A level music technology
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/186
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
187 Terms
1
New cards
what is an envelope
the attack, sustain release and decay of a sound over time
2
New cards
what is the names for an oscillator on a synth
vco, osc, dco
3
New cards
what does an oscillator do in a synthesiser
generates the waveform(s)/ sound
4
New cards
describe the quality of white noise
a high pitched hiss
5
New cards
describe the quality of a triangle wave
duller than square wave
6
New cards
describe the quality of a sine wave
very smooth with 0 harmonic content
7
New cards
describe the quality of a square wave
hollow and woody
8
New cards
describe the quality of a sawtooth wave
rich and bright
9
New cards
what are the four types of analog wave forms
sawtooth, square, sine, triangular, white noise
10
New cards
How is sound measured
In decibels (dB)
11
New cards
How does dB increase
in powers of 10 (logarithmically )
12
New cards
State the human range of hearing
0-130dB
13
New cards
what is the threshold of hearing
0dB
14
New cards
What is the threshold of pain
130dB
15
New cards
What is frequency measured in
Hertz (Hz)
16
New cards
what is the human frequency range
20Hz to 20kHz
17
New cards
How is frequency measured/determined
through the number of cycles per second (c.p.s)
18
New cards
If frequency increases what else does?
pitch
19
New cards
if pitch increases what else dose
frequency
20
New cards
what is a rarefaction
A rarefaction is a sound wave region with spread-out air particles and lower pressure than surrounding areas.
21
New cards
what is timbre
the tone/ sound quality
22
New cards
define sound
physical kinetic energy traveling through a medium (usually air)
23
New cards
define harmonics
a member of the fundamental frequency that occur in a periodic waveform. (set of an integer/whole number)
24
New cards
what does the fundamental frequency determine
the pitch of the tone
25
New cards
what is the 1st harmonic
the lowest pitch in a harmonic sound
26
New cards
what does each harmonic increase by (e.g 1st, 2nd, 3rd harmonic)
e.g if the 1st harmonic is 2, the 2nd harmonic would be 4 and rhe 3rd would be 6. Each harmonic increases by the value of the 1st harmonic x number of the harmonic (e.g 1st harmonic value x 3 to find 3rd harmonic)
27
New cards
what is an inharmonic
An inharmonic is a sound wave that does not have a frequency that is a whole-number multiple of the fundamental frequency.
28
New cards
give an example of an instrument that is inharmonic
percussive instruments e.g the drums
29
New cards
what sort of wave would a pure tone with no harmonic frequency make
sine wave
30
New cards
what are mid frequencies
3-5kHz
31
New cards
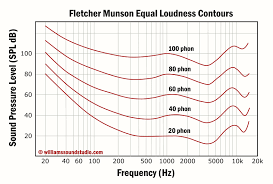
what does the fletcher Munson equal loudness graph tell us
The Fletcher Munson graph shows how our ears perceive various frequencies at different loudness levels. At lower listening volumes we only hear mid frequencies
32
New cards
What is steven’s rule
above 2000Hz, perceived pitch goes up with increased loudness. Bellow 2000Hz, perceived pitch goes down with increased loudness
33
New cards
Define masking
if 2 sounds are at the same pitch, the louder sound will mask the other
34
New cards
define SPL (sound pressure level)
SPL stands for Sound Pressure Level, which is a measure of the intensity of sound waves in decibels (dB).
35
New cards
define phase
the position of a sound wave in time
36
New cards
define in-phase
In-phase refers to two or more waves that have the same frequency and are aligned and subsequently reinforcing their amplitude
37
New cards
define out of phase
"Out of phase" refers to two waves or signals that are not synchronized and have a phase difference between them subsequently cancelling their amplitude.
38
New cards
what happens if there are 2 identical waves, but wave b is 180 degrees out of phase wi
39
New cards
When do phase issues occur
* when multiple microphones are recorded on the same source (e.g 2 mics on a drum kick)
* when a DI box = microphone(s) are recorded on the same source
* samples layered with acoustic drums
* samples being stacked to create drum sounds
* different plug-ins being used on related tracks
* when parallel is applied
* when a DI box = microphone(s) are recorded on the same source
* samples layered with acoustic drums
* samples being stacked to create drum sounds
* different plug-ins being used on related tracks
* when parallel is applied
40
New cards
In what scenario are phase issues the most audible in a DAW
when the mix is summed to Mono
41
New cards
describe ways of fixing phase issues
* using a micro-delay plugin (e.g Logic/s sample delay)
* Manually moving the waveform
* Using an auto align plug-in
* using plug-in delay compensation in a DAW
* using the 3:1 rule with a microphone on the same source (e.g if the mics are 1ft from the source, place mics 3ft apart)
* use a goniometer (e.g phase scope/vector scope)
* use a phase correlation meter
* Manually moving the waveform
* Using an auto align plug-in
* using plug-in delay compensation in a DAW
* using the 3:1 rule with a microphone on the same source (e.g if the mics are 1ft from the source, place mics 3ft apart)
* use a goniometer (e.g phase scope/vector scope)
* use a phase correlation meter
42
New cards
What are the 2 types of microphones
dynamic and condenser
43
New cards
what is a transient response
the quickness of the microphone to respond to sound waves
44
New cards
what are microphones
transducers
45
New cards
what are transducers
something which converts acoustic energy into electrical energy
46
New cards
What are the 2 types of dynamic microphone
moving coil and ribbon
47
New cards
how are condensers polarised
permanently and externally polarised using phantom power
48
New cards
describe the moving coil microphone
* most widely used
* simple, rugged design
* broad frequency response
* limited transient response
* simple, rugged design
* broad frequency response
* limited transient response
49
New cards
describe a ribbon microphone
* incredible response to transient waves
* very fragile
* warm tone
* not all ribbons can tolerate phantom power
* very fragile
* warm tone
* not all ribbons can tolerate phantom power
50
New cards
how does a condenser create sound
acoustic energy stimulates the diaphragm. Changes in the capacitance (the diaphragm itself) create an electrical analogue of the signal. The plates are charged by external power.
