Test 1 revision
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Operating System
A program that acts as an intermediary between the user of a computer and the computer hardware
Provides an environment in which a user can execute programs in a convenient and efficient manner
Performs no useful functions by itself.
Application Software
Allows the user to perform some intended task, function or activity and includes productivity tools
System Software
Provides an interface with hardware and serves as a platform for running programs and maintaining the efficiency of the system. Can be divided into operating systems and utility programs.
Resource
Anything that is needed for an executing program to run.
E.g.:
Memory
Space on disk
CPU
Resource Abstraction
The process of hiding the tasks needed to manage and use resources
Allows user programs to use resources via simpler commands.
Types of Resource Sharing
Space-multiplexed sharing
Time-multiplexed sharing
Space-multiplexed sharing
A method for sharing where the resource is divided into >= 2 distinct units, with each unit being allocated to different processes
Time-multiplexed sharing
A method of sharing where the entire resource is allocated to a process for a period of time, after which it is then allocated to another process and so on.
Preferred in cases where users interact with the computer at different points during the execution of the program.
Multiprogramming
A technique for sharing the CPU among runnable processes
Accomplishes CPU sharing automatically
OS Strategies
Used to provide OS services and refers to the general characteristics of the programmer’s abstract machine.
Batch processing
Timesharing
Personal computers and workstations
Others
Process control and real-time
Network
Distributed
Small computers
Batch Processing
Uses multiprogramming
Job prepared offline
Batch of jobs given to OS at one time
OS processes jobs one after the other
No human-computer interaction
OS optimizes resource utilization
Preferred when executing a collection of programs where humans do not interact with the program when it executes. It is important to maximize the utilization of the system’s resources.
Timesharing Systems
Uses multiprogramming
Support interactive computing model
Tends to propagate processes
Considerable attention to resource isolation
Tend to optimize response time
OS Services
Provides convenience
UI
Program execution
I/O operations
File-system manipulation
Communicationss
Error detection
Ensures efficient operations of the system
Resource allocation
Accounting
Protection and security
Functions of an OS
Device management
Process, thread and resource management
Memory management
File management
Device Management
Refers to the way generic devices and handled
Includes disk, tapes, terminals, printers, etc…
Special management approaches for processor and memory
Partitioning design simplifies adding and upgrading of devices
Process, Thread and Resource Management
Creates abstractions of processes, threads, and resources
Allocates processor resources equitably
Allocates and tracks abstract resources such as queues, semaphores, and messages
Cooperates with the memory manager to administer the primary memory
Memory Management
Administers and allocates primary memory
Enforces resource isolation
Enables sharing between processes
Provides virtual memory extensions
File Management
Creates abstractions of storage devices i.e. I/O operations
Range from byte stream files to indexed records
Local and Remote file systems
OS Requirements
Time/space-multiplexing
Exclusive use of a resource
Isolation
Managed sharing
Implementation mechanisms
Processor modes
Kernels
Method of invoking system service
Processor Modes
Distinguishes between trusted and untrusted software
Determines execution capability and accessible memory areas
2 modes:
Supervisor
User
Supervisor Processor Mode
Can execute all instructions, including privileged/protected instructions.
I/O, Memory related instructions, Processor mode-change instructions
Can access all memory locations, including System and User space.
User Processor Mode
Can only execute non-privileged instructions
Can only access memory area used by application processes (User space)
Kernels
Part of the OS that is critical to correct operation
Implements the basic mechanisms that assure secure operation of the entire OS
Executes in supervisor mode
Program
File of instructions (Source file)
High level programming language
e.g. C, Java, Python
Low level programming language
e.g. assembly language (processor specific)
Machine language (processor specific)
Von Neumann Architecture
Forms the basis for almost all modern computer systems.
Most other specialized systems evolved from this
architecture.
Has a fixed set of electronic parts, which can be
manipulated to perform various tasks determined by a
variable program.
Consists of the following parts:
A central processing unit (CPU)
A primary memory unit
A collection of I/O Devices
Buses to interconnect the components
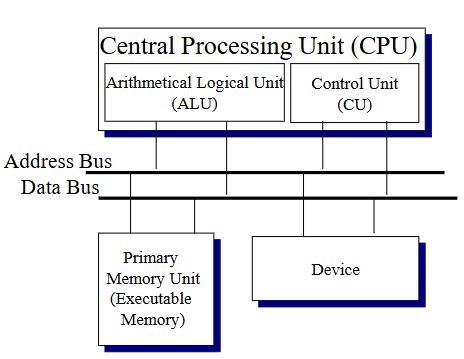
Central Processing Unit
The brain of the computer
Made up of
Arithmetical-Logical Unit
Control Unit
ALU
Can be thought of as a very fast calculator.
