Disorders of the Penis - MedPath
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What does this refer to
Penile foreskin (prepuce) is “too tight.”
Foreskin cannot be retracted back over the glans
Causes
Poor hygiene or chronic infections
Symptoms: Edema, erythema, and tenderness of the prepuce and purulent discharge
Treatment: circumcision
Phimosis
What does this refer to
Foreskin is retracted and cannot be moved forward (reduced) to cover the glans.
Causes edema of the glans
Treatment: Surgery
Severe paraphimosis: medical emergency
Paraphimosis
What does this refer to
Fibrous plaques (thickening) slowly develop in the tunica albuginea causing penile curvature during erection.
Occurs in middle-aged men and causes painful erections and intercourse
No definitive treatment is available.
Treatment:
Pharmacologic agents
Collagenase (Xiaflex) injection
Surgery (plication, grafting, penile device implantation (if coexisting ED)
Peyronie disease
What does this refer to
Condition of prolonged penile erection
Painful and not associated with sexual arousal
Urologic emergency
Idiopathic in 60% of cases
Associated with spinal cord trauma, sickle cell disease, leukemia, pelvic tumors or infections, or penile trauma
Also associated with cocaine use
Treatments
Iced saline enemas
Ketamine administration
Spinal anesthesia
Needle aspiration of blood from the corpus through the dorsal glans, followed by catheterization and pressure dressings to maintain decompression
Aggressive surgical treatments: creation of vascular shunts to maintain blood flow
Priapism
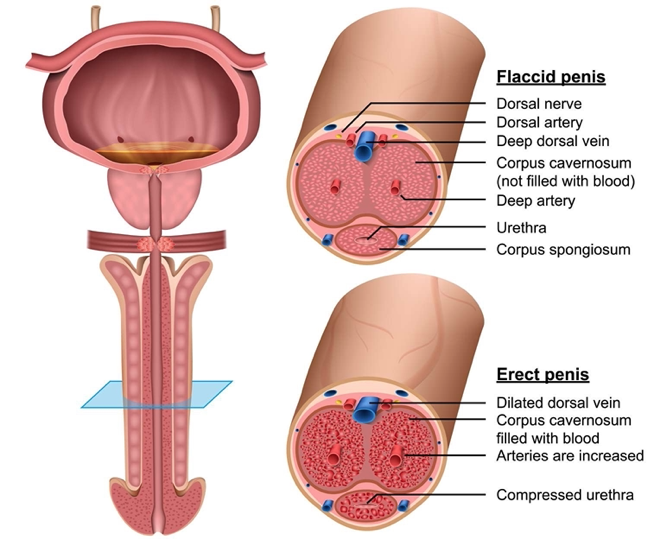
What does this refer to
look at these
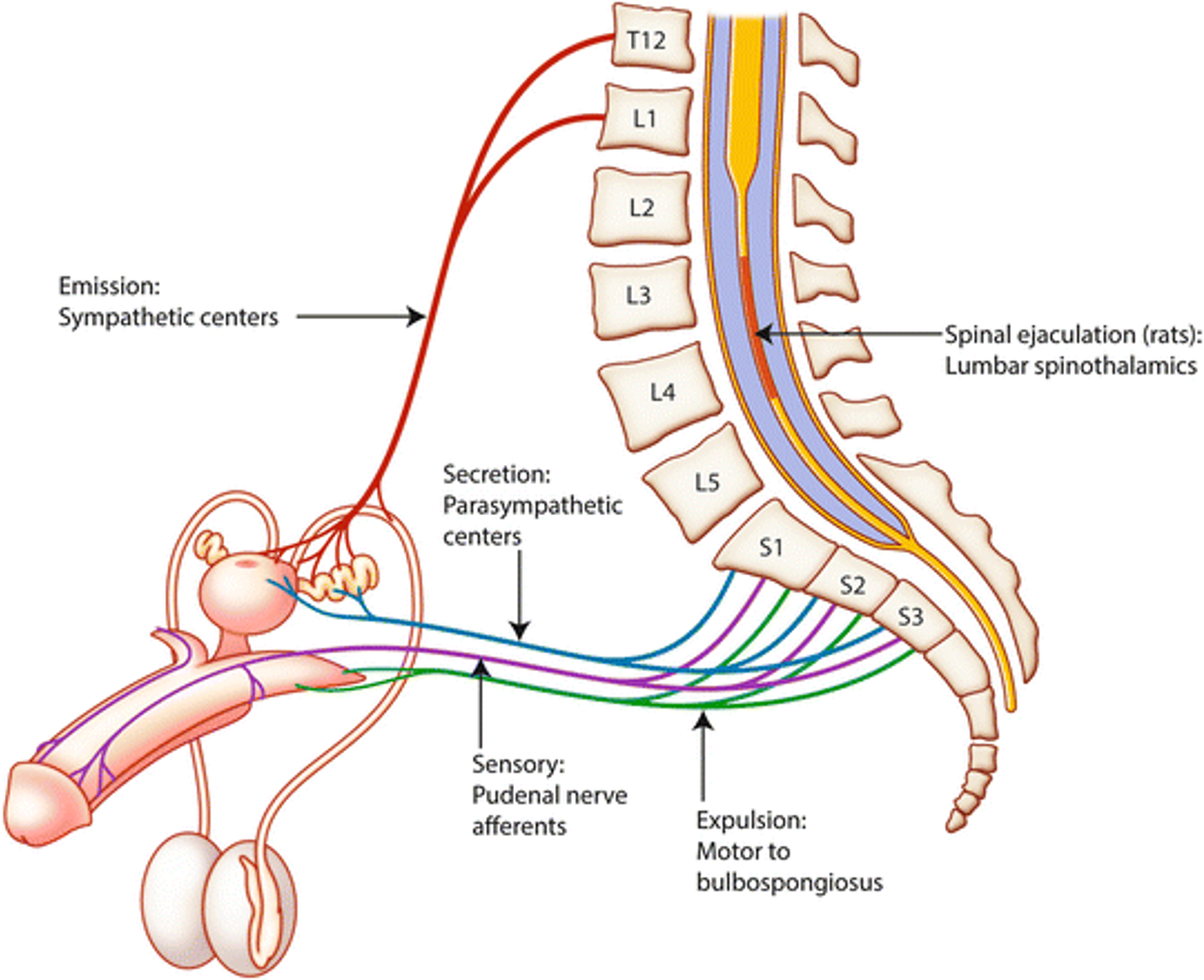
What does this refer to
Inflammation of the glans penis
Usually associated with foreskin inflammation (posthitis)
Accumulation under the foreskin (smegma), causing irritation of the glans
Phimosis, inadequate cleansing under the foreskin, skin disorders, and infections
Most commonly in men with poorly controlled diabetes mellitus and candidiasis
Treatment: antimicrobial agents to treat infection; circumcision to prevent recurrences and to be considered after the inflammation has subsided
Balanitis
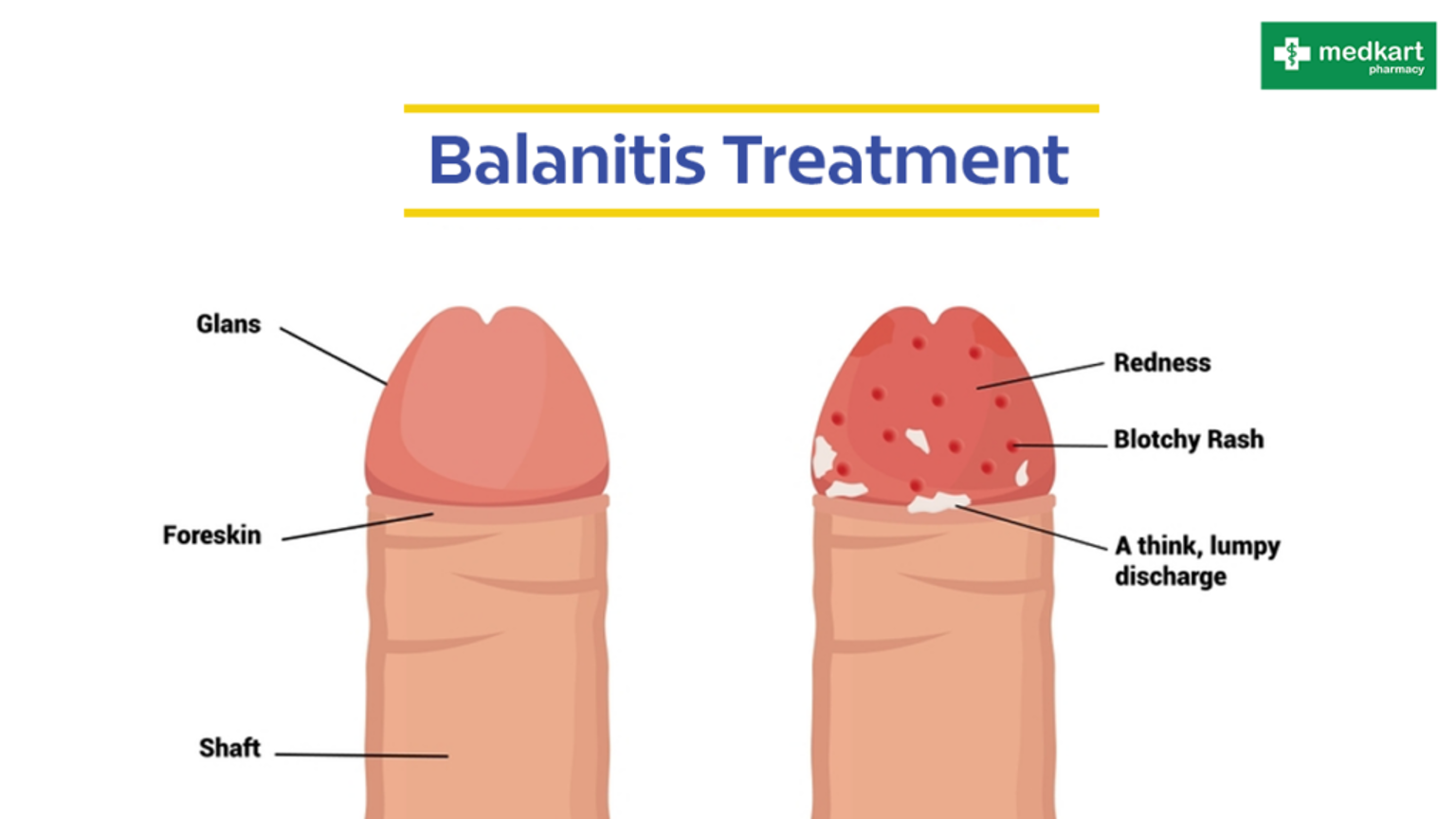
What does this refer to
Rare
Mostly squamous cell carcinomas
Risk factors: human papillomavirus (HPV), smoking, psoriasis treated with a combination involving the drug psoralen and ultraviolet (UV) light
Often diagnosed in men older than 55 years of age
Thick white plaque (leukoplakia), typically involving the meatus
Penile carcinoma: higher incidence in uncircumcised men
Treatment: surgery, radiation, chemotherapy
Penile cancer
What does this refer to
Inflammation and dilation of the veins in the spermatic cord
