AP Psychology: Topic 2.1 - Perception
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
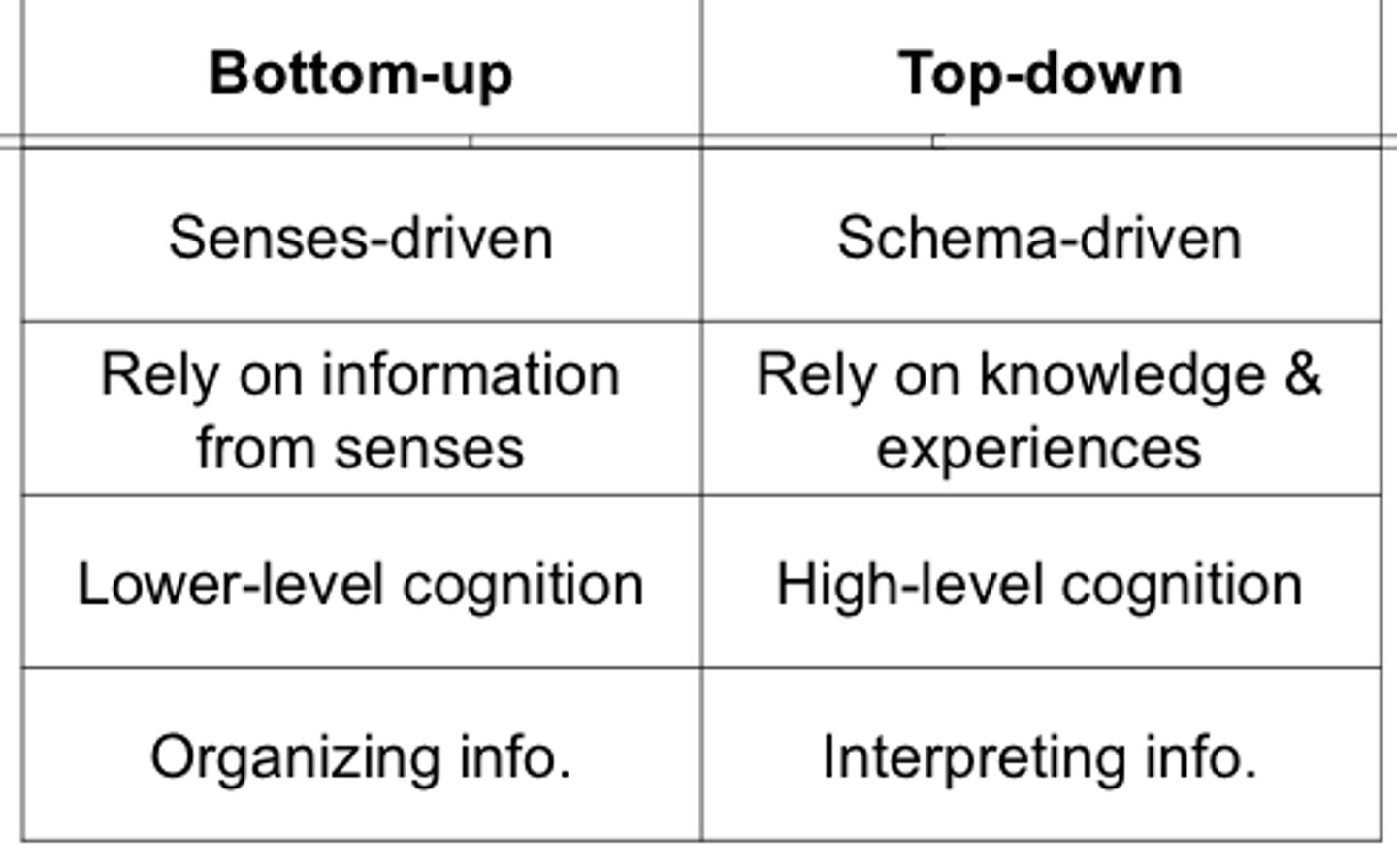
analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain's integration of sensory information
Bottom-up processing
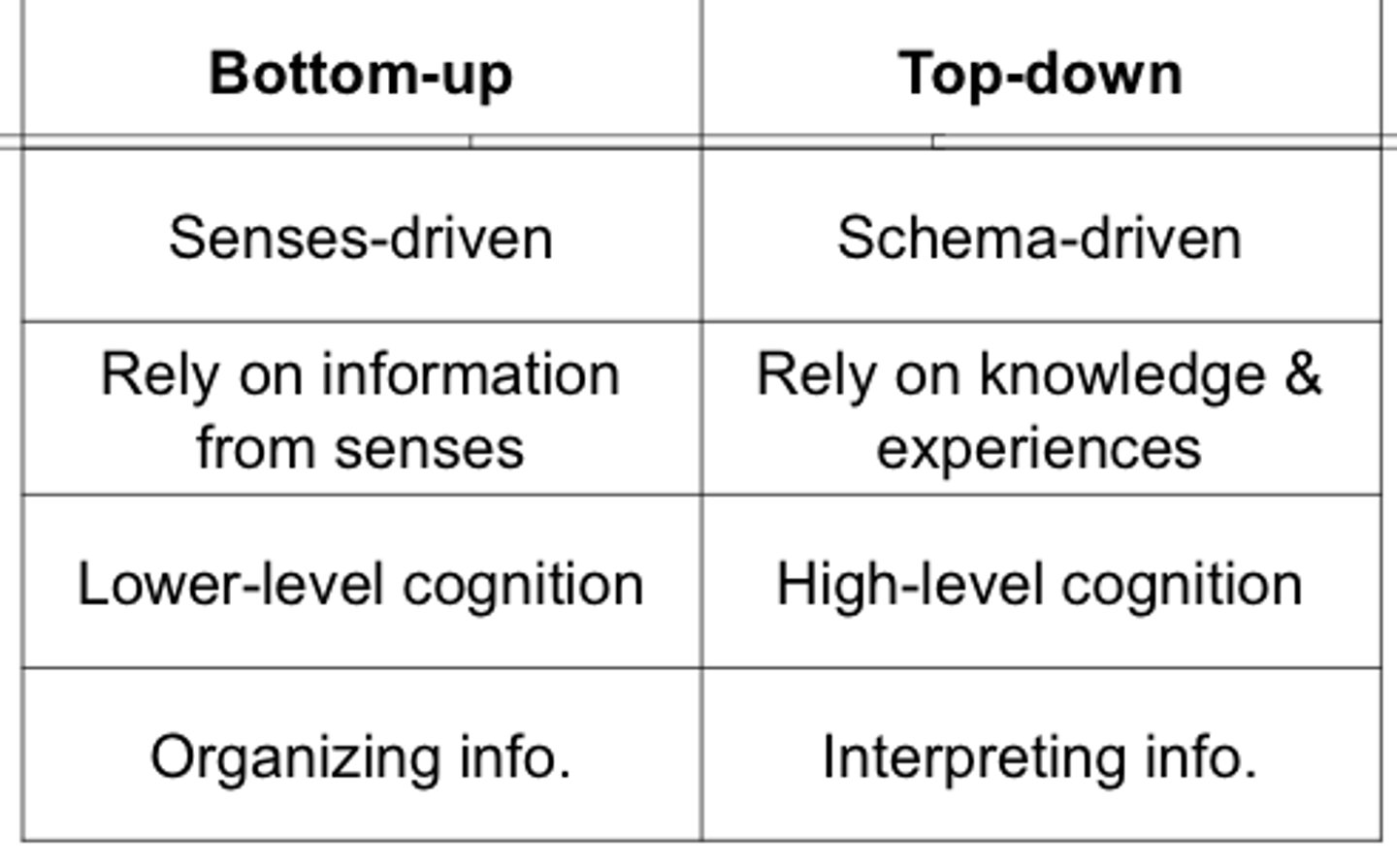
information processing guided by higher-level mental processes, as when we construct perceptions drawing on our experience and expectations
Top-down processing
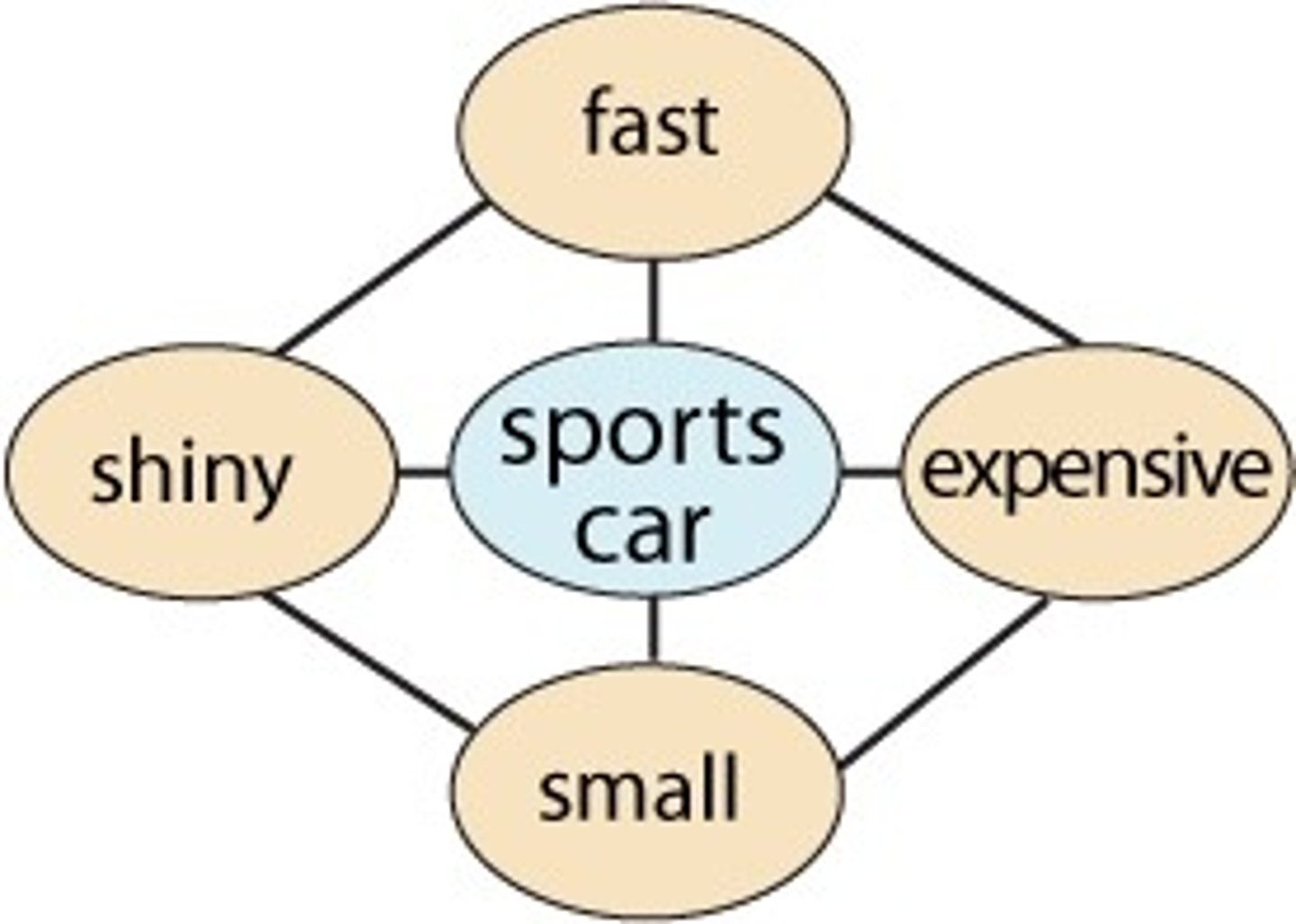
a conceptual framework a person uses for organizing and perceiving new information
Schema
a predisposition or readiness to perceive something in a particular way and to ignore other perceptions
Perceptual set

