BPK 207 Lec 2 Methods to Study Motor Behaviour
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
2 categories of performance measures
performance outcome measures (motor skills)
performance production measures (movement components)
list 2 examples of performance measures
time to complete a task - ex: time to run a mile
reaction time - ex: time between the gun and the runner’s beginning of movement
list 2 examples of performance production measures
displacement, velocity, joint angle, EEG
for joint angle - ex: angle of each joint in the arm when hitting ball
3 common ways to assess movement
movement error/accuracy
movement magnitude
movement time and speed
ways to quantify movement error/accuracy (3)
constant error (CE)
variable error (VE)
root mean square error (RMSE)
constant error (CE)
amount of direction of deviation from target
not equal to variability of error
variable error
the variability in the movement outcomes/scores
the standard deviation of the CE
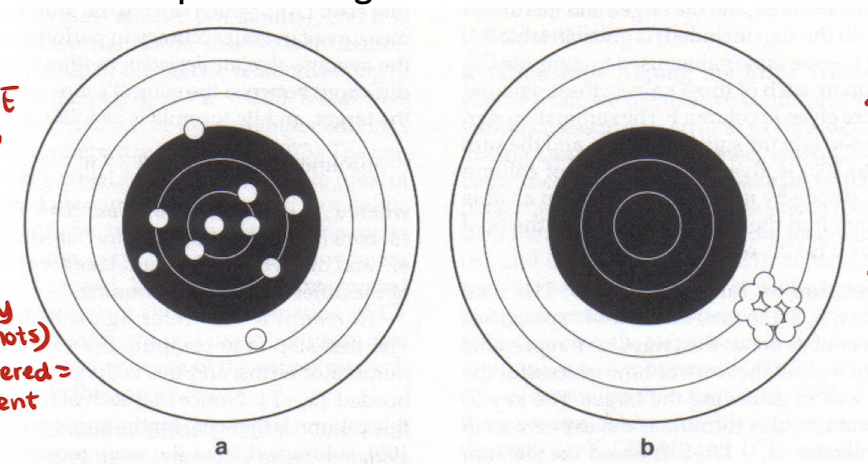
describe the CE and VE for these diagrams
CE is small because most of the shots are within the black circle, which is the target. VE is large because the shots are very scattered among one another.
CE is large because the shots are far away from the target (black circle). VE is small because the shots are located very close to one another.
CE and VE provide what info to a coach
to correct CE, athlete needs to shift their position, thereby improving performance. VE harder to correct.
CE and VE are primarily for ___ skills
discrete (clear start and end)
root mean square error (RMSE)
overall error or spread of the movement across the duration of the performance.
used for continuous skills (no distinct beginning or end)
ways to quantify movement magnitude
root mean square
also many ways to quanity movement magnitude, like the distance a limb travels during a movement, the peak to peak differences in a signal, area under a curve, etc.
root mean square (RMS)
magnitude of the set of data across time
NOT SAME AS RMSE
why use RMS
detects the magnitude of a sine wave oscillating around zero when an average would give us a value of 0
ways to qualitfy movement time and speed
for reaction time paradigms:
Reaction time (RT)
simple -RT tasks
choice- RT tasks
movement time (MT)
Response time
reaction time
time between onset of a stimulus and onset/beginning of a response.
NOT same as Response Time
onset of movement or muscle activity
simple RT tasks
only one response choice available
choice RT tasks
multiple response choices available and/or multiple stimuli presented.
