Cardio/Renal 23 - Disorders of RBCs and WBCs (Dr. Griffin)
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
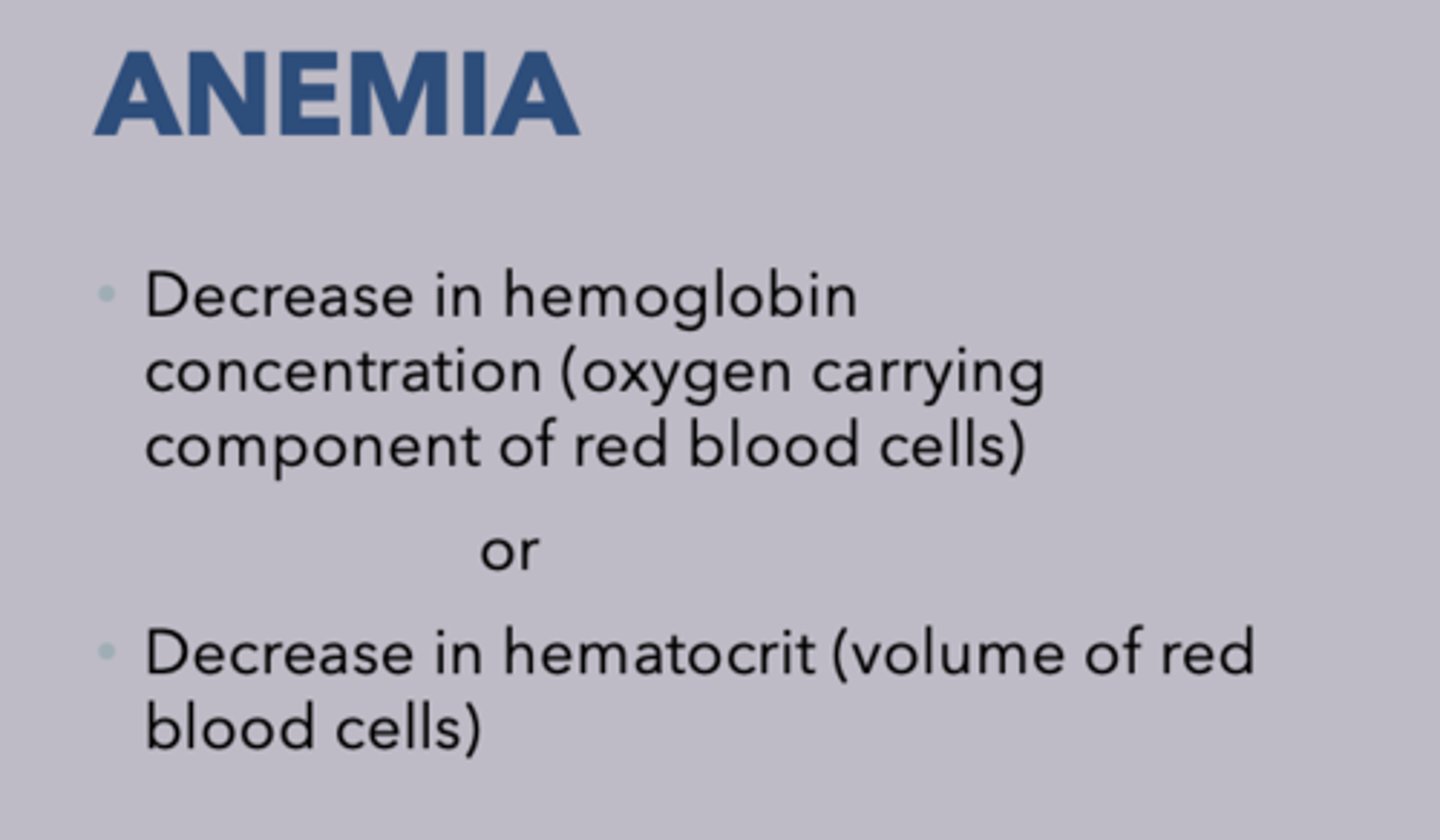
What is the following:
•Decrease in hemoglobin concentration (oxygen carrying component of red blood cells)
or
•Decrease in hematocrit (volume of red blood cells)
Anemia
Rather than being a disease itself, anemia is often a sign of an underlying disease such as...
•Renal failure
•Liver disease
•Chronic inflammatory conditions
•Malignancies
•Vitamin or mineral deficiencies

4 common causes of anemia are:
- Excessive blood loss
- Decreased red cell production
- Increased destruction (sickle cell)
- Increased demand (pregnancy)
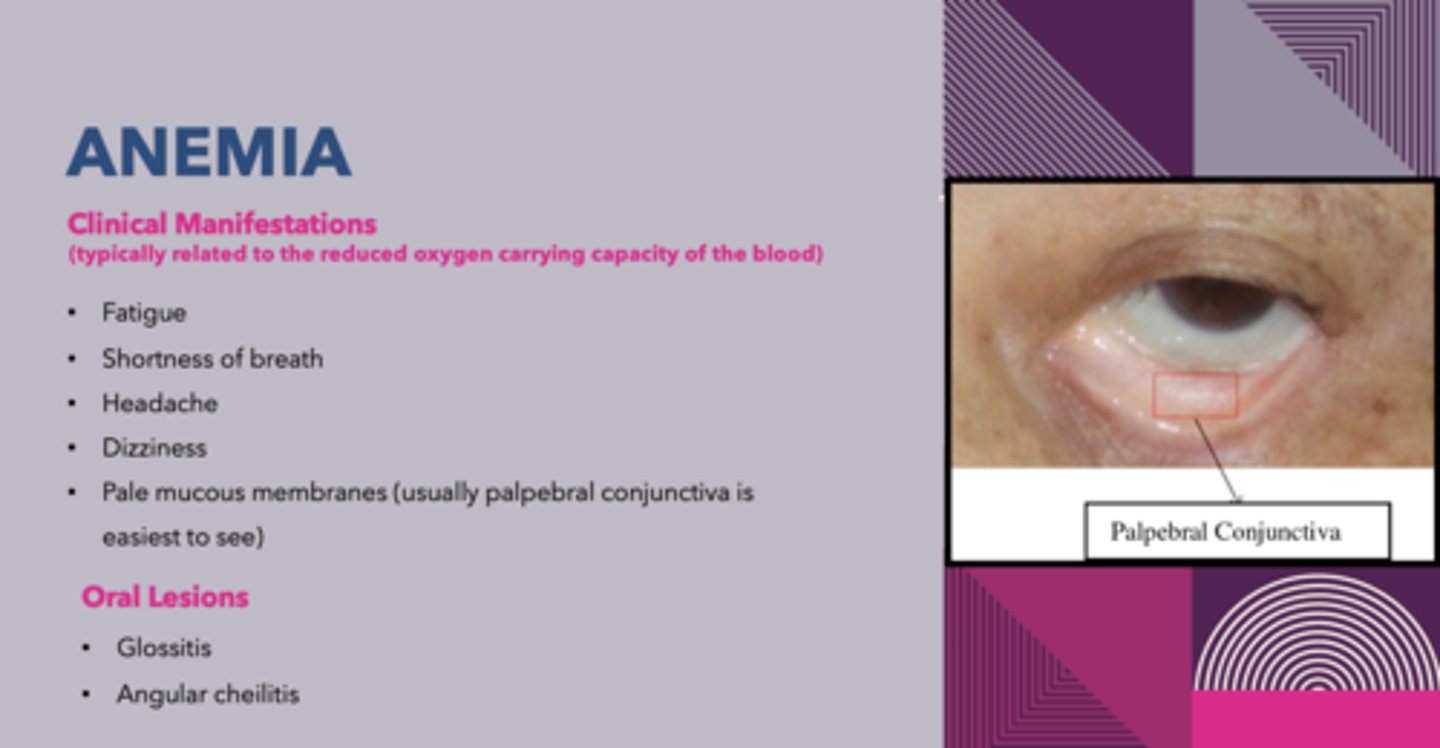
what are 2 oral manifestations that can occur in patients with anemia?
glossitis and cheilosis
what is the most common cause for anemia?
iron deficiency

Excessive blood loss, decreased iron intake, decreased absorption of iron, increased demand for RBCs are all causes for _______________
Iron deficiency anemia

Define the following:
Amount of iron available to body can't keep pace with need for iron in red blood cells
iron deficiency

dental concerns for patients with iron deficiency-related anemia:
low risk, normal protocol, maintain stress-free environment
treatment for iron deficiency related anemia:
eat iron rich diet
iron supplements
treat underlying disease

what population is know to get Paterson-Kelly Syndrome anemia?
women of Scandinavian or Northern European origin

What condition is the following:
Premalignant condition, associated with oral and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, have iron-deficiency anemia
Paterson-Kelly Syndrome (aka Plummer-Vision syndrome)

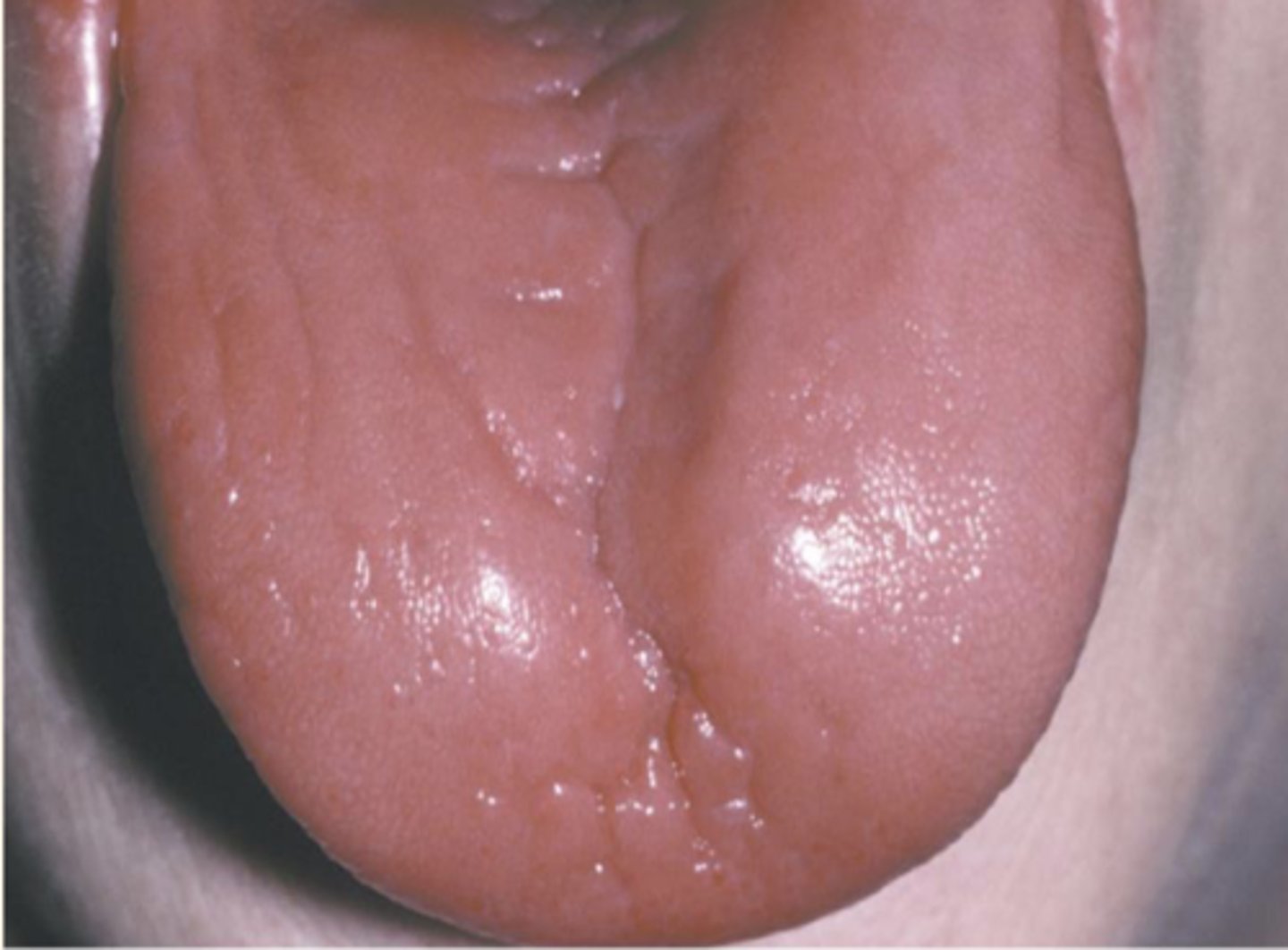
Define the following:
Burning sensation of oral mucosa (mucositis) and tongue
Glossitis
All of the following symptoms are associated with what disorder?
- Burning sensation of oral mucosa, tongue (glossitis)
- Angular cheilitis
- Bald tongue
- Esophageal webbing
- Spoon-shaped, brittle nails
Paterson-Kelly Syndrome (aka Plummer-Vision syndrome)

_______________ is caused by an autoimmune attack on gastric mucosa & suppress the intrinsic factor, resulting in the poor absorption of Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) & inhibition of vitamin B12-normal nucleic acid synthesis
pernicious anemia

T/F: Vitamin B12 is very abundant in many foods so it is usually not a dietary deficiency
Trye

What anemia have an increased risk for gastric carcinoma?
Pernicious anemia

two types of megaloblastic anemias:
folic acid deficiency anemia
pernicious anemia
patient presents with generalized weakness, painful tongue, and numbness/tingling of extremities. What is the diagnosis?
pernicious anemia

What is the treatment for pernicious anemia?
• Intramuscular injections of Vitamin B12
• High dose of oral Vitamin B12
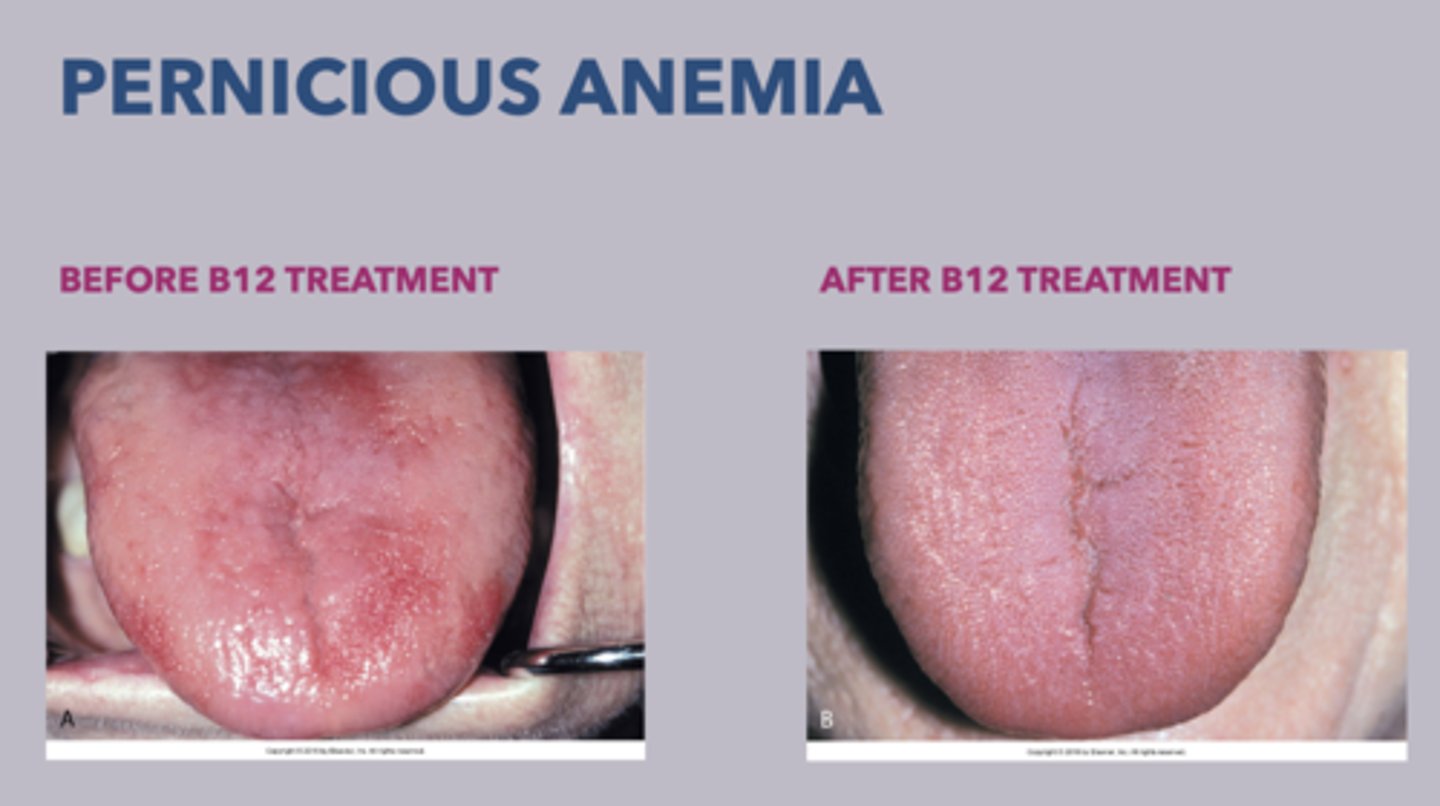
what is the classic triad for pernicious anemia?
generalized weakness
painful tongue
numbness/tingling of extremities