a psychological approach that emphasizes that we often perceive the whole rather than the sum of the parts
Gestalt psychology
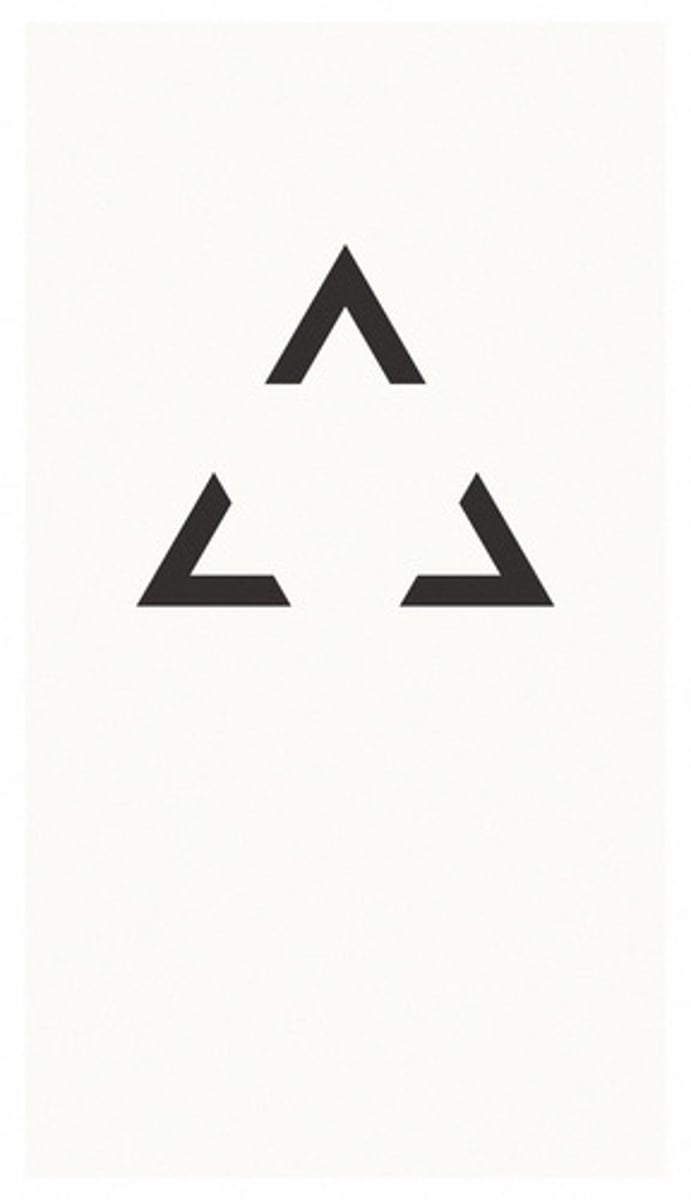

