Anatomy and Physiology 1 Lab practical 4
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Fibrous joints
Connections between two bones that are held together by fibrous connective tissue
Little to no movement
usually synarthroses or amphiarthroses
examples of fibrous joint
coronal suture
Cartilaginous joints
Hold two bones together by a pad of cartilage
little to no movement
usually synarthroses or amphiarthroses
example of cartilaginous joints
pubic symphysis
synovial joints
contain synovial fluid and allow considerable movement between articulating bones
normally freely movable
diarthrosis
example of synovial joint
bursa of the knee
glenohumeral joint
example of hinge joints
knee joint (tibiofemoral)
elbow joints (ulnohumeral joint)
example of ball and socket joints
hip joints (acetabulofemoral)
shoulder joints (glenohumeral)
Flexion
bending movement that decreases the angle of the joint to bring the articulating bones closer together
angular
Extension
straigtening movement that increases the angle of the joint to straigten the articulating bones
angular
hyperextension
extension of a joint beyond the anatomical position (180 degrees)
angular
plantar flexion
movement of the foot toward the plantar surface (as when standing on toes)
angular
Dorsiflexion
movement of the foot toward the shin (as when walking on the heels)
angular
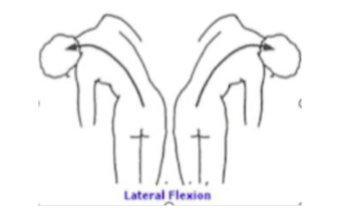
lateral flexion
bending at the waist to one side
angular
abduction
movement away from the midline'
angular
adduction
movement toward the midline
angular
rotation
turning of a structure around its long axis
