loans transacted through each FRBs discount window
Supervision and regulation
Each FRB (Federal Reserve Banks) has supervisory and regulatory authority over the activities of state-chartered member banks and bank holding companies located in their districts
Consumer protection and community affairs
Possess authority to implement federal laws intended to protect consumers in credit and other financial transactions
Government services
Serves as the commercial bank for the U.S. Treasury
Functions Performed by Federal Reserve Banks (FRBs) (Continued)
New currency issue
Responsible for the collection and replacement of currency (paper and coin) from circulation
Check clearing
Operates a central check clearing system for U.S. banks, routing interbank checks to DIs on which they are written and transferring the appropriate funds from one bank to another
Wire transfer services
FRBs and member banks are linked electronically through the Federal Reserve Communications System
Research services
Each FRB uses professional economics to conduct research
New currency issue
Responsible for the collection and replacement of currency (paper and coin) from circulation
Check clearing
Operates a central check clearing system for U.S. banks, routing interbank checks to DIs on which they are written and transferring the appropriate funds from one bank to another
Wire transfer services
FRBs and member banks are linked electronically through the Federal Reserve Communications System
Research services
Each FRB uses professional economics to conduct research
Balance Sheet of the Federal Reserve
Liabilities
Major liabilities on the Fed’s balance sheet are currency in circulation and reserves, the sum of which is referred to as the Fed’s monetary base or money base
Total reserves can be classified into two categories:
Required reserves are those the Fed requires banks to hold by law
Excess reserves are additional over and above required reserves
Assets
Major assets are Treasury and government agency (i.e., Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac) securities, Treasury currency, and gold and foreign exchange
Interbank loans are a small portion of total assets, but they plan an important role in implementing monetary policy
Balance Sheet of the Federal Reserve (Liabilities)
Major liabilities on the Fed’s balance sheet are currency in circulation and reserves, the sum of which is referred to as the Fed’s monetary base or money base
Total reserves can be classified into two categories:
Required reserves are those the Fed requires banks to hold by law
Excess reserves are additional over and above required reserves
reserves | monetary base or money base
Major liabilities on the Fed’s balance sheet are currency in circulation and _________, the sum of which is referred to as the Fed’s ________________________.
Total reserves can be classified into two categories:
Required reserves are those the Fed requires banks to hold by law
Excess reserves are additional over and above required reserves
Required reserves
____________________ are those the Fed requires banks to hold by law
Excess reserves
_______________ are additional over and above required reserves
Balance Sheet of the Federal Reserve (Assets)
Major assets are Treasury and government agency (i.e., Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac) securities, Treasury currency, and gold and foreign exchange
Interbank loans are a small portion of total assets, but they plan an important role in implementing monetary policy
Federal Reserve uses the following to implement monetary policy:
Open market operations
Discount rate
Reserve requirements
Major link by which monetary policy impacts the macroeconomy occurs through the Federal Reserve influencing the market for bank reserves
Federal Reserve’s monetary policy seeks to influence either the demand for, or supply of, excess reserves at depository institutions and in turn the money supply and the level of interest rates
Federal Reserve Monetary Policy Activities
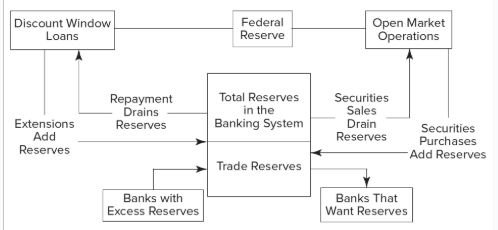
Depository institutions trade excess reserves held at their local Federal Reserve Banks among themselves
Rate of interest (or price) on these interbank transactions is a benchmark interest rate, called the fed funds rate
Financial Services Regulatory Relief Act of 2006 authorized the Federal Reserve to pay interest on reserve balances
Interest on excess reserves (IOER) and required reserves (IORR)
Federal Reserve can take one of two basic approaches to affect the market for banks’ excess reserves
Target the quantity of reserves in the market
Target the interest rate on those reserves (the fed funds rate)
Open market operations
When a targeted monetary aggregate or interest rate level is determined by the FOMC, it is forwarded to the Federal Reserve Board Trading Desk at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York (FRBNY) through a statement called the policy directive
Manager of Trading Desk uses policy directive to instruct traders on daily amount of open market purchases or sales to transact
Federal Reserve Board Trading Desk | policy directive
When a targeted monetary aggregate or interest rate level is determined by the FOMC, it is forwarded to the ________________________________ at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York (FRBNY) through a statement called the ________________.
