MicroBio Exam 1: Ch.1 review
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
what are micro-organisms?
organisms that are too small to see with the unaided eye
What are the types of microbes?
Bacteria, fungi (mold/yeast), protozoa (brain eating ameba), microscopic algae, viruses
What are pathogenic?
disease producing
What is the main function of microbes?
to decompose organic waste
What is a Microbiome?
a group of microbes that live stably on/in the human body
How many bacterial cells does an adult human have?
40 trillion bacterial cells (the body has more bacterial cells than body cells)
Are bacteria larger than body cells?
No, bacterial cells are far more smaller than body cells
Where do the microbiome begin?
Begin to be acquired as new borns (passing through vagina)
May colonize the body fleetingly (making them transient microbiota)
Where can colonization occur?
only at body sites that provide nutrients and the right environment for the microbes to flourish
What is one example of a transient microbiota?
Staphylococcus- on the skin/ can survive high salt concentration of the skin
What are probiotics?
a way to get good bacteria, can be found in certain foods or supplements
what are prebiotics?
help encourage the growth and activity of beneficial microorganisms, compounds in foods
Who came up with the naming system (scientific nomenclature) of microorganisms?
Carolus Linnaeus
What year did Carolus Linnaeus come up with the naming system of microorganisms?
1735
How are scientific names written?
Italicized
First letter is capitalized
second letter is lowercase
Ex: Escherichia coli
After the first use of scientific name the name can then be….
abbreviated
Ex: E. coli
Escherichia coli is found where?
in the large intestine
Where is Staphylococcus aureus found?
on the skin
What are prokaryotes?
simple cells
What are Eukaryotes?
Complex cells/ multi-cellular
What are some examples of prokaryotes?
Bacteria
Archaea
What are some examples of eukaryotes?
Fungi
Protozoa (brain eating ameba)
Algae
Multicellular Animal Parasites
What are some characteristics of bacteria?
Prokaryotes
Peptidoglycan cell walls (carbohydrate in cell walls)
What are some characteristics of Archaea?
Prokaryotes
Lack peptidoglycan in cell walls
Often live in extreme environments
What are some characteristics of Fungi?
Eukaryotes (complex cells/multicellular)
Chitin cell walls
Mold (multicellular)
Yeast (unicellular)
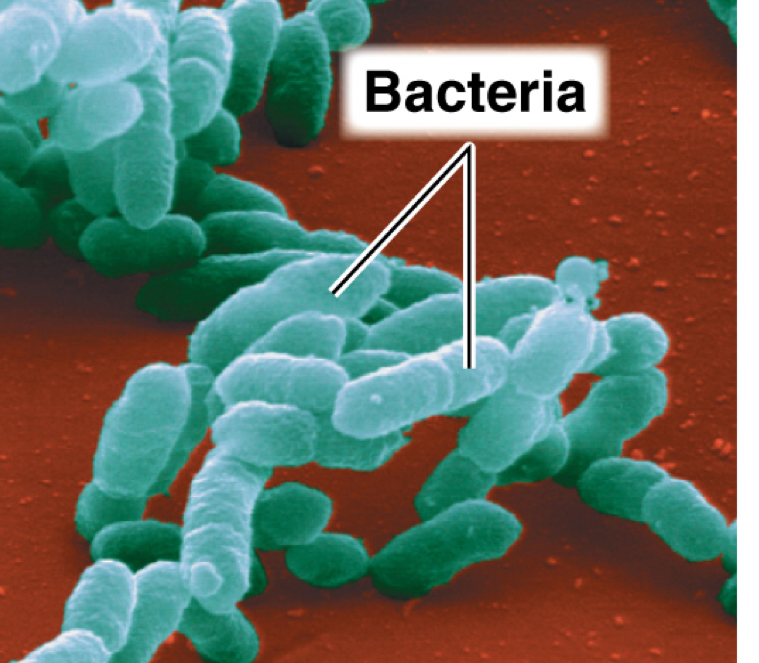
What does bacteria look like?
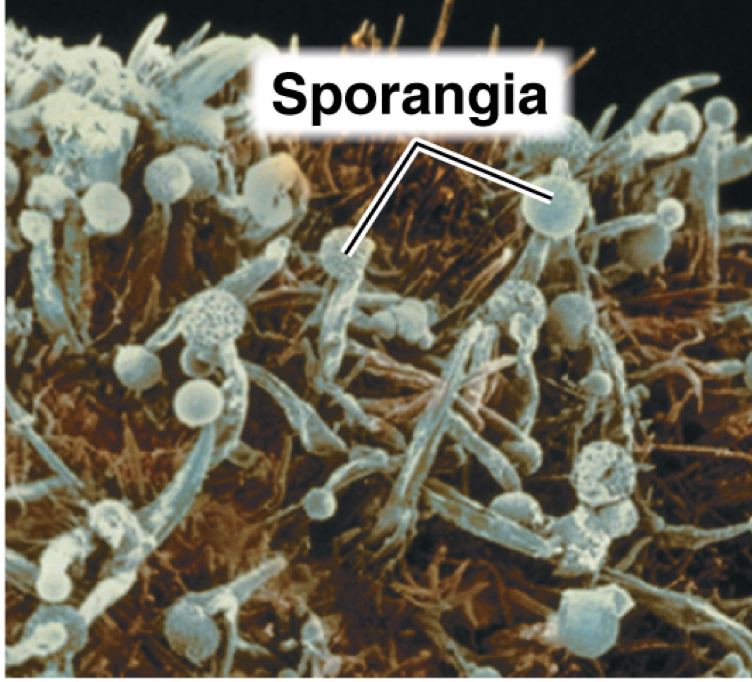
What does Fungi look like?
