Topic 2: Kinematics of Particles
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
a = dv/dt
what is the equation to calculate non-constant acceleration
v dv = a ds
what is the equation to calculate acceleration as a function of displacement
v = ds/dt
what is the equation to calculate non-constant velocity
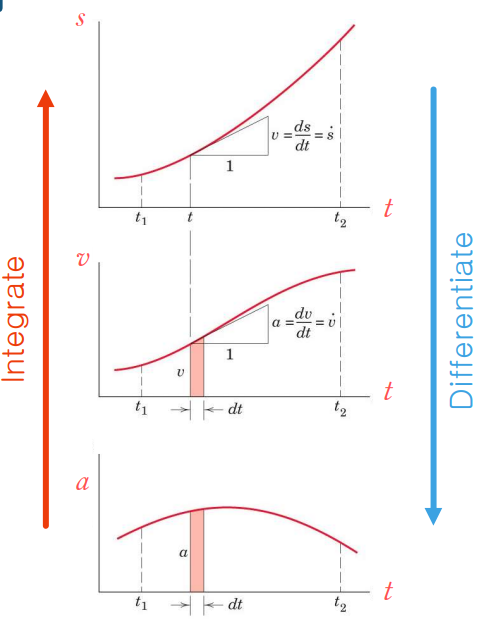
velocity is the slope of the s-t curve
acceleration is the slope of the v-t curve
when v=0, s(t) is at a turning point
when a=0, v(t) is at a turning point
describe the key points of the displacement-time, velocity-time, and acceleration-time graph
identify provided information and what is required
sketch the motion and identify points of interest
choose a coordinate system, the origin will determine displacement
construct the kinematic conditions table for each axis of motion
for each interval, identify the type of acceleration and choose the appropriate equation(s) to use
solve the equations for the required information
check that your answers make sense
what are the steps to be taken when solving kinematics of particles problems
the direction of the travel tangential to the path
in what direction does the velocity vector point
the magnitude of v changing
acceleration is tangential to path → responsible for change in speed
the direction of v changing
acceleration is normal to the point → responsible for change in velocity
what causes the acceleration vector to arise
0
what is the value of acceleration in the x-direction for an object in projectile motion
-9.81 m/s²
what is the value of acceleration in the y-direction for an object in projectile motion
no drag force/motion
no buoyancy force
no aerodynamic force
object acts as a particle
mass of object is constant
what are the assumptions made for an object in projectile motion
an acts towards the centre of the circle
at acts tangent to the circle
in what direction do the normal and tangential components of acceleration act
ω = dθ/dt
what is the equation to calculate angular velocity
α = dω/dt
what is the equation to calculate angular velocity
v = rω
what is the equation to calculate the velocity of an object in circular motion
an = rω2 = v2/r
what is the equation to calculate the normal acceleration of an object in circular motion
at = rα
what is the equation to calculate tangential acceleration for an object in circular motion
0 (r is infinite)
what is the normal acceleration for an object that is travelling in a straight line or is at a point of inflection in its path