movement time (MT)
time between initiation of a response to completion of the movement
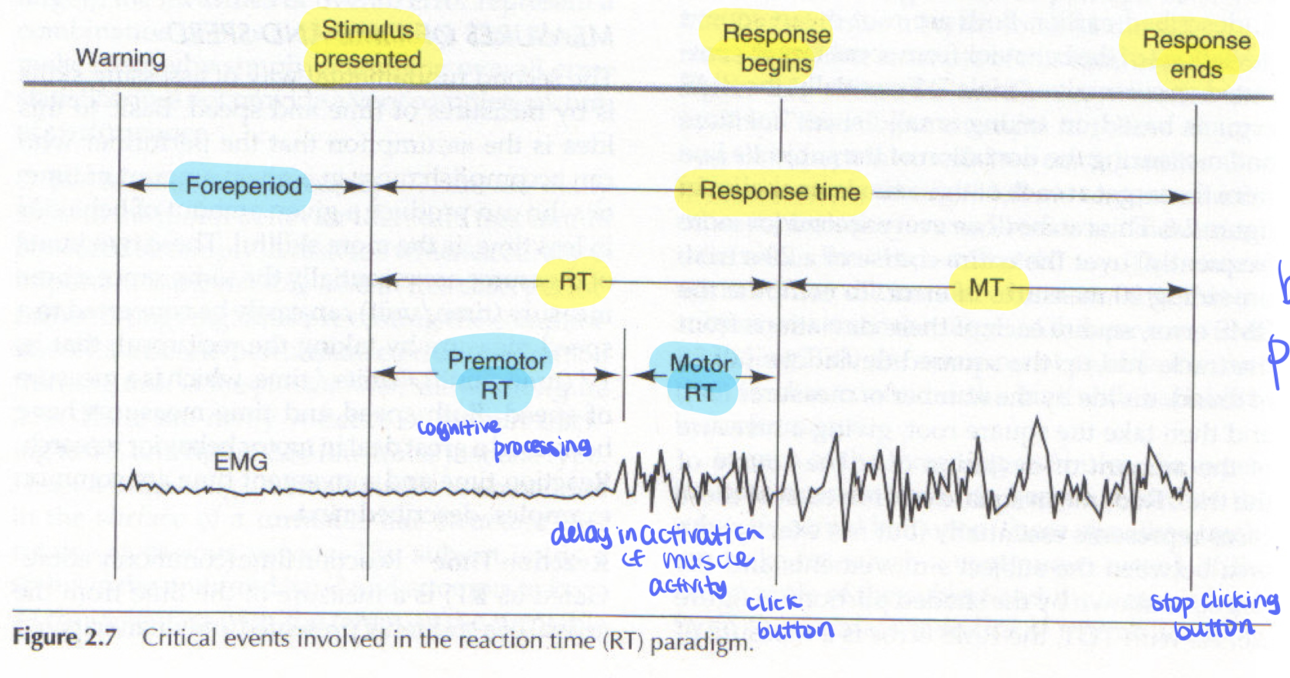
response time
sum of Reaction time (RT) and movement time (MT)
from the onset of stimulus and completion of response