Premature destruction of red blood cells, can be acquired or inherited:
hemolytic anemia
hyperbilirubinemia and jaundice are associated with what type of anemia?
hemolytic anemia
2 types of hemolytic anemia:
- Sickle cell anemia
- Thalassemia
what is the most common type of hemolytic anemia?
sickle cell anemia
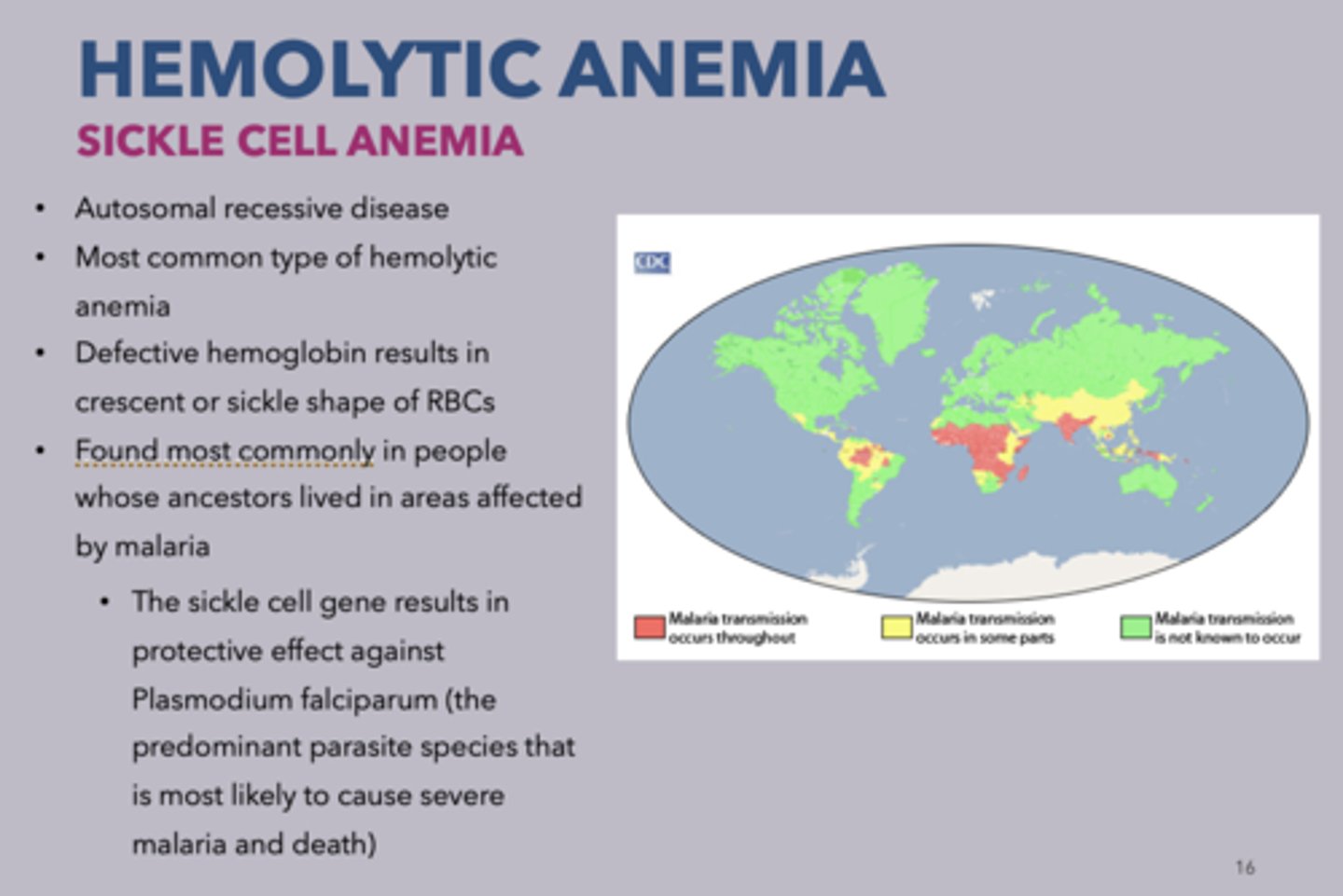
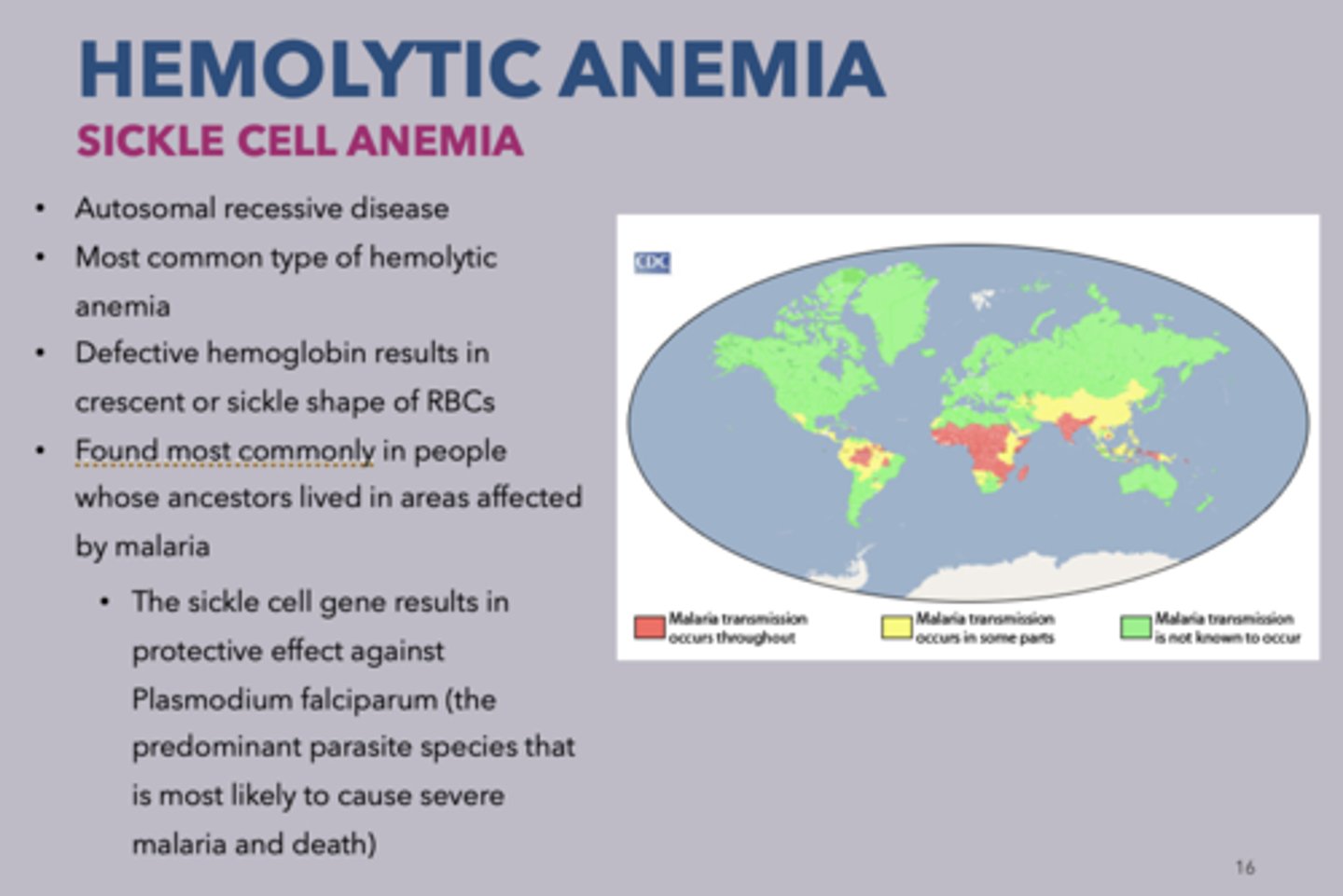
Where is hemolytic anemia most commonly found?
In people whose ancestors lived in areas affected by malaria
patients presents with Malaise and weakness, Muscle rigidity and Wide-spread ischemia leads to death. What is the diagnosis?
sickle cell disease
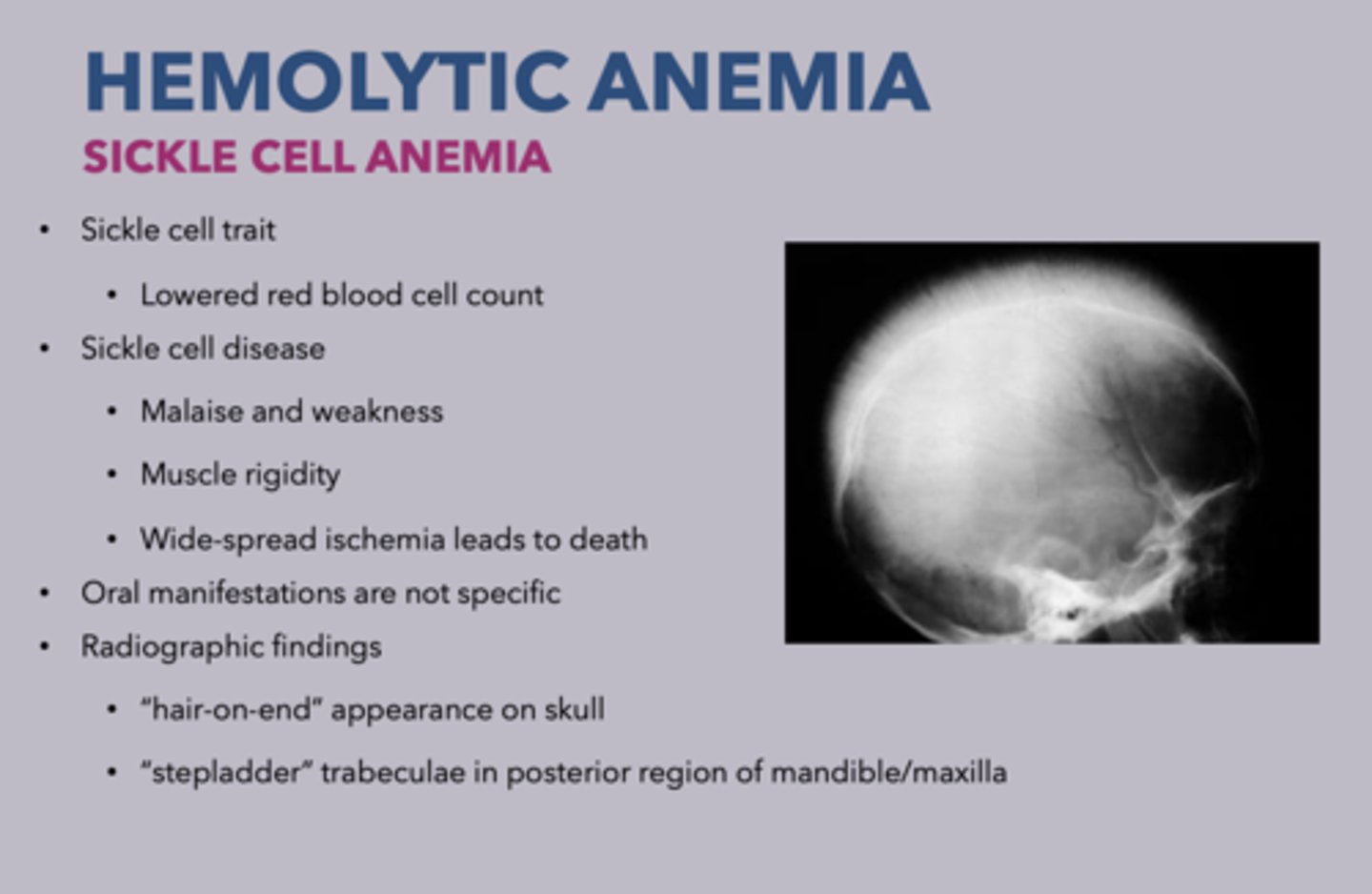
oral manifestations of sickle cell anemia:
none
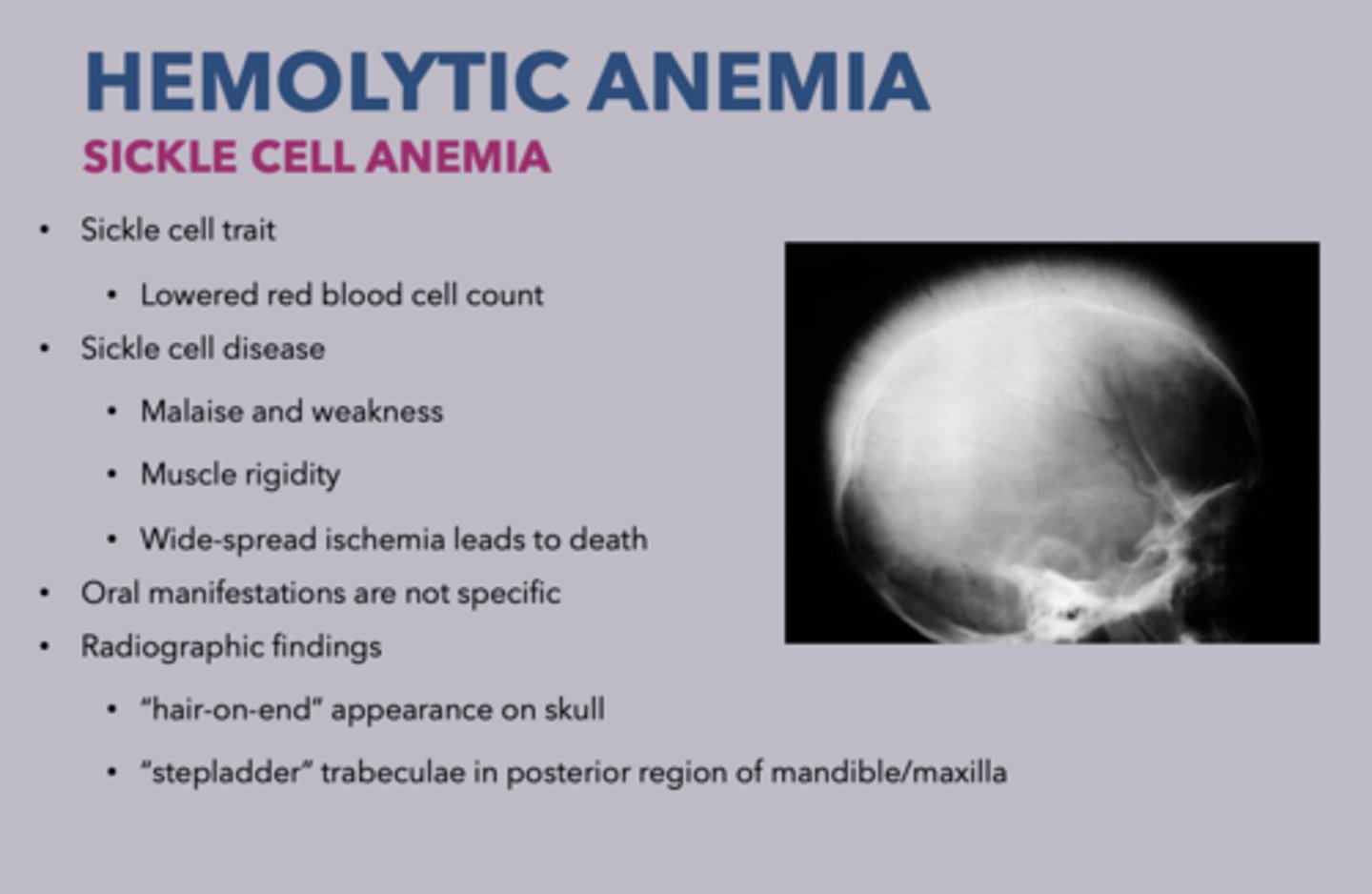
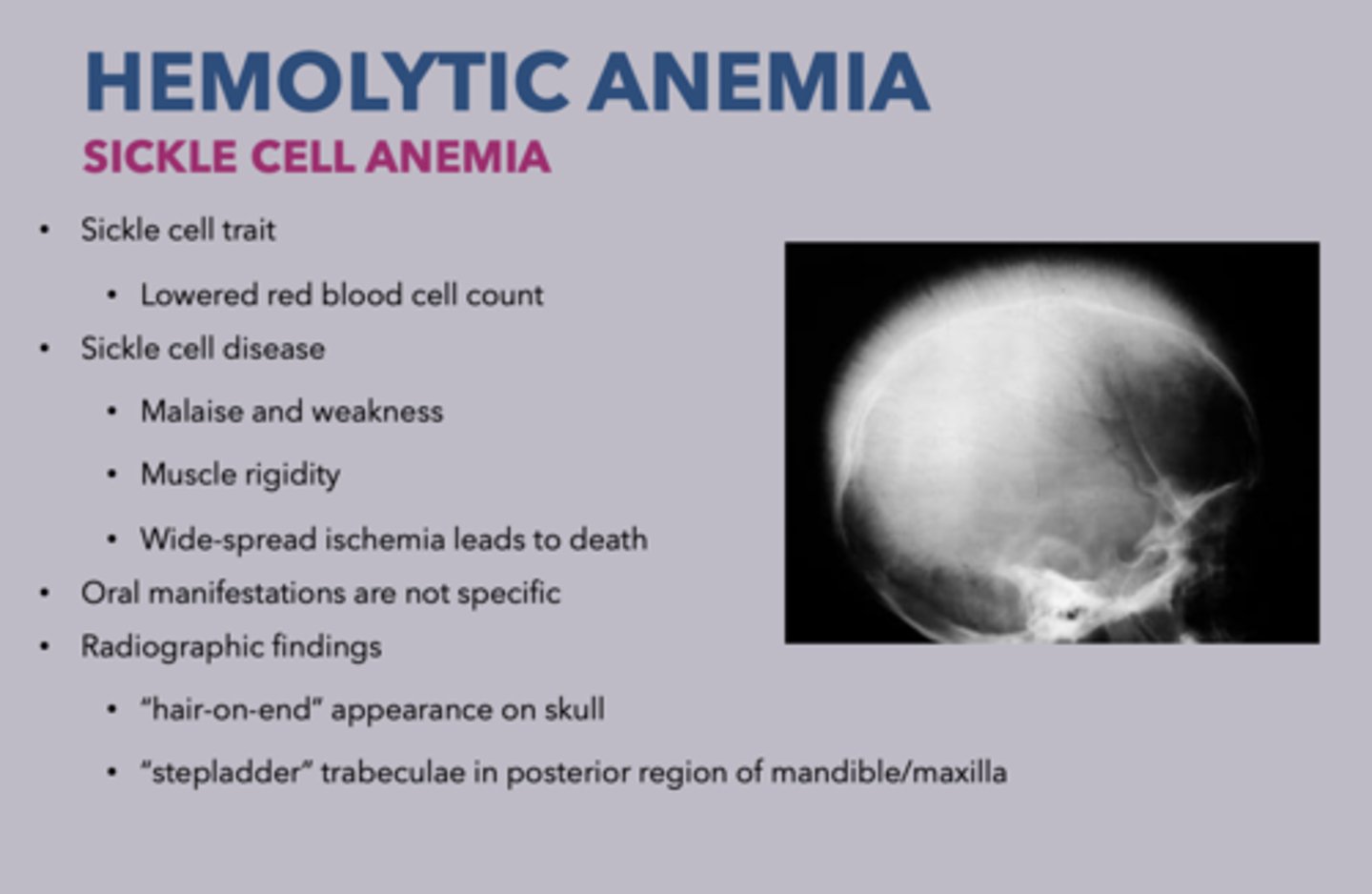
2 radiographic findings of sickle cell anemia:
- "Stepladder" trabeculae in posterior region of mandible/maxilla
- "Hair-on-end" appearance on skull
A form of hemolytic anemia that reduces synthesis of alpha/beta globin chains, red blood cells are microcytic and hypochromic
Thalassemia

what forms of anemia can present with "Hair-on-end" appearance on skull?
sickle cell anemia
β-Thalassemia
patients with 1 β-thalassemia chromosomal defect:
Thalassemia minor or β-thalassemia minor trait

clinical manifestations of β-thalassemia minor trait:
none

patients with 2 β-thalassemia chromosomal defects:
Thalessemia major (Cooley/Mediterranean anemia)

clinical manifestations of Cooley or Mediterranean anemia:
Severe microcytic, hypochromic anemia after 3-4 months
Bone marrow hyperplasia
Lymphadenopathy

Patient presents with Severe microcytic, hypochromic anemia after 3-4 months, bone marrow hyperplasia & lymphadenopathy. What is the diagnosis?
Thalessemia major (Cooley/Mediterranean anemia)

Patient presents with "Chipmunk face" appearance. On radiograph, you observe "Hair on end" appearance of skull. During head and neck exam you find lymphadenopathy. What is the diagnosis?
Thalessemia

On radiograph, you observe "Hair on end" appearance of skull. "Stepladder" trabeculae appearance presents on periapical radiographs. Blood smear shows some C shaped blood cells. What is the diagnosis?
sickle cell anemia
Severe form of leukopenia (neutropenia) resulting in a decrease production or increased destruction of those cells:
agranulocytosis

what cells are affected by agranulocytosis?
leukocytes and neutrophils

patient presents with constant bacterial/fungal infections. Oral cavity presents with necrotizing, punched out ulcerations involve palate, buccal mucosa, tongue. What is the diagnosis?
agranulocytosis

Oral lesions involve palate, buccal mucosa, tongue
Necrotizing, punched out ulcerations
Gingiva resembles necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis are all...
oral manifestations of agranulocytosis

treatment for patients with agranulocytosis:
oral hygiene instructions with chlorhexidine rinse

a life-threatening hematologic disorder where hematopoietic precursor cells do not produce adequate numbers of blood cells & cell do not undergo normal maturation
aplastic anemia

what cells are dysfunctional in aplastic anemia?
hematopoietic precursor cells

t/f: splenomegaly is a common symptom of aplastic anemia
false, aplastic anemia does not cause splenomegaly

patient presents with constant fungal/bacterial infections, tachycardia and light-headness. Patient is known to bleed and bruise easily. Oral examination shows oral petechiae, hemorrages, pale oral mucosa and gingival hyperplasia. What is the diagnosis?
aplastic anemia

oral manifestations of aplastic anemia:
Hemorrhage
Petechiae
Pale oral mucosa
Gingival hyperplasia

