Classical Art & Archaeology Midterm 2 Review
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
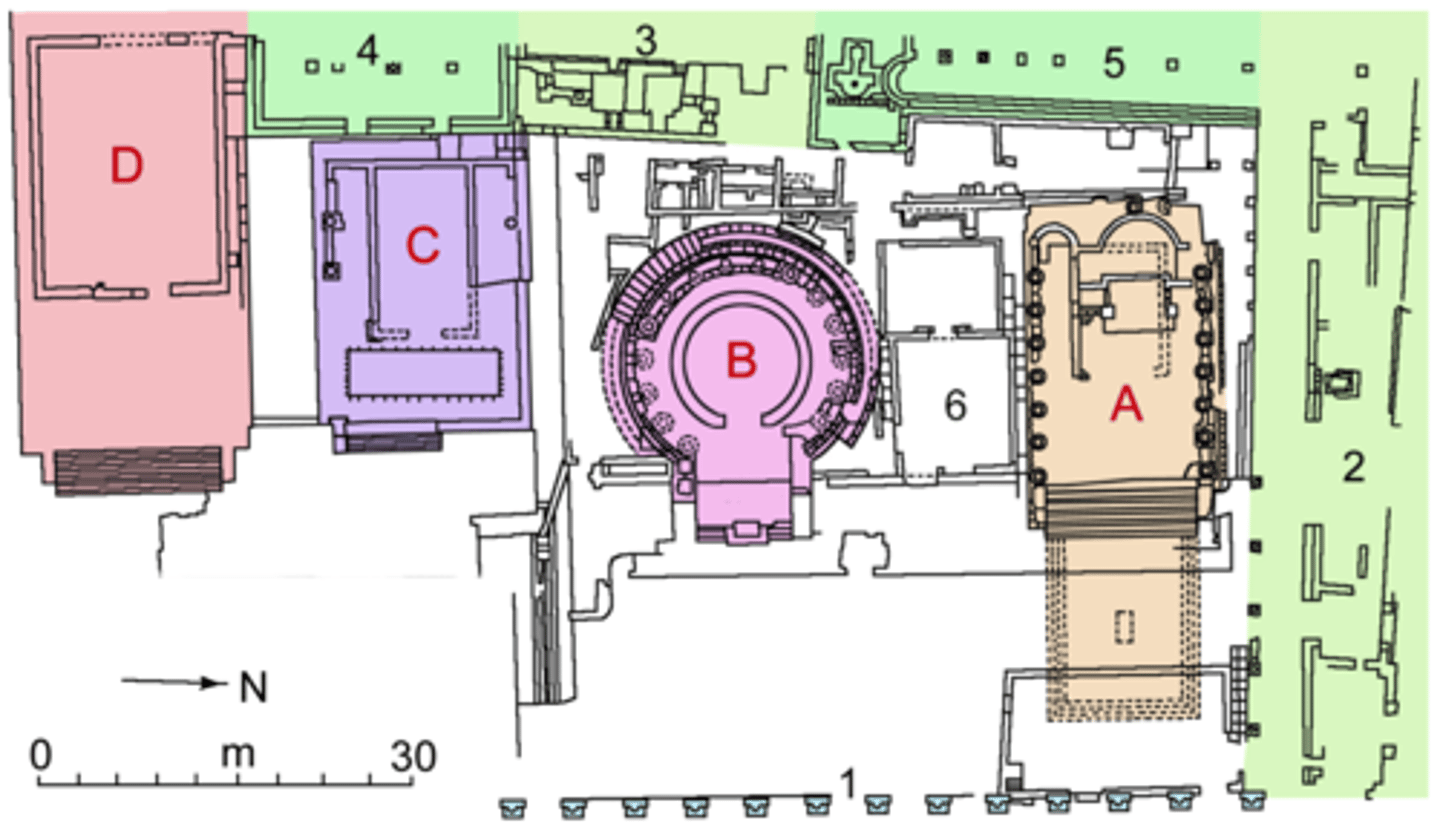
Largo Argentina
Series of 4 Republican period temples built very close to one another. (most seem to have been victory dedications by roman general from the Minuciae clan)
- Temple A (built in mid-late 3rd century): Temple of Juturna built by Gaius Lutatlus Catulus