Closurethe tendency of the brain to complete figures that are incomplete
Closure

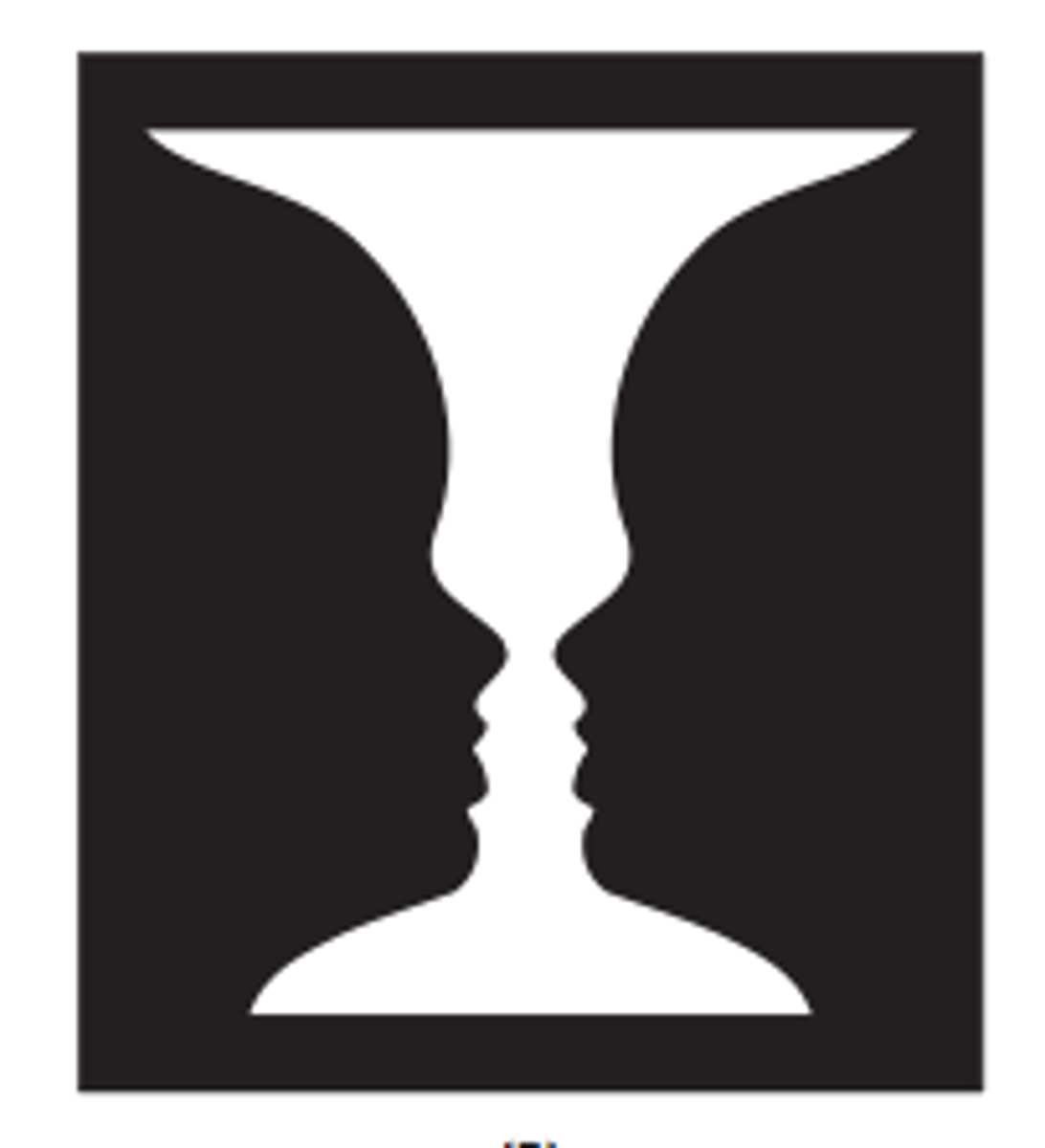
a human's ability to visually differentiate between an object and its background
Figure and ground