Deficiency of this can cause fatigue, tachycardia, lightheadness
RBCs

Deficiency of this can cause easy brusing/bleeding
platelets

Deficiency of this can lead to fungal and bacterial infections
White blood cells

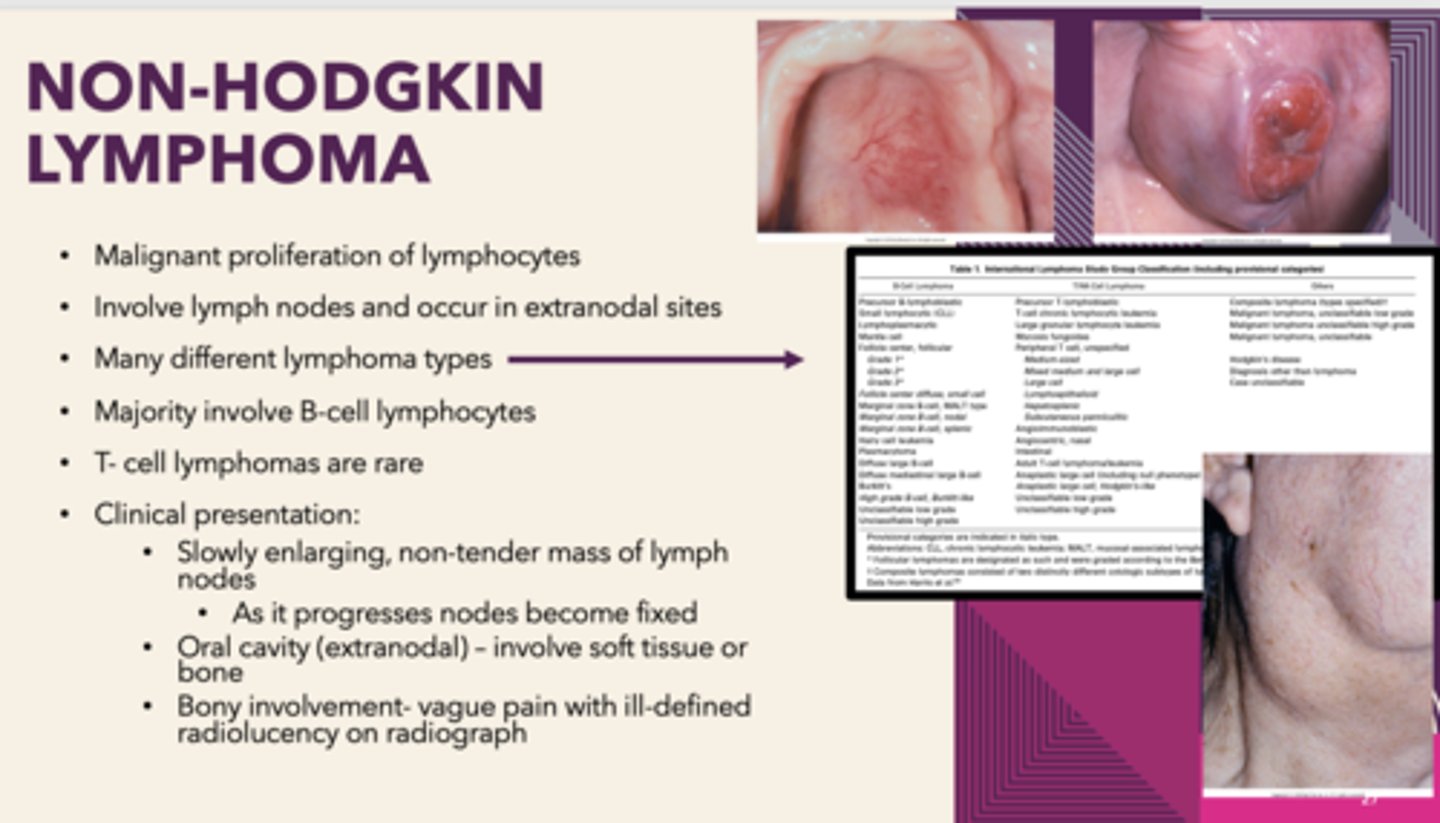
which type of lymphoma has oral manifestations?
Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
which type of lymphoma is not present in oral cavity?
Hodgkin Lymphoma (HL)
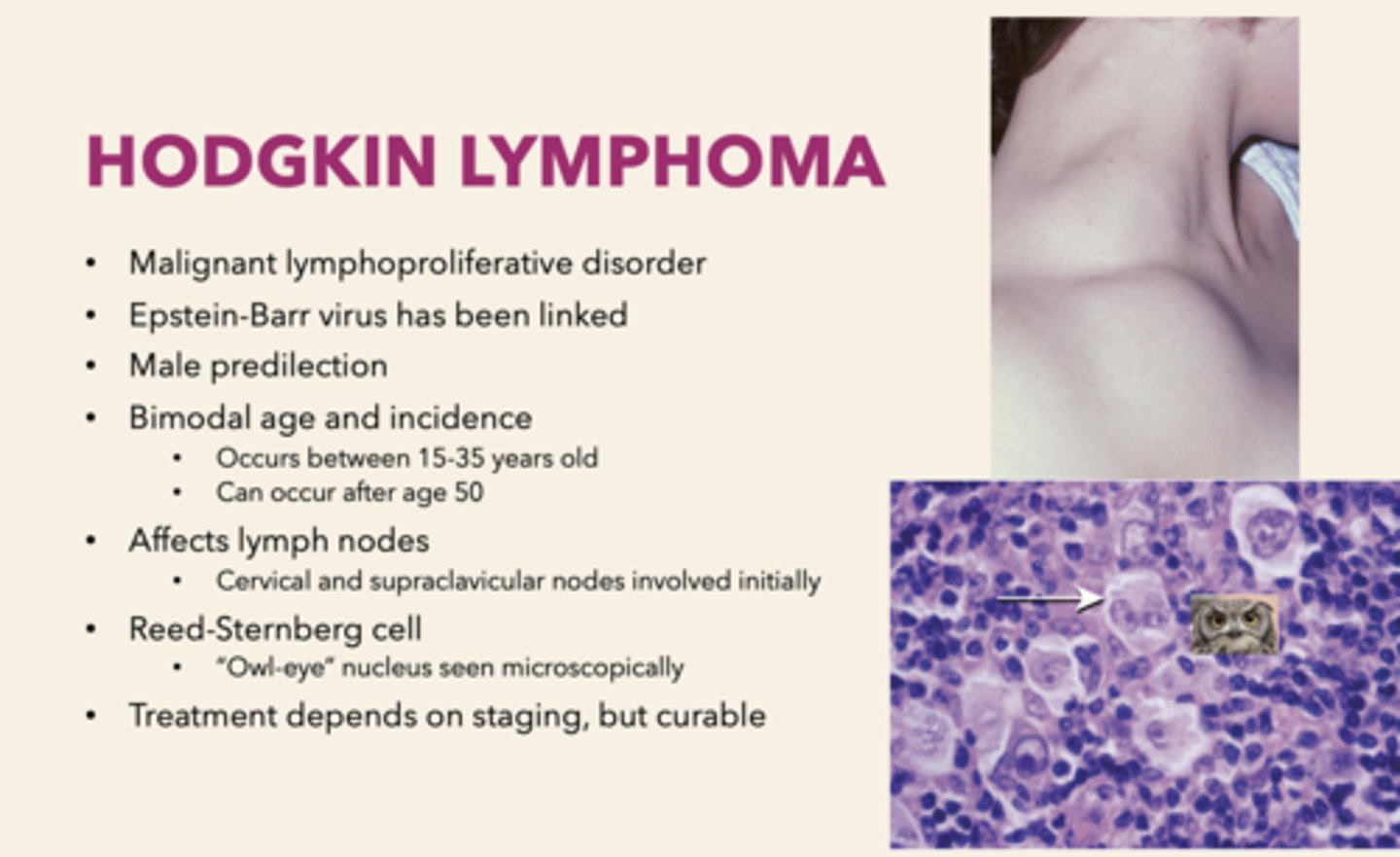
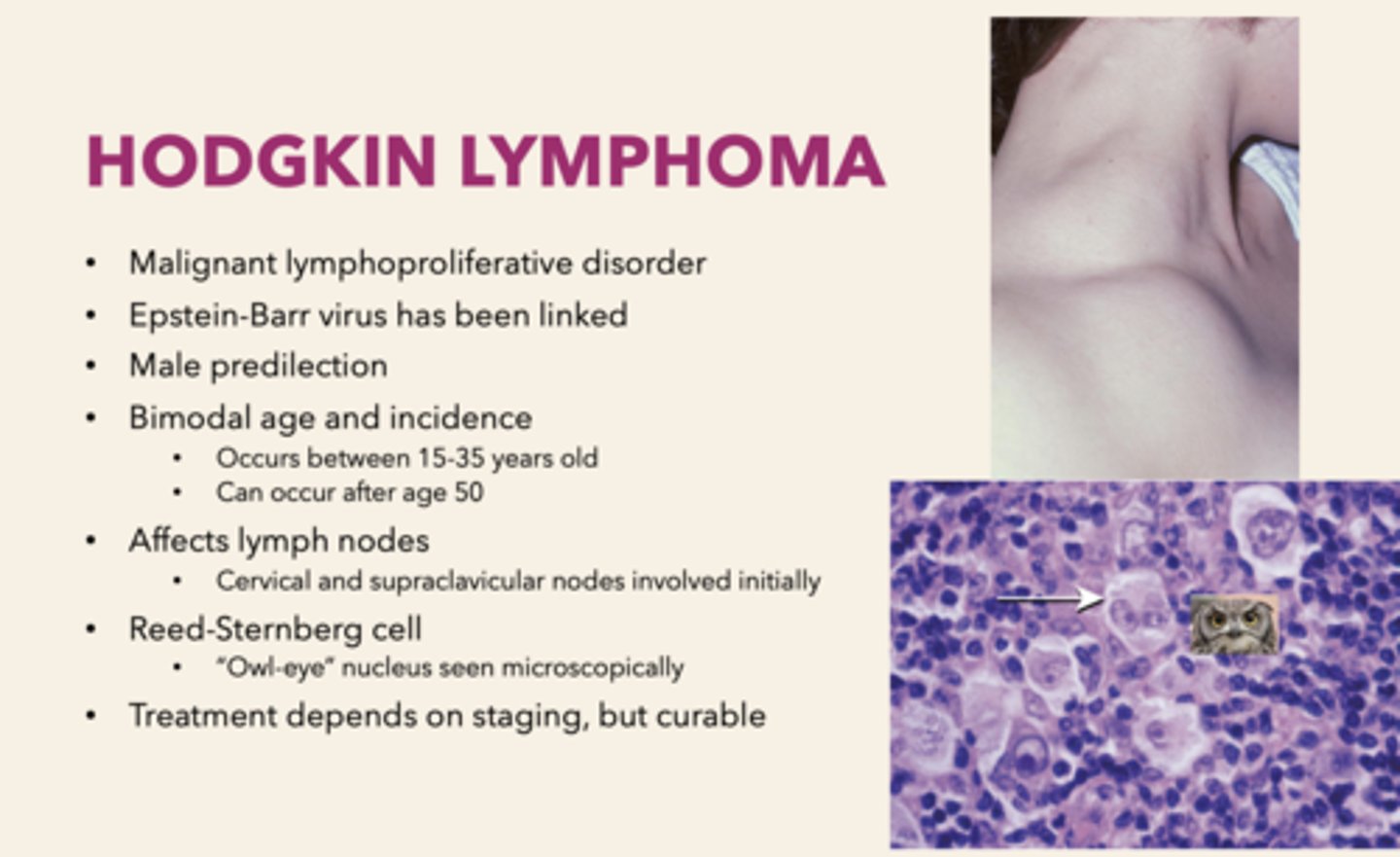
a malignant lymphoproliferative disorder that affects cervical and supraclavicular lymph nodes. It is Epstein-Barr virus has been linked and has a male predilection:
Hodgkin's Lymphoma
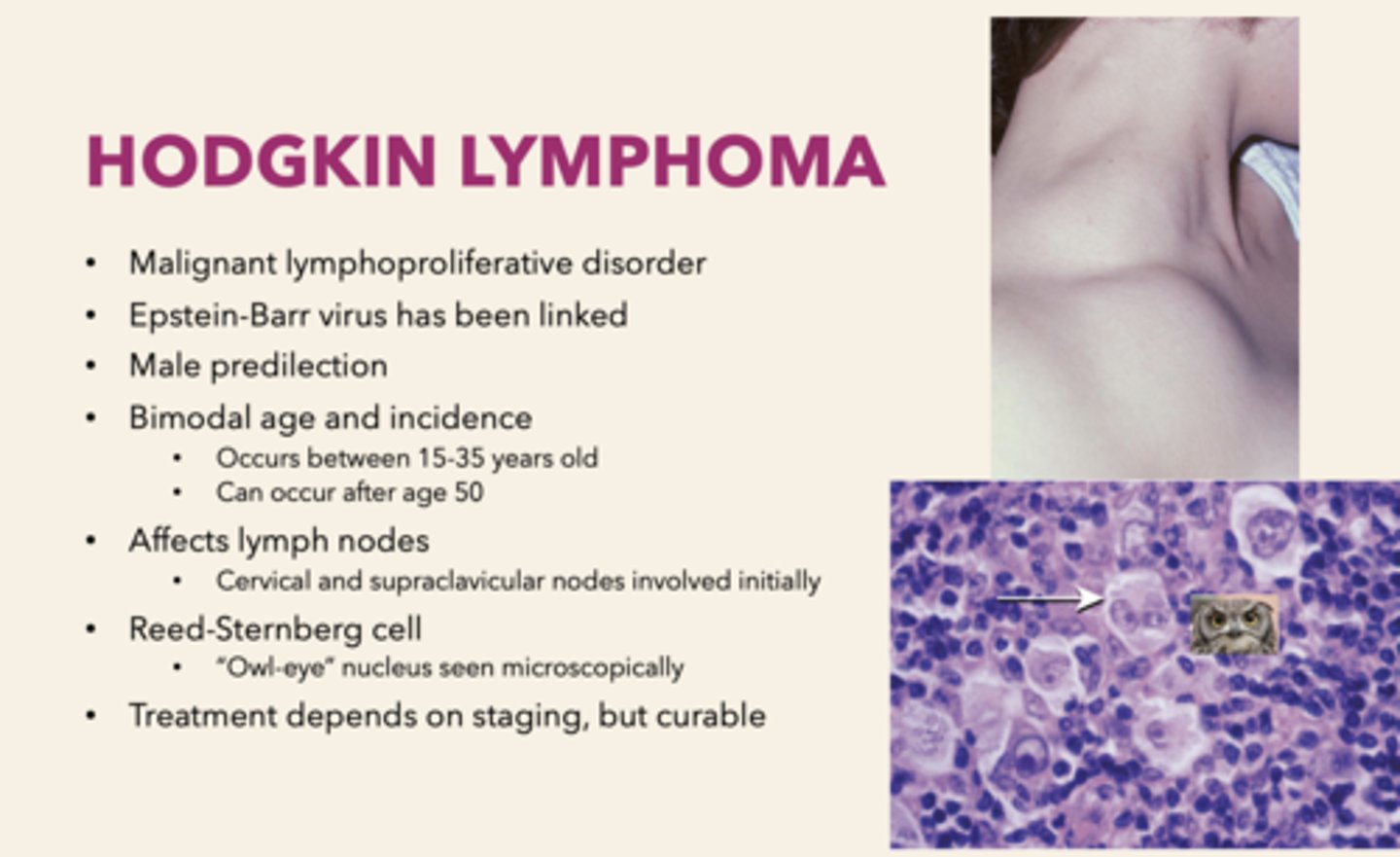
the Reed-Sternberg ("Owl-eye" nucleus) cell can be observed in which pathology?
Hodgkin's lymphoma
lymphomas are malignancies of what cells?
lymphocytes
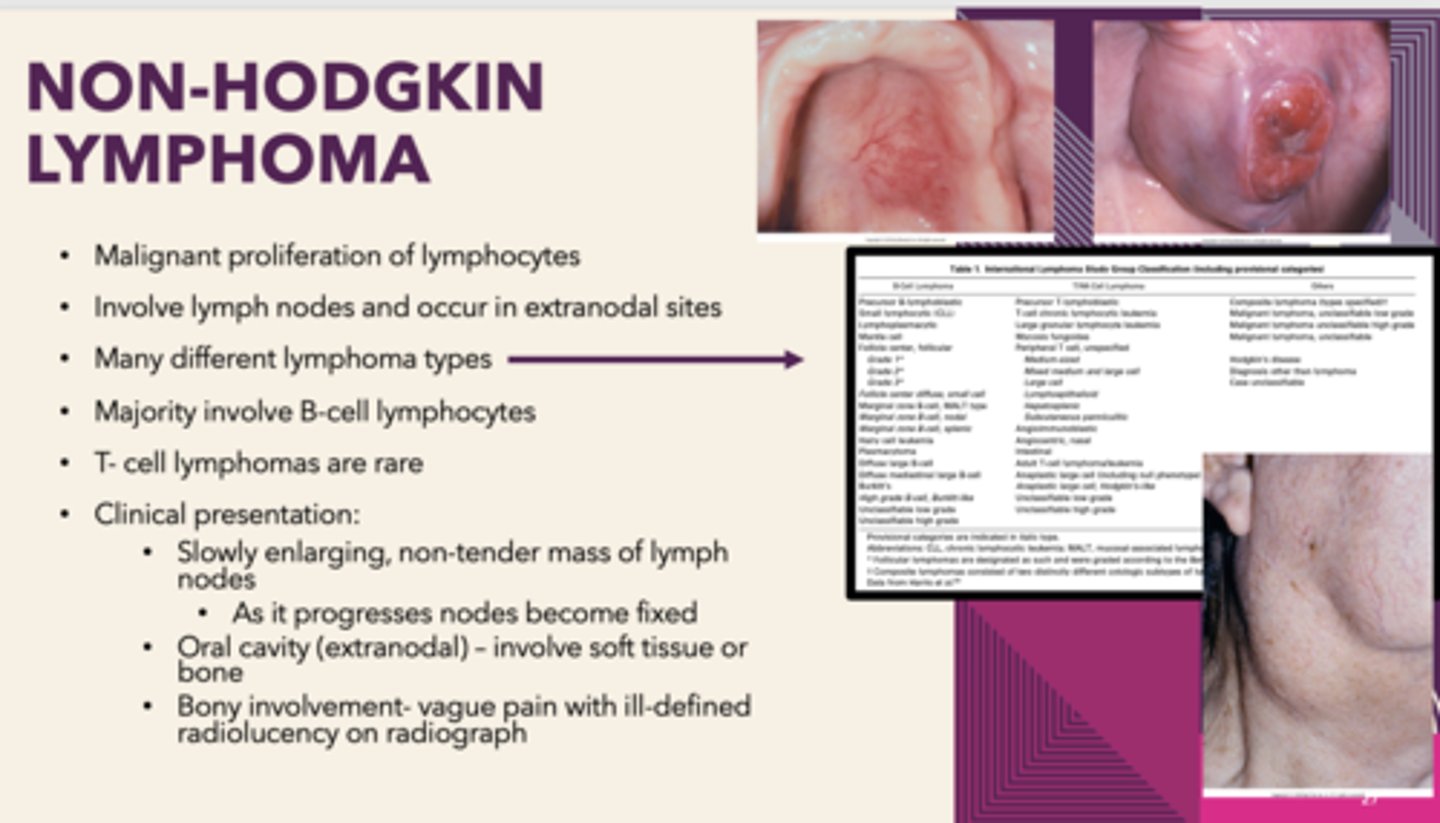