What is a Protoza?
Eukaryote
Is an amoeba (brain eating)
What are some characteristics of Algae?
Eukaryotes
Use photosynthesis for energy
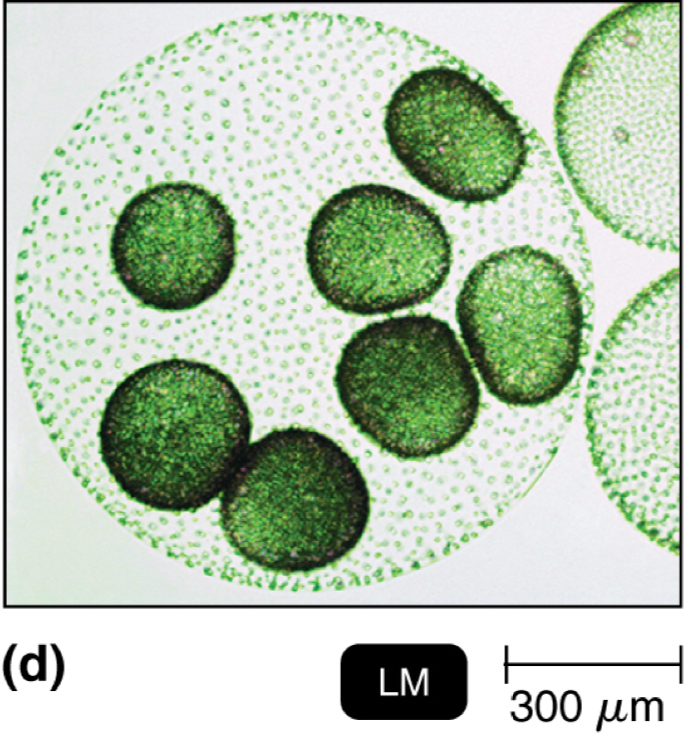
What does Algae look like?
What are some characteristics of Viruses?
Acellular/nonliving (not made up of cells)
they are codependent (piggy back on other cells)
What is the agent that caused COVID-19?
SARS-CoV-2, this is an example of a virus
What are helminths (multicellular animal parasites)?
parasitic flatworms and roundworms
Who introduced the 3 domain system?
Carl Woese
In what year did Carl Woese introduce the 3 domain system?
1978
What are the 3 domains?
Bacteria
Archaea
Eukarya
What are the 3 domains based on?
cellular organization
What did Robert Hooke build?
The first compound microscope
What did Robert Hooke report?
living things are composed of little boxes or “cells”
What theory did Robert Hooke create?
The cell theory
In what year did Robert Hooke report the cell theory?
1665
What did Anton van Leeuwenhoek do from 1623-1673?
used microscope to see microorganisms
What year and what did Anton van Leeuwenhoek discover?
Year 1623: discovered “Animalcules”
What is Spontaneous generation?
hypothesis that life arises from nonliving matter
What is the hypothesis that living cells arise only from preexisting living cells called?
Biogenesis
What is the name of the person that first proved biogenesis? 1668
-”Maggots come from flies”
Francesco Redi
Who demonstrated that microorganisms are present in the air by using shaped flasks?
Louis Pasteur
What year did Louis Pasteur demonstrated microorganisms in the air by using shaped glass?
1861
What shaped glass did Louis Pasteur use?
S shaped glass
What did Louis Pasteur show microbes were responsible for?
Fermentation
What is fermentation?
Sugar to alcohol in the absence of air
What uses air to spoil wine by turning it to vinegar?
Bacteria
What is pasteurization?
adding heat to kill harmful micro-organisms
What is an example temperature of pasteurization?
63 degrees C (145 F) maintained for 30 minutes
Who introduced the practice of handwashing in the 1840s?
Ignaz Semmelweis
Why did Ignaz Semmelweis introduce the practice of hand washing in hospitals?
to prevent transfer of germs from morgues to maternity ward
Who was the 1st to discover disease causing organisms and developed Koch’s postulates (with how disease spreads) in 1876?
Robert Koch
What did Payton Rous first show in?
viruses can cause tumors
Who was the first vaccine administered by and what year?
Edward Jenner in 1796
Definition of Antibiotics
chemicals produced by bacteria and fungi that inhibit or kill other microbes
What did Alexander Fleming do in 1928?
Accidentally discovered the first antibiotic called penicillin
What is the study of fungi called?
Mycology
What did Rebecca Lancefield do in 1895-1981?
She classified pathogenic Streptococci (strep throat) into several different groups based on chemical composition of their cell walls
Classification are known as Lancefield groups and range from A to V (excluding I and J)
What is the study of viruses called?
Virology
What did Dmitri Iwanowski first discover?
Viruses (tobacco mosaic virus)
In 1892 what experiment did Dmitri Iwanowski conduct?
an experiment that showed infectious agents causing tobacco mosaic disease could pass through filters that would normally trap bacteria
What did Tu Youyou do?
extracted artemisinin from the Chinese sage plant and used it to treat Malaria
She believed it would work, she volunteered to be the first human subject
What is an alternative instead of using chemical pesticides?
Bacillus Thuringiensis (Bt)
What is Bacillus Thuringiensis (Bt)
it is an infection that are fatal in many insets but harmless to animals and plants
What are microbes normally present on or in the human body called?
Normal microbiota
What are Biofilms?
when bacteria joins together as a group (bacterial gangs)
What can biofilms cause?
can cause infections
What can biofilms often be resistant to?
Antibiotics
Are Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) good or bad?
Bad
What is Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)?
a bacteria that becomes resistant to many antibiotics