(27.8) Regulation of Male Reproductive System
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Define Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonagal Axis
Refers to the relationship between the structures that regulate the production of gametes and sex hormones
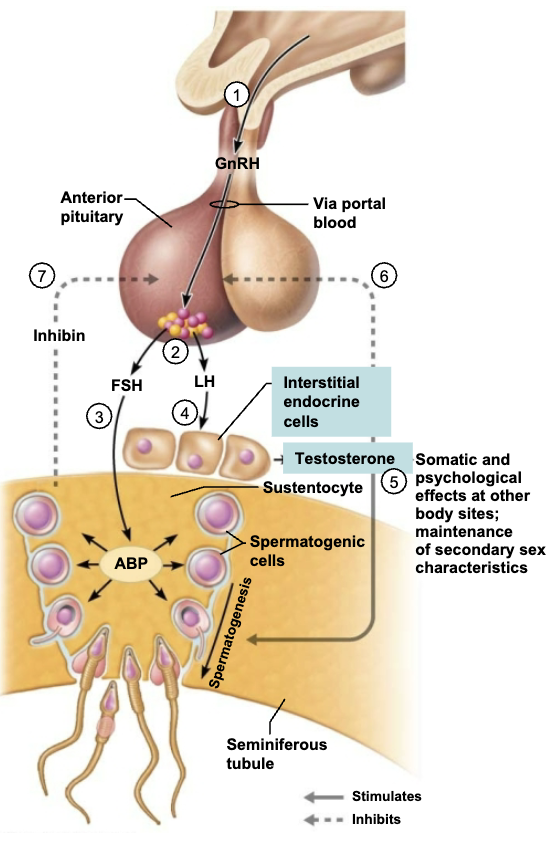
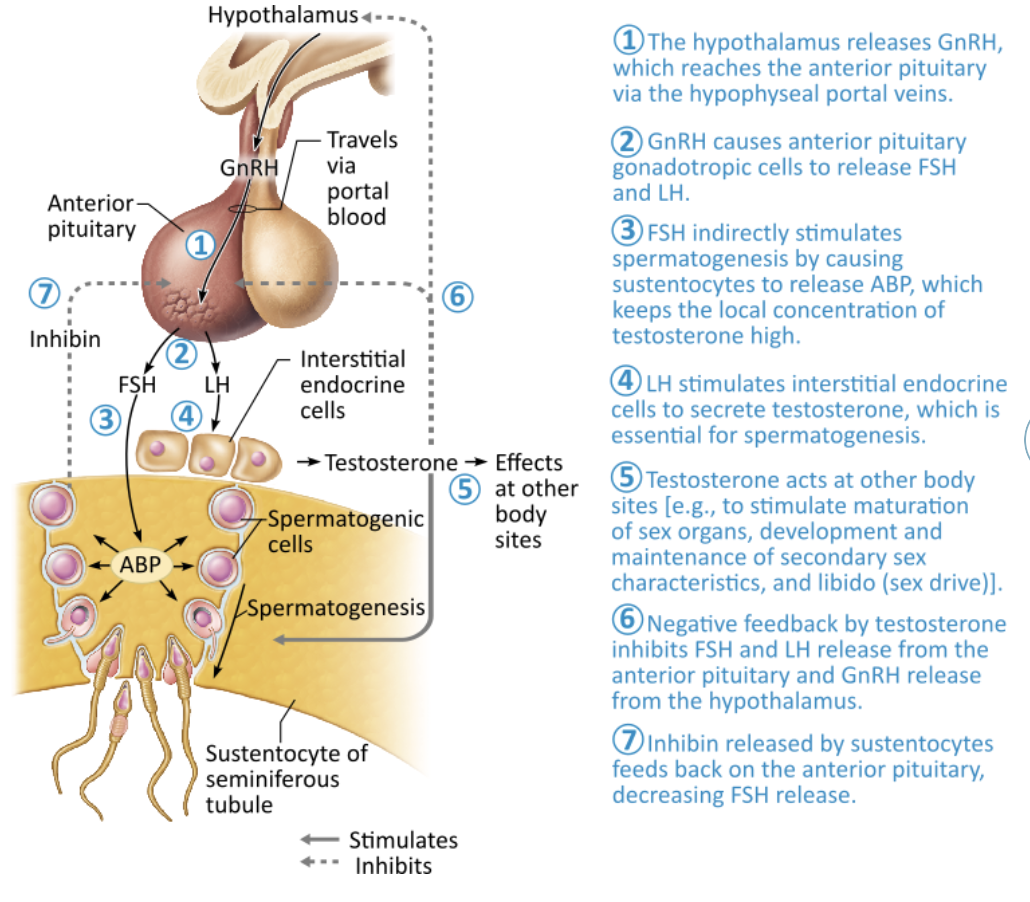
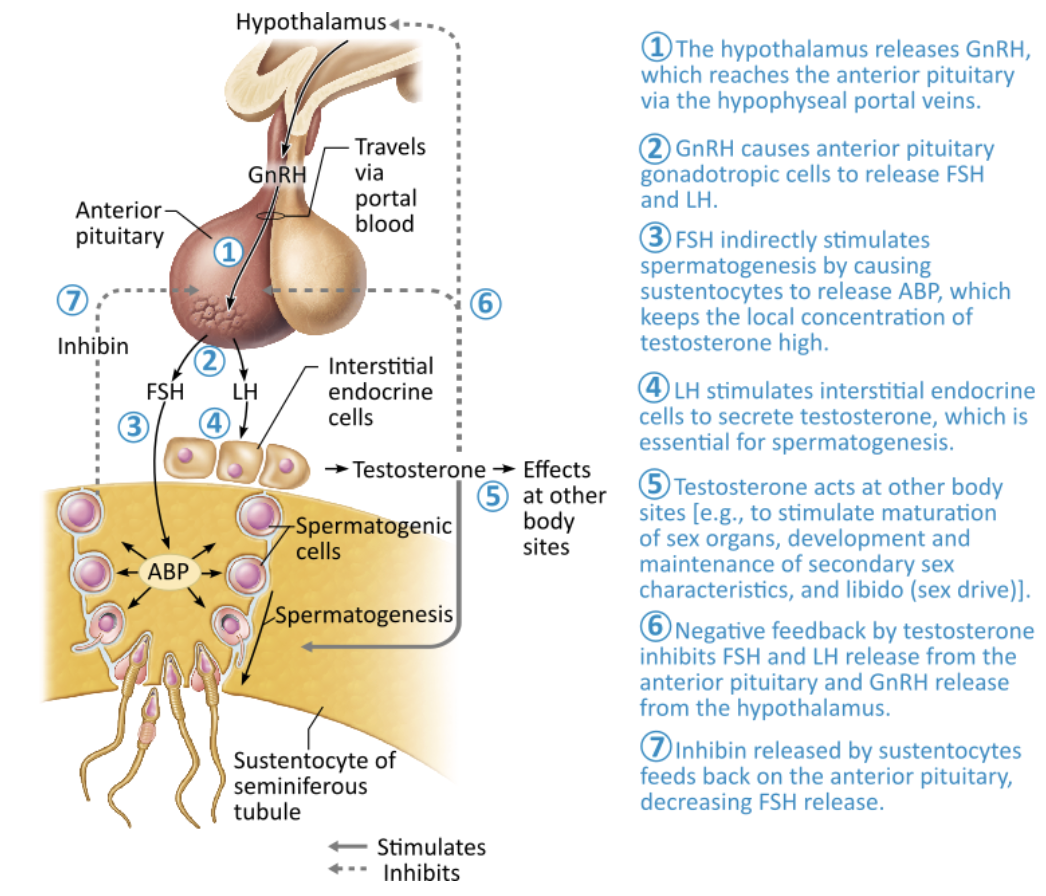
Discuss Hormonal Regulation of Testicular Function.