“Bag of worms”
Cause: inadequate or absent valves in the spermatic veins
Treatment: ligation of the spermatic vein or occlusion of the vein by percutaneous methods, such as balloon catheter and sclerosing fluids
Scrotal support: if disorder is mild and fertility is not an issue
Varicocele
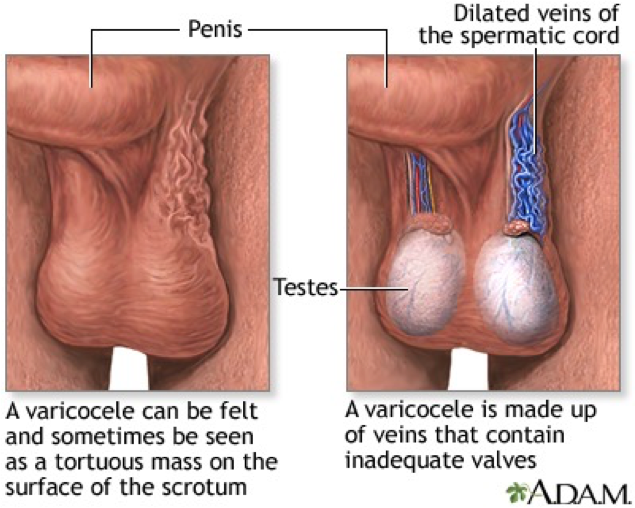
What does this refer to
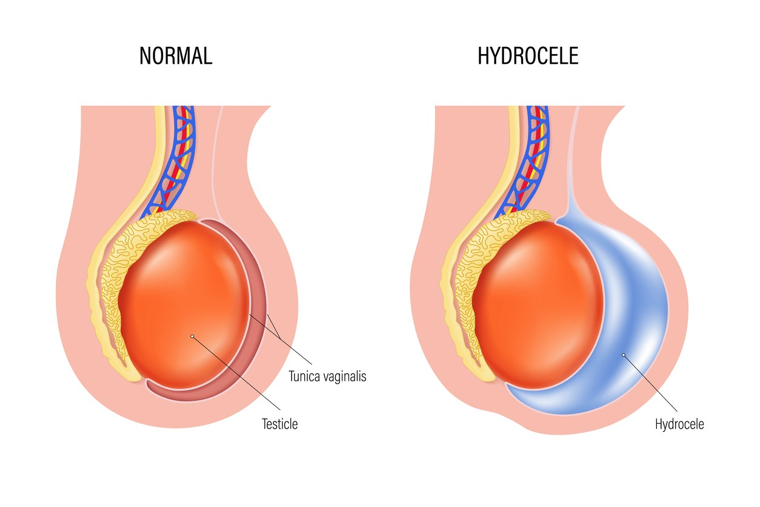
Scrotal swelling caused by the collection of fluid in the tunica vaginalis
Imbalance between fluid secretion and reabsorption
Treatment
Usually not required unless disorder causes considerable physical discomfort or undesirable cosmetic appearance
For uncomplicated hydrocele: aspiration of the fluid and injection of a sclerosing agent into the scrotal sac
Goals: to remove the hydrocele and to prevent recurrence by sclerosing or excising the tunica vaginalis
Hydrocele
What does this refer to
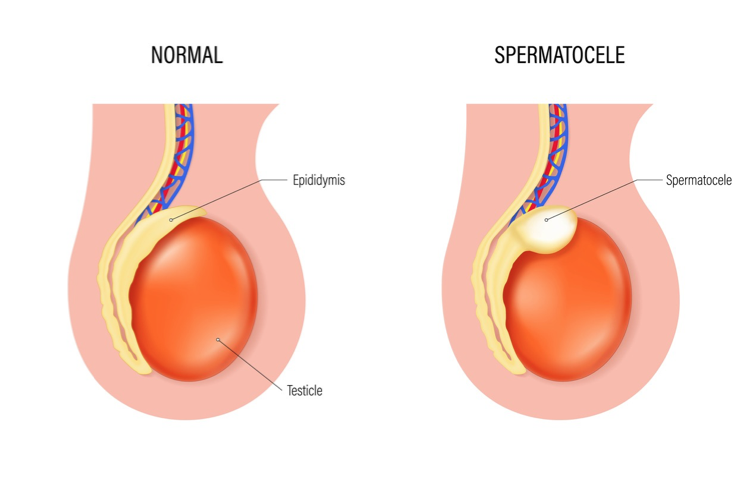
Epididymal cysts
Benign cystic collections of fluid of the epididymis located between the head of the epididymis and the testis
Milky fluid that contains sperm and does not cover the entire anterior scrotal surface
Exhibits discrete, firm, freely mobile masses distinct from the testis that may be transilluminated
Treatment: none or excised or scrotal support
Spermatocele
What does this refer to
