Nasal and Oral Cavities
1/170
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
171 Terms
what is above the nasal cavity and what separates them?
anterior cranial fossa, perforated cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone
what is lateral to the upper half of the lateral wall of the nasal cavity?
ethmoid air sinus
what is lateral to the ethmoid sinus?
the medial wall of the orbit
what is lateral to the lower half of the lateral nasal walls?
maxillary air sinus
what is below the floor of the nasal cavity, and what separates them?
oral cavity, hard palate
what is the nasal cavity continuous with posteriorly?
the nasopharynx
what makes up the roof of the nasal cavity?
nasal cartilages, nasal bone, nasal spine of the frontal bone, cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone, anterior and inferior aspects of the body of the sphenoid bone
what makes up the floor of the nasal cavity?
palatine process of maxilla, horizontal plates of palatine bone
what makes up the medial wall of the nasal cavity?
nasal septum- made of septal cartilage, perpendicular (vertical) plate of ethmoid bone, vomer
what makes up the lateral wall of the nasal cavity?
maxilla, ethmoid bone (superior and middle conchae), inferior concha, palatine bone
what 4 passages do the nasal conchae divide the nasal cavity into?
sphenoethmoidal recess, superior meatus, middle meatus, inferior meatus
how do secretions from the orbit and paranasal sinuses drain into the nasal cavity?
through openings in the lateral wall
how do tears produced by the lacrimal gland get removed from the orbit?
the nasolacrimal apparatus- the nasolacrimal duct drains to the inferior meatus of the nasal cavity
hiatus semilunaris
curved depression found in the middle meatus
what drains via the hiatus semilunaris?
anterior ethmoidal sinus, frontal sinuses, maxillary sinuses
bulla ethmoidalis
swelling on the superior border of the hiatus semilunaris
paranasal sinuses
air filled extensions of the respiratory part of the nasal cavity into the frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, and maxillary bones
frontal sinuses
between the outer and inner tables of the frontal bone, posterior to the superciliary arches and the root of the nose
what does each of the frontal sinuses drain through, and where does that lead?
frontonasal duct, opens into the semilunar hiatus of the middle nasal meatus
ethmoidal cells (sinuses)
small cavities in the ethmoid bone between the nasal cavity and the orbit
sphenoidal sinuses
located in the body of the sphenoid, are separated by a bony septum
what important structures are separated from the sphenoidal sinuses only by thin plates of bone?
optic nerves and optic chiasm, pituitary gland, internal carotid arteries, cavernous sinuses
where do the sphenoidal sinuses drain?
the sphenoethmoidal recess
maxillary sinuses
largest of the paranasal sinuses, occupy the bodies of the maxillae and communicate with the middle nasal meatus
the medial wall of the maxillary sinus forms the…
inferior part of the lateral wall of the nasal cavity
the roof of the maxillary sinus is formed by the…
floor of the orbit
the floor of the maxillary sinus is formed by the…
alveolar part of the maxilla of the oral cavity
maxillary ostium
the openings in the maxillary sinus that allow for drainage
each maxillary sinus drains by the maxillary ostium into the ____ nasal meatus of the nasal cavity by way of the _______
middle, semilunar hiatus
vestibule
space between the teeth and mucosal lining of the lips and cheeks (labial and buccal mucosa)
oral cavity proper
space between upper and lower dental arches
lips
controlled by muscles of facial expression which are innervated by CN VII
philtrum
external midline feature of the lips
buccinator
thin, flat, rectangular muscle that arises from the pterygomandibular raphe and attaches laterally to the alveolar processes of the maxillae and mandible, opposite the molar teeth
it occupies a deeper plane than the other facial muscles and is more closely related to the buccal mucosa than the skin of the face
where does the parotid (stensen’s) duct open?
in the oral vestibule opposite the crown of the second molar
palate
forms the roof of the oral cavity proper and floor of nasal cavity, has 2 distinct parts: hard and soft
hard palate
forms rigid surface for food during chewing, formed from palatine process of maxilla and horizontal plate of palatine bone (includes posterior nasal spine)
what foramen are associated with the hard palate?
incisive fossa, greater palatine foramen, lesser palatine foramen
incisive fossa
behind the central incisors, nasopalatine nerve and sphenopalatine vessels pass through
greater palatine foramen
on the lateral posterior aspect of the palate, greater palatine nerves and vessels pass through
lesser palatine foramen
posterior to the greater palatine foramen, lesser palatine nerve and vessels pass through
soft palate
rises as a reflex to close off nasopharynx during swallowing, sides are attached to pharyngeal walls
what muscles make up to soft palate?