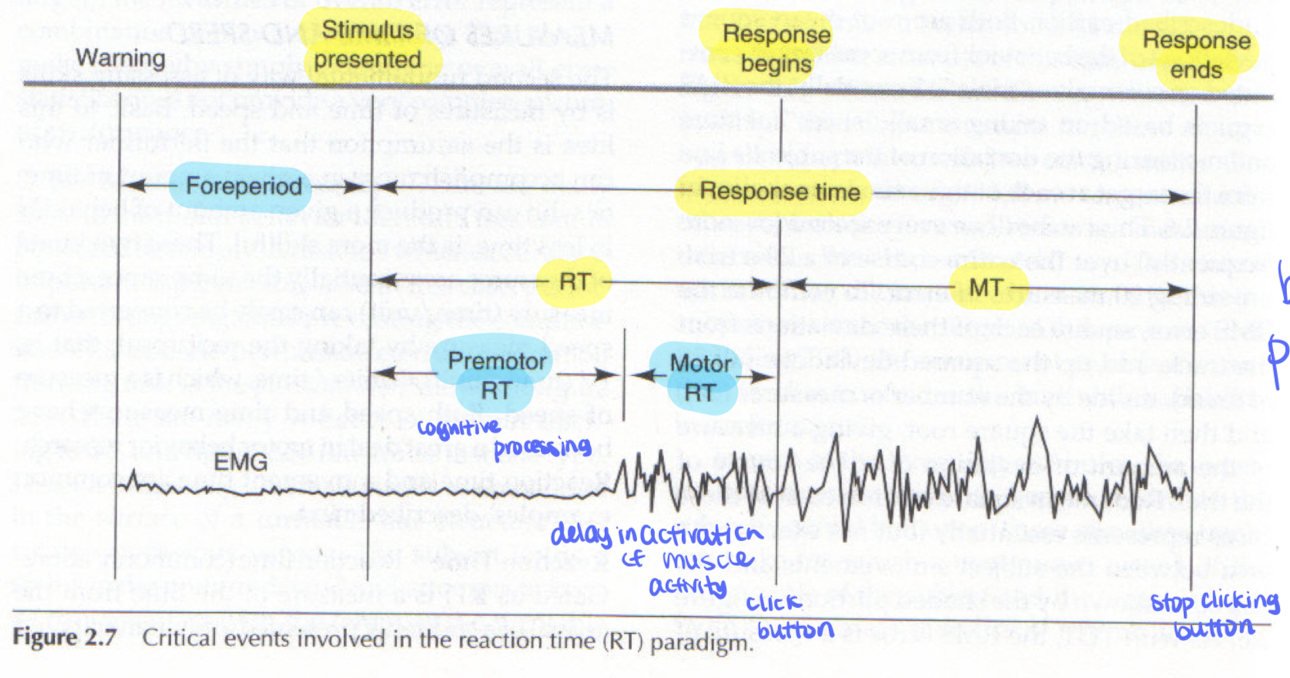
premotor RT
time for central processing (perception of stimulus and decision making)
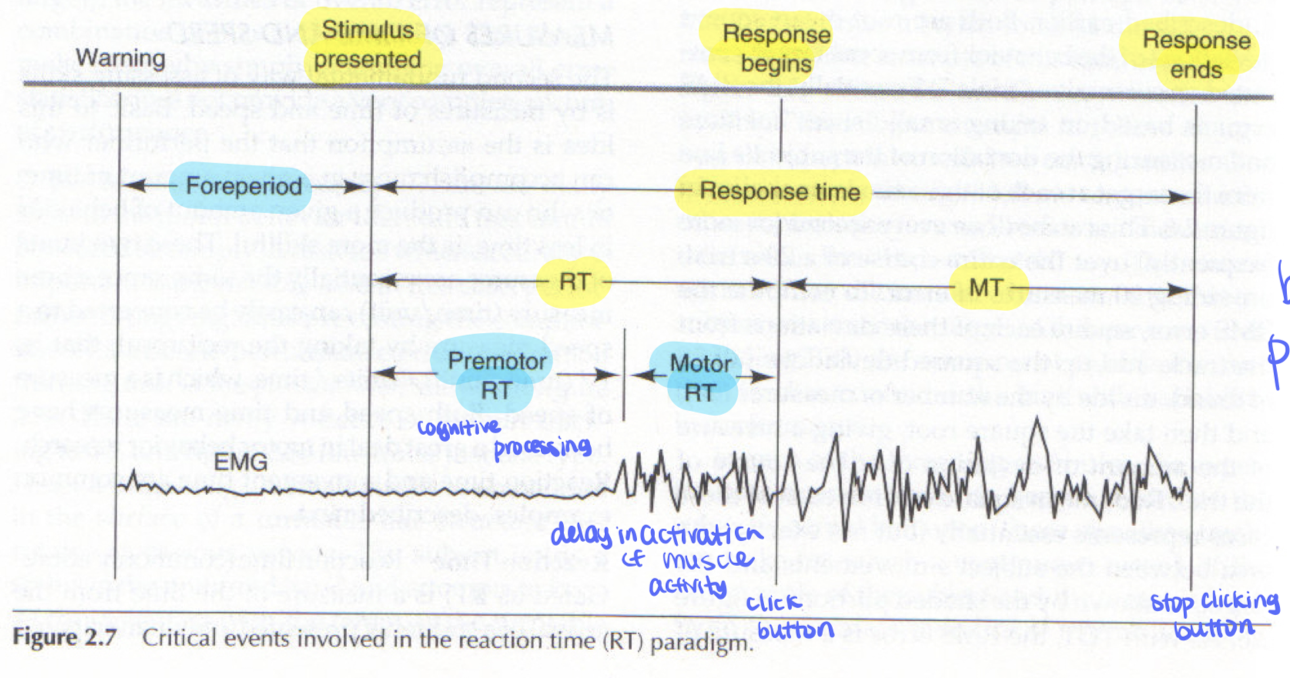
foreperiod
between when warning is made and onset of stimulus.