a tendency of the brain to perceive that things which are closer to each other as more related than things farther apart
Proximity
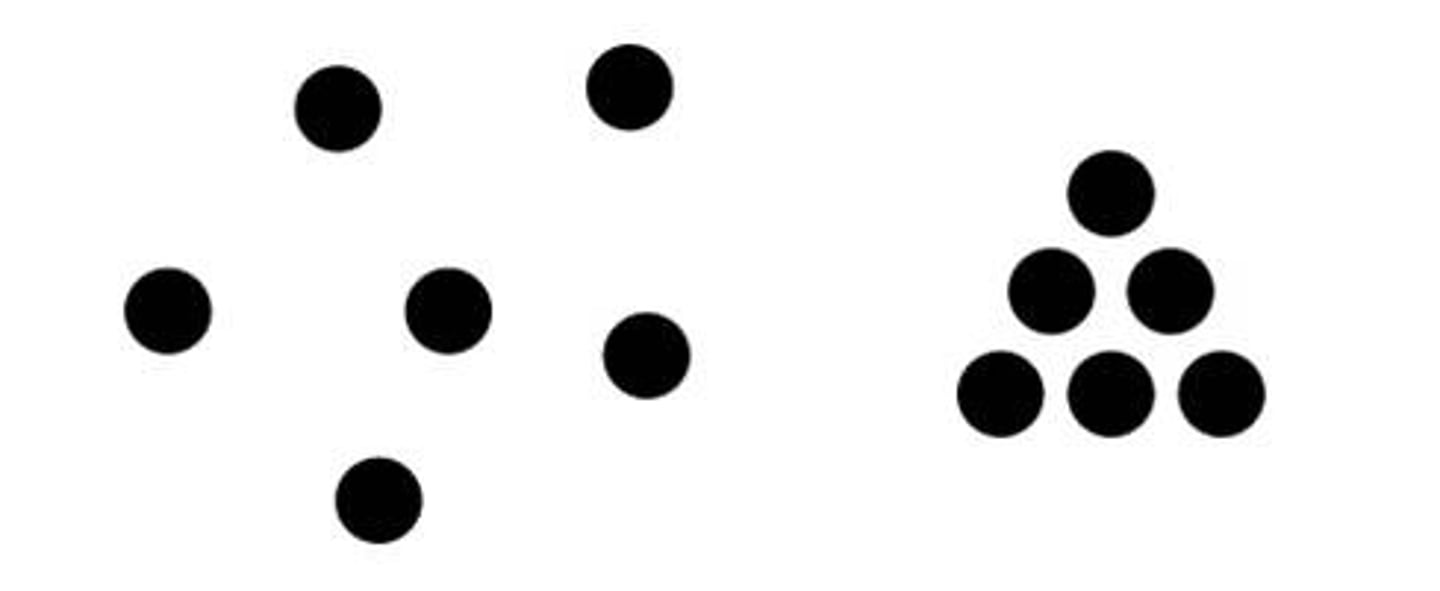
when things appear similar to each other, the brain tends to group them together and perceive that they have the same function
Similarity
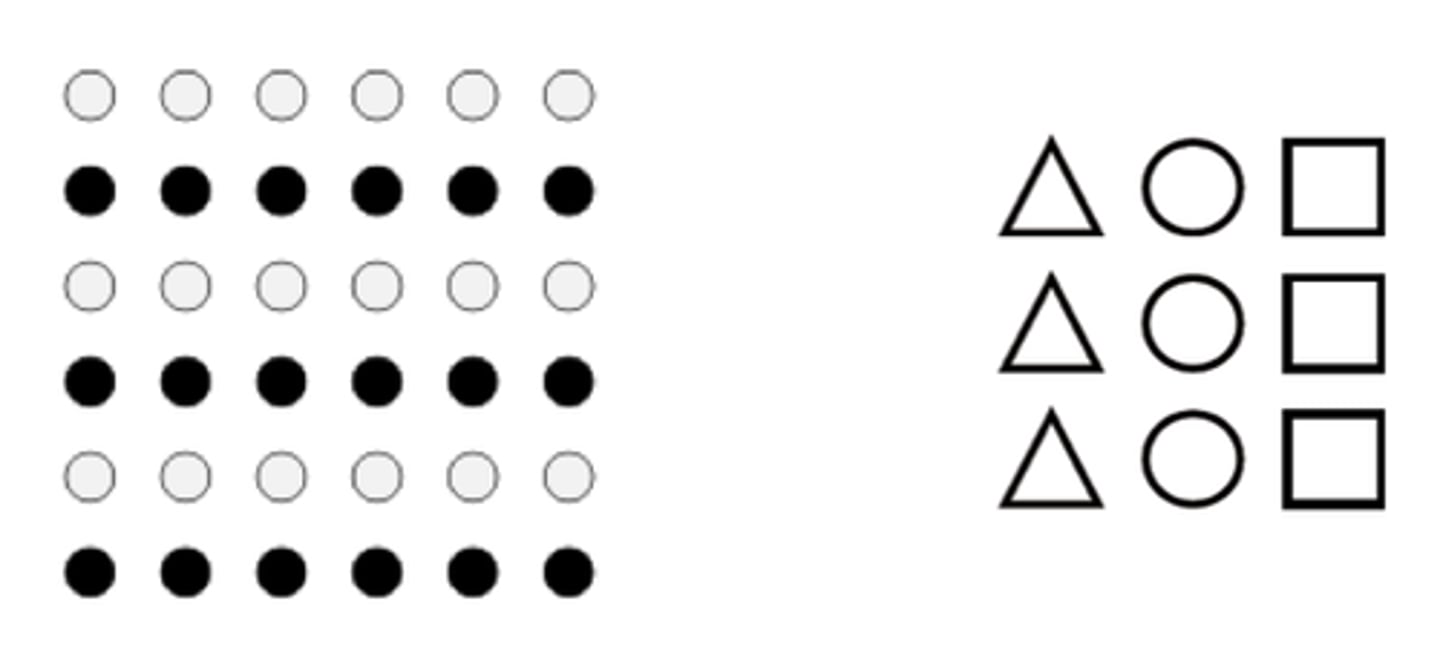
focusing awareness on a narrowed range of stimuli or events
Attention
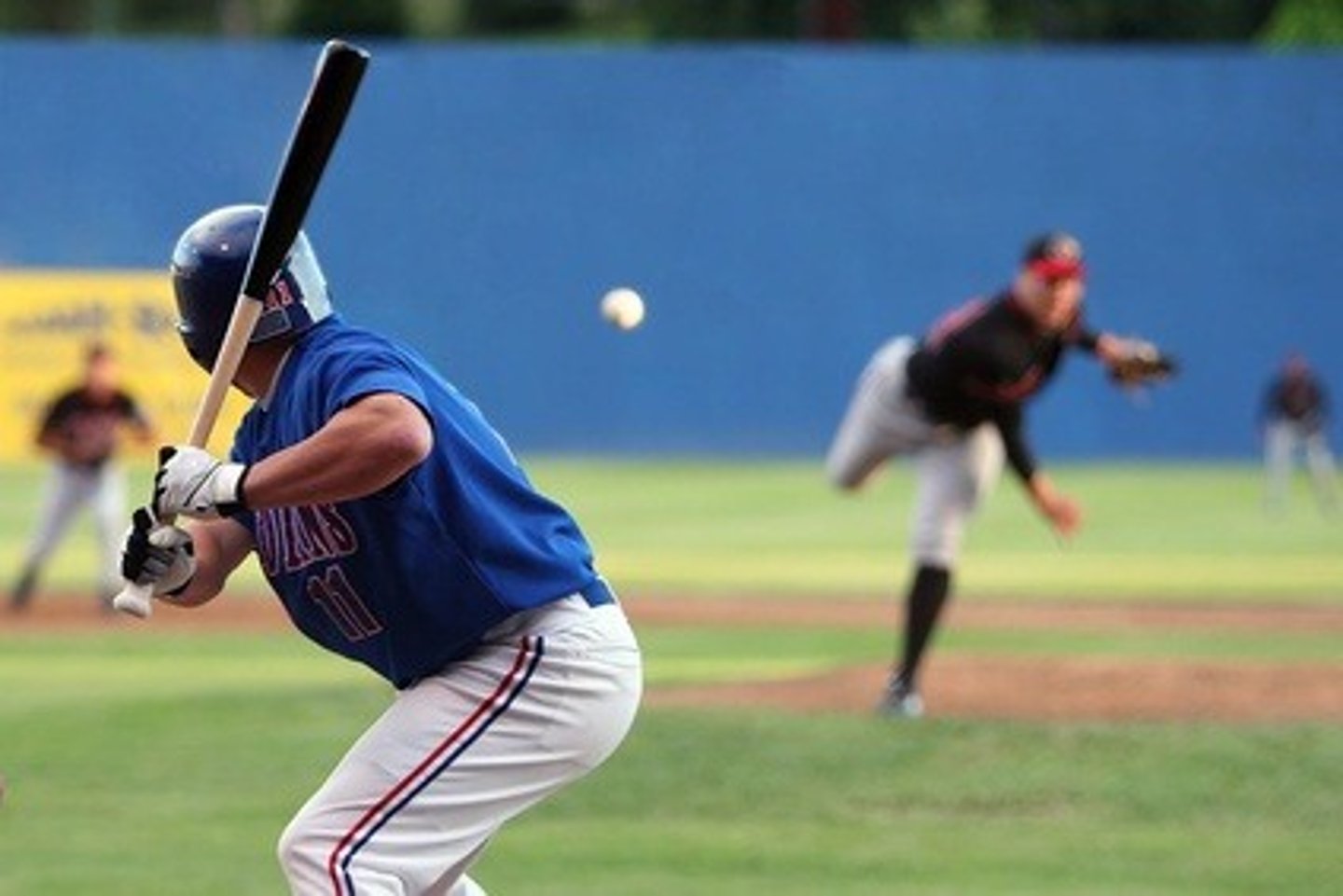