as in rotating the head to shake the head no
or rotating the arm or the entire body
circular
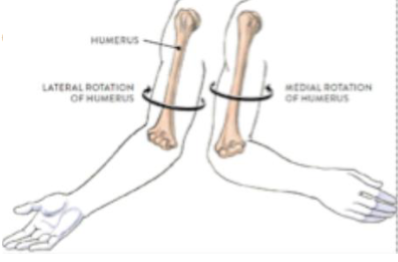
Medial vs lateral rotation
Medial rotation of the humerus with the forearm flexes/brings the hand toward the body
lateral rotation of the humerus brings the hand away from the body
Pronation
rotation of the forearm so that the palm faces posteriorly in relation to anatomical position
circular
supination
rotation of the forearm so that the palm faces anteriorly in relation to anatomical position
circular
elevation
moves a structure superiorly
as in elevation of the scapula
special
Depression
moves a structure inferiorly
as in depression of the scapula
special
lateral excursion
moving the mandible to either the right or the left of the midline
medial excursion
returns the mandible to the midline position
Origin, insertion, and action of temporalis
origin: temporal fossa
insertion: mandibular ramus and coronoid process
action: elevates mandible
O, I, A of sternocleidomastoid muscle
origin: manubrium and clavicle
insertion: mastoid process and superior nuchal line
action: flexes neck
O, I, and A of rectus abdominus
origin: pubic crest and symphysis
insertion: xiphoid process and inferior ribs (5-7)
action: compresses abdomen
O, I, and A of Pectoralis major
origin: clavicle, costal cartilages of ribs 1-6 and sternum
insertion: greater tubercle of the humerus and intertubercular crest
action internally rotates arm
O, I, and A of Latissimus dorsi
origin: ilium, spinous processes of T7-S3, ribs 10-12
insertion: intertubercular groove of humerus
action: internallly (medially) rotates arm