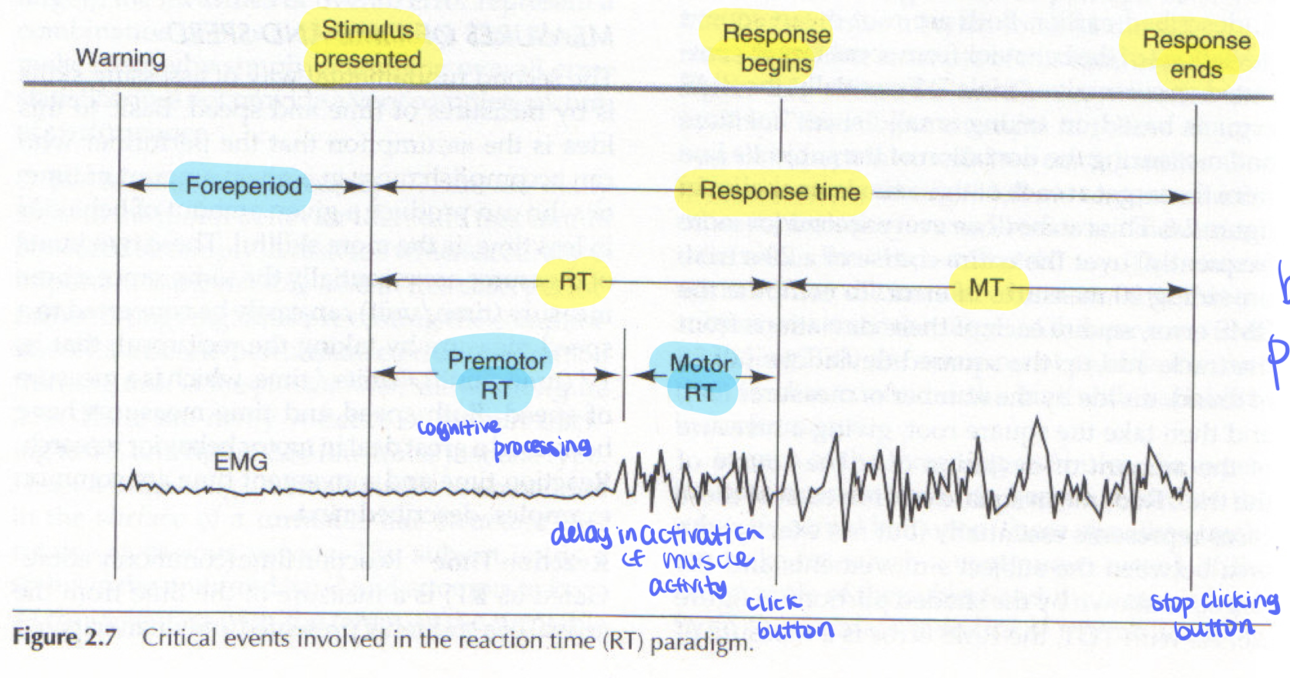
Motor RT
delay in onset of muscle activity or movement
types of equipment for studying movement
force plates
motion capture pictures
electromyography (EMG)
eye tracking
neuroimaging, neurostimulation, and neural recording equipment
force plates
embedded on a ground surface or on a moveable platform; measure kinetic data (forces that cause movement'/ physical properties of motion)
motion capture cameras
measure kinematic data (displacement, velocity during a movements)
electromyogrpahy (EMG)
record muscle electrical activity
eye tracking
head mounted systems that monitor eye movements
neuroimaging, neurostimulation, and and neural recording equipment
study NS activity and function related to movement
equipment vs technique
equipment= records activity
techniqye = manipulation of activity (ex: stimulus applied to brain to alter brain activity)
→ can be invasive/involve breaking of skin
force plates determine
how hard or fast a person loads a surface. also measures the COP.