Malignant proliferation of lymphocytes that involves lymph nodes and occur in extranodal sites, MALT lymphoma (extranodal marginal B-cell lymphoma) can be associated with Sjogren syndrome:
Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
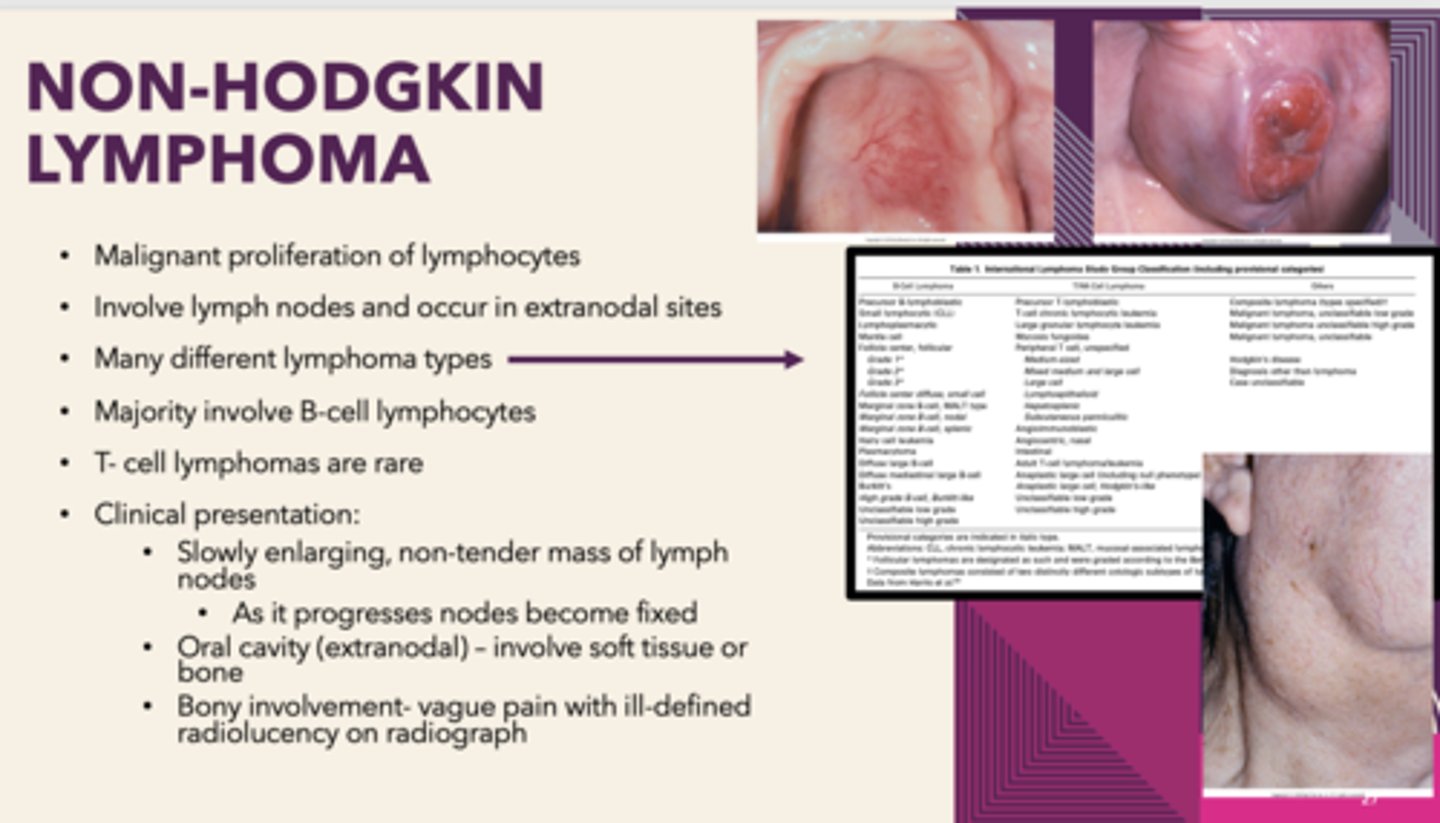
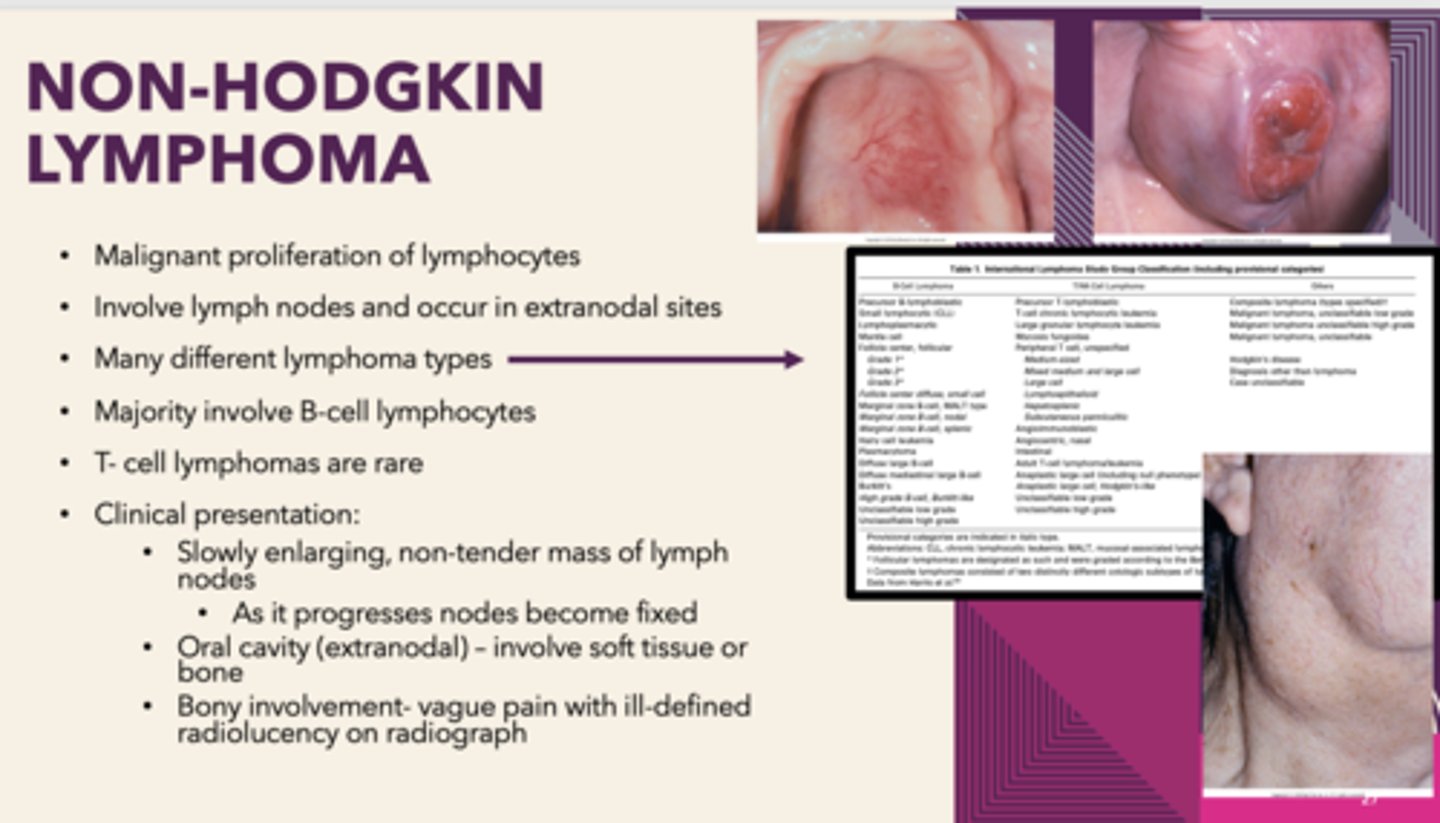
patients presents with Sjogren syndrome. Patient has enlarging non-tender mass of cervical lymph nodes. In the oral cavity, the soft tissue appears erythematous and boggy. Bony involvement-vague pain with ill-defined radiolucency on radiograph: What is the diagnosis
Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
the Epstein Barr virus is associated with what pathologies?
Burkitt's lymphoma (Non- Hodgkin's)
Hodgkin's Lymphoma
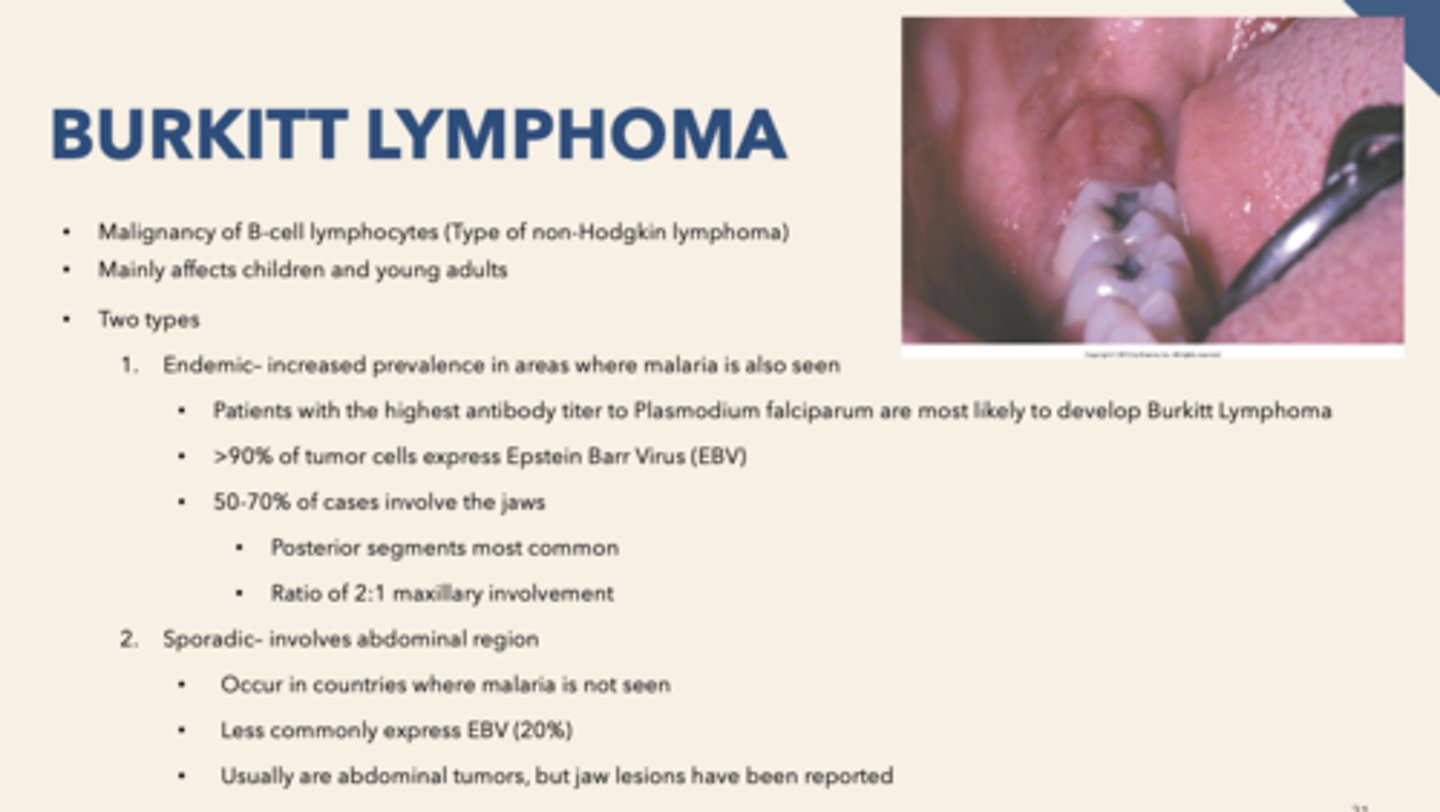
what population does endemic Burkitt's lymphoma affect:
Africans
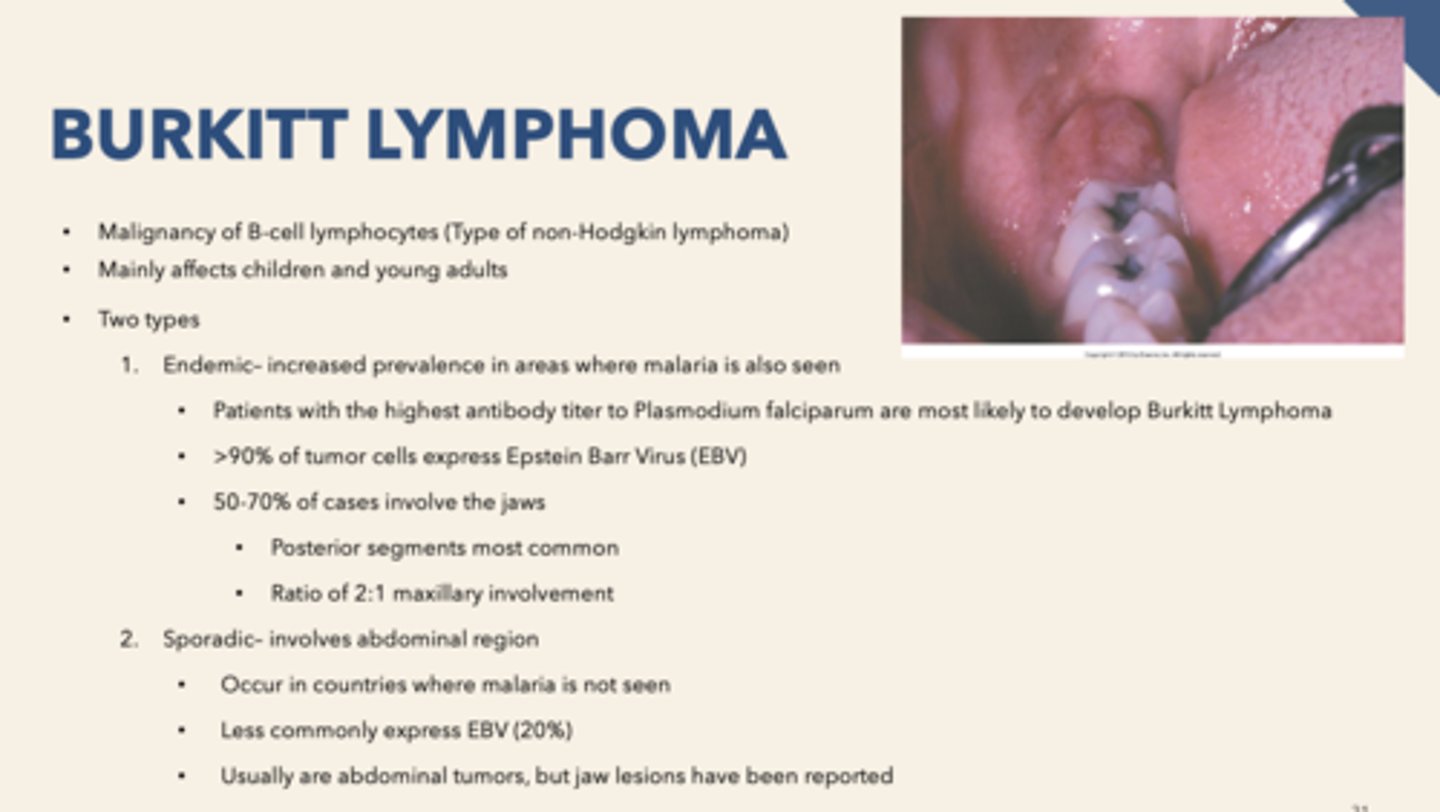
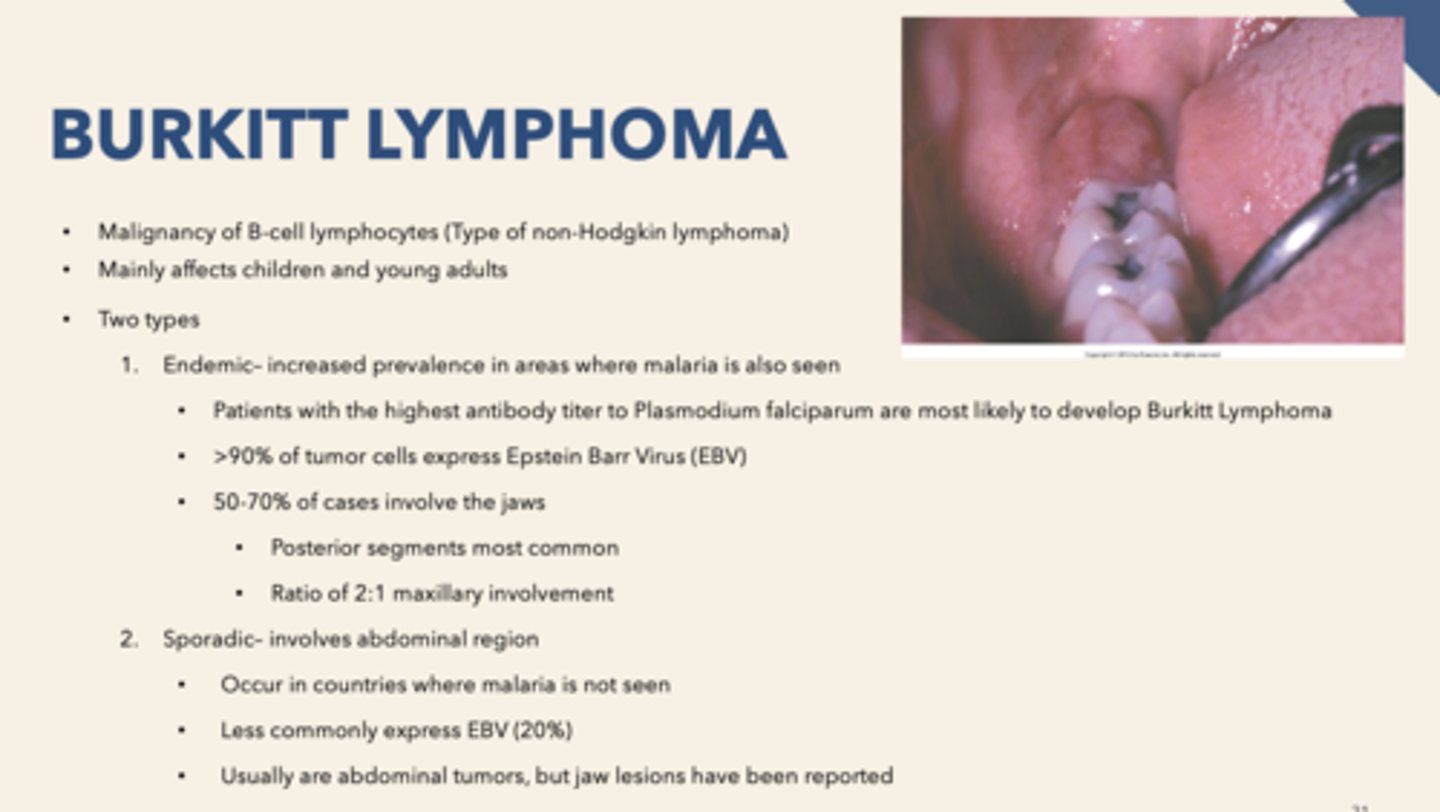
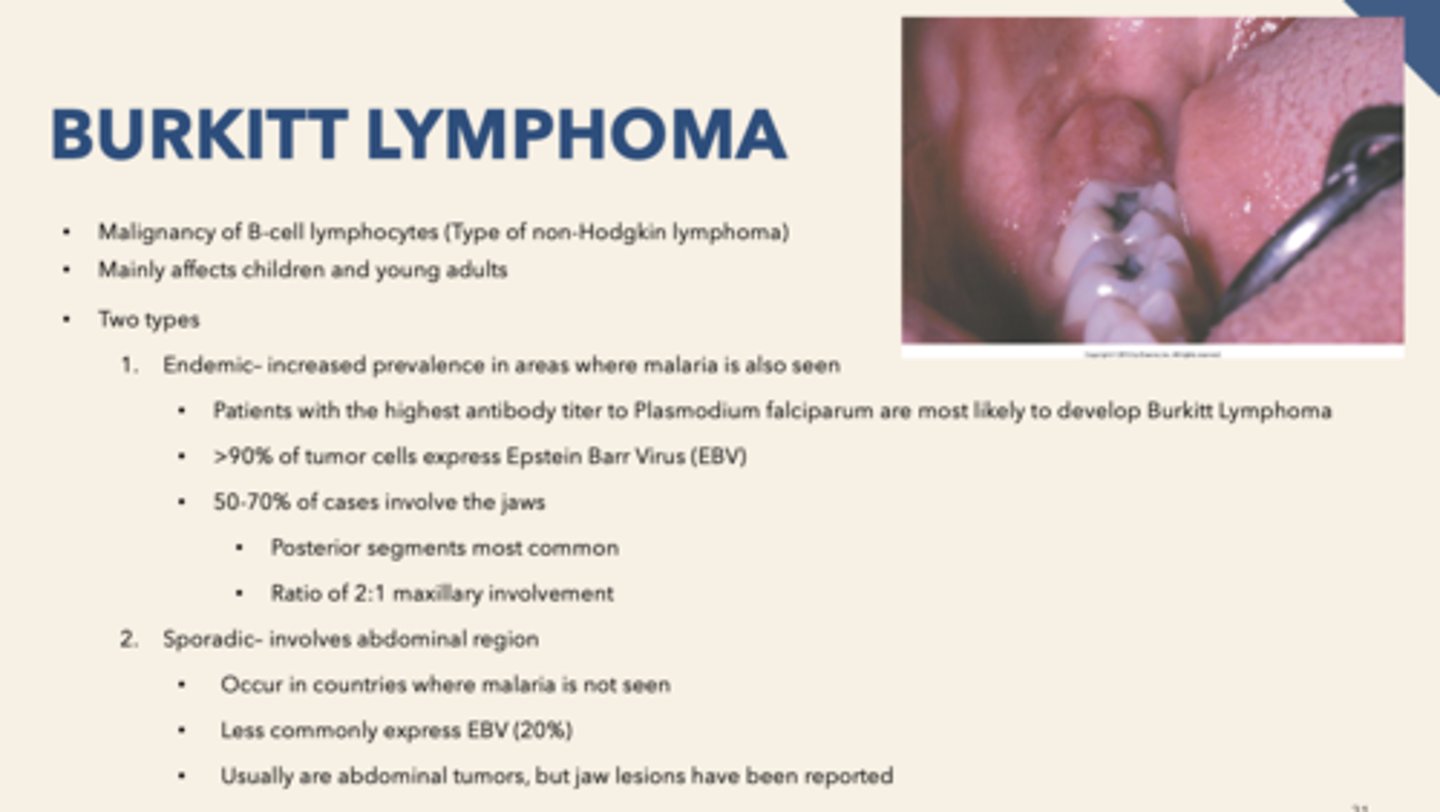
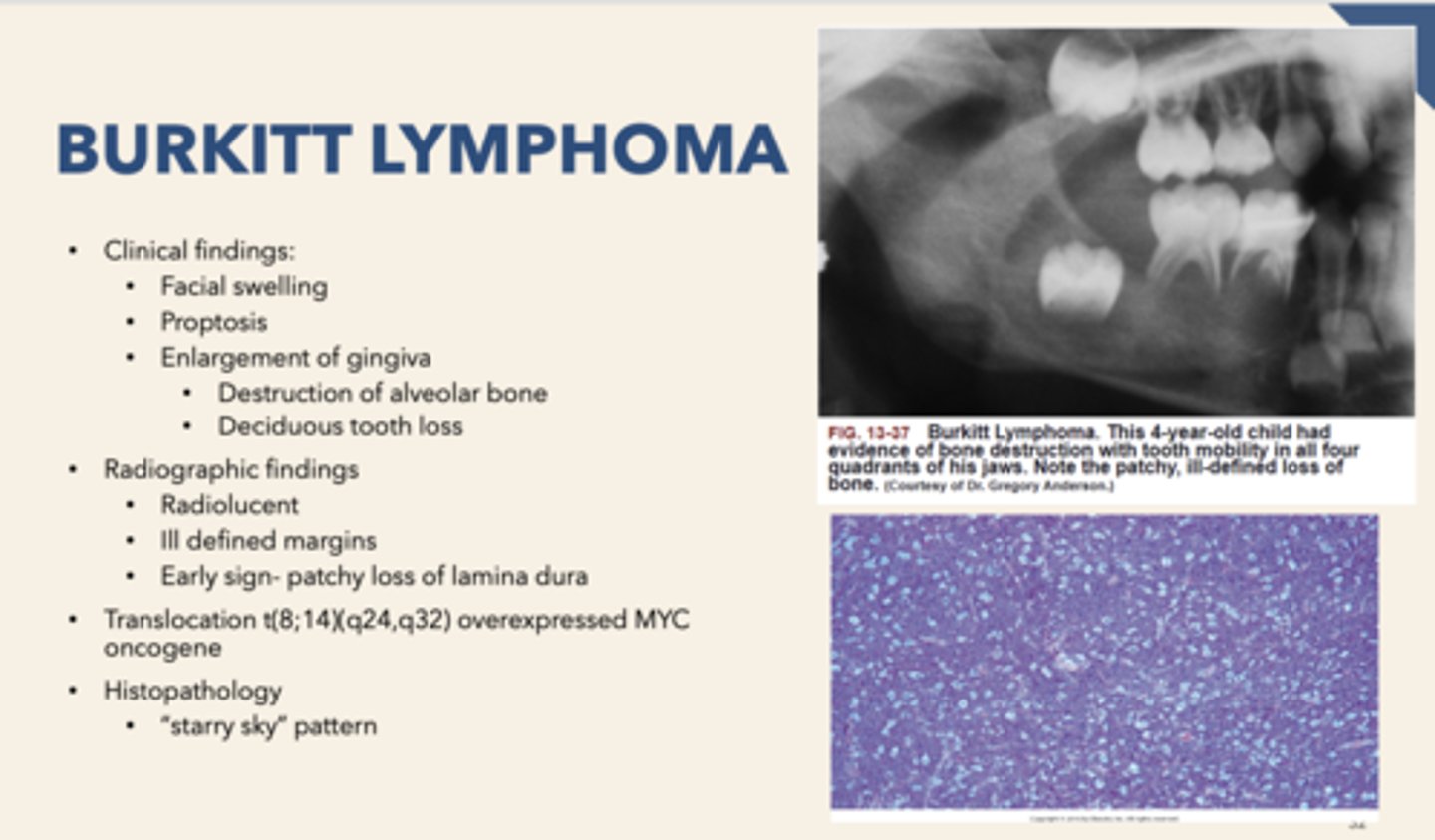