Failure of one or more of the testes to descend from the abdominal cavity into the scrotum
Complication: testicular cancer; if untreated, infertility
Treatment: hormones or surgery
Cryptorchidism
What does this refer to
Testis that has strayed from the normal pathway of descent
Ectopic testis
What does this refer to
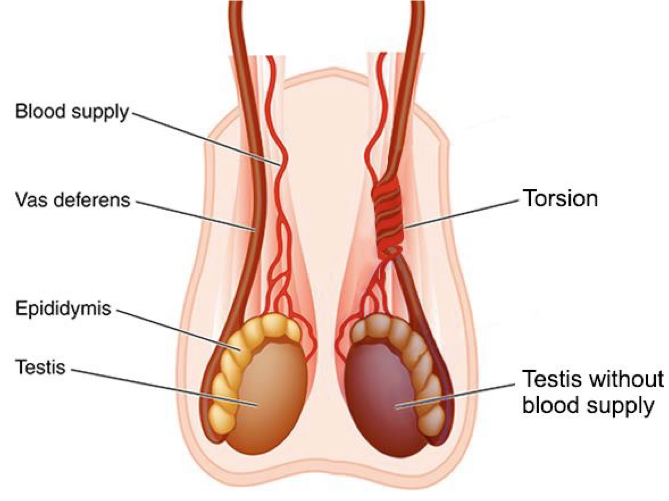
Rotation of a testis
Rotation, causing twisting of the blood vessels in the spermatic cord
Painful and swollen testis
May be spontaneous or follow physical exertion or trauma
Medical emergency
Treatment: if torsion cannot be reduced manually, then surgery must be performed within 6 hours after the onset of symptoms to preserve normal testicular function
Torsion of a testis
What does this refer to
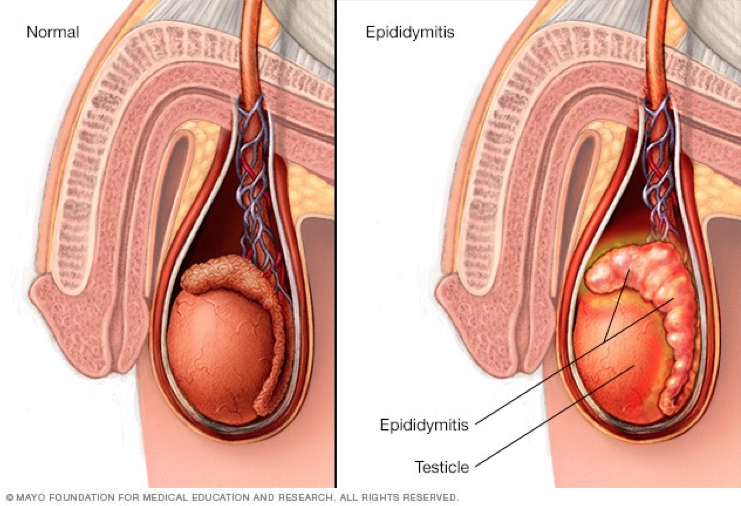
Is an inflammation of the epididymis
Is common in sexually active young men
Pathogenic microorganism reaches the epididymis by ascending the vas deferens from an already infected bladder or urethra
Main symptoms: pain and the Prehn sign (positive if pain is relieved by elevation of the scrotum)
Treatment: antibiotics, analgesics, ice, and scrotal elevation
Epididymitis
What does this refer to
Acute infection of the testis
Complication of a systemic disease (mumps) or related to epididymitis
Treatment
Bed rest, scrotal support, elevation of the scrotum, hot or cold compresses, analgesic agents for relief of pain