O, I, and A of Biceps brachii
Origin:
long head: glenoid fossa
short head: coracoid process of scapula
Insertion: radial tuberosity
Action: flexes elbow
O, I, A of triceps brachii
Origin:
long head: infraglenoid tubercle of scapula
lateral and medial head: humerus
insertion: olecranon process of ulna
Action: extends elbow
O, I, A of deltoid
origin: clavicle, acromion process, and scapular spine
insertion: deltoid tuberosity of humerus
action: abducts arm
O, I, A of Extensor digitorum
origin: lateral epicondyle of the humerus
insertion: 4 tendons and distal phalanges of fingers 2-5
action: extends digits 2-5 at MCP joint and wrist
O, I, A of Flexor digitorum superficialis
origin: medial epicondyle of humerus, coronoid process of ulna, radius
Insertion: 4 tendons that divide and attach to the sides of the medial phalanges of fingers 2-5
Action: flexes wrist
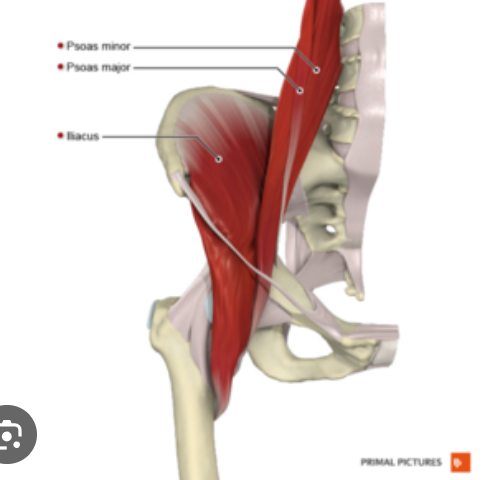
O, I, A of Iliopsoas
Origin:
Iliacus: ilium
psoas major & minor: intervertebral cartilages, along bodies and transverse processes of L1-L5, body of T12, sacrum
Insertion
Iliacus: lesser trochanter of femur and shaft
psoas major and psoas minor: pectinal line and iliopectineal eminence of ilium
action: flexion of hip
O, I, A of Gluteus Maximus
Origin: iliac crest, sacrum, coccyx, and lumbar fascia
Insertion: greater trochanter of femur, gluteal tuberosity of femur
action: extension of hip
O, I, and A of Rectus femoris
Origin: iliac spine and acetabulum
Insertion: patella
action: extension of knee
O, I, A of biceps femoris
origin:
long head: iscial tuberosity of coxal bone
short head: linea aspera and lateral condyle of femur