patient presents with facial swelling, proptosis (eye buldging) and enlarged gingiva with some alveolar bone destruction. Biopsy is performed and "starry sky" pattern is observed. What is the diagnosis?
Burkitt's lymphoma
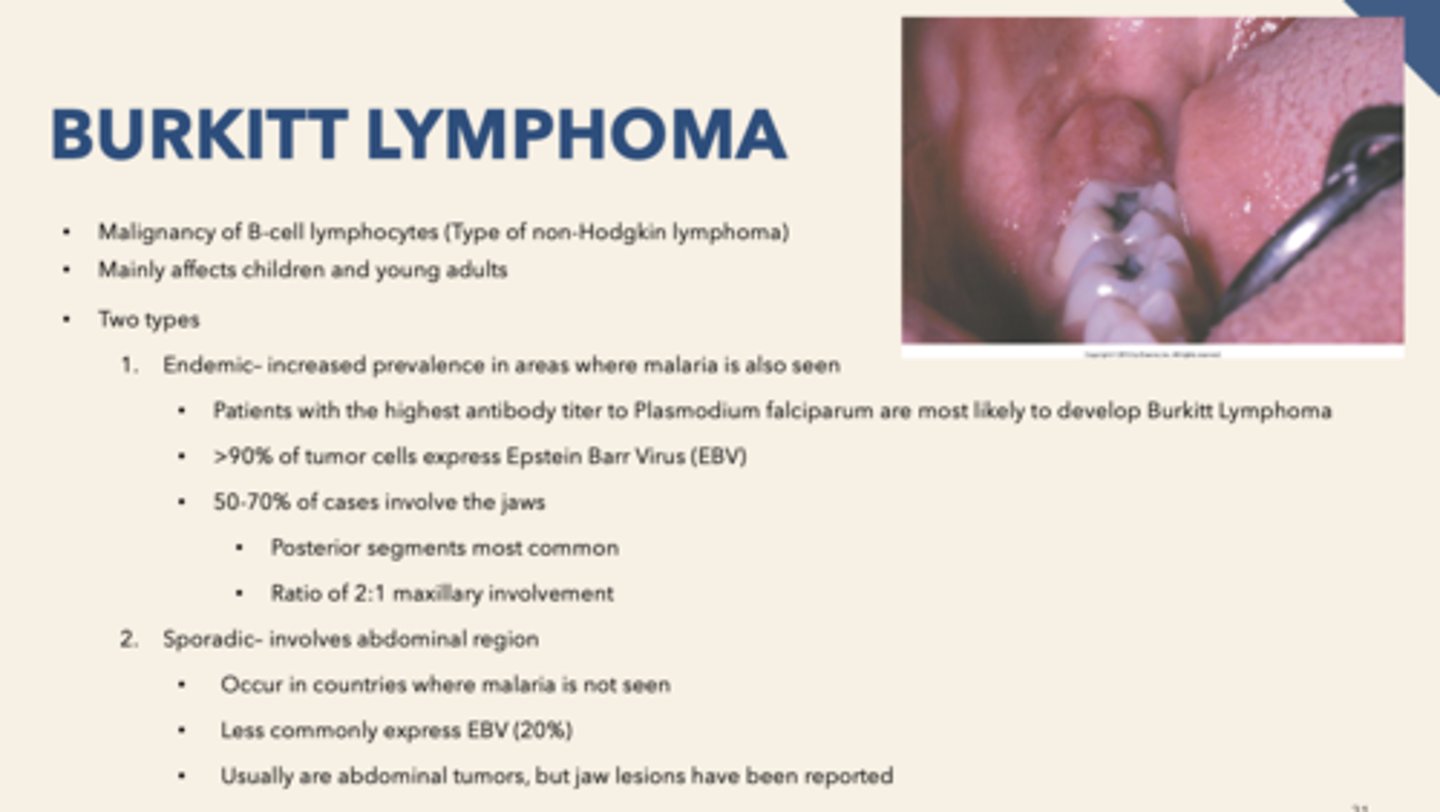
For Burkitt Lymphoma, endemic- increased prevalence in areas where ____________ is also seen
Malaria
What percent of Burkitt Lymphoma tumor cells express the Epstein Barr Virus (EBV)?
>90%
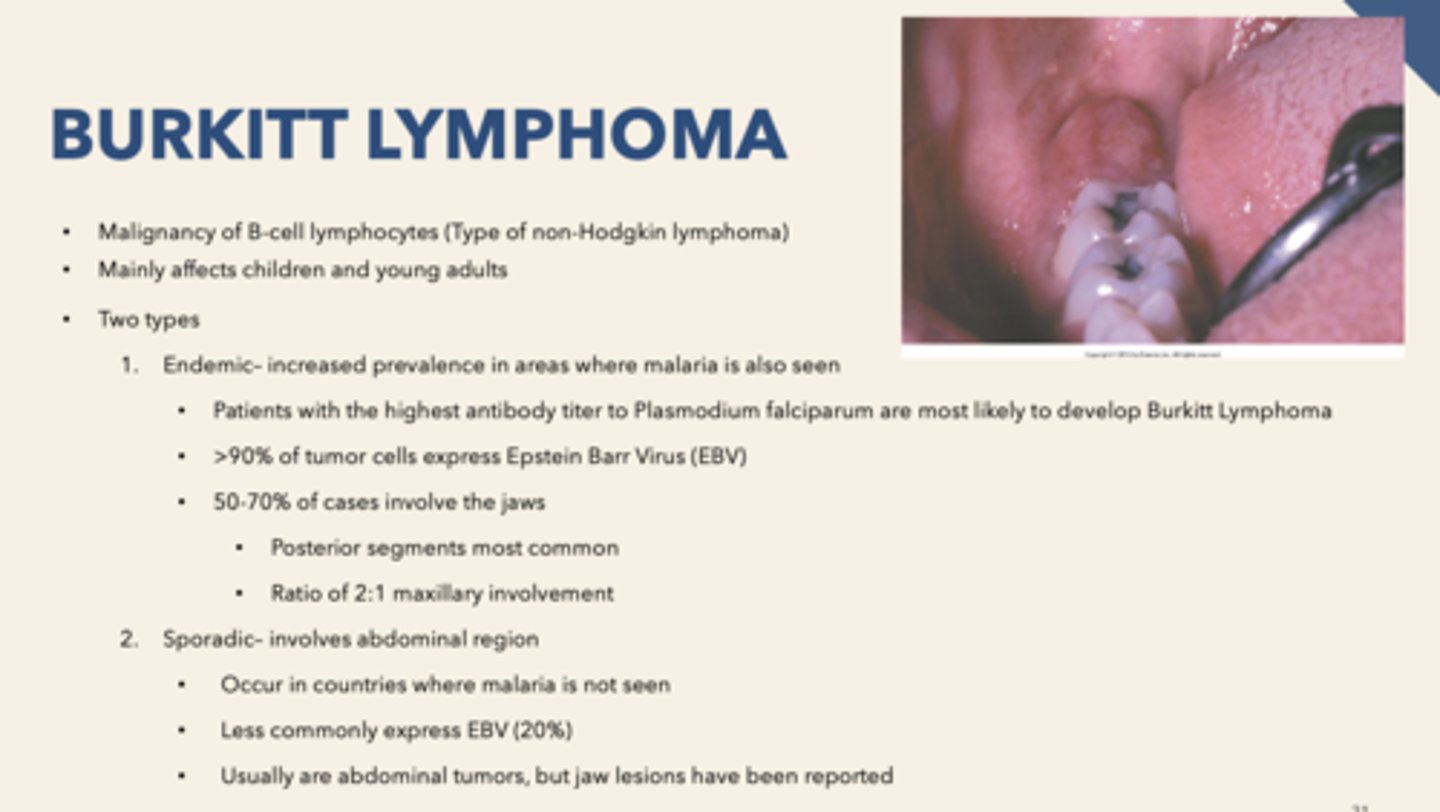
What percent of Burkitt Lymphoma cases involve the jaws?
50-70%
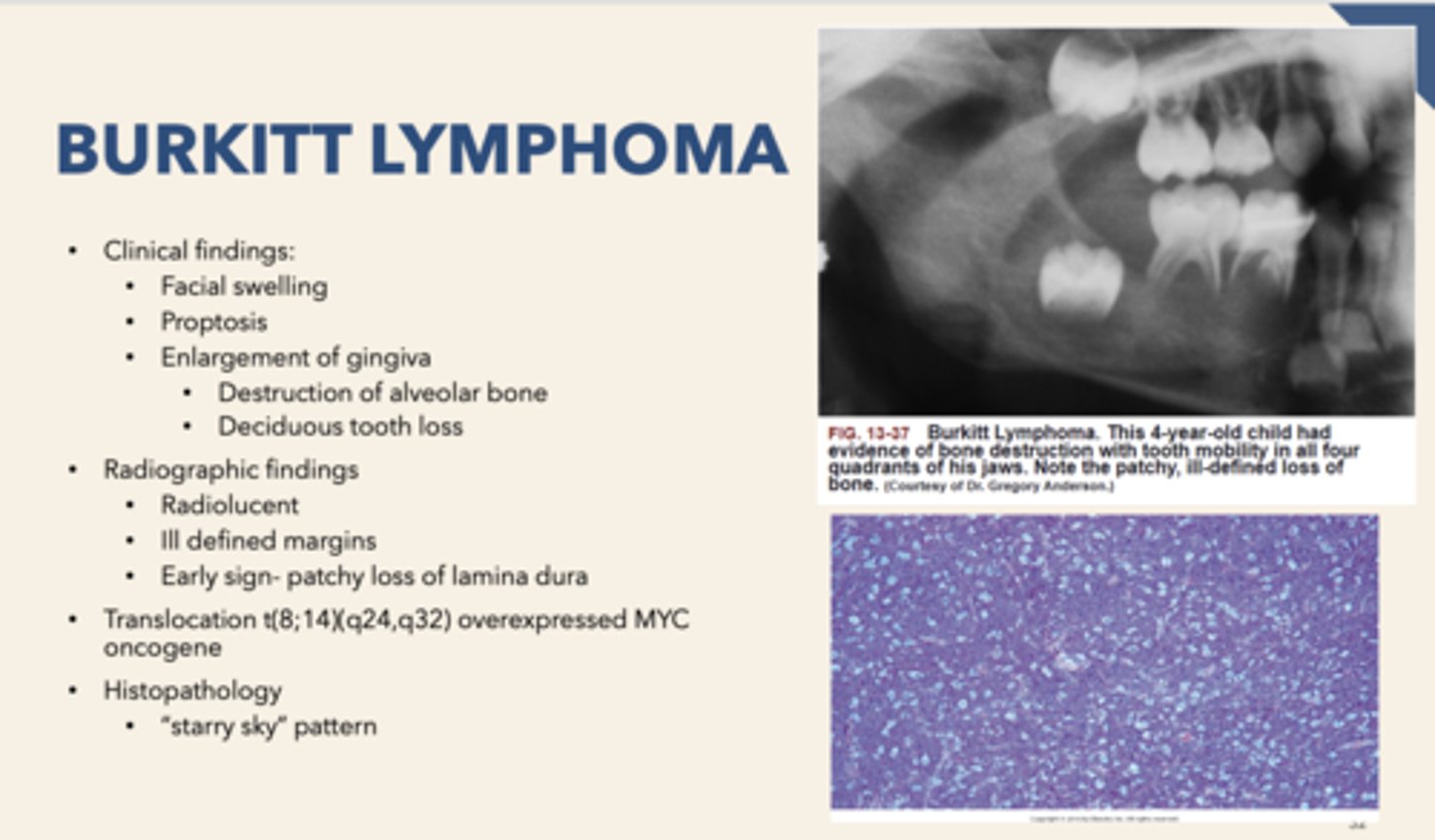
Concerning histopathology, the "starry sky" pattern is associated with
Burkitt Lymphoma
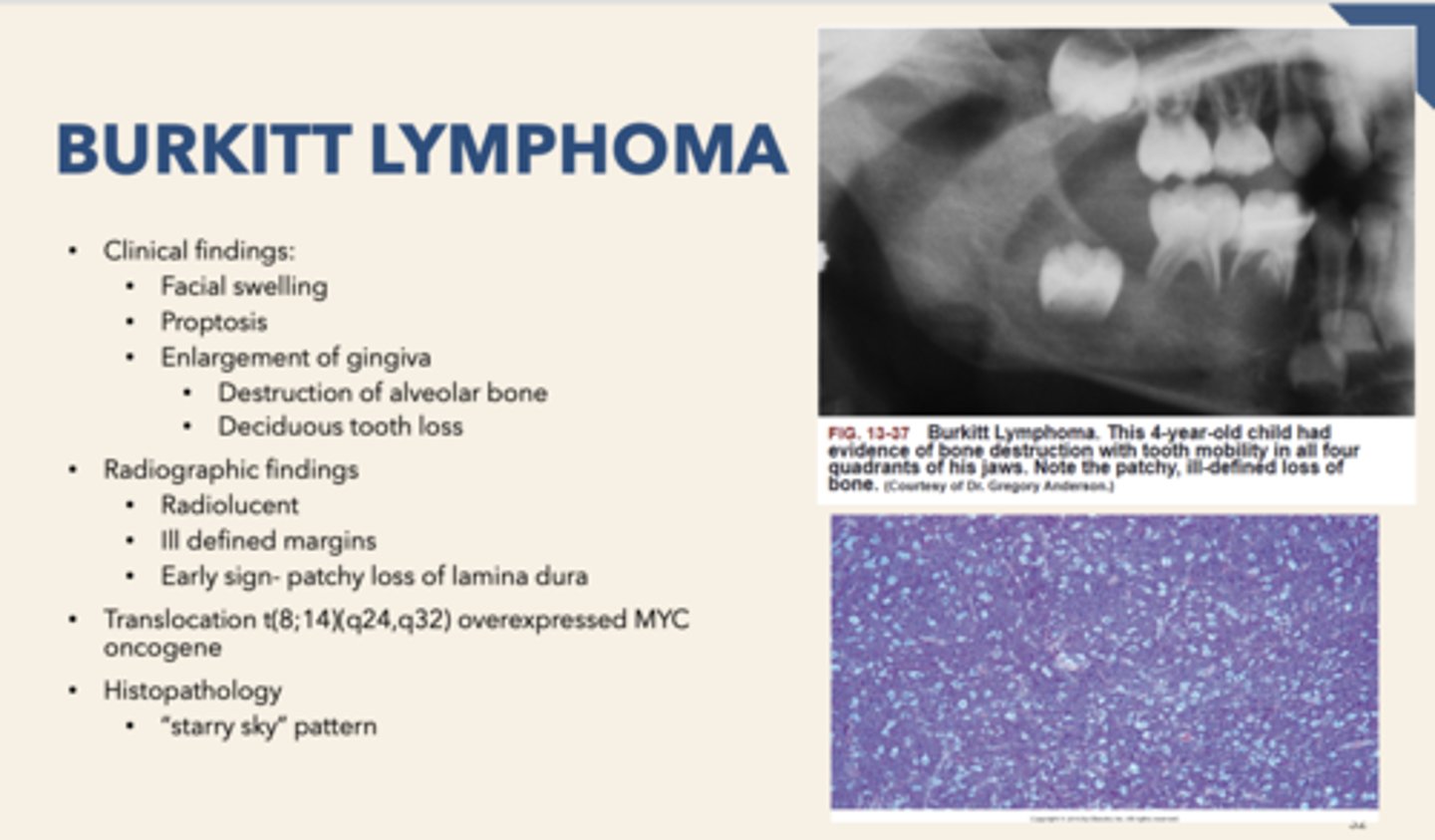
the "sky" in a "Starry sky" appearing biopsy are what cells?
lymphocytes
the "stars" in a "Starry sky" appearing biopsy are what cells?
macrophages
Malignancy of hematopoietic stem cells
- Proliferation of abnormal white blood cells
- Increase in immature white cells (Leukocytosis)
- Occurs in bone marrow and proliferates into peripheral blood
Leukemia