Open market operations are the primary determinant of changes in bank excess reserves in the banking system
Directly impact the size of the money supply and/or the level of interest rates (e.g., the fed funds rate)
Treasury securities
Open market operations are primarily conducted using ______________, but others can be used as well
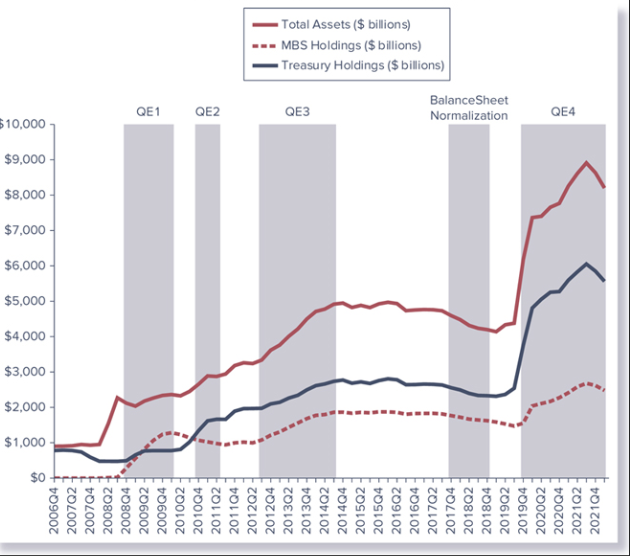
Federal Reserve’s Balance Sheet and Large-Scale Asset Purchases
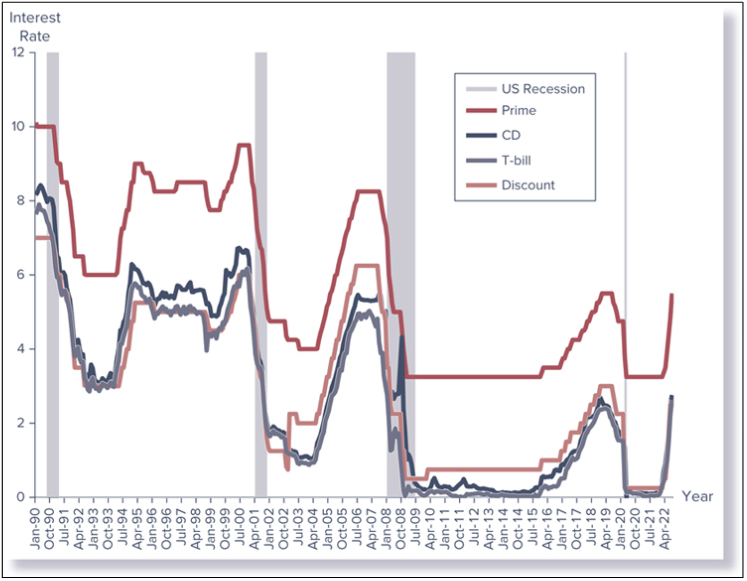
Recall, the discount rate is the rate of interest Federal Reserve Banks charge on loans to FIs in their district
Raising the discount rate signals a desire to see a tightening of monetary conditions and higher interest rates in general
Lowering the discount rate signals a desire to see more expansionary monetary conditions and lower interest rates in general
Federal Reserve has rarely used the discount rate as a monetary policy tool for the following reasons:
It is difficult for the Fed to predict changes in bank discount window borrowing when the discount rate changes
Because of its “signaling” importance, a discount rate change often has great effects on the financial markets
Various U.S. Interest Rates
Historically, discount window lending was limited to depository institutions (DIs) with severe liquidity needs
Fed made changes to discount window lending that increased the cost of borrowing but eased the terms in January 2003
(Not tested but should learn for self) Three lending programs are now offered through the Fed’s discount window:
Primary credit is available to generally sound DIs on a very short-term basis, typically overnight, at a rate above the Federal Open Market Committee’s target rate for federal funds
Secondary credit is available to meet backup liquidity needs when its use is consistent with a timely return to a reliance on market sources of funding or the orderly resolution of a troubled institution
Seasonal credit is available to DIs that can demonstrate a clear pattern of recurring intrayearly swings in funding needs
Reserve requirements determine the minimum amount of reserve assets that DIs must maintain by law to back transaction deposit accounts held as liabilities on their balance sheets
Requirement is usually set as a ratio of transaction accounts
Very rarely used by the Federal Reserve as a monetary policy tool
Reserve Requirements (Reserve Ratios) Choices in increase vs Decrease
A(n) decrease (increase) in the reserve requirement ratio means that DIs may hold fewer (must hold more) reserves against their transaction accounts, allowing them to lend out a greater (smaller) percentage of their deposits and increasing (decreasing) credit availability in the economy