- Temple B (ca. 100 BC): Fortuna Huiusce Diei (roman goddess) built by Quintus Lutatius Catulus
- Temple C (3rd or 4th century BC probably): dedicated to a female goddess (Feronia?) burned in 80 AD and rebuilt
- Temple D (2nd century BC): dedicated to the Lares Permarini
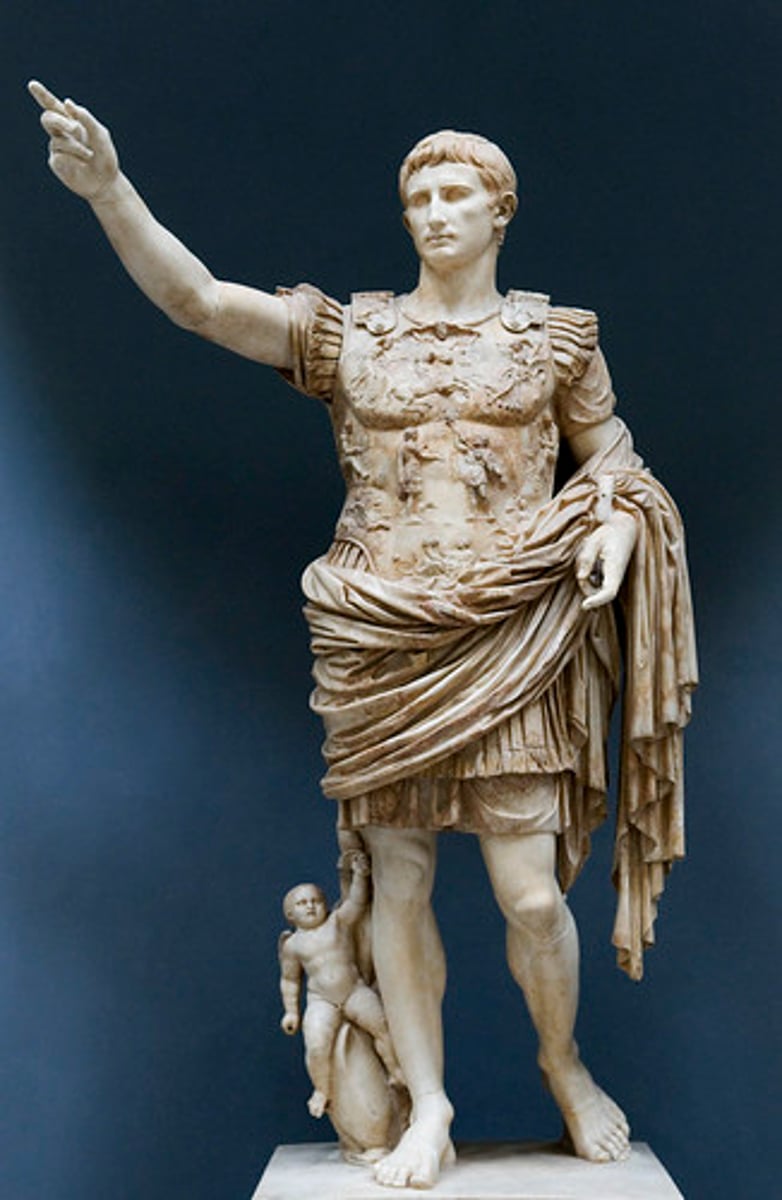