Antimicrobial drugs for bacterial orchitis
Corticosteroids for nonspecific granulomatous orchitis (autoimmune inflammatory disease in middle-aged men)
Orchitis
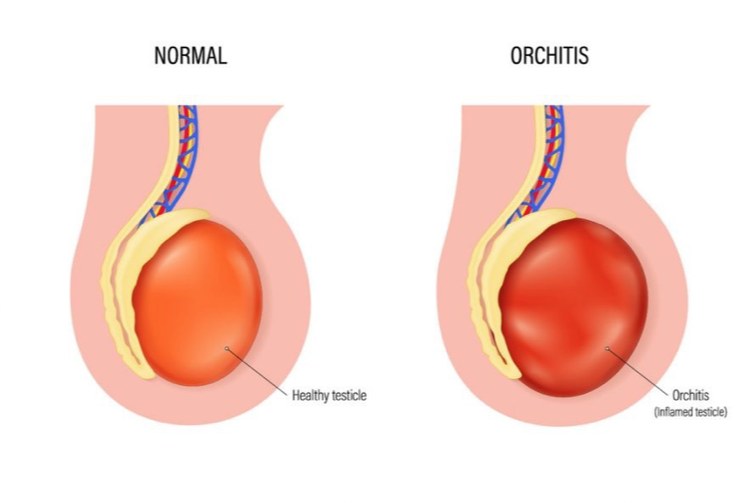
What does this refer to
Is among the most curable of cancers
Is common in men between 15 and 35 years of age
Risk factors
High androgen levels, genetic predisposition
History of cryptorchidism, trauma, or infection
Causes painless testicular enlargement
Treatment: is based on the type of tumor, stage of the disease, general health, and age
Surgery
Radiation and chemotherapy, singly or in combination
Cancer of the testis
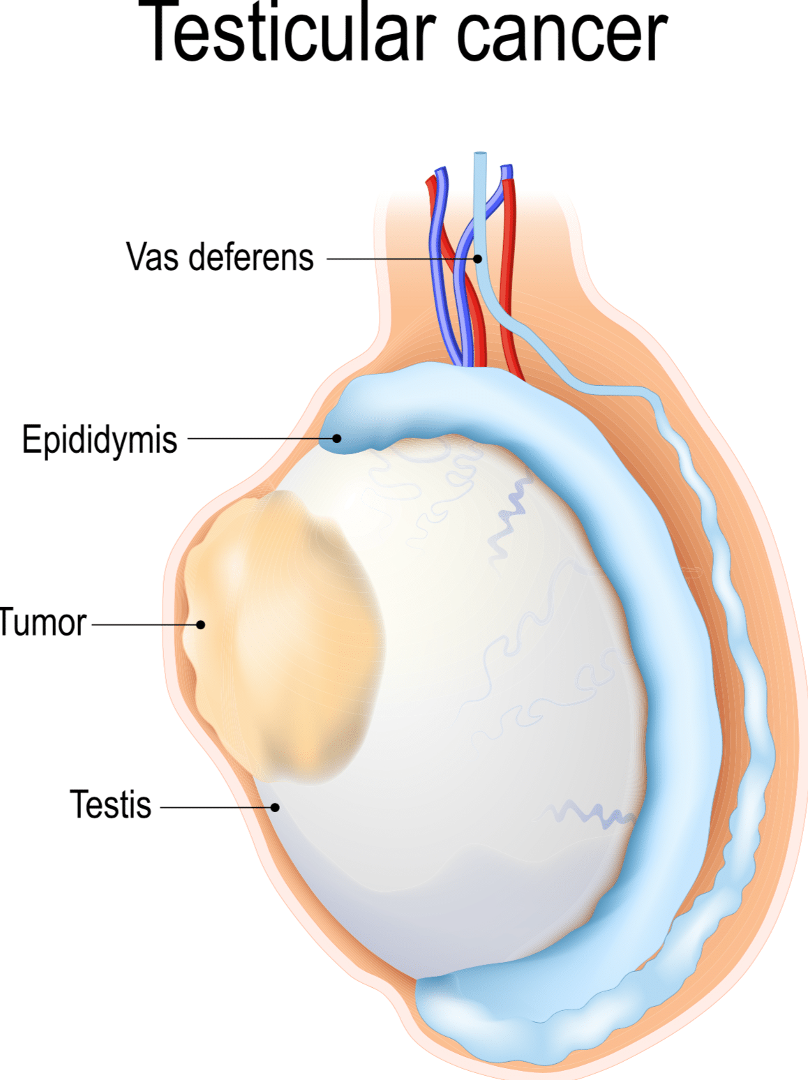
What does this refer to
Is an enlargement of the prostate gland
Is also called benign prostatic hypertrophy
Symptoms associated with urethral compression
Urge to urinate often
Some delay in starting urination
Decreased force of the urinary stream
Has a relationship to aging
Evaluation
Digital rectal examinations
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) monitoring
Treatment: drugs, minimally invasive therapies, and surgery
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
What does this refer to
Inflammation of the prostate
Acute bacterial infection: ascending infection of the urinary tract
Symptoms: signs of infection
Treatment: antibiotics, analgesics, antipyretics, bed rest, adequate hydration; Foley catheter contraindicated