insertion: lateral condyle of tibia and head of fibula
action: extension of hip, flexes knee
O, I, A of gastrocnemius
Origin:
Medial head: medial condyle of femur
lateral head: lateral condyle of femur
insertion: calcaneus via calcaneal tendon
action: plantar flexion of ankle
O, I, A of Tibialis anterior
Origin: Tibia
insertion: medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bone
action: inversion of the foot
O, I, A of suprapsinatus
Origin: supraspinous fossa of the scapula
Insertion: greater tubercle of the humerus
Action: stabilizes GHJ
O, I, A of Infraspinatus
Origin: infraspinous fossa of the scapula
Insertion: greater tubercle of the humerus
action: Stabilizes GHJ
O, I, A of Teres minor
Origin: lateral border of the scapula
Insertion: greater tubercle of the humerus
action: stabilizes GHJ
O, I, A of subscapularis
origin: subscapular fossa of scapula
insertion:: lesser tubercle of humerus
action: stabilizes GHJ
Iliopsoas
pectoralis major
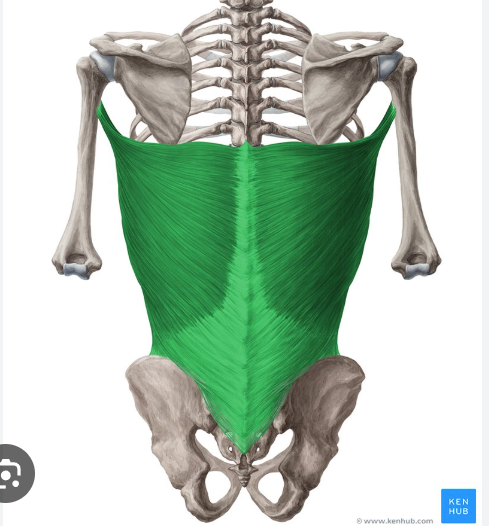
latissimus dorsi
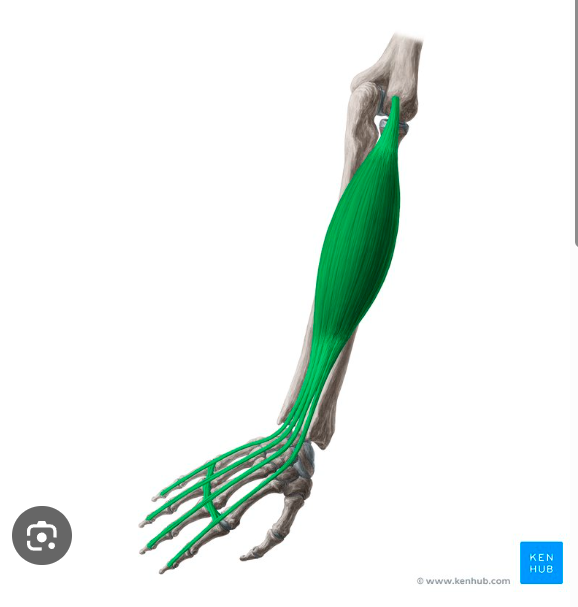
extensor digitorum
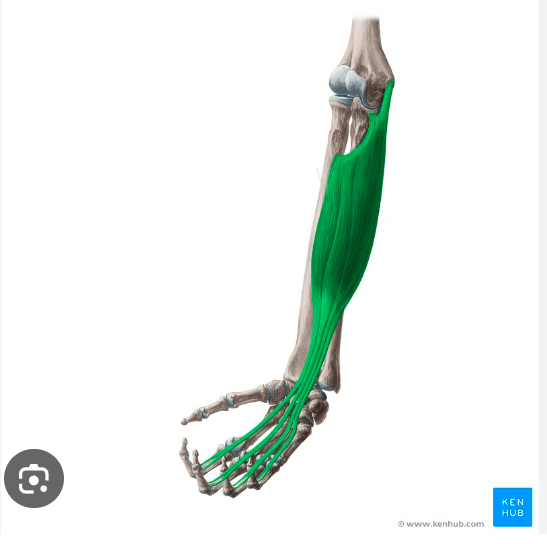
flexor digitorum superficialis
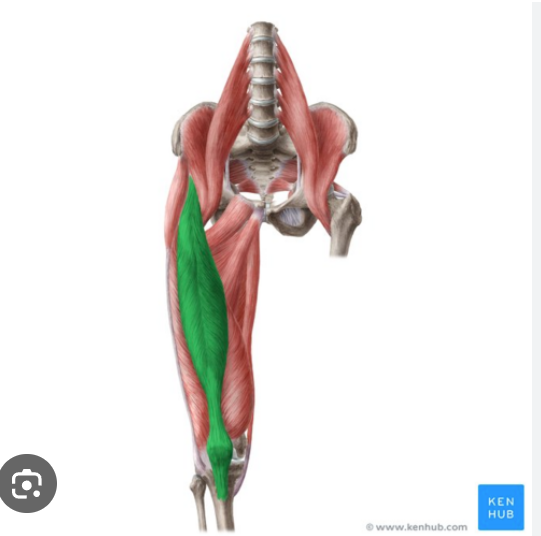
rectus femoris
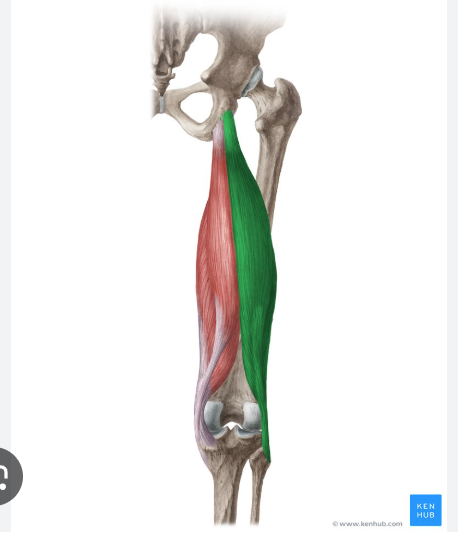
biceps femoris
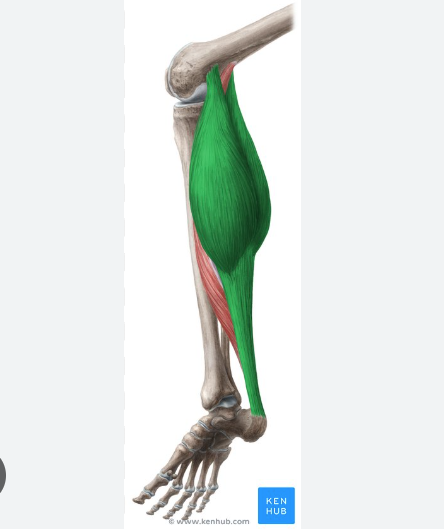
gastrocnemius
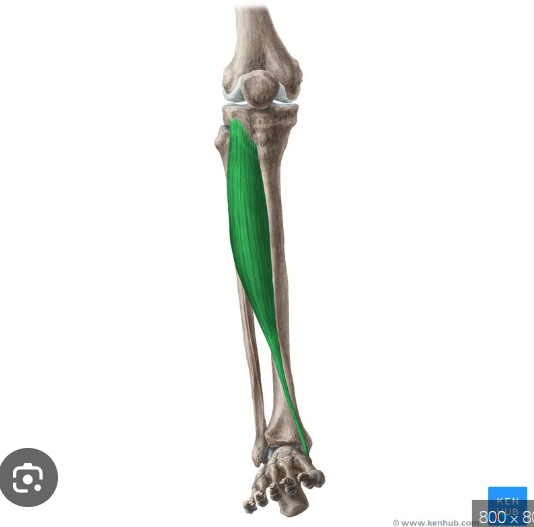
tibialis anterior
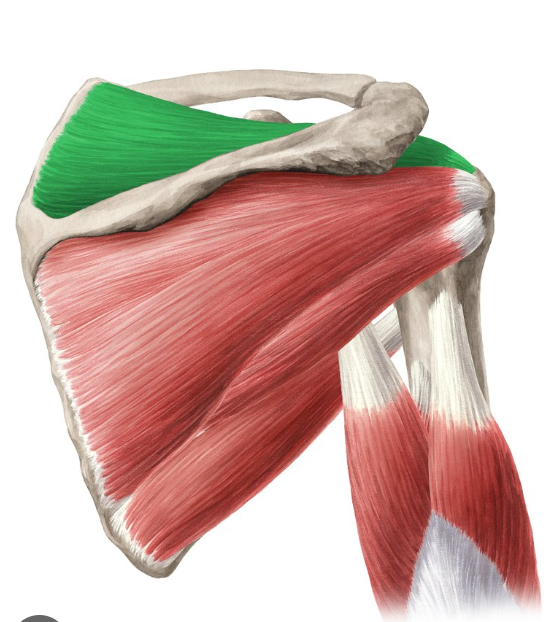
supraspinatus
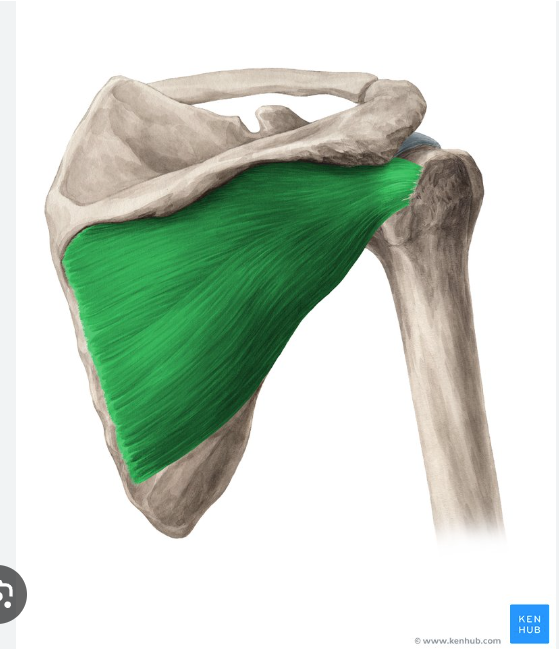
infraspinatus
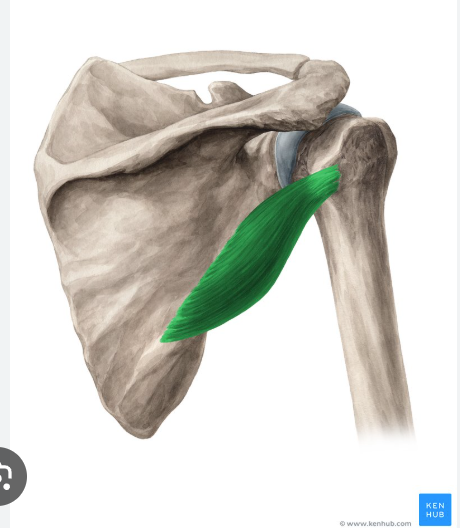
Teres minor
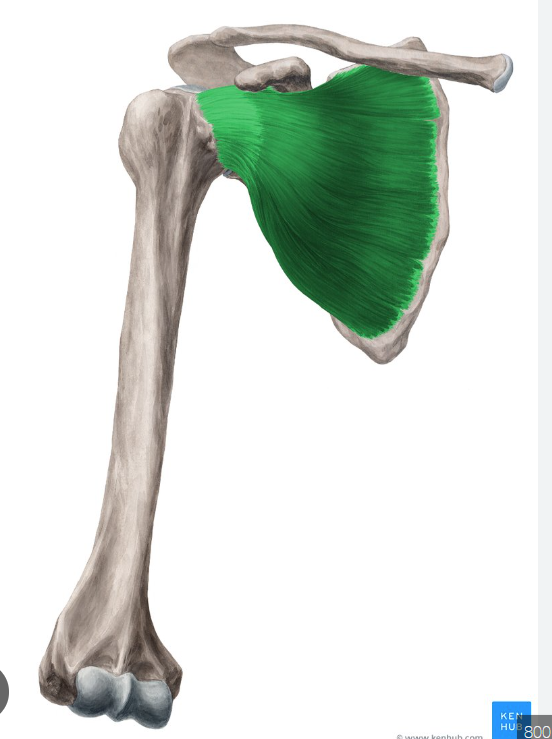
subscapularis