51
New cards
Compare the sensitivity of the 3 types of transducers
Condenser has a high sensitivity whereas moving coil is medium and ribbon is low
52
New cards
Compare the robustness of the 3 types of transducers
moving coil has an excellent robustness whereas condenser is good and ribbon is poor
53
New cards
Compare the sound quality of the 3 types of transducers
ribbon has an excellent sound quality whereas condenser is good/excellent and moving coil is good
54
New cards
Compare the affect of moisture on the 3 types of transducers
the dynamic microphones aren’t effected by moisture whereas condensers are
55
New cards
Compare how the 3 types of transducers are affected by movement
Moving coil and condenser is good under movement whereas ribbon is poor (as its very fragile)
56
New cards
Compare the reliability of the 3 types of transducers
all good reliability
57
New cards
Compare the cost of the 3 types of transducers
ribbon has a high cost whereas condenser is medium/high and moving coil is low
58
New cards
what sort of mics have directional qualities
all types
59
New cards
define spill
hearing sounds from one instrument to spill into another microphone (e.g the drum in the guitar microphone)
60
New cards
In what scenario would we want all round sound
in a church
61
New cards
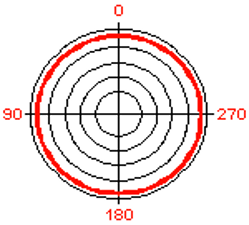
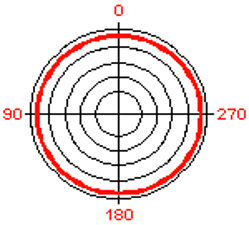
define a non-directional mic
a microphone which picks up sound equally from all directions (omni-directional)
62
New cards
define omni-direcrional
a mic that can pick up sound in all directions equally.
63
New cards
define a directional mic
a mic which picks up sound from certain directions
64
New cards
what are the 3 main types of polar patterns
cardioid, super/hyper-cardioid and figure-of-eight
65
New cards
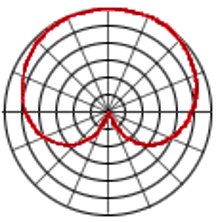
describe a cardioid polar patten
a heart shaped pattern which picks up sound from the front only (most common)
66
New cards
describe a hyper-cardioid polar pattern
narrowest polar pattern used when maximum rejection from the slides and back is required (image is hyper-cardioid)
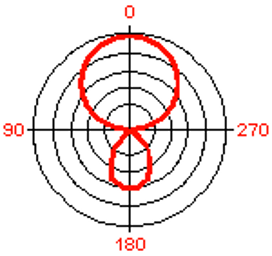
67
New cards
describe the figure-of-eight polar pattern
a figure of eight shaped pattern used for maximum sound rejection from the sides
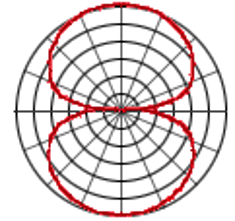
68
New cards
describe the super-cardioid polar pattern
slightly less narrow polar pattern used when maximum rejection from the slides and back is required
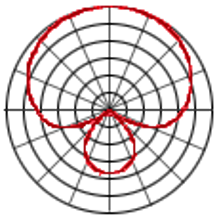
69
New cards
what happens to the bass of a song as you get closer to a directional microphone
it increases (bass boost)
70
New cards
what is the roll off switch on some microphones
a button which rolls off the bass, setting a high pass filter
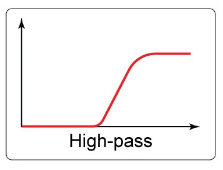
71
New cards
what is the pad switch and what does it do
a switch which reduces the sensitivity of a microphone (normally -6dB)
72
New cards
define dynamic range
the distance between the loudest possible level and the lowest possible level expressed in dB
73
New cards
What sort of problems will recorders have regarding dynamic range
If the recording level is set too high the recorder will distort the sound at the loudest part.