Leukemia is a malignancy of what cells?
hematopoietic stem cells

type of leukemia that involves the Philadelphia Chromosome-(9,22):
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML)

most common leukemia in adults:
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)

most common leukemia in children:
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)

type of leukemia has a broad age range:
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)

Crowding out normal hematopoietic stem cells (white and red blood cells) by malignant cells:
Myelophthisic anemia
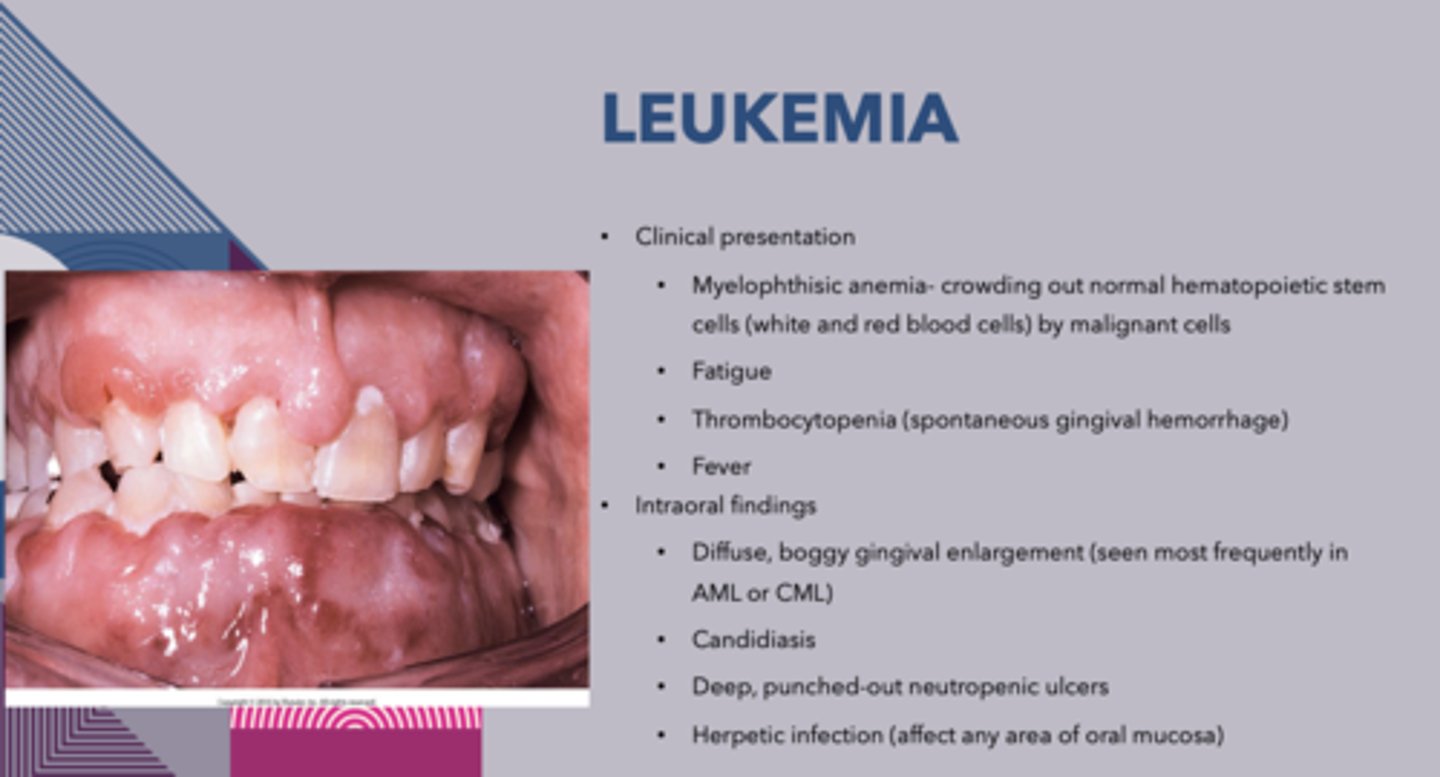
patient presents with fatigue, thrombocytopenia and fever. The oral cavity presents with diffuse, boggy gingival enlargement candidiasis, deep, punched-out neutropenic ulcers and herpetic infection. Blood work shows crowding out normal hematopoietic stem cells (white and red blood cells) by malignant cells What is the Diagnosis?
Leukemia
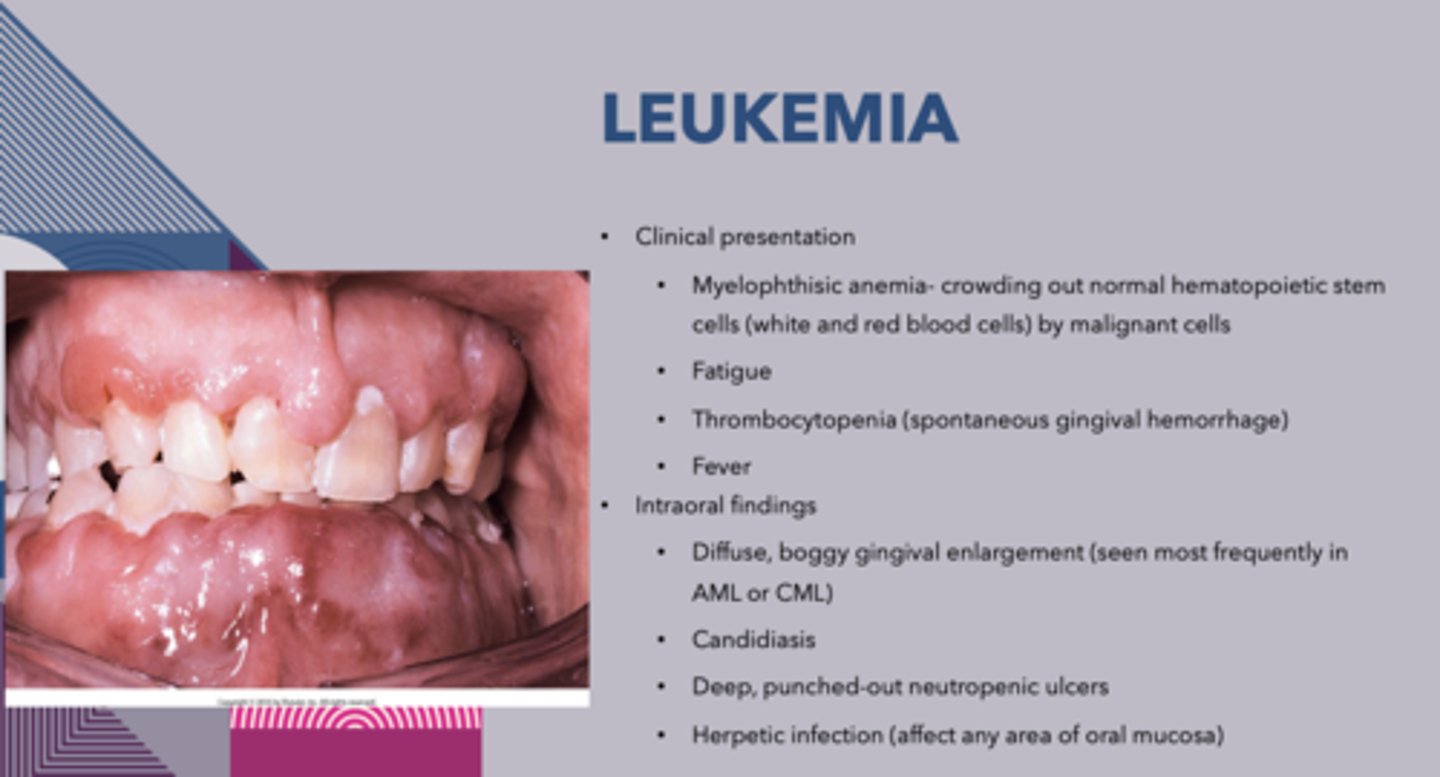
The following are intraoral findings of _____________:
1. Diffuse, boggy gingivial enlargement
2. Candidiasis
3. Deep, punched-out neutropenic ulcers
4. Herpetic infection
Leukemia
Multiple myeloma is a malignancy of what cells?
plasma cells
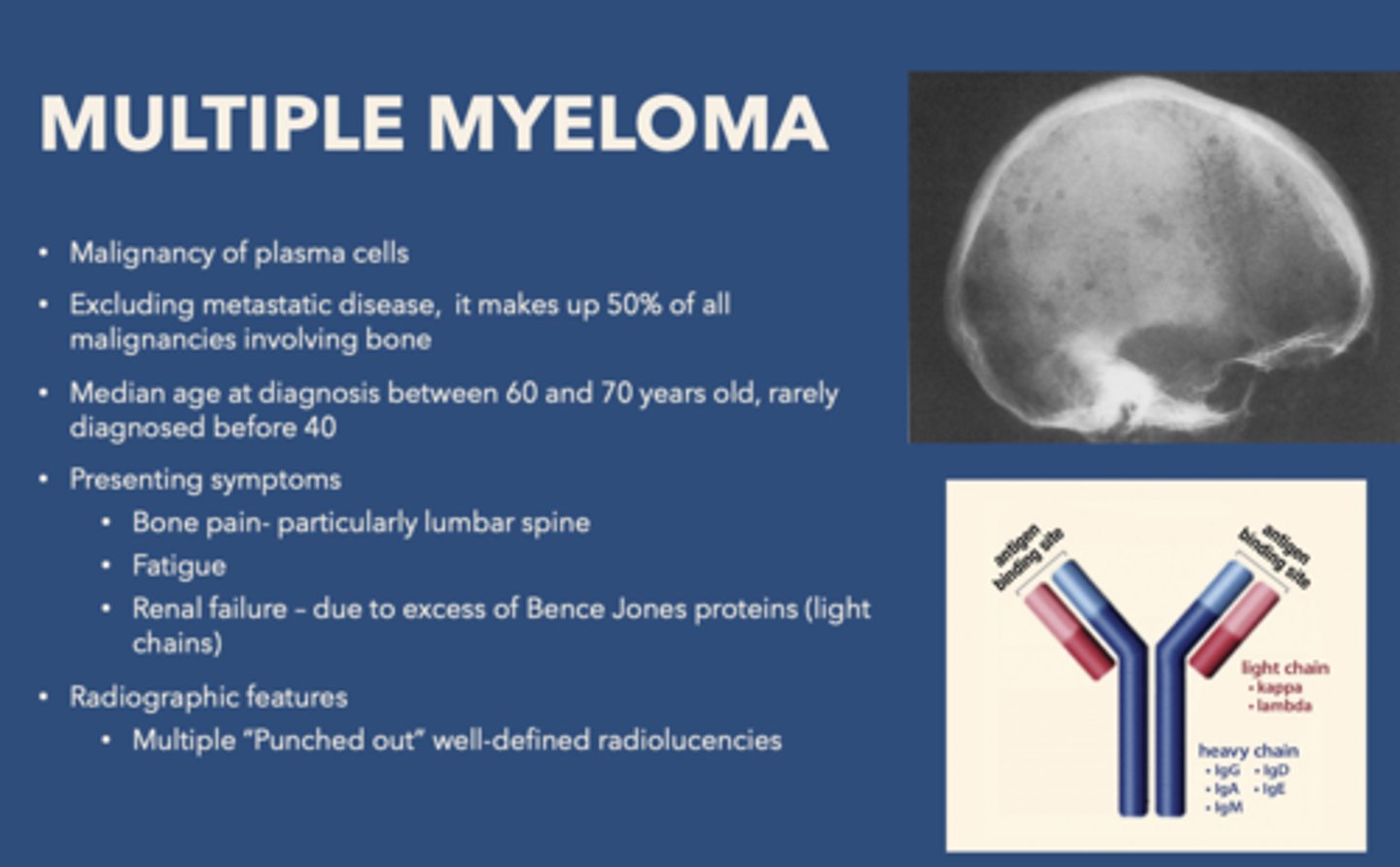
African American patient presents with bone pain, fatigue and renal failure (due to excess of Bence Jones proteins). Radiograph shows “punched out” well-defined radiolucencies. What is the diagnosis?
Multiple myeloma
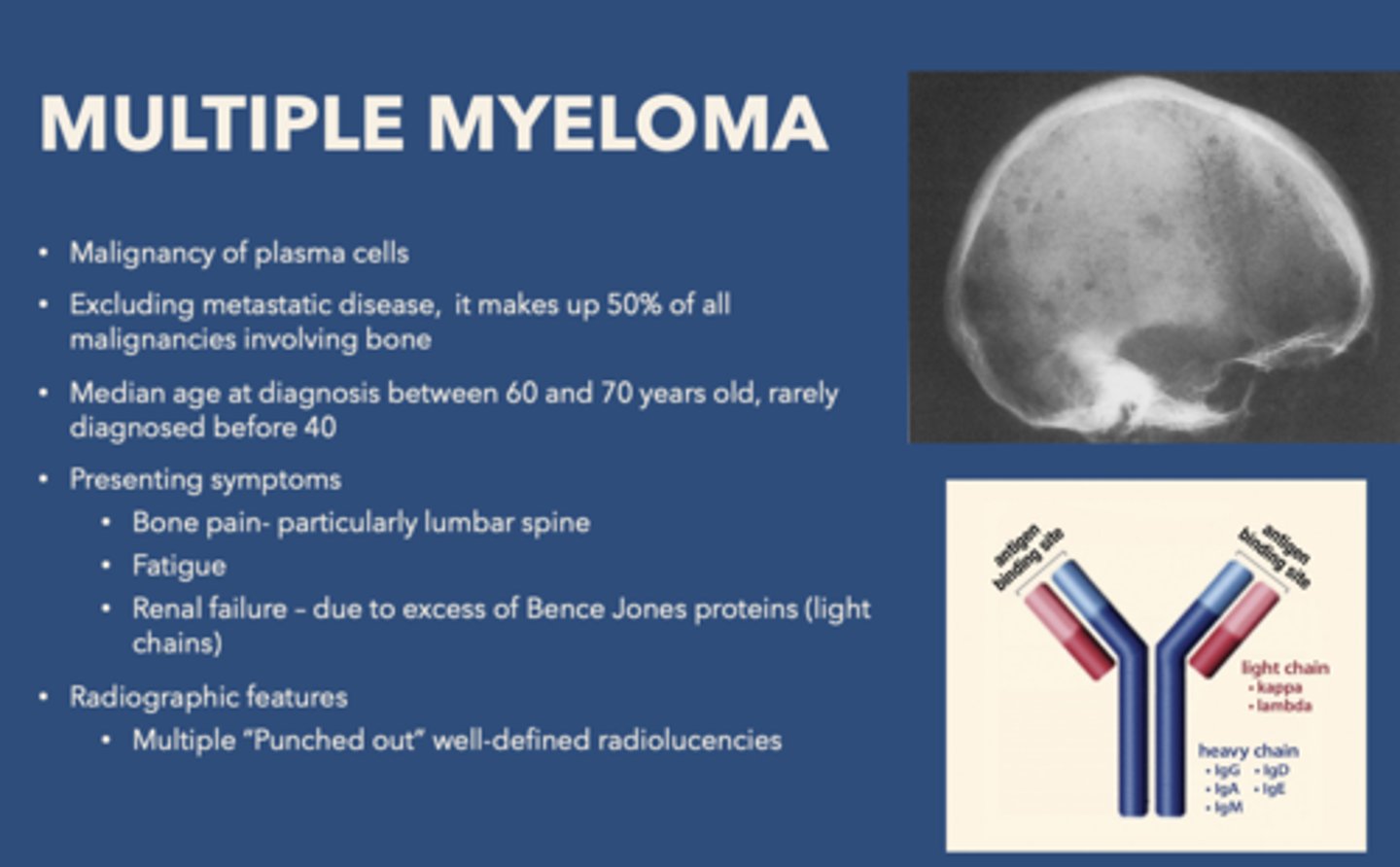