levator veli palatini, tensor veli palatini, palatoglossus, palatopharyngeus, musculus uvulae
what is the function of the levator veli palatini?
elevate the soft palate
what is the function of the tensor veli palatini?
flatten and tense the soft palate
what is the function of the palatoglossus muscle?
elevates the posterior 1/3 of the tongue
what is the function of the palatopharyngeus muscle?
elevate the pharynx and larynx
what is the function of the musculus uvulae?
retract and elevate the uvula
tonsils
aggregates of lymphoid tissue, palatine, lingual, and pharyngeal
palatine tonsils
bilateral, located at boundary of oral cavity and pharynx
lingual tonsils
located on dorsal surface of posterior tongue
pharyngeal tonsils
single mass, located in roof of nasopharynx (adenoids)
sulcus terminalis
location where the anterior 2/3 and posterior 1/3 of tongue meet
tongue
has ventral and dorsal surfaces, composed of intrinsic and extrinsic muscles
lingual frenulum
a midline fold of mucous membrane running from the lingual gingiva behind the mandibular central incisors posteriorly to the undersurface of the tongue
sublingual papilla (caruncle)
located on either side of the frenulum and is the opening of the duct of the submandibular gland (wharton’s duct)
what is the purpose of the extrinsic muscles of the tongue?
move the tongue around (up/down, side to side)
what is the bony attachment of the genioglossus?
superior genial (mental) spine
what is the bony attachment of the hyoglossus?
hyoid bone
what is the bony attachment of the styloglossus?
styloid process
what is the action of the genioglossus?
depresses and protrudes the tongue
what is the innervation of the genioglossus?
hypoglossal nerve
what is the action of the hyoglossus?
depresses and retracts the tongue
what innervates the hyoglossus?
hypoglossal nerve
what is the action of the styloglossus?
retracts tongue
what innervates the styloglossus?
hypoglossal nerve
what is the action of the palatoglossus?
elevates posterior part of tongue
what innervates the palatoglossus?
pharyngeal plexus via CN X
what is the function of the intrinsic muscles of the tongue?
change the shape of the tongue
what nerve are all the intrinsic muscles of the tongue innervated by?
CN XII
what is the main artery to the tongue?
lingual artery, branch of the external carotid artery
what does the dorsal lingual artery supply?
the root of the tongue
what does the deep lingual artery supply?
the body of the tongue
what does the sublingual branch of the lingual artery supply?
the floor of the mouth
where do the veins of the tongue and floor of the oral cavity travel?
with the arteries of the same name
where do the deep lingual veins run?
posteriorly under the mucous membrane of the underside of the tongue at the side of the lingual frenulum
where do all branches of venous drainage in the tongue and floor of the oral cavity drain to?
the lingual vein to the internal jugular vein
where do the lymphatics of the tip of the tongue drain to?
submental group
where do the lymphatics of the side of the tongue drain to?
submandibular group
where do the lymphatics of the central part of the tongue drain to?
jugulo-omohyoid group
where do the lymphatics of the posterior 1/3 of the tongue drain to?
jugulo-digastric group and jugulo-omohyoid group
mylohyoid muscles
a muscular diaphragm that fills the U shaped gap between the sides and body of the mandible, paired muscles
what are the attachments of the mylohyoid muscle?
mylohyoid line of the mandible to the median raphe and hyoid bone
what innervates the mylohyoid?
nerve to mylohyoid from inferior alveolar nerve
geniohyoid
two cord-like muscles above the diaphragm, run from the mandible to the hyoid
what are the attachments of the geniohyoid?
inferior mental spines of the mandible to the body of the hyoid bone
what nerve innervates the geniohyoid?