If the recording level is set too low, quiet sounds may get lost in the mix
If the recording level is set too low, quiet sounds may get lost in the mix
74
New cards
How can we solve problems recording dynamic range
using a compressor
75
New cards
Why does using a compressor solve problems regarding dynamic range
* A compressor acts like an automatic volume control
* Turns down the volume when the signal goes over a certain threshold
* helps to avoid overloading the recoding instruments with a wide dynamic range
* ‘flattens‘ the sound as the overall level goes up
* Turns down the volume when the signal goes over a certain threshold
* helps to avoid overloading the recoding instruments with a wide dynamic range
* ‘flattens‘ the sound as the overall level goes up
76
New cards
when is compression applied
when tracklaying to control recording levels of instruments and vocals and at the mastering stage to give overall punch and loudness to a stereo mix
77
New cards
What are some negatives of using compression in a mix
* Transients can be destroyed
* clarity can be lost
* music can become monotonously loud
* clarity can be lost
* music can become monotonously loud
78
New cards
what are the 2 types of microphone placement
close miking and distant/ambient miking
79
New cards
how close is close miking
3-10cm from source
80
New cards
what sort of result does close miking give
tight sound (if too close 2 big instruments, only captures specific qualities)
81
New cards
how far is distant miking
3+ ft
82
New cards
what sort of result does distant miking give
more sound of the instument and more ‘room‘
83
New cards
what sort of mic should be used for close miking
dynamics for very loud instruments, condensers to capture the full quality
84
New cards
what sort of mic should be used for distant/ambient miking
condenser/ribbon
85
New cards
Describe the spaced pair (AB) mic technique
It involves two **microphones** positioned apart using the 3:1 rule, meant to capture the same sound source
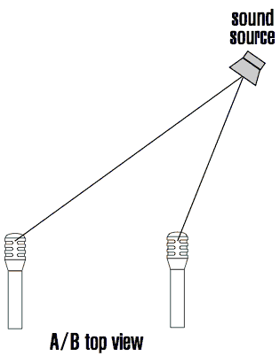
86
New cards
Describe the coincident/crossed (XY) mic technique
two cardioid microphones placed on top of eachother diagonally in an X shape
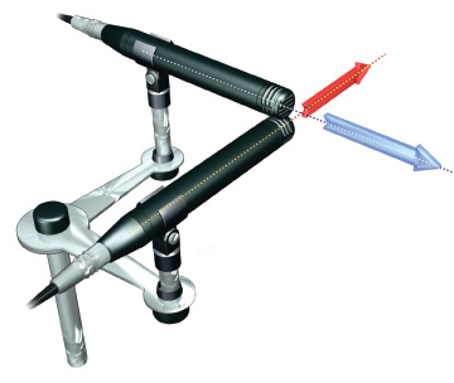
87
New cards
Described the advantages of spaced mic techniques
* often uses omni polar pattern (smooth lows)
* spacious sound
* comb filtering when combined
* spacious sound
* comb filtering when combined
88
New cards
what is comb filtering
when the same sound arrives at the listener's ears (or a microphone) at different times with a very small delay between the signals
89
New cards
describe a disadvantage of spaced mic placement
less precise
90
New cards
describe some advantages of coincident mic placement
* no comb filtering
* more detail
* less spacious
* more detail
* less spacious
91
New cards
describe the middle and side mic technique
The middle mic is set up facing the centre of the sound source (either, omni, cardioid or fig-8) The side mic is aimed 90 degrees off-axis from the sound source (must be fig-8). when put into a daw the side mic must be copied and the phase reversed
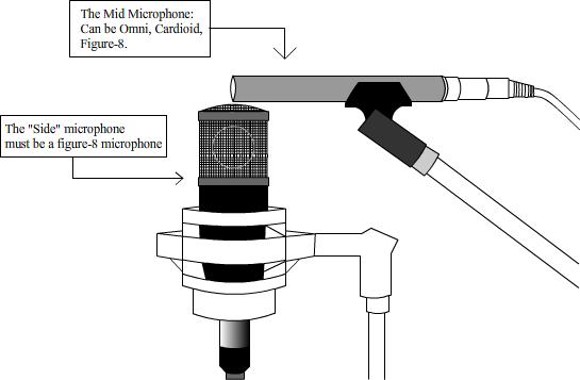
92
New cards
what is the ORTF stero technique
2 microphones placed 17cm apart at 110 degrees angle
93
New cards
ORTF stero has a wider stero image than what crossed technique
XY
94
New cards
ORTF stero technique mimics what
the ears
95
New cards
describe the blumlein mic tehcnique
2 fig-8 mics placed in a 90 degree coincident configuration
96
New cards
what sort of sound does the blumlein tehcnique proudce
a spaceous sound with room ambience
97
New cards
what is the binaural recording technique
uses stereo (omni) microphones mounted on a human head (or head-shaped object) in order to create a fully believable ambient environmental sound recording,
98
New cards
\
Which type of EQ is best suited to live sound situations?
Which type of EQ is best suited to live sound situations?
Graphic Equaliser
99
New cards
\
Which type of EQ is most accurate for studio use?
Which type of EQ is most accurate for studio use?
Parametric EQ
100
New cards
Which type of EQ is found on 'tone' controls of a radio?
Which type of EQ is found on 'tone' controls of a radio?