COP (for force plates)
weighted average of all downward forces acting on the force plate
COP measures
postural sway
posturography
assesses standing balance usually with a force plate
computerized dynamic posturography (CDP)
platform with an embedded force plate and visual surround, Used for the sensory organization test (SOT). the force plate and the visual surround can move, which is manipulated to create conflicting sensory information
sensory organization test (SOT)
surround sway referenced
support sway referenced
surround sway referenced
visual surround moves in direct proportion to person’s away
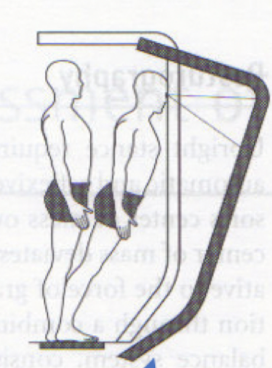
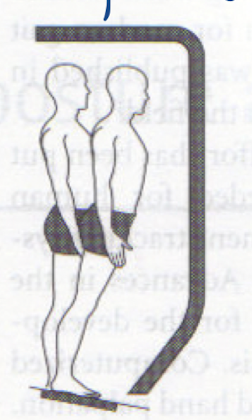
describe the states for the visual, vestibular, and somatosensory system in this image
visual system detects no optic flow = not moving.
vestibular system detects head acceleration = moving
somatosensory detects change in muscle length, cutaneous receptors, joint receptors = moving
support sway referenced
force plate moves in direction proportion to person’s sway
describe the states of the visual, vestibular, and somtosensory systems
visual system detects optic flow = you are moving
vestibular system detects head acceleraton = you are moving
somatosensory system detects no change in muscle length, joint receptors, cutaneous receptors = not moving
when blindfolded, does the visual system determining if your moving or not moving
when visual system gone, it does not contribute to perception of movement.
motion capture cameras function
equipment that records kinematic data independent from the forces that caused the movement. Includes displacement, velocity, acceleration.
motion capture equipment purpose in reality
quantify movement for designing videogames and making movies
goniometers vs accelerometers
goniometers: record kinematic data, measure joint angles
accelerometers: record kinematic data, measure body/limb acceleration
electromyography function specifics
record electrical activity of muscles. electrode inserted into individual muscles and on skin above muscles
Head mounting eye tracking
equipment to record eye movements. Various different eye trackers, such as tracking path of gaze
Microneurography
technique that records the electrical activity of a single neuron’s axon within a nerve. Thin electrode embedded through skin, into nerve, and into nerve fascicles, where the electrode tip is on 1 or more axon sheaths of a neuron’s axon. The receptive field of the neuron is stimulated with a vibration.