what disease is associated with "punched out" well defined-radioluciencies.
Multiple myeloma
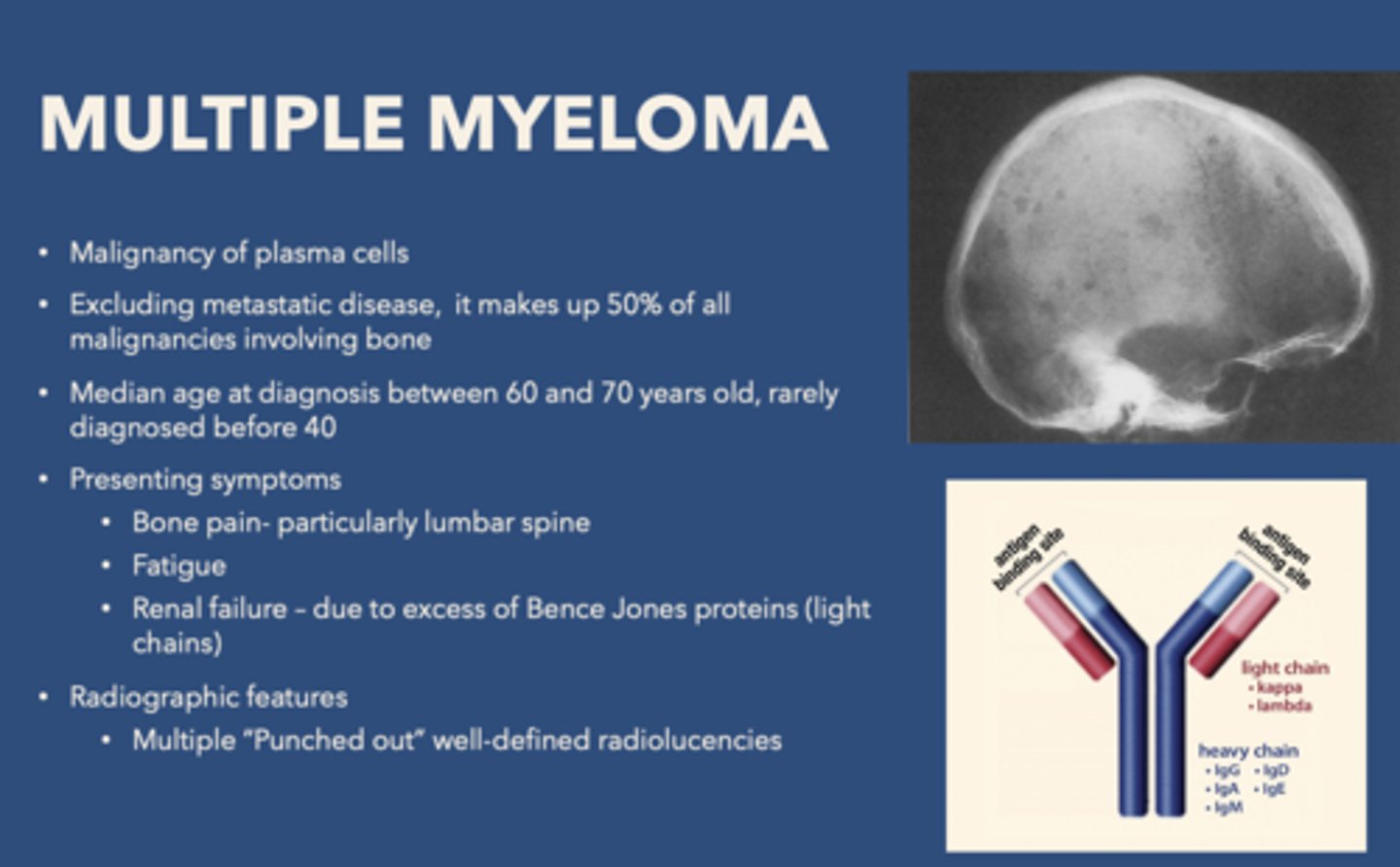
What is the purpose of platelets?
hemostasis/clot formation
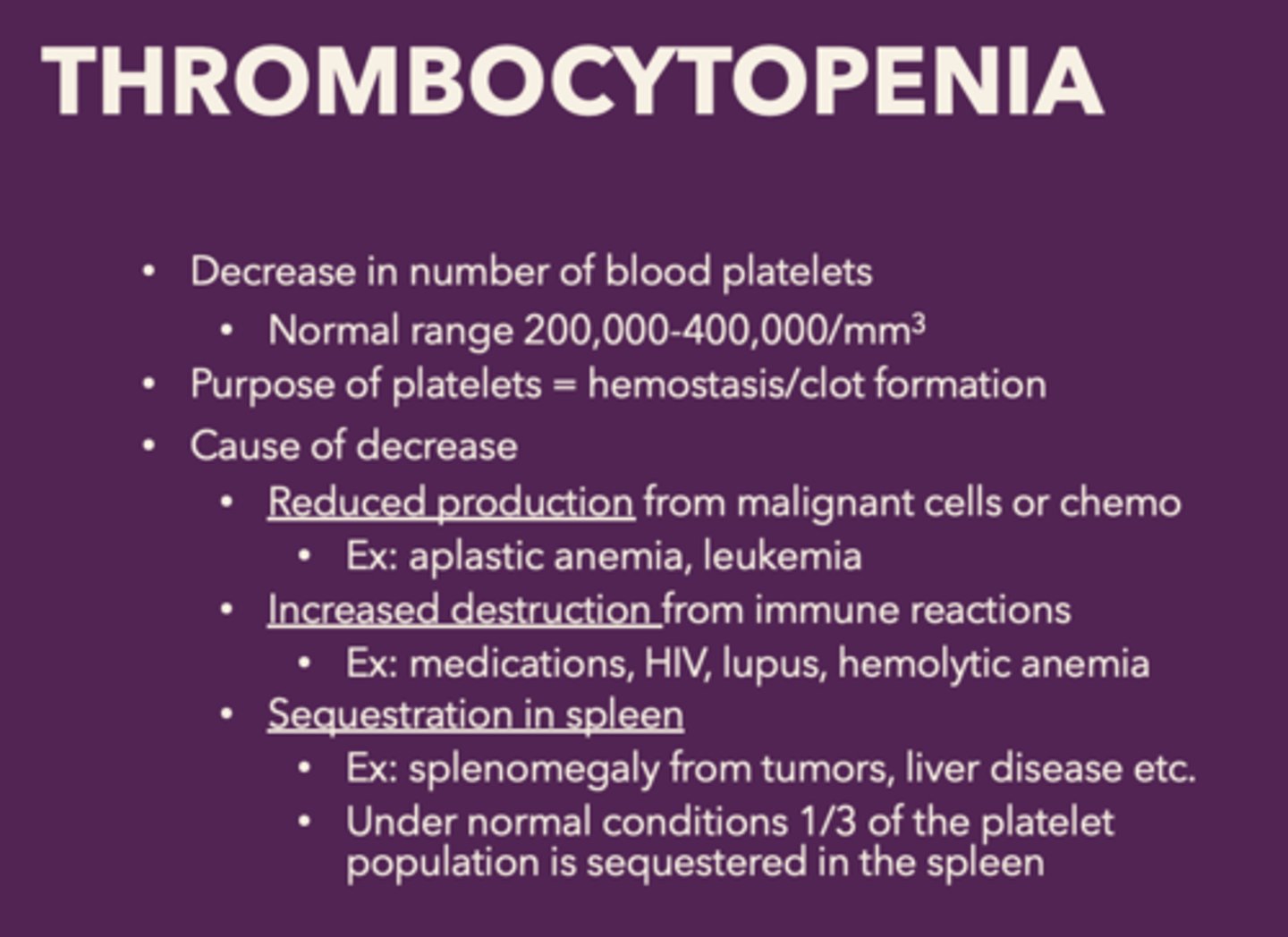
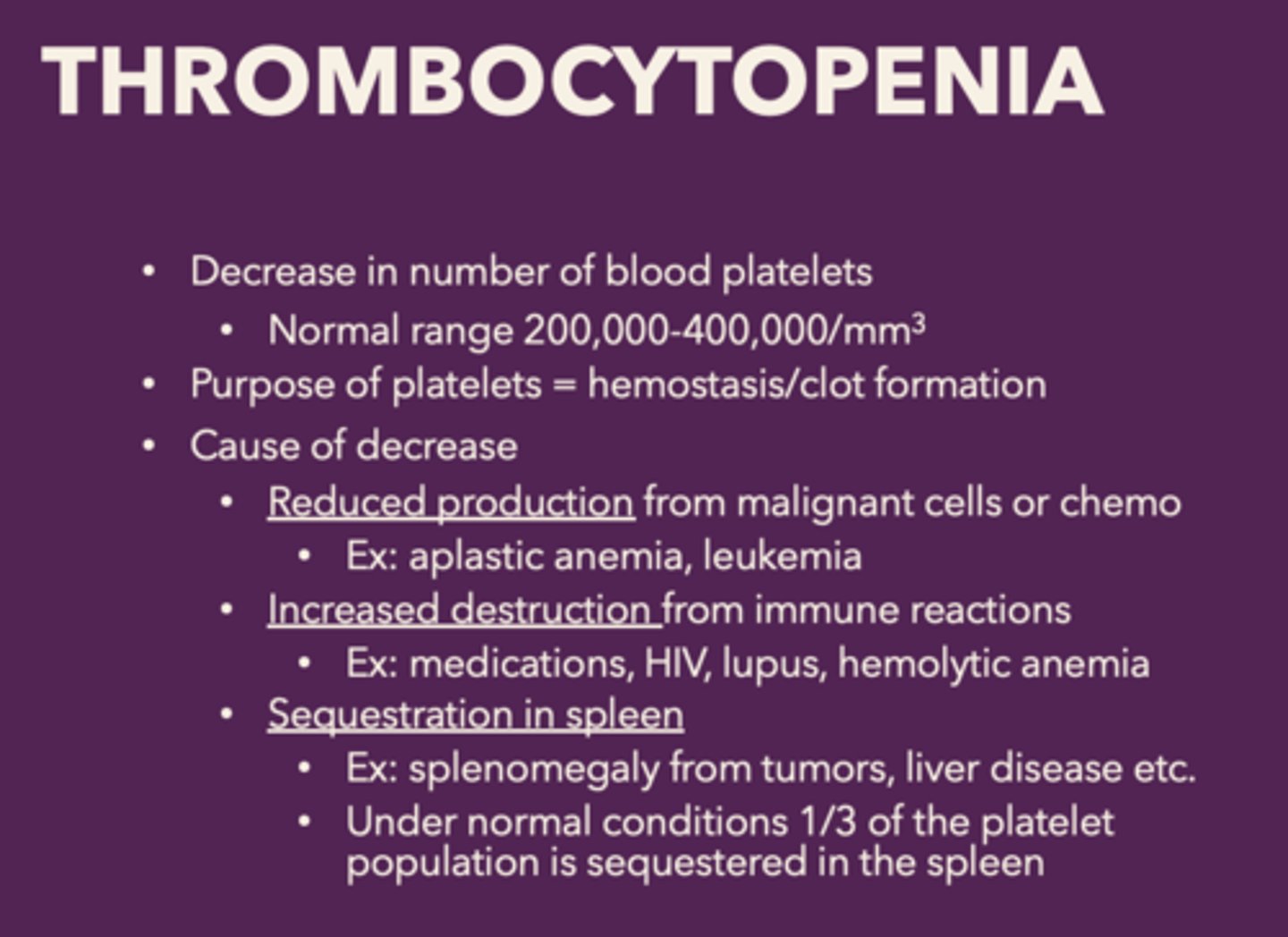
thrombocytopenia is a decrease in the
number of blood platelets, patients will not be able to form clots - constantly bleed
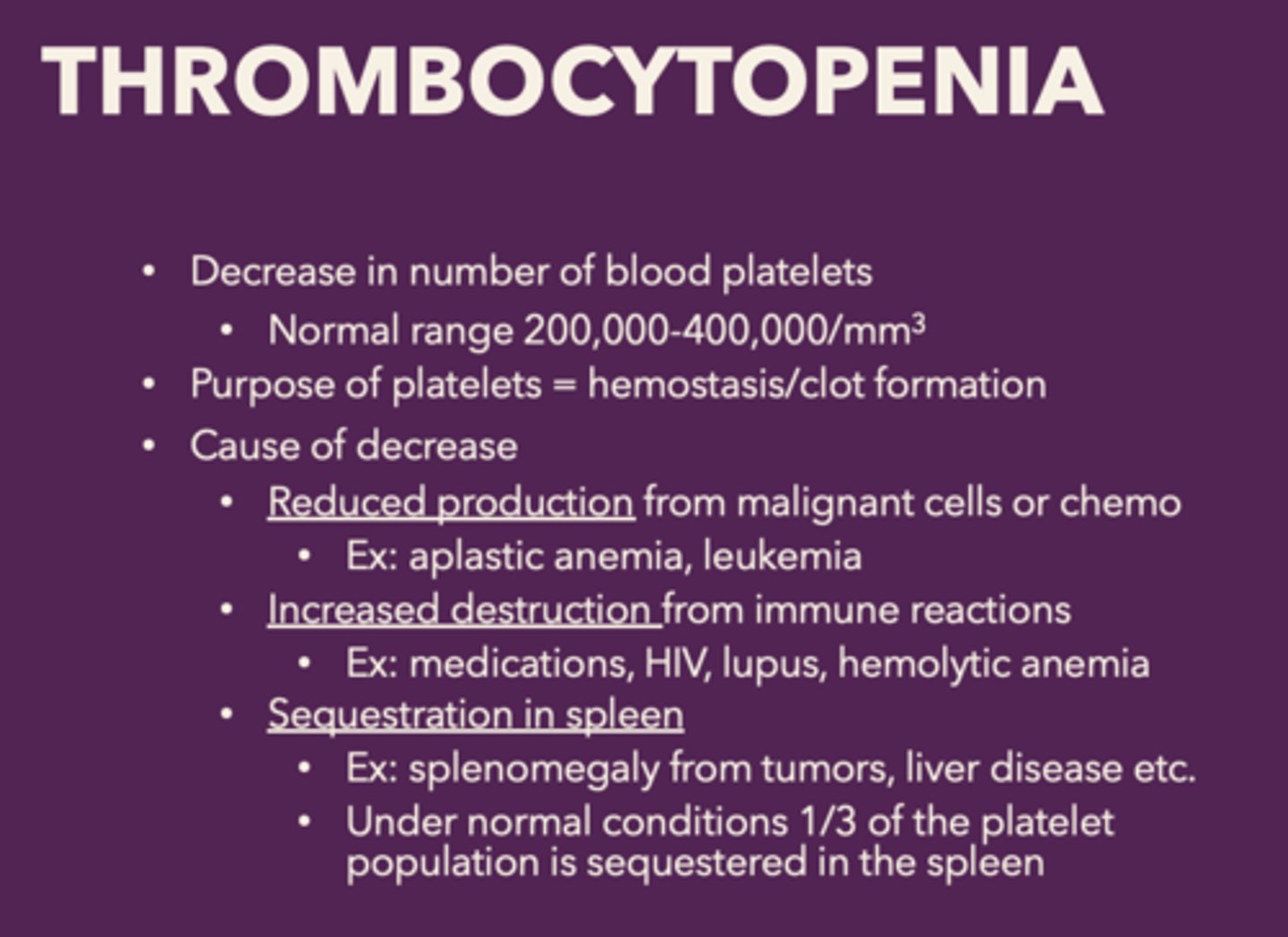
What are the causes of decrease of platelets in thrombocytopenia:
• Reduced production from malignant cells or chemo
• Increased destruction from immune reactions
• Sequestration in spleen
Clinical features of thrombocytopenia
- Spontaneous gingival
- Hemorrhage
- Petechiae
- Ecchymosis
- Hematoma
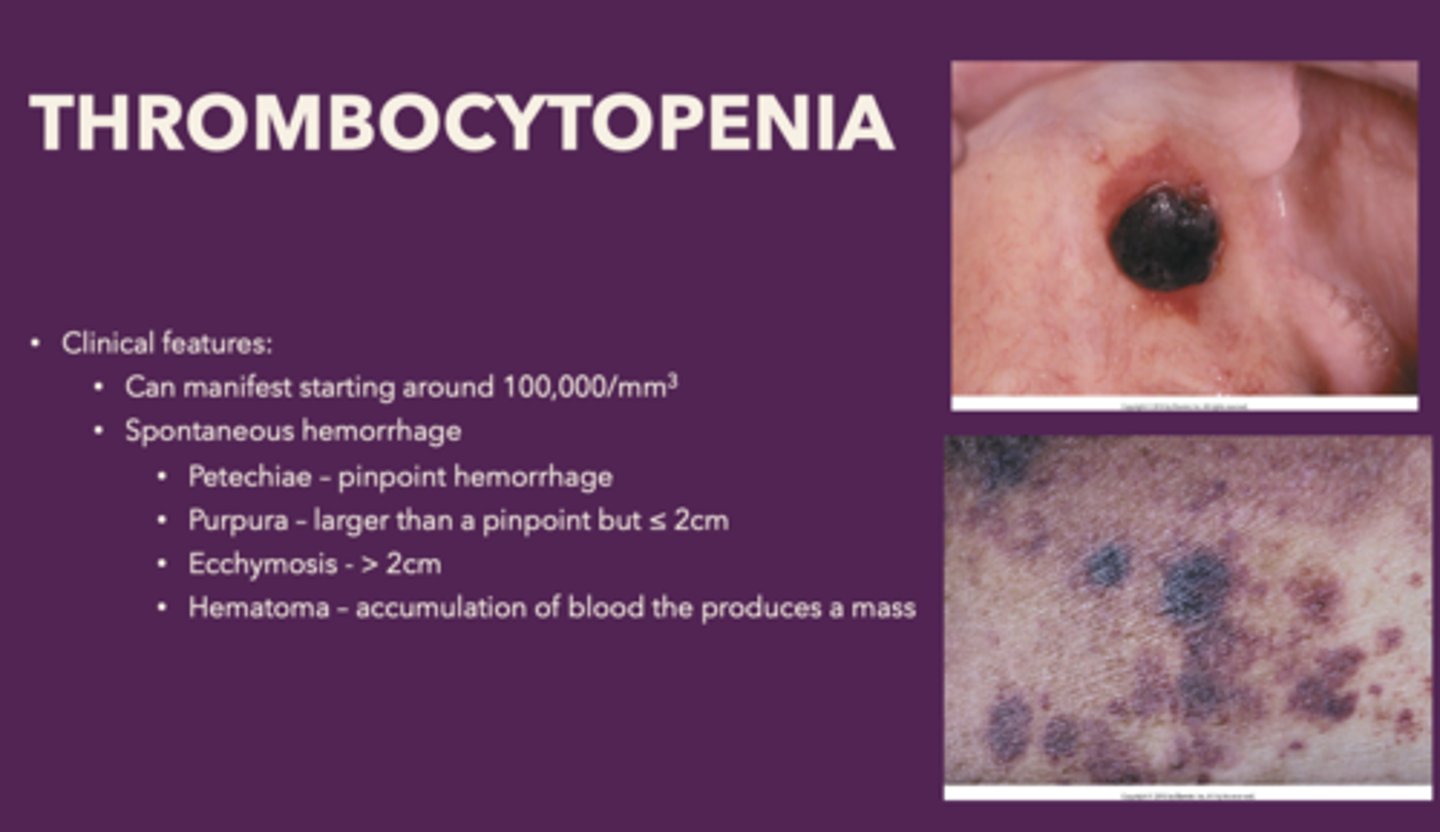
Define the following:
Pinpoint hemorrhage
Petechiae
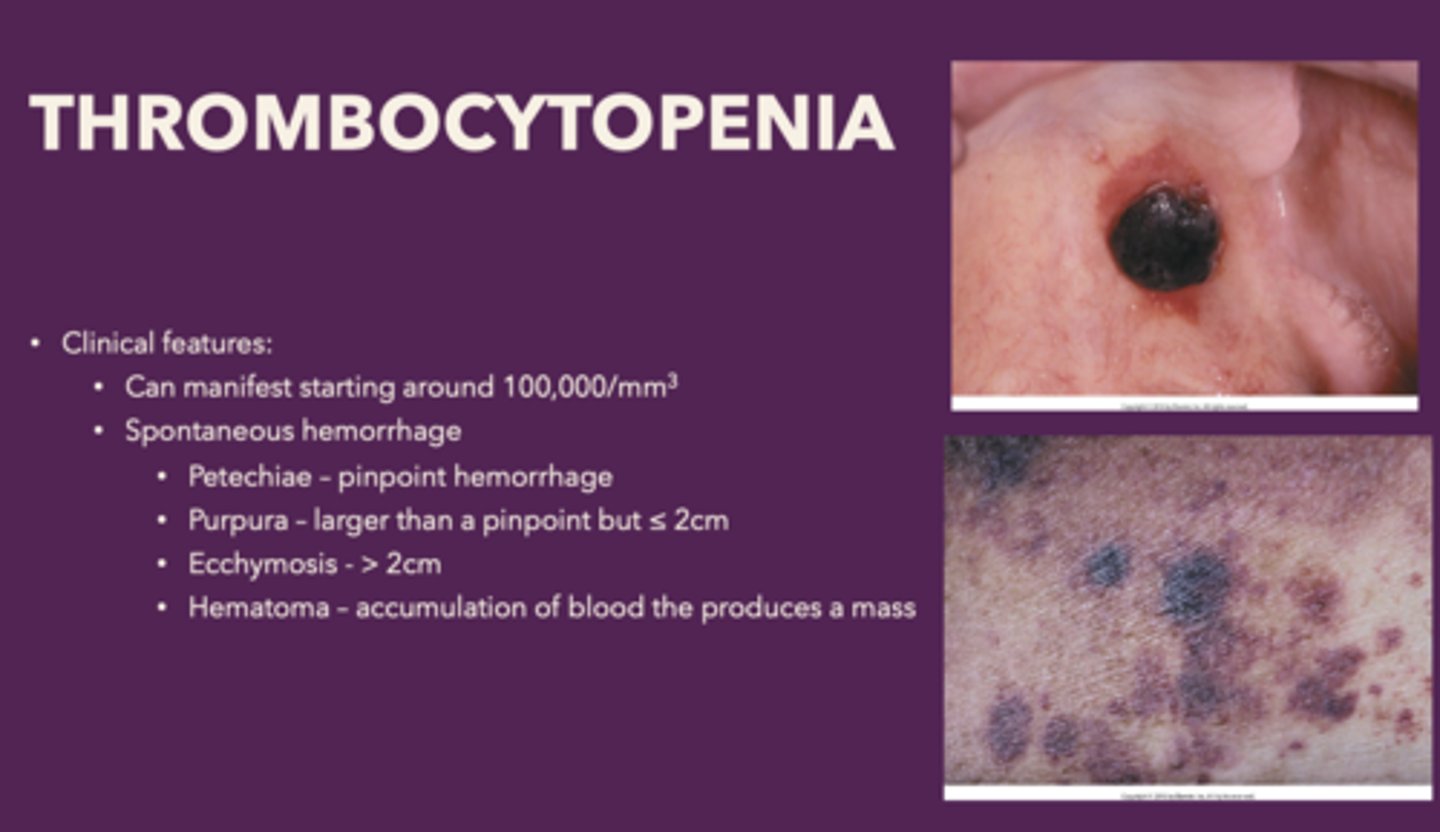
Define the following:
Bleed that is larger than a pinpoint but ≤ 2cm
Purpura
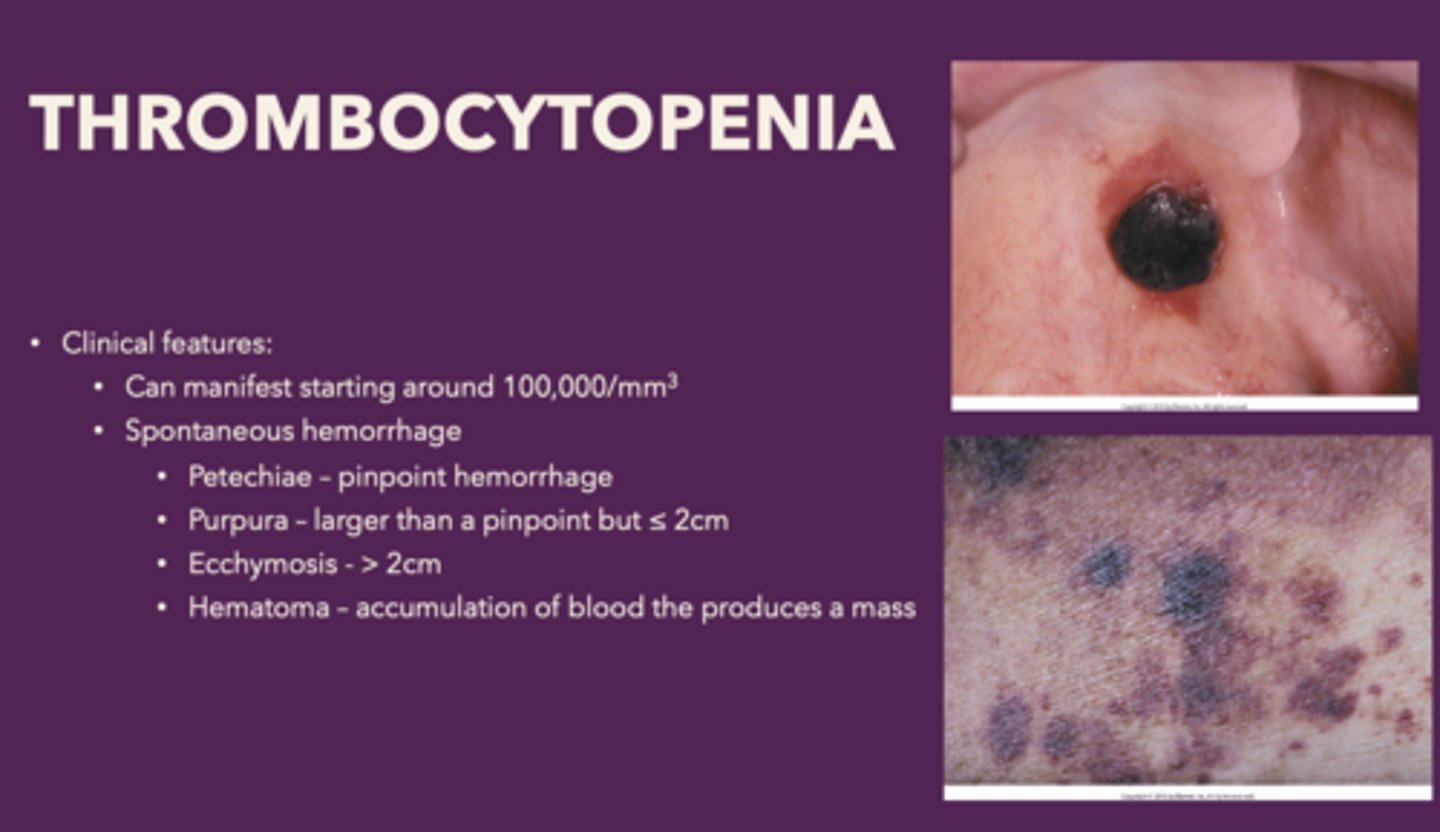
Define the following:
Bleed that is >2cm
Ecchymosis
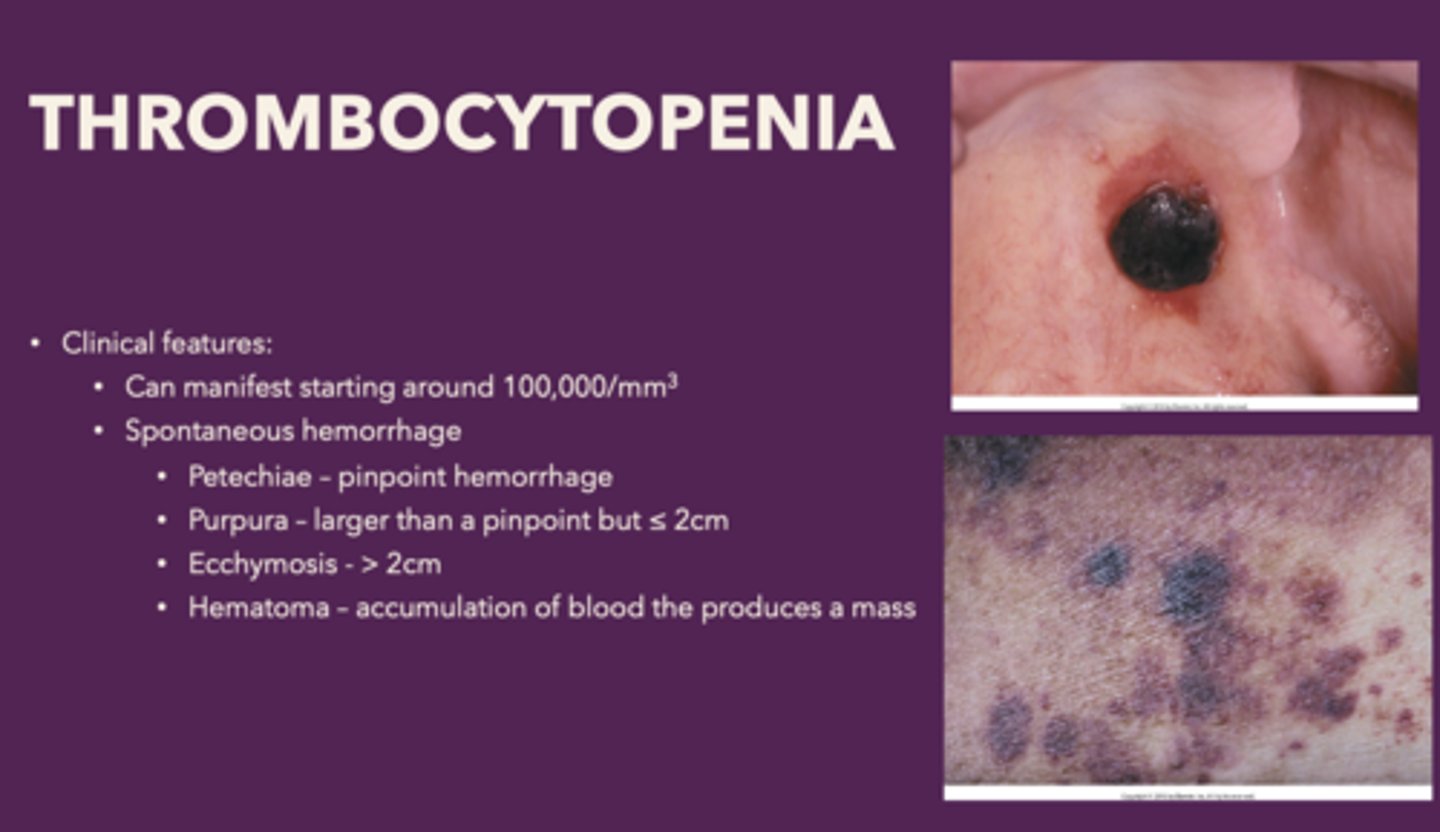
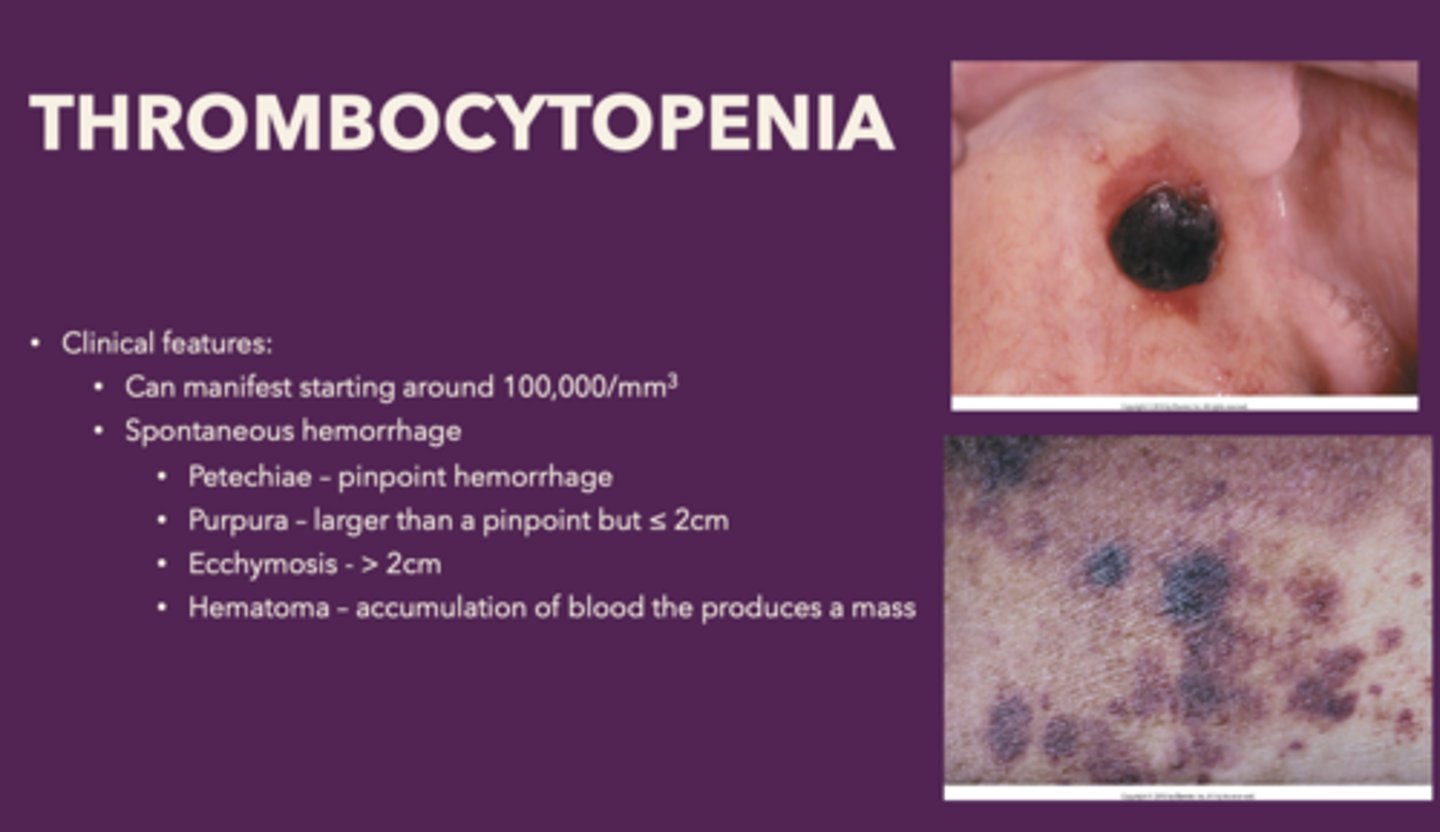
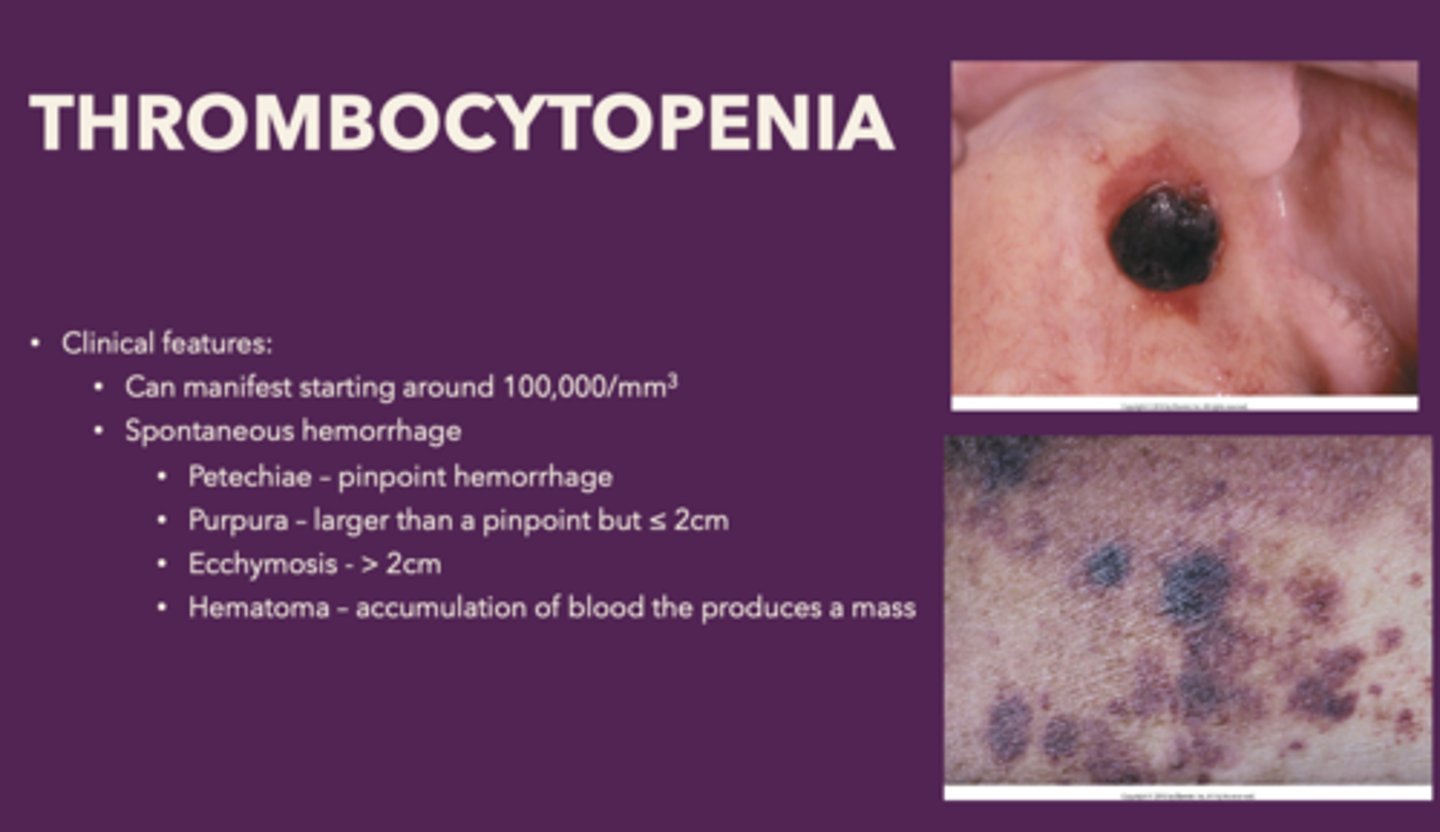
Define the following:
Accumulation of blood the produces a mass
Hematoma
You have a patient that presents with spontaneous gingival hemorrhage (Petechiae, Ecchymosis and sometimes Hematoma). Patient has a history of leukemia. Patient blood work shows around 100,000 platelet count. What is the diagnosis?
thrombocytopenia
what is the most common inherited bleeding disorder?
Von Willebrand Disease