the focusing of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus and not others
Selective attention

the ability to attend to only one conversation among many
Cocktail party effect
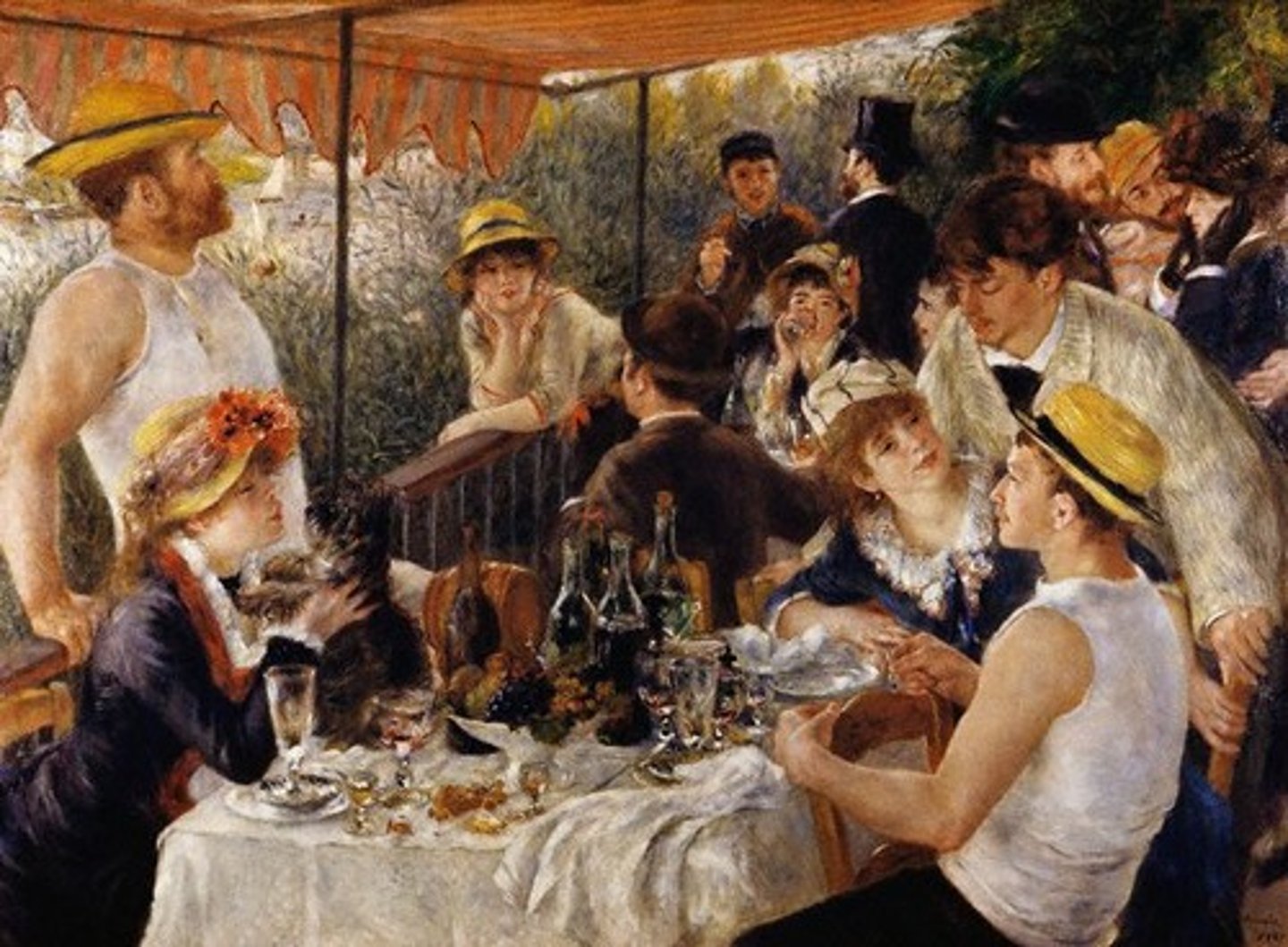