Chronic bacterial infection: recurrent urinary tract symptoms and persistence of pathogenic bacteria
Treatment: surgery
Nonbacterial infection
Chronic prostatitis or chronic pelvic pain syndrome: no pathogenic bacteria is localized to the prostate
Nonbacterial infection: complaint of pain or a dull ache that is continuous or spasmodic in the suprapubic, infrapubic, scrotal, penile, or inguinal area
Treatment: hot sitz baths, bed rest, alpha-blockers, anticholinergics, and antiinflammatory drugs
Prostatitis
What does this refer to
Most commonly diagnosed nonskin cancer in men in the United States
Considered to be the second most frequently diagnosed cancer and the sixth leading cause of death worldwide
Asymptomatic until its advanced stages
Cancer of the prostate
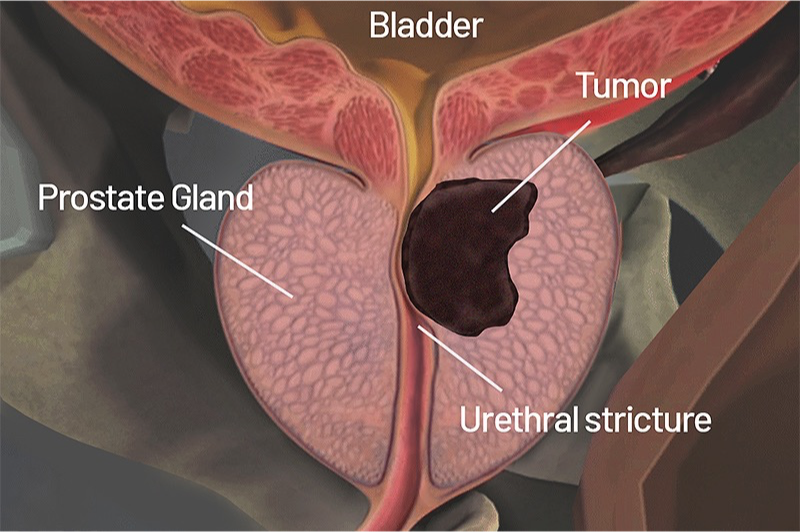
What does this refer to
Dietary factors
Change in diet from animal products to vegetables and fruits may decrease the incidence of prostate cancer.
Hormones
Prostate is the equivalent to the uterus.
Estrogens participate in the pathogenesis and development of benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer by activating estrogen-receptor α.
Exposure to arsenic or estrogens can disrupt normal deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) methylation patterns and histone modifications.