Defect in platelet adhesion and coagulation. An autosomal dominant disorder. Causes spontaneous bleeding from mucous membranes:
Von Willebrand Disease

What is the following condition:
- X-linked recessive disorder, most common hereditary cause of serious bleeding, Primarily affects males
-Reduced Factor VIII activity
Hemophilia A

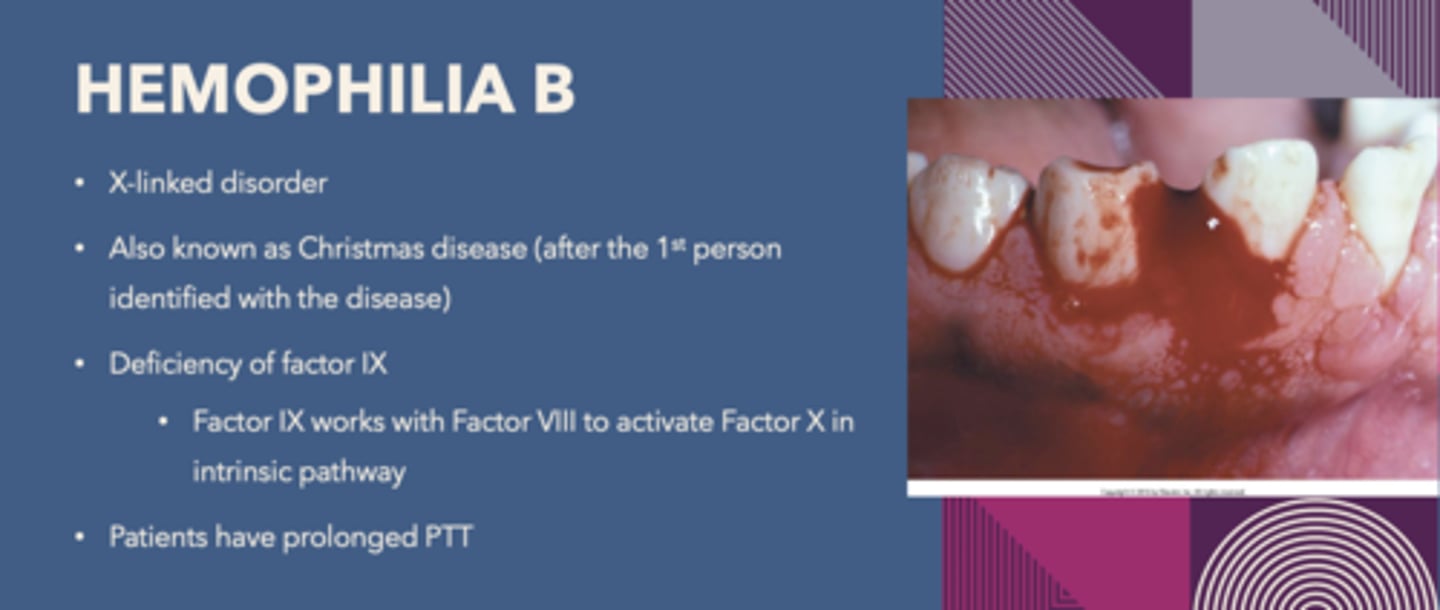
What is the following condition:
X-linked disorder, Known as Christmas disease
-Deficiency of Factor IX
Hemophilia B

a reduction of Clotting Factor VIII activity is indicative of what disorder?
Hemophilia A

a reduction of Clotting Factor IX activity is indicative of what disorder?
Hemophilia B
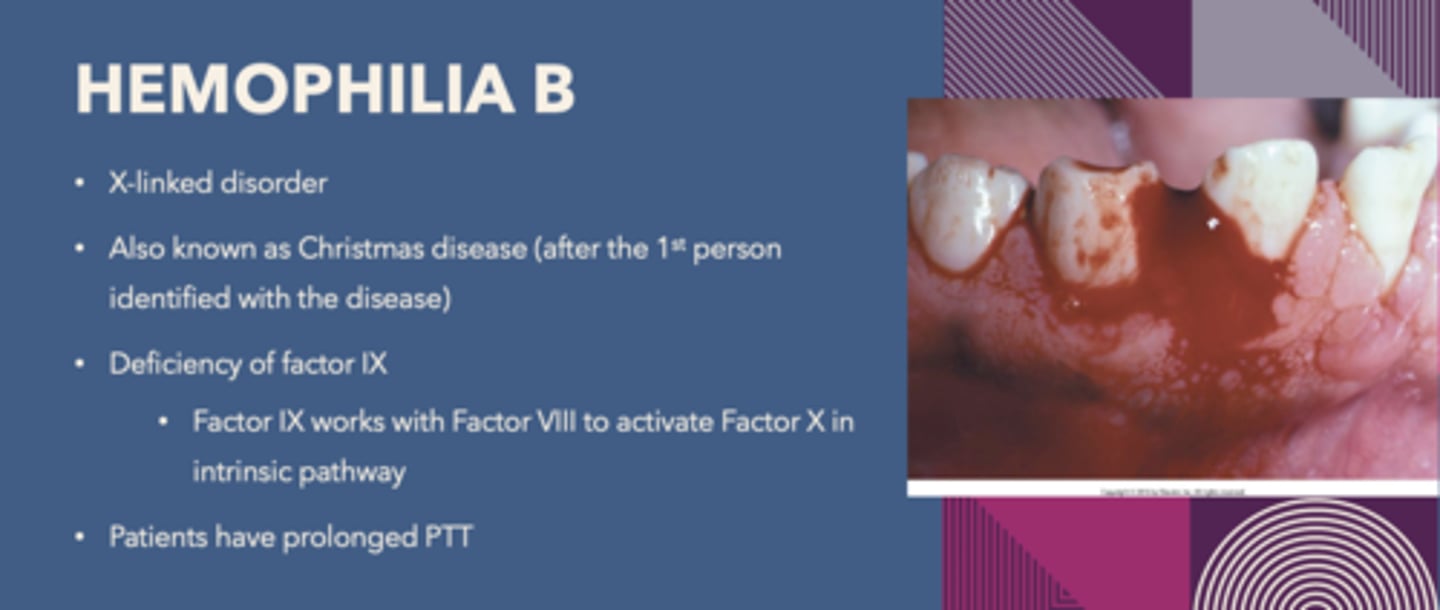
disease known as Christmas Disease:
Hemophilia B