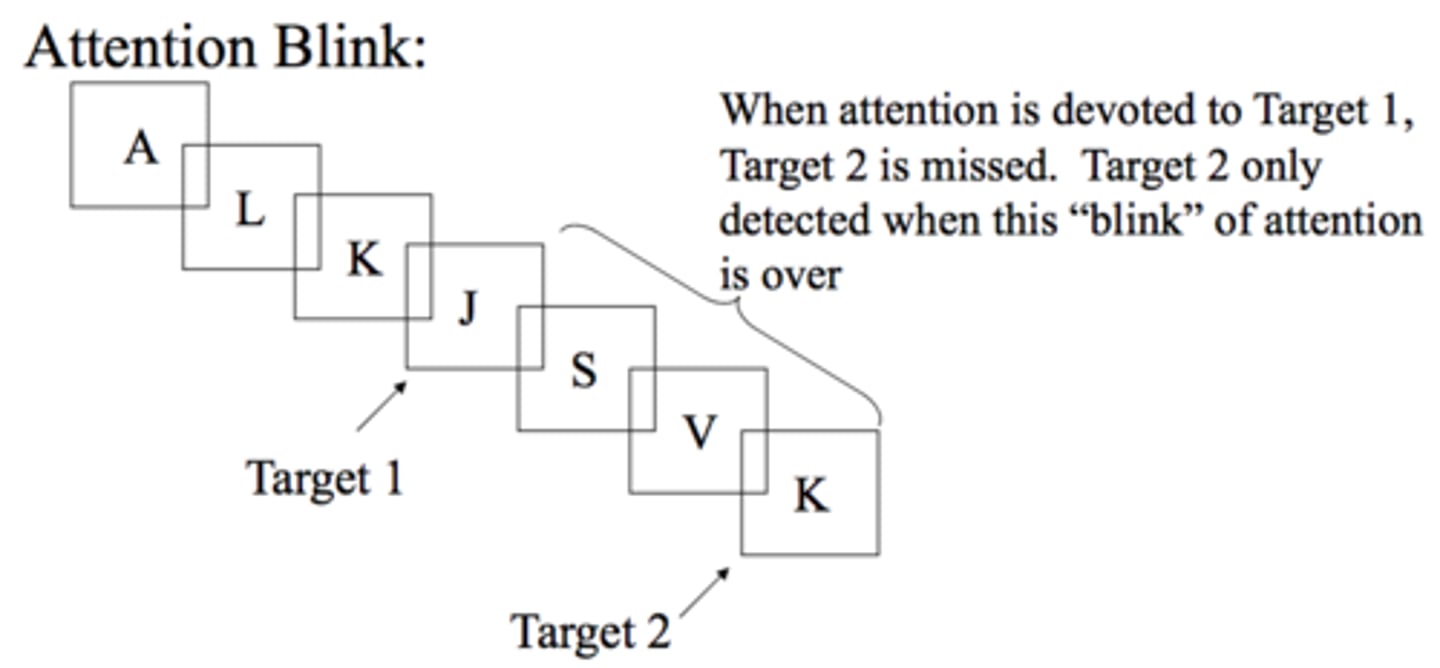
a failure to perceive stimuli that are not the focus of attention
Inattentional blindness
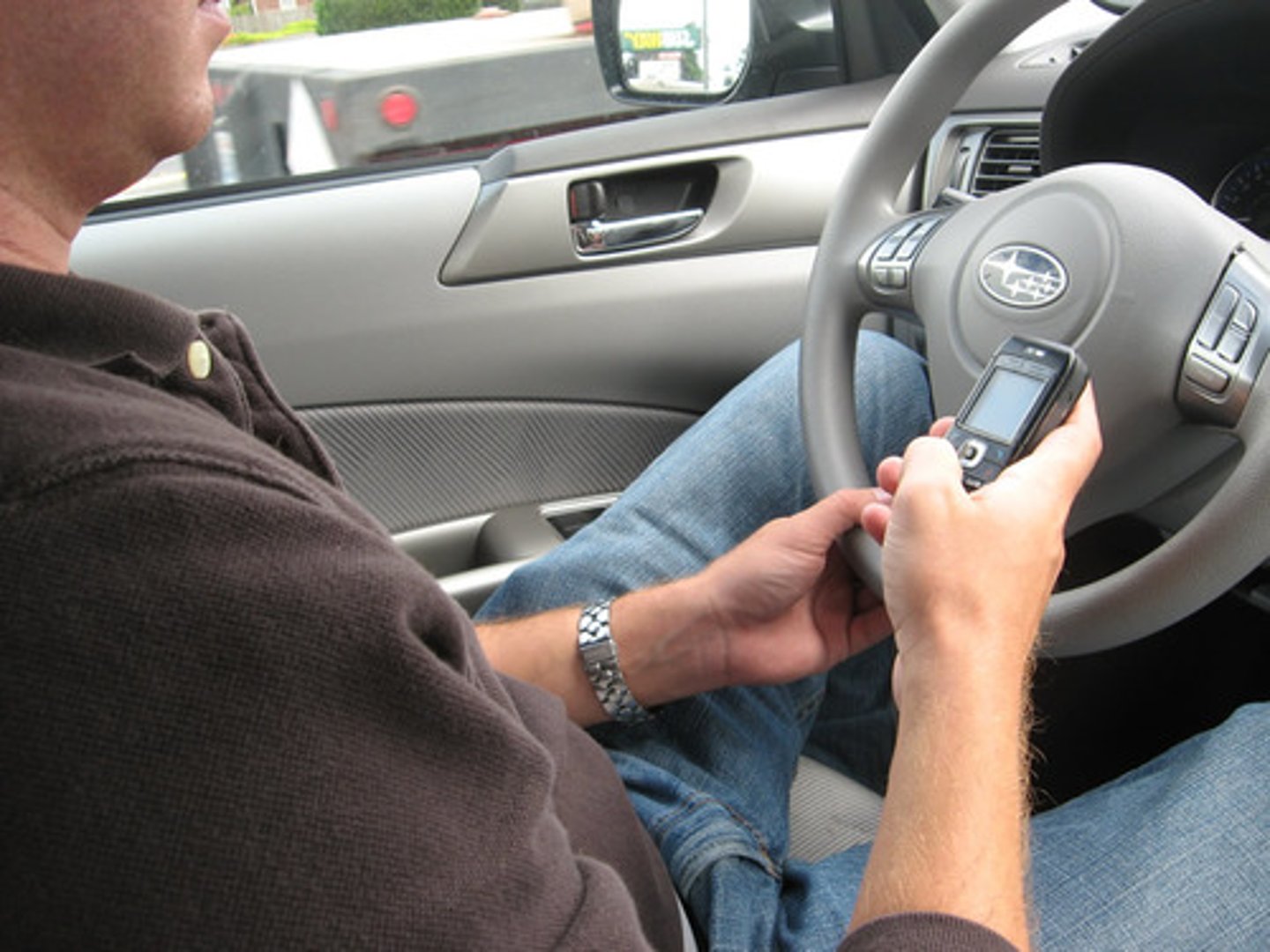

failing to notice changes in the environment; a form of inattentional blindness
Change blindness
cues of depth perception that arise from the fact that people have two eyes
Binocular depth cues

a binocular cue used to perceive depth between two near objects
Retinal disparity

Convergence a binocular cue for depth resulting from the eyes converging inward when looking at an object
Convergence