Cancer of the prostate
What does this refer to
Androgen-receptor signaling
Stromal androgen receptors are the priority.
Prostatic epithelial neoplasia
Vasectomy
Circulating free testosterone is elevated.
Chronic inflammation
Risk for prostate cancer is increased.
Genetic and epigenetic factors
Has a strong familial tendency; BRCA2 mutations
Stromal environment
Multifactorial hypothesis of prostate carcinogenesis
Androgens act as strong tumor promoters to enhance DNA toxic carcinogens (reactive estrogen metabolites and estrogen, and prostate-generated reactive oxygen species).
Alterations in autocrine/paracrine growth-stimulating and growth-inhibiting factors between the prostate tumor cells and the microenvironment influence cancer athogenesis.
Possibly unknown environmental-lifestyle carcinogens may contribute to prostate cancer.
Cancer of the prostate
What does this refer to
Treatment
No treatment
Watchful waiting
Surgical treatments
Total prostatectomy
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP)
Cryotherapy
Nonsurgical treatments
Radiation therapy
Hormone therapy
Chemotherapy
Immunotherapy
Cancer of the prostate
What does this refer to
Causes
Physical or psychologic factors that impairs erection, emission, or ejaculation
Vascular, endocrine, and neurologic disorders
Chronic diseases
Renal failure and diabetes mellitus
Penile diseases and penile trauma
Iatrogenic factors
Surgery and pharmaceuticals
Erectile Dysfunction
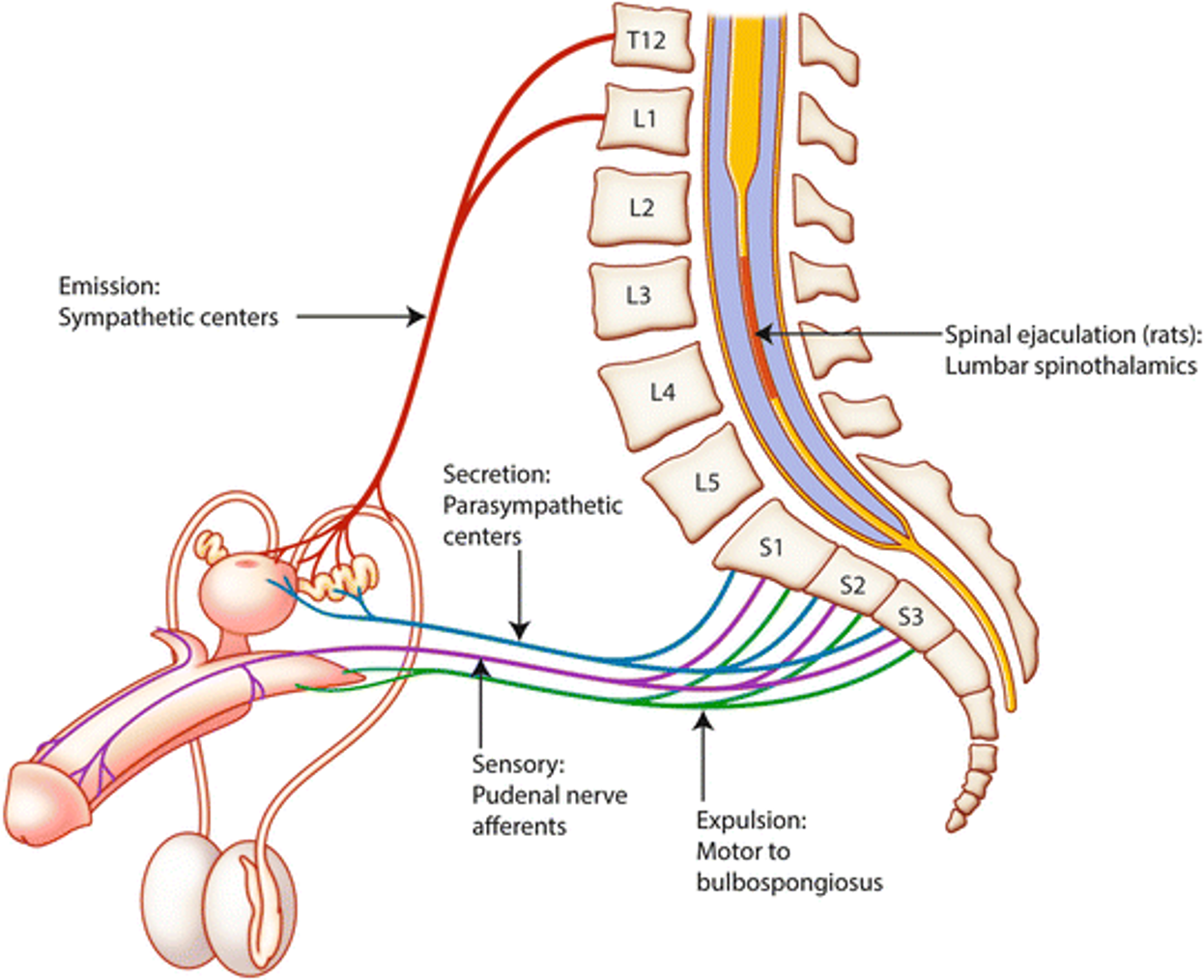
What does this refer to
Vascular disorders
Prevent erection
Endocrine disorders
Reduce testosterone production, which affects sexual function and libido
Neurologic disorders
Interfere with the important sympathetic, parasympathetic, and central nervous (CNS) mechanisms required for erection, emission, and ejaculation.