applied to peripheral nerves
manipulate activity via vibration stimulus
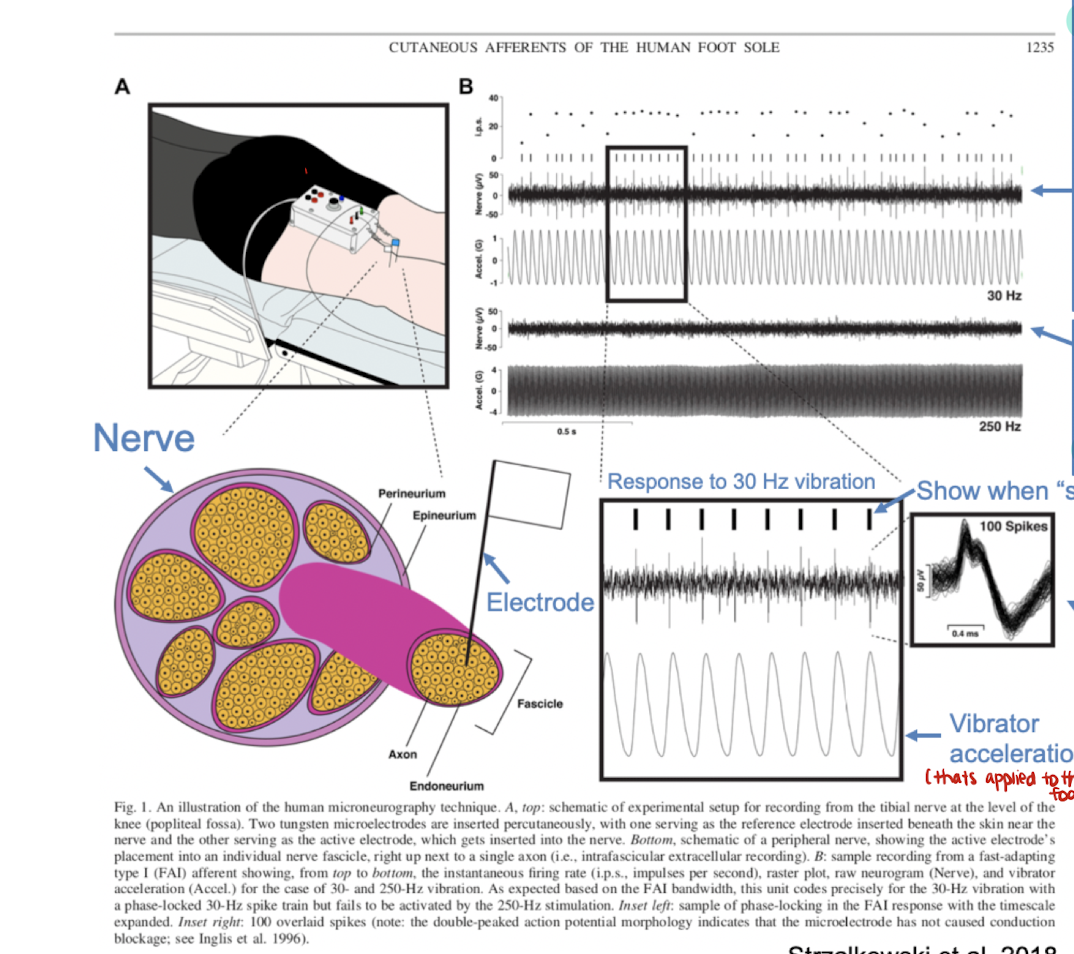
describe this image
the electrical activity of a receptor when 30Hz vibration is applied to the foot. the receptor at row 2 encodes this frequency of 30Hz because (a) the spikes or action potentials occur at the same time with the peaks of the vibration stimulus, and (b) the spikes are the same shape, so the activity is from one neuron.