Can perform various arithmetic and logical operations
Typically has 32 to 64 registers
Comprises of
Functional Unit
Performs operations
Registers
Control Unit
Causes a sequence of instructions stored in the
memory to be retrieved and executed.
Comprises
Fetch Unit – Fetches an instruction from memory.
Decode Unit – Decode an instruction.
Execute Unit – Signal ALU to execute instruction.
Instruction Register (IR) - Contains a copy of the
current instruction.
Program Counter register (PC) - Contains the memory
address of the next instruction the unit is to load.
Works based on fetch-execute cycle
Control Unit Operation
When the computer is powered up, the control
unit begins to execute the fetch-execute cycle
until the computer is shut down.
Fetch phase
Instruction retrieved from memory at location specified by Program Counter (PC)
Loaded into Instruction Register (IR)
PC is incremented
Execute phase
ALU operation
Cause memory data reference, I/O operation
Primary Memory Unit
Stores both programs and data while they are being operated on by the CPU
Interface between CPU and memory consists of 3 registers:
Memory address register MAR
Stores address of data to be read from or written to
Memory data register MDR
Stores data that is read or to be written
Command register CMD
Stores the command to be executed
Stores programs and data in binary format
Often referred to as random access memory (RAM)
I/O Devices
Each device operation is controlled by a device
controller
Device controller connects device to the
computer’s address and data bus
Provides an interface which the OS (Device
manager) can use to manipulate device
Interfaces varies among controllers
OS provides abstraction to hide differences from
programmer
Device-Controller-Software Relationship
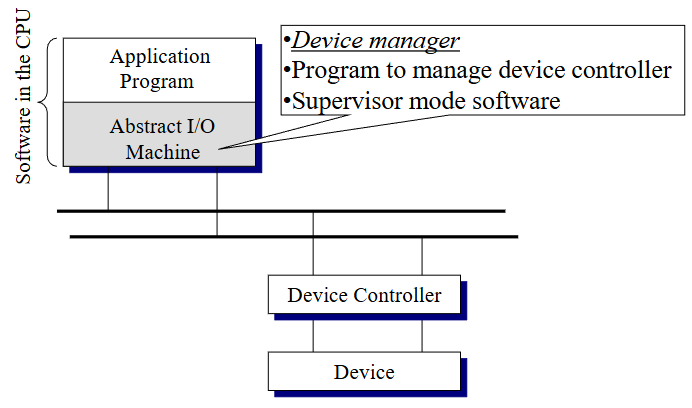
Device Controller Interface
Device may need constant attention/monitoring
during operation
Device controller does this with mainly hardware
algorithms
Software interface (device driver) provided by
controller allows OS to operate and synchronize
its behavior with the device operation
Device controller include the following as part of
the interface
Data registers
Command registers
Status flags with includes done, busy and error code
Polling/Interrupt
Notifies the CPU when I/O is done
Polling
Device implements the status of the device as a flag
If the I/O is not done, the CPU executes a busy-wait command to wait for the I/O to end, but the CPU is effectively waiting and doing nothing.
Wastes precious processor cycles
Interrupt
When device I/O is done, the device sets a flag to signal the end of IO
The CPU on its fetch cycle, would detect the flag and proceed to execute a set of routines to service the IO.
Direct Memory Access (DMA)
Able to read/write data from/to memory without CPU intervention
Functions like a mini CPU, which is able to perform the tasks that the CPU would otherwise have to perform
Can work in parallel with the CPU to significantly increase the machine’s I/O performance.
Device manager
Manages the collection of device drivers, which works devices
Enables the OS to provides a standard set of system calls to application programs, which use the devices.
Device Status Table
Used by the Device Manager to keep track of the status of the various devices
Consists of information of:
Device ID
Device Status
Queue of processes waiting for the device
Buffering
A temporary memory-based storage area that stores the data from an I/O operation
Types of Buffering
Input
Output
Hardware
Double
Circular
Randomly Accessed Storage Devices
Allows a driver to access block of data in the device in any order.
Non-volatile memory also falls into this category
Role of the Operating System
Allows other programs/software to be run, and handles system processes/services
3 main registers
Memory Address Register (MAR)
Memory Data Register (MDR)
Command Register (CR)