cues of depth perception that are perceived by one eye, rather than by both working together
Monocular depth cues
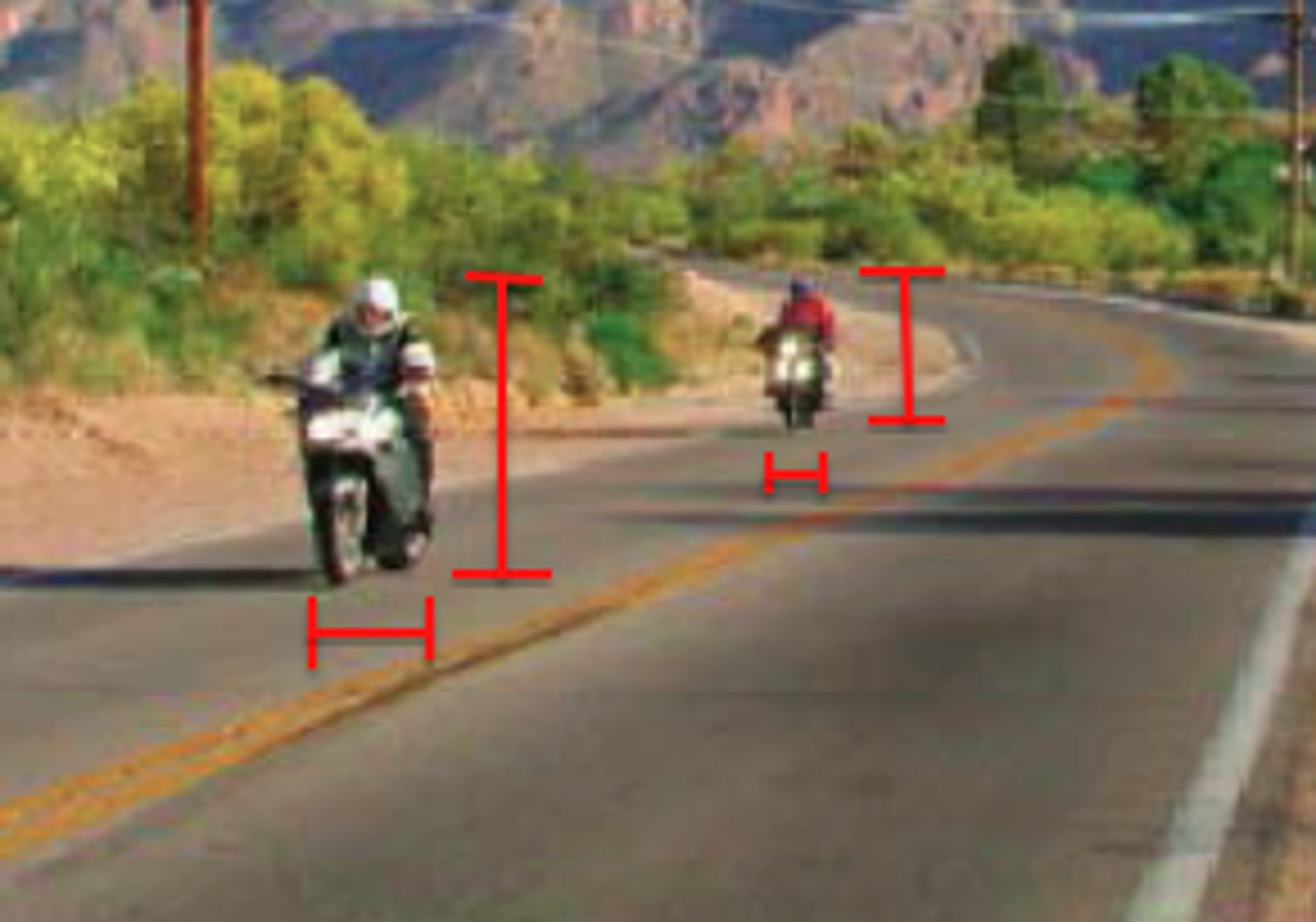

a monocular cue for perceiving depth in which distant objects appear hazy or blurry while near object are sharp and clear
Relative clarity
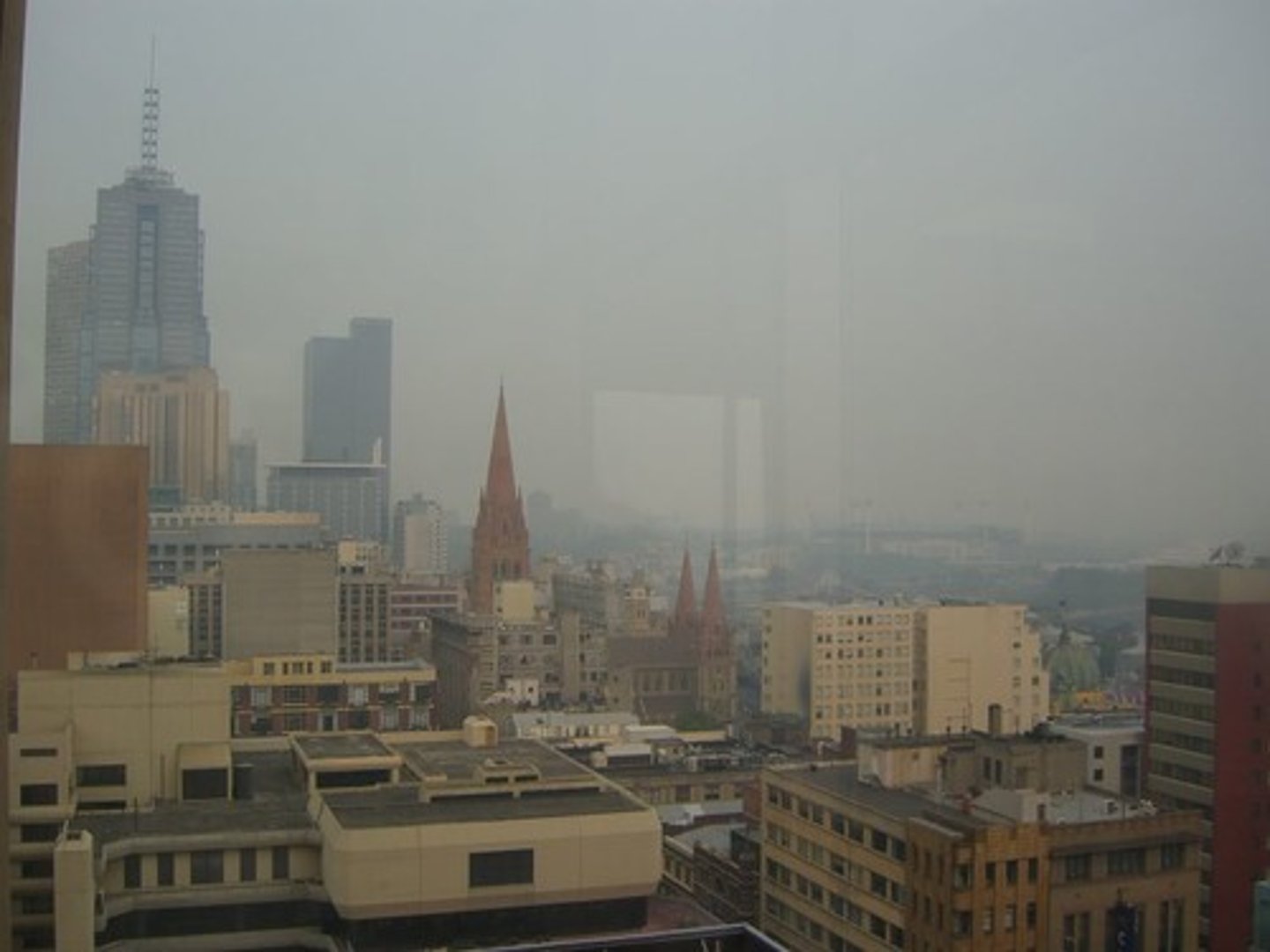

a monocular cue that perceives objects of a known size to be farther away because they appear to be small
Relative size