Hypothalamus releases gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which controls the release of the anterior pituitary hormones follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) in males
FSH indirectly stimulates spermatogenesis by stimulating the sustentocytes to release androgen-binding protein, which keeps testosterone in the vicinity of the spermatogenic cells high
LH stimulates the interstitial endocrine cells to produce testosterone
Locally, testosterone entering blood acts as a final trigger for:
Spermatogenesis
Stimulates sex organ maturation
Development/maintenance of secondary sex characterisc
Libido
Rising levels of testosterone inhibit hypothalamic release of GnRH and act directly on the anterior pituitary gland to inhibit gonadotropin release
Inhibin is produced by the sustentocytes and released when sperm count is high, inhibits GnRH and FSH release
Relationship between Testosterone and Sperm Production
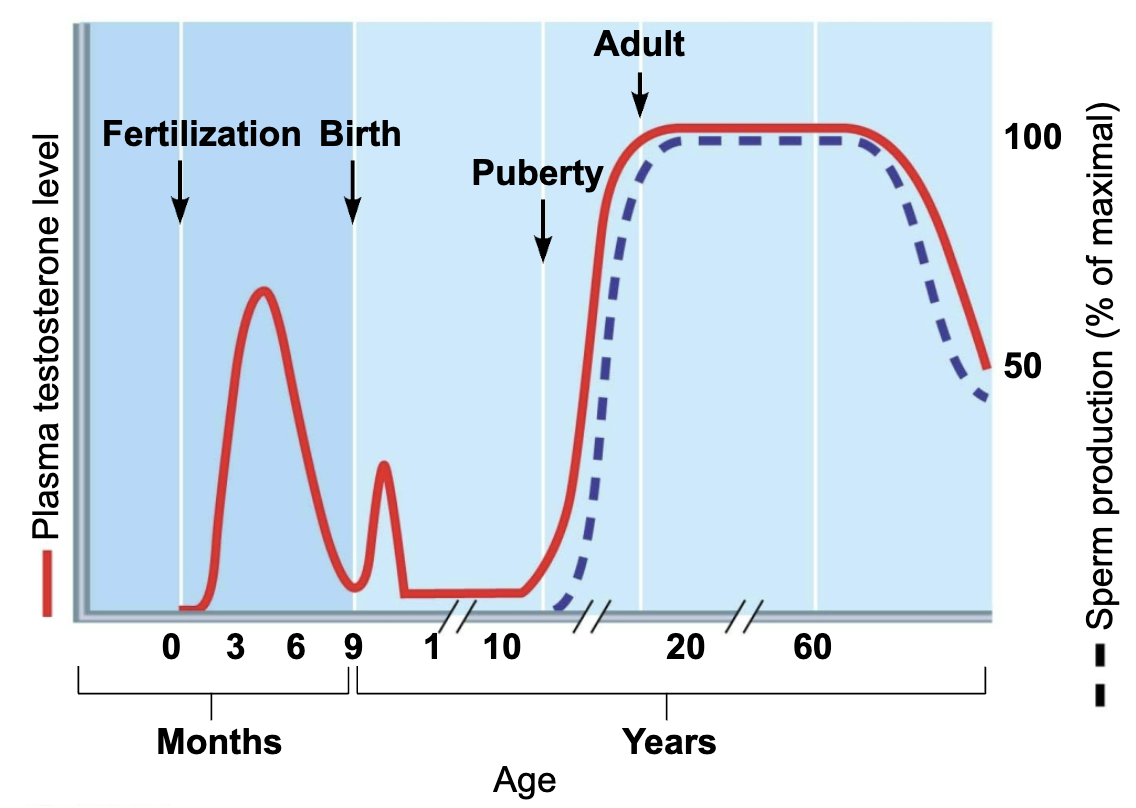
Amount of testosterone and sperm produced by testes reflects balance among three interacting sets of hormones
Balance takes 3 years to achieve, after which testosterone and serpm production are fairly table throughout life
Without GnRH and gonadotopins, testes atrophy, and sperm and testosterone production ceases
T/F: Testosterone remain same before and after birth
Before birth → male infant has testosterone levels 2/3 of adult
After birth → levels recede and remain low through childhood until puberty
Physiological effects of Testosterone on male reproductive anatomy.
Testosterone is synthesized from cholesterol and exerts its effects by activating specific genes, causing specific proteins to be synthesized
In some cells, testosterone must be converted to another hormone: dihydrotestosterone in the prostate or estradiol in some neurons of the brain
Targets accessory organs, initiating spermatogenesis, and acts on ducts, glands, and the penis, causing them to grow and assume adult size and function
Induces male secondary sex characteristics
Appearance of pubic, axillary, and facial hair
Deepening of the voice
Thickening of the skin and increase in oil production
Increase in bone and skeletal muscle size and mass
Increases basal metabolic rate
Masculinizes the brain
Basis of sex drive (libido)
Continues to exert effect into adulthood
T/F: Adrenal glands in males also produce other androgens
→ TRUE
Although adrenal glands also produce androgens in small amounts, production is insufficient to maintain normal testosterone-mediated functions
Effect and Treatment of Testosterone Deficiency
EFFECT
Leads to atrophy of accessory organs
Semen volume declines
Erection/ejaculation are impaired
TREATMENT
Testosterone replacement
Which of the following reduces circulating blood levels of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) when the sperm count is high?
→ inhibin
Sustentocytes respond to elevated sperm counts by releasing inhibin, a hormone that suppresses release of FSH
What is the testicular target for follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)?
→ Sustentocytes (Sertoli cells)
Sustentocytes in the walls of the seminiferous tubules respond to FSH by releasing androgen-binding protein, which maintains high testosterone levels near developing sperm cells
Which hormone promotes the formation of male secondary sex characteristics such as the appearance of pubic, axillary, and facial hair; enhanced hair growth on the chest; and a deepening voice?
→ Testosterone