The receptor at row 4 does not encode at this frequency. The spikes of the receptor are inconsistent with the peaks of the vibration stimulus.
single neuron recording
extracellular recording (measures electrical activity outside the cell membrane) where an electrode is in the brain within 50 to 150 micrometres away from the neurons and requires cell sorting.
applied to cortical neurons
manipulates activity (similar technique to microneurography)
describe other forms of neuronal recording
awake behaving vs anesthetized recording and stimulation
awake studies examine how behaviour related to brain
both microneurography and single neuron recording use similar ____ techniques
cell sorting: microelectrode recording electrical activity of all cells witin 100 micrometers. Of the many neurons near the microelectrode, only a few of the neuron’s signals are strong enough to be isolated and studied as individual neurons. Typically the action potentials of the neurons align with some event.
all or none action potential meaning
action potentials all have the same shape and amplitude. Only the frequency and timing of action potentials is encoded.
labelled line concept
NS knows what info each neuron carries and what their firing pattern means.
T/F baseline frequency means smt
F. baseline frequency does not matter until theres a change in the baseline frequency of the neuron
electrical microstimulation
electrodes emit electrical current to neurons, artificially stimulating action potentials, which activate other neurons via neuron circuitry.
electrical microstimulation on the motor cortex
artificially stimulates muscle activity from different muscles depending on the region of the cortex.
stimulation vs recording
neural recording: provides info about neural function but doesnt alter it
electrical stimulation: uses electrodes to manipulate neural acticity
T/F stimulation is invasive, recording is not
neural stimulation and recording is invasive
neuroimaging is invasive, and manipulates activity
F. it is not invasive and records brain activity
name 3 neuroimaging technologies
functional MRI
MEG
EEG
T/F neuroimaging has high spatial resolution
low spatial resolution; records activity from many neurons
functional fMRI
measures local change in blood flow caused by brain activity
expensive
MEG
measures weak magnetic fields generated by brain’s electrical activity
cheaper than FMRI
EEG
electrodes placed on scalp that record electrical activity of brain
noninvasive neurostimulation techniques definition
study brain function of specific regions via enhancing, activating, or disrupting brain activity
list noninvasive neurostimulation techniques (2)
transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
Transcranial electrical stimulation (tES)
transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
technique where a stimulation coil is placed on head and generates a magnetic field that induces an electrical current in the brain, activating the axons of neurons
coil’s center has the strongest stimulation
describe TMS when stimulation coil over the hand region of the motor cortex
the stimulation coil generates a motor evoked potential (MEP)/activation of muscles in the hand, recorded by EMG. MEP is the electrical activity of the muscles.
TMS used to (5)
map connectivity of the cortex
map motor excitability of cortex
cause virtual lesions to study function of a region
assess the plasticity and recovery of function
rehabilitation of motor function
map connectivity in cortex
what TMS can be used for
stimulate a region see what other regions activated
map motor excitability in cortex
what TMS can be used for
excitability of motor map quantified by size of the motor evoked potential (MEP)
cause virtual lesions to study regional function
whatTMS can be used for
certain stimulation parameter can temporarily disrupt brain activity, like a stroke. Can test how this disruption affects specific tasks.
assess plasticity and recovery of function
what TMS can be used for
assessed via size of MEP
rehabilitation of motor function
what TMS can be used for
through repetitive stimulation, can help activate a brain a brain region so that its more plastic (more likely to recover after injury)
tES
transcranial electrical stimulation.
2 or more electrodes placed onto scalp to conduct electrical current in the brain
changes the membrane potential of neurons in the brain
TMS vs tES
TMS activates the axons of neurons.
tES changes the membrane potential or threshold of a neuron. does not directly activate cortical neurons
types of tES (3)
transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS)
transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS)
transcranial random noise stimulation (tRNS)
types of tES based on
differences in stimulation parameters (polarity/ the direction of current)
tDS polarity
tDS: polarity/direction of current doesnt change between electrodes
tACS
tACS: polarity/direction of current alternates like a wave between electrodes.
tRNS
tRNS: polarity/direction of current alternates.
describe the electrodes used in tES
anode electrode - current enters brain from anode
cathode electrode - current exits brain to cathode
anodal stimulation/cathodal stimulation - placed over brain area trying to modify
effect of tDS last up to ___
90 min depending on stimulation parameters and brain area.