Working memory
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is working memory?
A system that combines information storage and processing for ongoing mental activities.
How does short-term memory relate to working memory?
Short-term memory is the temporary storage component of working memory.
What factors improve reliability in WM measurement?
Multiple tasks
Different domains (verbal vs visuospatial)
Complexity (simple vs complex tasks)
What is the typical WM capacity?
About 4 chunks of information.
How does WM change across the lifespan?
Improves through childhood, declines in later adulthood.
Is WM intact in hippocampal amnesia and which disorders show WM deficits
Yes, mostly intact - ADHD and other cognitive impairments.
How is WM related to intelligence?
Central to intelligent behavior
Correlates with fluid intelligence, complex cognition, academic attainment
Kane et al. (2007): Higher WM → more on-task thoughts during challenging tasks.
What limits WM capacity?
Time and capacity constraints (do we have enough space for multiple WM activities)
Interference (similar items or environmental distractions)
Attention
Stress and other state factors
How can WM performance be optimized?
Focus attention
Active maintenance (rehearsal, refreshing)
Use strategies
Link to LTM knowledge
What determines what we remember?
What we pay attention to.
Visual cueing (arrows pointing to important information)
Value-directed prioritization (focus on high-value items and they are more likely to be recalled)
How does LTM support WM?
Better recall for meaningful sequences (e.g. you can recall words better in a sentence that makes sense then if the word were random → representations of LT
Words easier than nonwords (same letter in different order)
Structured patterns aid visual WM
How does WM support LTM?
Phonological WM aids language learning
Nonword repetition predicts vocabulary growth
Visual WM predicts visual LTM
What did Patient PV’s case show?
Stroke damaged left temporal-parietal region
Poor phonological STM (poor digit recall) → impaired new word learning. When learning new words in a language they were unfamiliar with they couldn’t
Written words easier due to existing LTM representations.
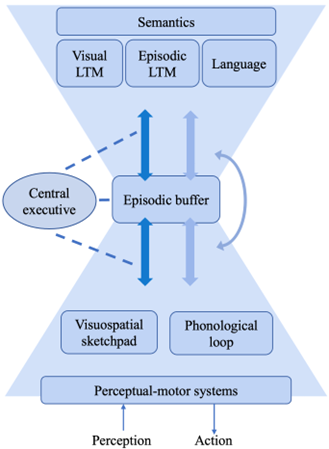
What is Baddeley’s multi-component model?
Phonological loop: Verbal info
Visuospatial sketchpad: Visual/spatial info
Episodic buffer: Integrates info from different sources for conscious awareness
What is verbal-visuospatial fractionation?
Independent impairments possible in verbal vs visuospatial STM.
What did Logie (1995) propose?
Visual cache: Passive store for form/color
Inner scribe: Active spatial rehearsal.
What is TBRS (Time-Based Resource Sharing)?
WM combines storage and processing; limited capacity shared between both; decay occurs over time without rehearsal.
the cognitive load of a task is switching between storage and processing
What is the embedded-processes model?
WM = activated LTM + focus of attention (~3–4 chunks); attention resources limit capacity (LTM is not separate like in other models)
Why is attentional control important?
Maintains focus on task-relevant info while resisting distractions; strongly linked to general intelligence (Engle, 2018).
What five principles do WM models agree on?
Limited capacity
Combines processing and storage
Attention is crucial
Unattended info is quickly forgotten
LTM can facilitate or interfere with WM.