C1
what glands are on the floor of the mouth?
submandibular duct and sublingual gland and ducts
what does the lingual nerve provide?
sensory from anterior 2/3 of the tongue
what does the hypoglossal nerve provide?
motor to intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue (-1 muscle)
what does Wharton’s duct connect?
submandibular gland to the oral cavity (opens lateral to lingual frenulum)
what does the sublingual duct connect?
the sublingual gland to the oral cavity or submandibular duct
where does the lingual nerve begin?
it is a branch of the posterior division of the mandibular nerve (CN V3) within the infratemporal fossa
what is the pathway the lingual nerve takes from the infratemporal fossa until it is joined by the chorda tympani?
curves downward and forward to emerge between the medial and lateral pterygoid muscles, where it is joined by the chorda tympani
what is the pathway of the lingual nerve after it is joined by the chorda tympani?
it continues anteriorly and downward to enter the floor of the mouth just medial to the root of the mandibular 3rd molar
what is the pathway of the hypoglossal nerve?
it leaves the skull through the hypoglossal canal and descends almost vertically in the neck to a level just below the mandible, it sharply angles forward and crosses the external carotid artery, continues forward and crosses the lingual artery to reach the hyoglossus muscle
it continues to travel on the external surface of the hyoglossus muscles and deep to the mylohyoid muscle to reach the tongue
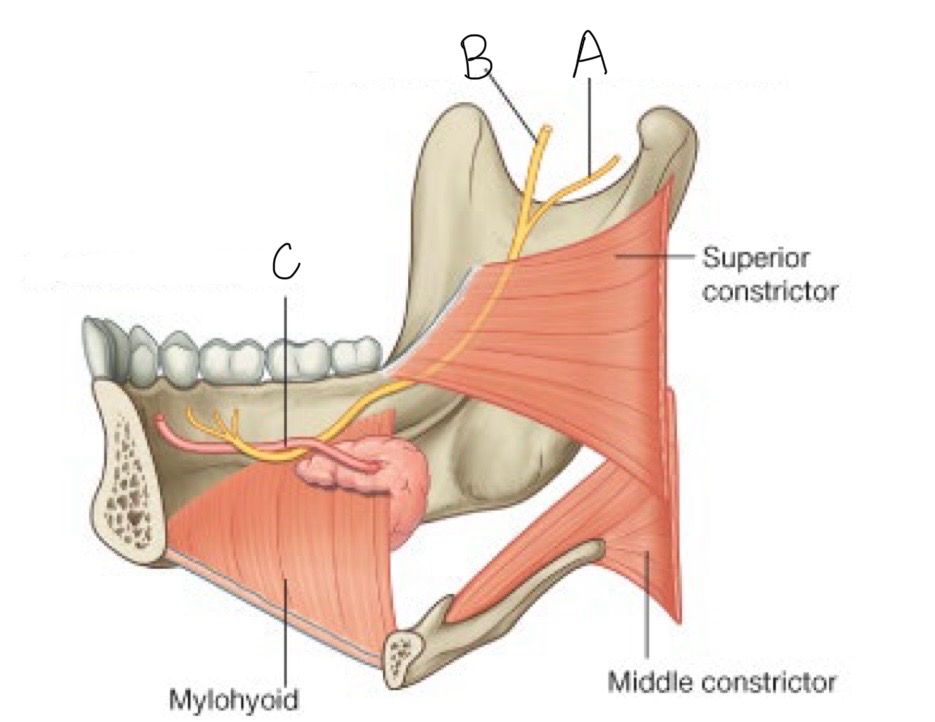
what structure is labeled A?
chorda tympani
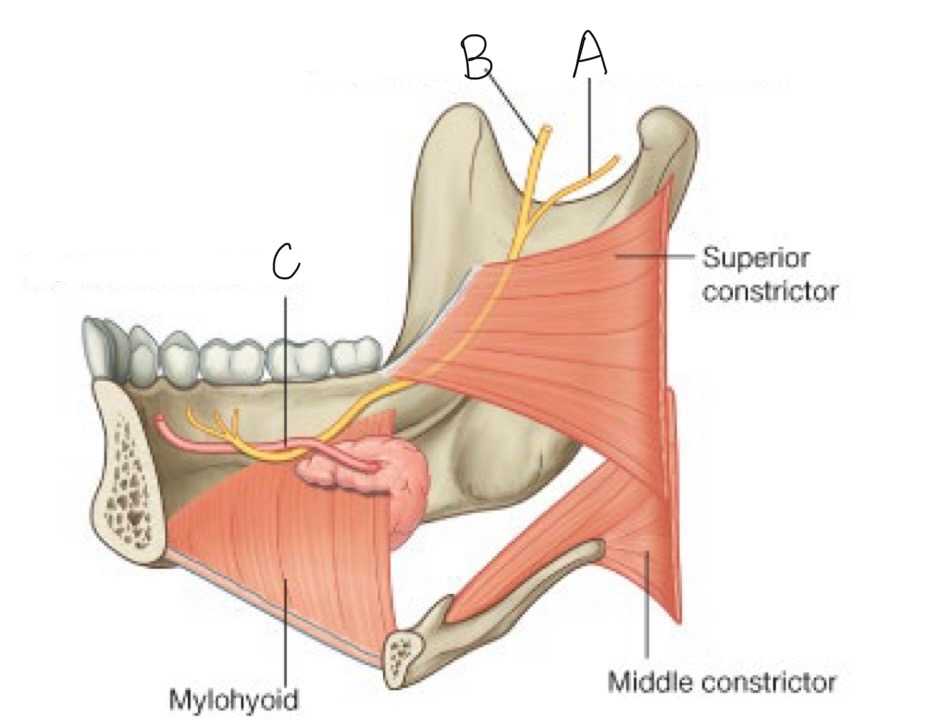
what structure is labeled B?