Chronic diseases
Can lead to erectile dysfunction, impotence, low energy levels, and low libido
Penile trauma
Damages the erectile tissue, disrupts the posterior urethra, and disrupts the pudendal arteries or nerves.
Erectile Dysfunction
What does this refer to
Iatrogenic factors
Certain surgeries can cause erectile dysfunction.
Caused by severing of the small nerve branches that are essential for erection.
Drug-induced sexual dysfunction
Decreased desire
Decreased erectile ability
Decreased ejaculatory ability
Decreased quality and quantity of sperm
Erectile Dysfunction
What does this refer to
Treatment
Nonsurgical interventions
Correct underlying disorders, particularly drug-induced dysfunction and endocrinopathy-related dysfunction (e.g., reduced testosterone associated with chronic renal failure).
Vasodilators and cessation of smoking can benefit individuals with vasculogenic erectile dysfunction.
Surgical interventions
Penile implants, penile revascularization, and the correction of other anatomic defects that contribute to sexual dysfunction
Erectile Dysfunction
What does this refer to
Spermatogenesis requires
Adequate secretion of FSH and LH by the pituitary glands
Sufficient secretion of testosterone by the Leydig cells
Sufficient function of the Sertoli cells, including secretion of androgen-binding protein, growth factors, inhibin B, and a number of other important (but poorly understood) peptides
Adequate spermatogonia
Sexual Dysfunction: Infertility
Sexual Dysfunction: Infertility
Disruptions of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis that reduce testosterone secretion
Testicular trauma or atrophy from any cause
Impaired spermatogenesis (sperm production by the testes)
Sexual Dysfunction: Infertility
Neoplastic disease, cryptorchidism, or any factor that causes testicular temperature to rise
Impaired sperm production
Sexual Dysfunction: Infertility
Chromosomal abnormalities resulting from genetic factors, irradiation, or toxins
Impaired sperm quality
Sexual Dysfunction: Infertility
Unfavorable constituents or characteristics of semen
Impaired sperm motility
What does this refer to
Hormone and growth factors for sperm production
FSH, LH, and testosterone
Androgen-binding protein, inhibin B, other peptides
Sperm count >20 million/mL for fertility
Sperm motility for fertility
Anti–sperm antibodies adversely affect fertility
Decreases sperm motility and number of sperm
Drugs and toxins in the semen adversely affect fertility
Sexual Dysfunction: Infertility
What does this refer to
Overdevelopment of the breast tissue in a man
Results from hormone alterations
Idiopathic and system disorders, drugs, or neoplasms
Estrogen/testosterone ratio altered
Estrogen levels may be excessively high, although testosterone levels are normal.
Testosterone levels may be extremely low although estrogen levels are normal.
Incidence greatest among adolescents and men older than 50 years of age
Gynecomastia
What does this refer to
Breast enlargement consists of hyperplastic stroma and ductal tissue
Treatment
Identification and treatment of the cause are likely to be followed by resolution of the gynecomastia.
Man should be taught to perform breast self-examination.
Examined at 6- and 12-month intervals if the gynecomastia persists
All unilateral breast enlargement in men
Evaluation for malignancy
Workup includes fine-needle aspiration, cytology, mammography, ultrasound, and biopsy.
Gynecomastia
What does this refer to
Most commonly seen after age 60
Different than female breast cancers with Luminal A and Luminal B most common
Symptoms: crusting and nipple discharge
Tends to be advanced by the time of diagnosis
Treatment
Endocrine therapy used more often for males since male tumors are hormone dependent
Modified mastectomy with axillary node dissection
Tamoxifen is standard adjuvant therapy
Chemotherapy
Male breast cancer