Seafloor Spreading and Subduction, Earth's layers, and Continental drift💀
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Science Unit flashcards for test next week
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is Seafloor spreading?
a geological process where tectonic plates expand and create new oceanic crust at mid-ocean ridges, leading to the movement of continents.
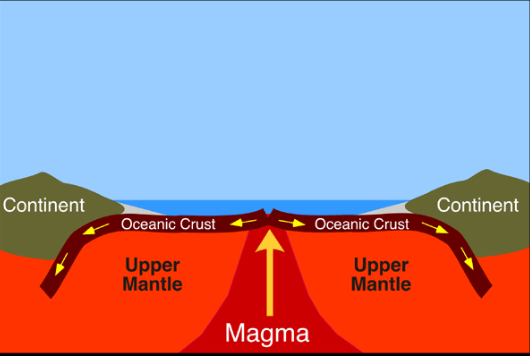
Where does Seafloor Spreading Occur?
At mid-ocean ridges, where tectonic plates diverge. `
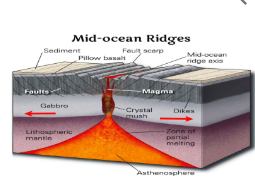
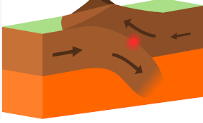
What is Subduction?
A geological process where one tectonic plate moves under another and sinks into the mantle, often causing volcanic activity and earthquakes.
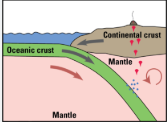
What is convection?
Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids, where warmer, less dense material rises and cooler, denser material sinks, playing a key role in driving plate tectonics.
What is happening at the Mid-Ocean Ridge
New oceanic crust is being formed as tectonic plates pull apart, allowing magma to rise.
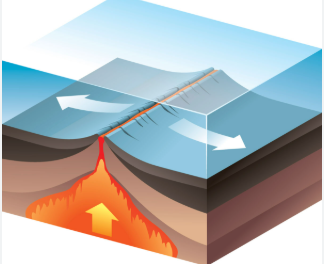
What plate boundary is associated with Seafloor Spreading
Divergent boundary where plates move apart.
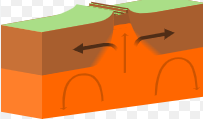
What plate boundary is associated with Subduction
Convergent boundary where one plate sinks below another.
Oceanic Crust found at the center of the mid ocean ridges is
younger than that found further away from the ridge.
Oceanic crust found further from the mid ocean ridge is
older than that at the center.
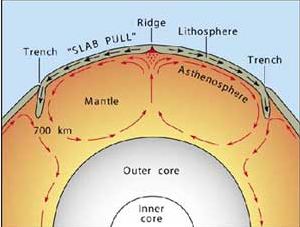
Seafloor spreading and Subduction are partly responsible for
the movement of tectonic plates.
1 evidence of seafloor spreading and subduction is
the symmetrical patterns of magnetic stripes on either side of mid-ocean ridges.
Another evidence for seafloor spreading and subduction is
the age of ocean floor rocks increases with distance from mid-ocean ridges.
And a final evidence for seafloor spreading and subduction is
drilling samples to find the age of rocks
Who is Alfred Wegner
A German meteorologist and geophysicist known for proposing the theory of continental drift, suggesting continents have moved over geological time.
Alfred Wegner’s theory states
that continents were once part of a single landmass called Pangaea, which broke apart and drifted to their current locations.
Pangea means
"all lands" in ancient Greek, referring to the supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras.
1 Evidence for Alfred Wegner’s theory is
the way the continents fit together like a jigsaw puzzle particularly the matching coastlines of South America and Africa.
Another evidence for Alfred Wegner’s theory
is the discovery of similar rock formations and fossils on continents that are now widely separated by oceans, indicating they were once connected.
Another evidence for Alfred Wegner’s theory
is that the chains of mountains in the eastern United States and the mountains in Scotland are of similar age and composition, suggesting these landmasses were once part of the same mountain range.
Another evidence for Alfred Wegener’s theory
is the presence of ice age debris, such as glacial deposits, found in now warm regions, indicating these areas were once closer to the poles.
Another evidence for Alfred Wegner’s theory
is that there were fern fossils, a warm weather plantfound in Antarctica, suggesting it was once located in a warmer climate. It also might mean that Antartica moved from near the equator.
Alfred Wegner’s theory was rejected because he could not
provide a reason for how continents could move.
The Lithosphere is a
rigid outer layer of the Earth, consisting of the crust and upper mantle, which is divided into tectonic plates that float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere. It is also a solid. It is made of Oceanic and Continental crust.
The Crust is
the outermost layer of the Earth, composed of solid rock that forms continents and ocean floors, varying in thickness and composition.
The Asthenosphere is
a semi-fluid layer beneath the lithosphere, allowing tectonic plates to move over it. It is part of the upper mantle and plays a crucial role in plate tectonics.
The Mantle is
the thick layer of the Earth located between the crust and the outer core, composed of semi-solid rock that flows slowly, facilitating the movement of tectonic plates. It comprises the upper and lower mantle, influencing geological activity. the layer responsible for convection currents that drive plate movements.
The mesosphere is
the lower part of the Earth's mantle located below the asthenosphere, characterized by increased pressure and temperature, where rock behaves more like a solid but can still flow slowly.
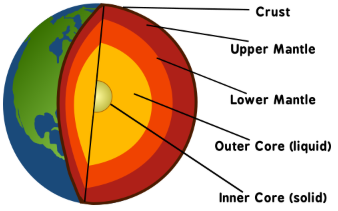
The outer core is
the liquid layer of the Earth's core located beneath the mantle and surrounding the inner core, composed mainly of iron and nickel. It is responsible for generating the Earth's magnetic field through the movement of its liquid metal.
The inner core is
the solid, innermost layer of the Earth, primarily composed of iron and nickel. It is extremely hot, with temperatures comparable to the surface of the sun, and its immense pressure keeps it in a solid state despite the high temperatures.
The order of the layers of the earth is
the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core, arranged from the surface to the center. Each layer has distinct properties and compositions.
Lithospheric plates are
the rigid segments of the Earth's lithosphere that move and interact at their boundaries, leading to geological phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanic activity, and mountain building.