lingual nerve
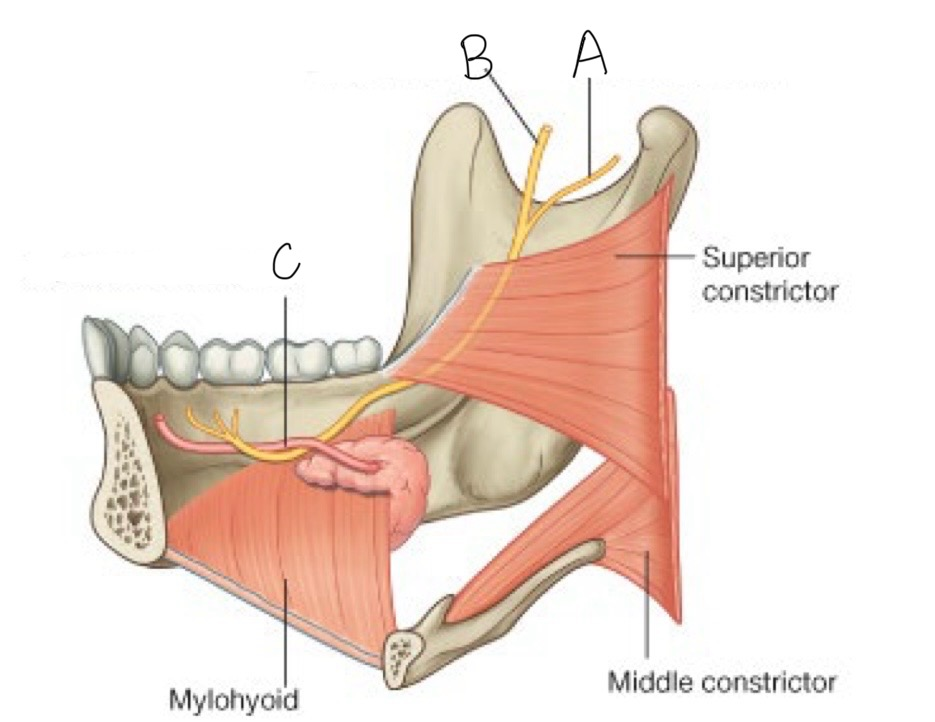
what structure is labeled C?
submandibular duct
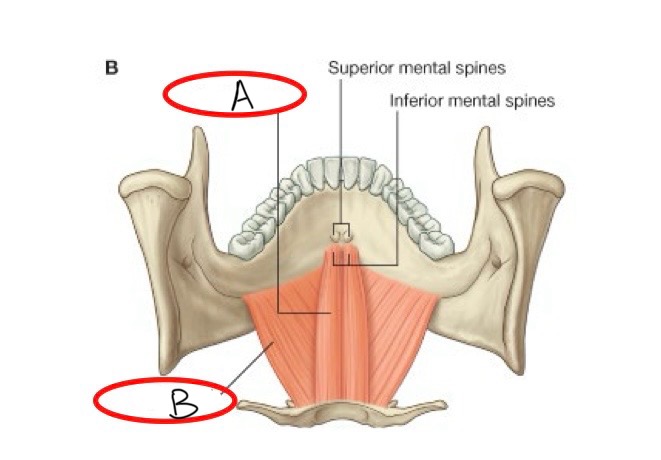
what structure is labeled A?
geniohyoid