a monocular cue in which a gradual change from a coarse distinct texture to a fine, indistinct texture signals increasing distance (e.g., objects far away appear smaller and more densely packed)
Texture gradient
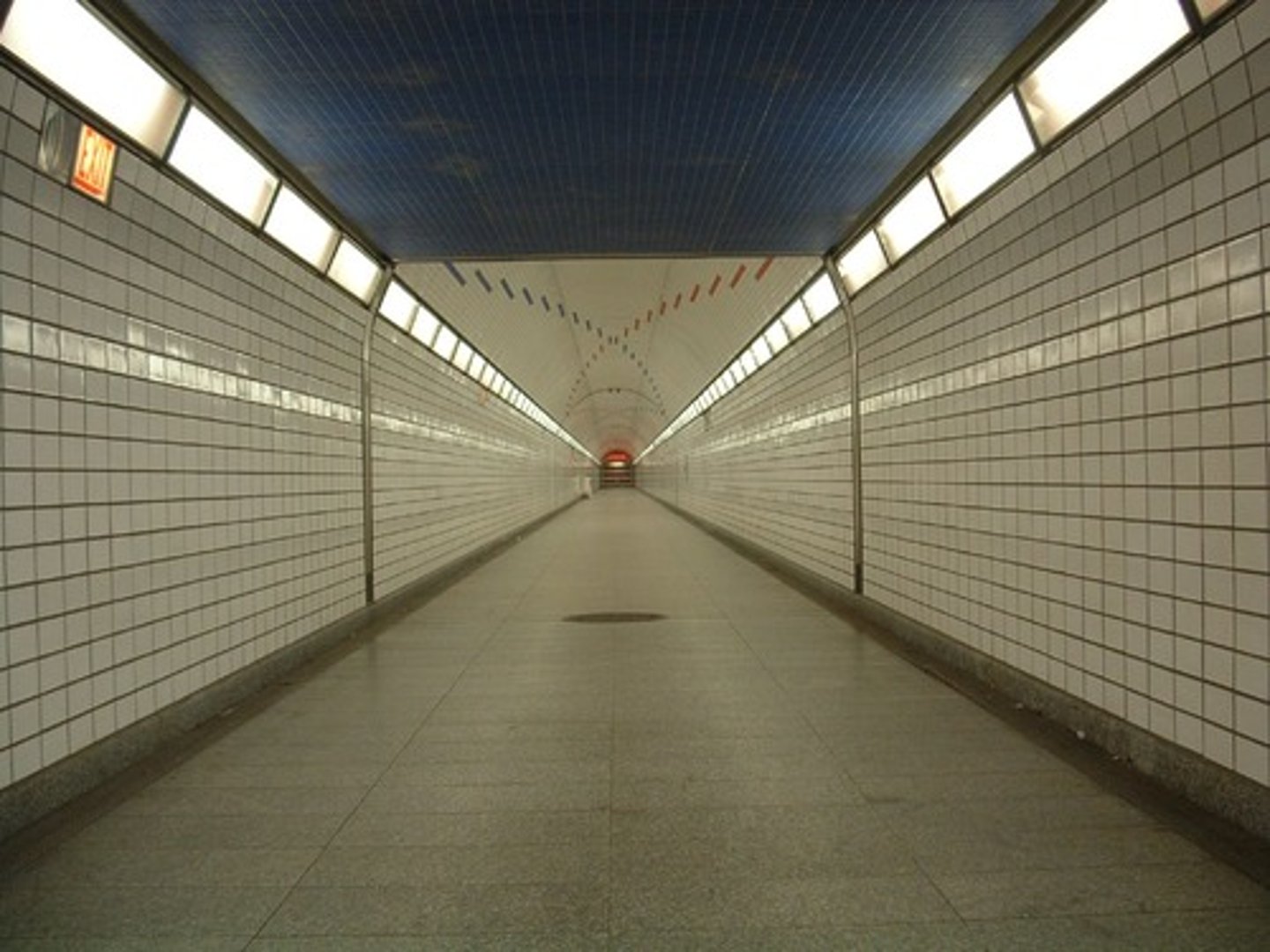
a monocular cue that perceives two parallel lines appearing to meet, thus signaling increasing distance
Linear perspective

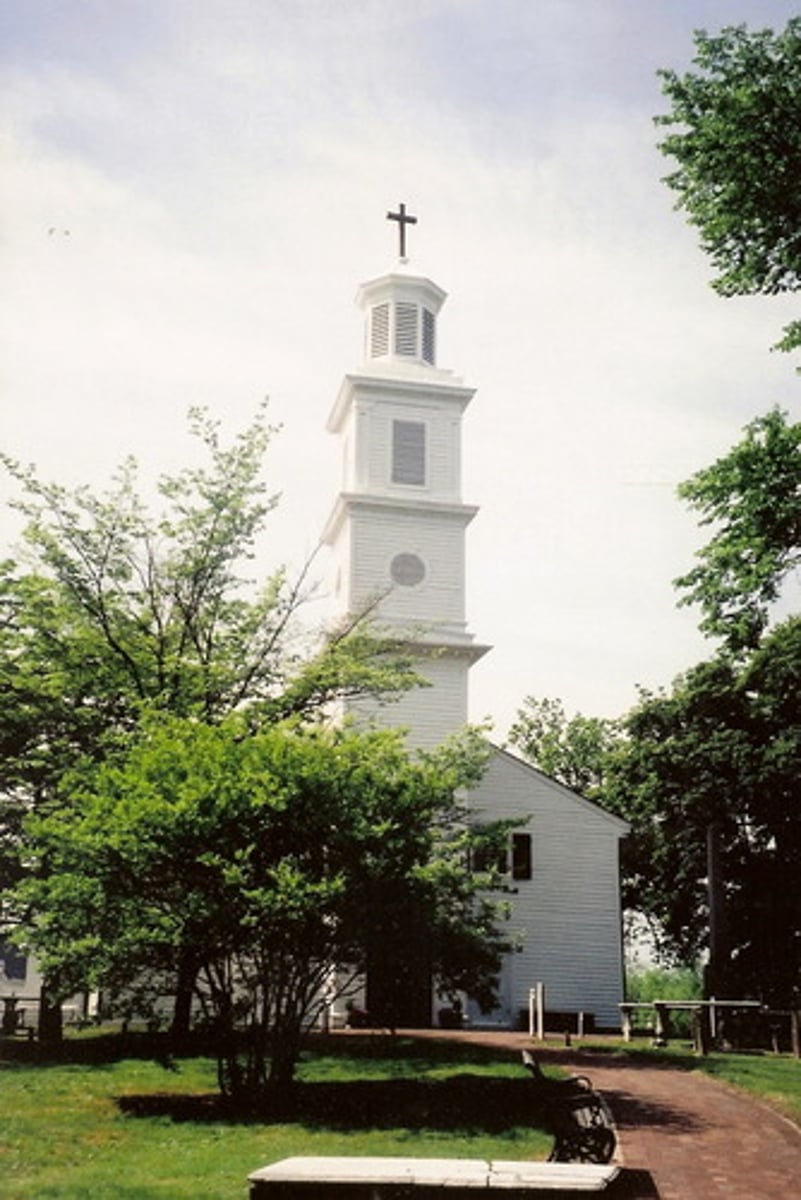
a monocular cue in which the distances of two separate objects are judged based on the fact that one object partially obscures or overlaps the other object
Interposition

an illusion of movement that occurs when stimuli in different locations are flashed one after another with the proper timing
Apparent movement