Decrease in the reserve requirement results in a multiplier increase in the supply of bank deposits and thus the money supply
Multiplier effect:

Increase in the reserve requirement results in a multiple contraction in deposits and a decrease in the money supply
Multiplier effect:

The Process of Monetary Policy Implementation
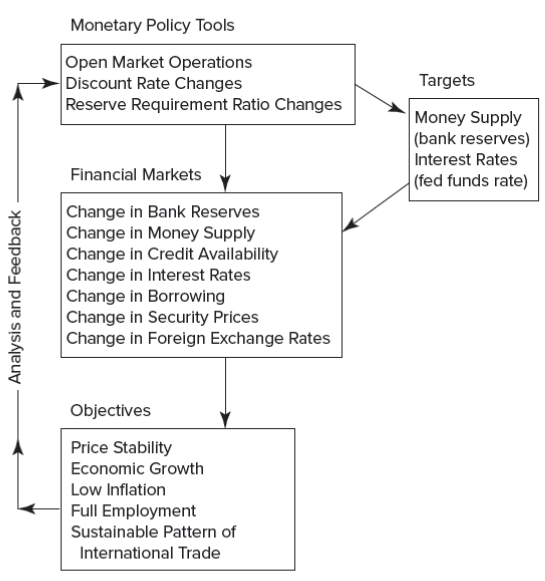
Expansionary Activities
Open market purchases of securities
All else constant, reserve accounts of banks increase
Discount rate decreases
All else constant, interest rates in the economy decrease
Reserve requirement ratio decreases
All else constant, bank reserves increase
Contractionary Activities
Open market sales of securities
All else constant, reserve accounts of banks decrease
Discount rate increases
All else constant, interest rates in the open market increase
Reserve requirement ratio increases
All else constant, bank reserves decrease
The Impact of Monetary Policy on Various Economic Variables
Federal Reserve can successfully target only one of these two variables (money supply or interest rates) at any one moment
If the money supply is the target variable used to implement monetary policy, interest rates must be allowed to fluctuate relatively freely
If an interest rate (e.g., fed funds rate) is the target, bank reserves and the money supply must be allowed to fluctuate relatively freely

Federal Reserve Monetary Policy Targets
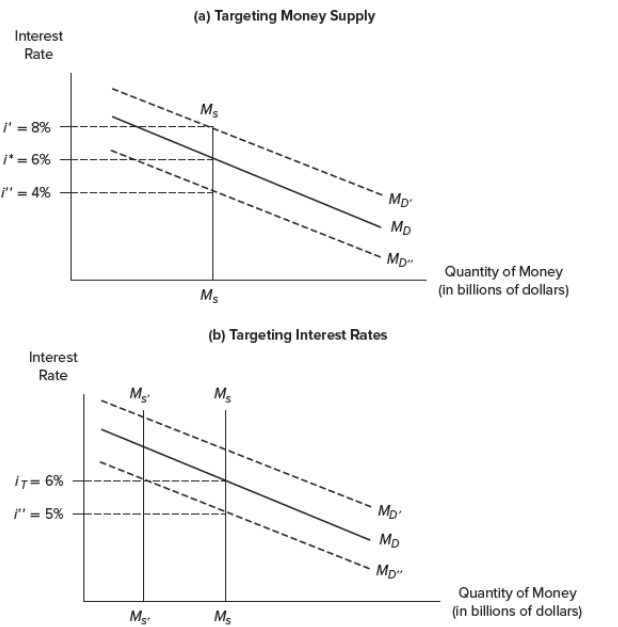
Fed announced that it would use interest rates—the federal funds rate—as the main target variable to conduct monetary policy in 1993
Guiding principle used by the Fed to set short-term interest rates is the Taylor rule, which states short-term interest rates should be determined by three conditions:
Where actual inflation is relative to the Fed’s targeted level
The extent to which the economy is above or below its full employment level
What short-term interest rates should be to achieve full employment
monthly FOMC meeting
Under the current regime, the Fed simply announces whether the federal funds rate target has been increased, decreased, or left unchanged after every ____________________.
Central banks guide the monetary policy in virtually all countries
Independence of a central bank generally means that the bank is free from pressure from politicians who may attempt to enhance economic activity in the short term at the expense of long-term economic growth
Other independent central banks, like the Federal Reserve:
European Central Bank (ECB) is the central bank for the EU
Bank of England is the central bank of the UK
Banks with less independence:
People’s Bank of China
Reserve Bank of India
Central Bank of Brazil
Systemwide Rescue Programs Employed during the Financial Crisis (2008)
Expansion of retail deposit insurance was widely used during the crisis to ensure continued access to deposit funding
Capital injections by central governments were the main mechanism used to directly support bank balance sheets
Debt guarantees allowed banks to maintain access to reasonably priced, medium-term funding.
They also reduced liquidity risk and lowered overall borrowing costs for banks
Asset purchases/guarantees removed distressed assets from bank balance sheets
Expansion of retail deposit insurance
_________________________ was widely used during the crisis to ensure continued access to deposit funding (Ex: FDIC insurance increased from $125k to $250k)
Capital injections
__________________ by central governments were the main mechanism used to directly support bank balance sheets (Ex: 2008 Central bank went to commercial banks and bought up their assets [ex: mortgages, securities, bonds, etc] to provide liquidity to the banks)
Debt guarantees
___________________ allowed banks to maintain access to reasonably priced, medium-term funding.
They also reduced liquidity risk and lowered overall borrowing costs for banks
Asset purchases/guarantees
_________________________ removed distressed assets from bank balance sheets
While the worst of the financial crisis subsided in the U.S. in the last half of 2009, throughout the spring of 2010 Greece struggled with a severe debt crisis
Problems in the Greek bond market then spread to other European nations with fiscal problems, such as Portugal, Spain, and Italy
In August 2018, Greece exited the third bailout program
In total, Greece now owes the EU and IMF roughly $330 billion, part of a public debt that has climbed to 180 percent of GDP
Challenges to central banks became even bigger in June 2016 when the people of the United Kingdom voted to leave the EU after 43 years (i.e., Brexit)
The pound fell more than 11 percent to its lowest point since 1985
The DJIA dropped 610.32 points, or 3.4 percent
The Stoxx Europe 600 index fell 7 percent, its steepest drop since 2008
Japan’s Nikkei Stock Average declined 7.9 percent
Bank of England (BoE) unveiled a four-point plan to prevent a post-Brexit recession
In August 2016, the BoE cut interest rates for the first time in more than seven years to a new record low of 0.25 percent