(UNIT 5) Chapter 15 - The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Why choose fruit flies?
Prolific breeders (single mating will produce hundreds of offspring)
New generation can be bred every two weeks
Only have four pair of chromosomes (easily distinguishable, three pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes)
Same sex chromosomes to humans
Wild vs Mutant Types
Wild Type: The most commonly observed phenotype.
Mutant Type: Less common phenotypes, due to alleles assumed to have originated as changes or mutations in the wild type allele.
How do sex-linked traits work?
A trait is passed on from its X or Y chromosome. If it’s X-linked the male will either have or not have the trait they cannot be carriers as they only need one X chromosome (XY). While, a female who has two X chromosomes needs two recessive X-linked alleles to display the trait and can be carriers.
Xr | Y | |
XR | XRXr | XRY |
Xr | XRXr | XrY |
When are genes linked and not?
Genes that are close together on a single chromosome are linked and do not assort independently (likely to be inherited together). Example: Sex-linked genes.
Genes that are on different chromosomes or far from each other are not linked.
X and Y Chromosomes (In mammals & humans)
Mammals have two types of sex chromosomes, designated X and Y. The Y chromosome is much smaller than the X chromosome. (XX is female, XY is male).
Short segments at either end of the Y chromosome are the only regions that are homologous with regions on the X.
The egg carries only X chromosomes while a sperm can carry a X or Y chromosome.
How are sex characteristics formed?
WNT4: A gene on chromosome 1 encodes a protein that promotes ovary development.The signs of sex emerge when the embryo is about 2 months old.
Sex is determined by the interactions of a network of gene products and is much more complicated than simple sex chromosomes. (Certain chromosomes other than the sex chromosomes can be involved with producing “sex” characteristics.)
Sex-linked genes + Types
Sex-linked gene: A gene located on either sex chromosome.
X-linked genes: The genes on the X chromosome.
Y-linked genes: The genes on the Y chromosome.
There are little Y-linked genes so fathers often do not pass disorders to their sons.
SRY: A gene on the Y chromosome (sex-determoining region of Y) is required for the development of testes. (In the absence it develops ovaries).
How are X-linked alleles passed?
Fathers pass X-linked alleles to all of their daughters but none to their sons while mothers can pass X-linked alleles to both sons and daughters.
X Inactivation in Female Mammals
One of the X chromosomes in each cell in female mammals become inactivated during early embryonic development so the cells of females and males have the same effective copy of most X-linked genes.
Barr Body: The inactive X condenses into this compact object. Lies along the inside of the nuclear envelope. Most genes on it are not expressed, however in the ovaries the Barr body chromosomes are reactivated in the cells that give rise to eggs, resulting in every female gamete having an active X after meiosis.
The selection of which X chromosome will form the Barr body occurs randomly and independently in each cell. Females consist of a mosaic of the two types of cells: ones with active X from the father and ones with active X from the mother. (The phenotype will be like codominance.)
Thus if a female is heterozygous for a sex-linked trait, about half of her cells will express one allele,while the others will express the other.
Linked Genes
Genes located near each other on the same chromosome that tend to be inherited together in genetic crosses.
Parental vs Recombinant types types
Parental types: Offspring that have the same combinations of phenotypes as their parents.
Recombinant types (recombinants): Offspring that have new combinations of phenotypes.
You say [number]% frequency of recombination.
What causes recombination of unlinked and linked genes?
The basis of recombination between unlinked genes is the random orientation of homologous chromosomes at metaphase 1 of meiosis, which leads to the independent assortment of the two unlinked genes.
Production of a small number of offspring with nonparental phenotypes (recombinants) between linked genes is due to crossing over.
Random fertilization increases even further the number of variant allele combinations that can be created.
Recombination Equation
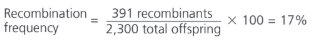
Genetic (Linkage) Map
Genetic map: An ordered list of the genetic loci along a particular chromosome.
The percentage of recombinant offspring depends on the distance between genes on a chromosome.
The farther apart the two genes are, the higher the probability that a crossover will occur between them (higher recombination frequency.)
The greater the distance between two genes, the more points there are between them where crossing over can occur.
Linkage Map: A genetic map based on recombination frequencies. (Protays the order of genes along a chromosome but not the precise locations.)
Map Units: Units used to express the distances between genes. One map unit = 1% recombination frequency.
The observed frequency of recombination in crosses involving two genes can have a maximum value of 50%, meaning it is certain a crossover will occur. (Unlinked genes.)