1 structure of eukaryotic cells
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
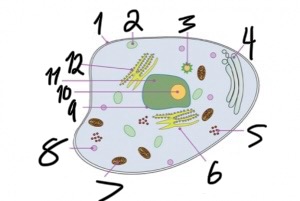
what structure is number 1?
cell membrane
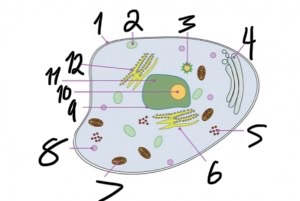
what structure is number 2?
vacuole
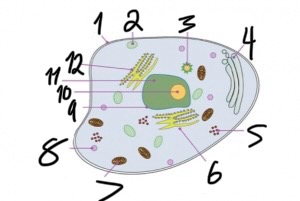
what structure is number 4?
golgi apparatus
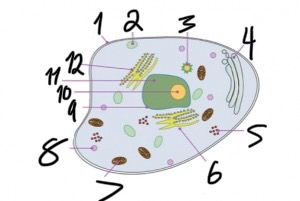
what structure is number 5?
ribosomes
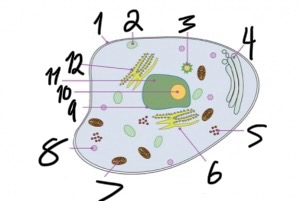
what structure is number 6?
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
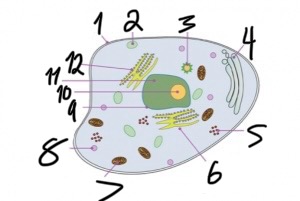
what structure is number 7?
mitochondria
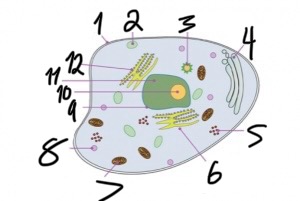
what structure is number 8?
lysosome
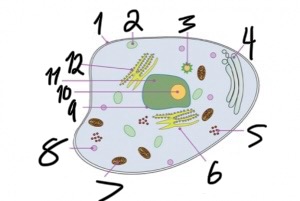
what structure is number 11?
nucleus
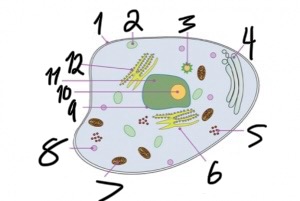
what structure is number 12?
rough endoplasmic reticulum
what’s the structure of the nucleus?
site of DNA replication and transcription (making rRNA)
contains the genetic code for each cell
what are the structures in the nucleus and what are their functions?
nuclear envelope - double membrane
nuclear pores
nucleoplasm - granular, jelly-like material
chromosomes - protein-bound, linear DNA
nucleolus - smaller sphere inside which is the site of rRNA production and makes ribosomes
what’s the function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
protein synthesis
what’s the function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
synthesis and store lipids and carbohydrates
what’s the structure of the endoplasmic reticulums?
rough and smooth ER both have folded membranes called cristernae
rough have ribosomes on the cristernae
what’s the structure for the golgi apparatus?
folded membranes making cristernae
secretary vesticles punch off from the cristernae
what’s the function of the golgi apparatus and vesticles?
add carbohydrates to proteins to form glycoproteins
produce secretory enzymes
secrete carbohydrates
transport, modify, and store lipids
form lysosomes
molecules are “labelled” with their destination
finished products are transported to cell surface in golgi vesticles where they fuse with the membrane and the contents in released
what’s the structure of lysosomes?
bags of digestive enzymes
what’s the function of lysosomes?
hydrolyse phagocytic cells
completely break down dead cells (autolysis)
exocytosis - release enzymes to outside of cell to destroy material
digest worn out organelles for reuse of materials
what’s the structure of mitochondria?
double membrane
inner membrane called the cristernae
fluid centre called the mitochondrial matrix
loop of mitochondria DNA
what’s the function of mitochondria?
site of aerobic respiration
site of ATP production
DNA to code for enzymes needed in respiration
what’s the structure of ribosomes?
small, made up of two sub units of protein and rRNA
80s - large ribosomes found in eukaryotic cells (25nm)
70s - smaller ribosomes found in prokaryotic cells, mitochondria and chloroplasts
what’s the function of ribosomes?
site of protein synthesis
what’s the structure of a vacuole?
filled with fluid surrounded by a single membrane called a tonoplast
what’s the function of a vacuole?
makes cells turgid and therefore provide support
temporary store of sugars and amino acids
the pigments may colour petals to attract pollinators
what’s the structure of chloroplasts?
surrounded by a double membrane
contains thylakoids (folded membranes embedded with pigment)
fluid filled stroma contains enzymes for photosynthesis
found in plants
what’s the function of chloroplasts?
site of photosynthesis
what’s the structure of a cell wall?
in plants and fungi
plants - made of microfibrils of the cellulose polymer
fungi - made of chitin, a nitrogen containing polysaccharide
what’s the function of a cell wall?
to provide strength to the cell
what’s the structure of the plasma membrane (cell membrane)?
found in all cells
phospholipid bilayer - molecules embed within and attached on the outside (proteins, carbohydrates, and cholesterol)
what’s the function of a plasma membrane (cell membrane)?
controls the entrance and exit of molecules