Prima Porta Augustus

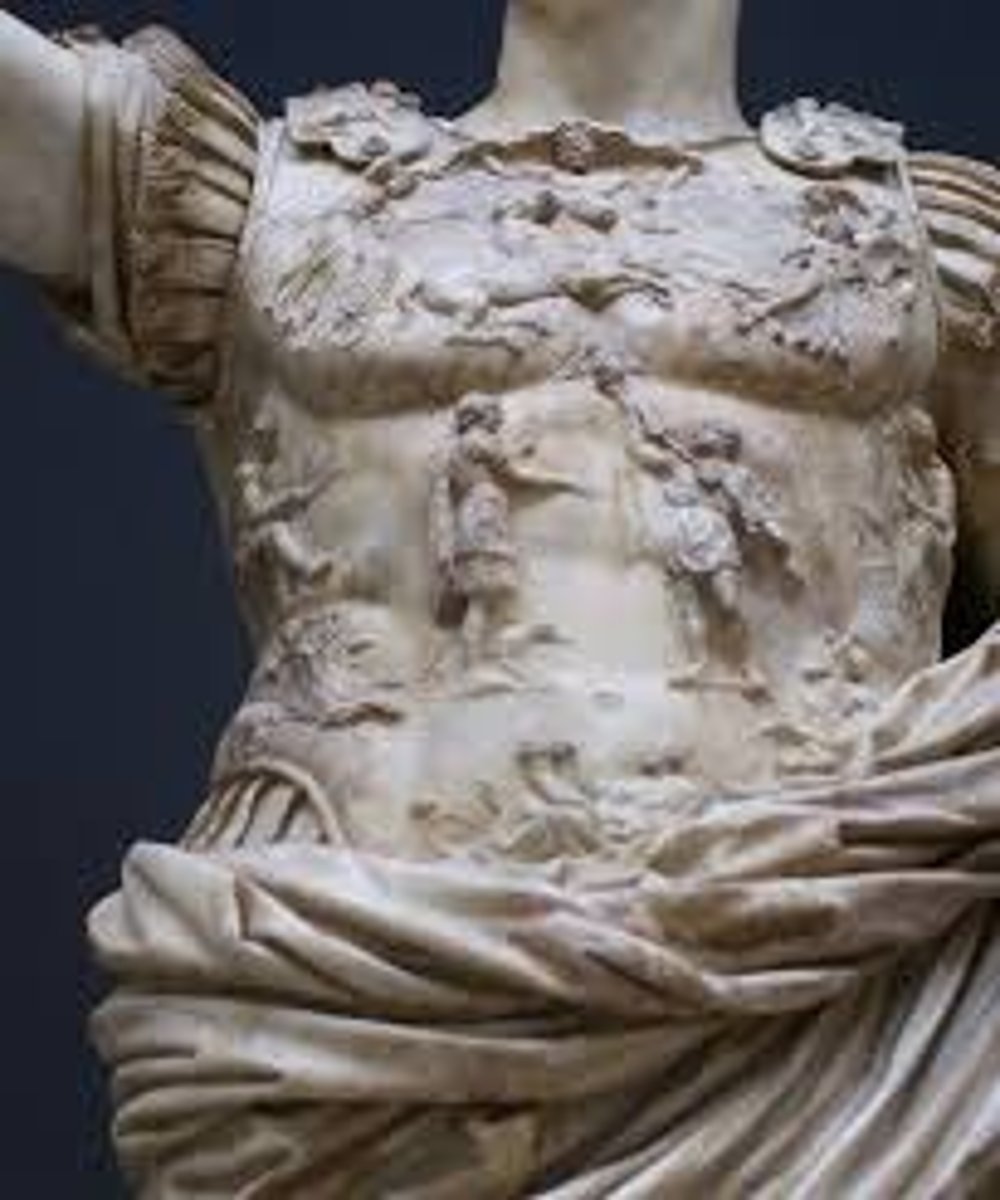
Prima Porta Augustus Breastplate
- Epaulettes: sphinxes
- Center: Parthians returning the standard to a Roman (Mars Ultor? Tiberius?)
- Top: Caelus, Aurora, and Luna
- Center left and right: subjugated peoples Apollo and Artemis
- Bottom: Tellus

Nereid Monument
- Late Classical
- 390-370 BCE
- Xanthos
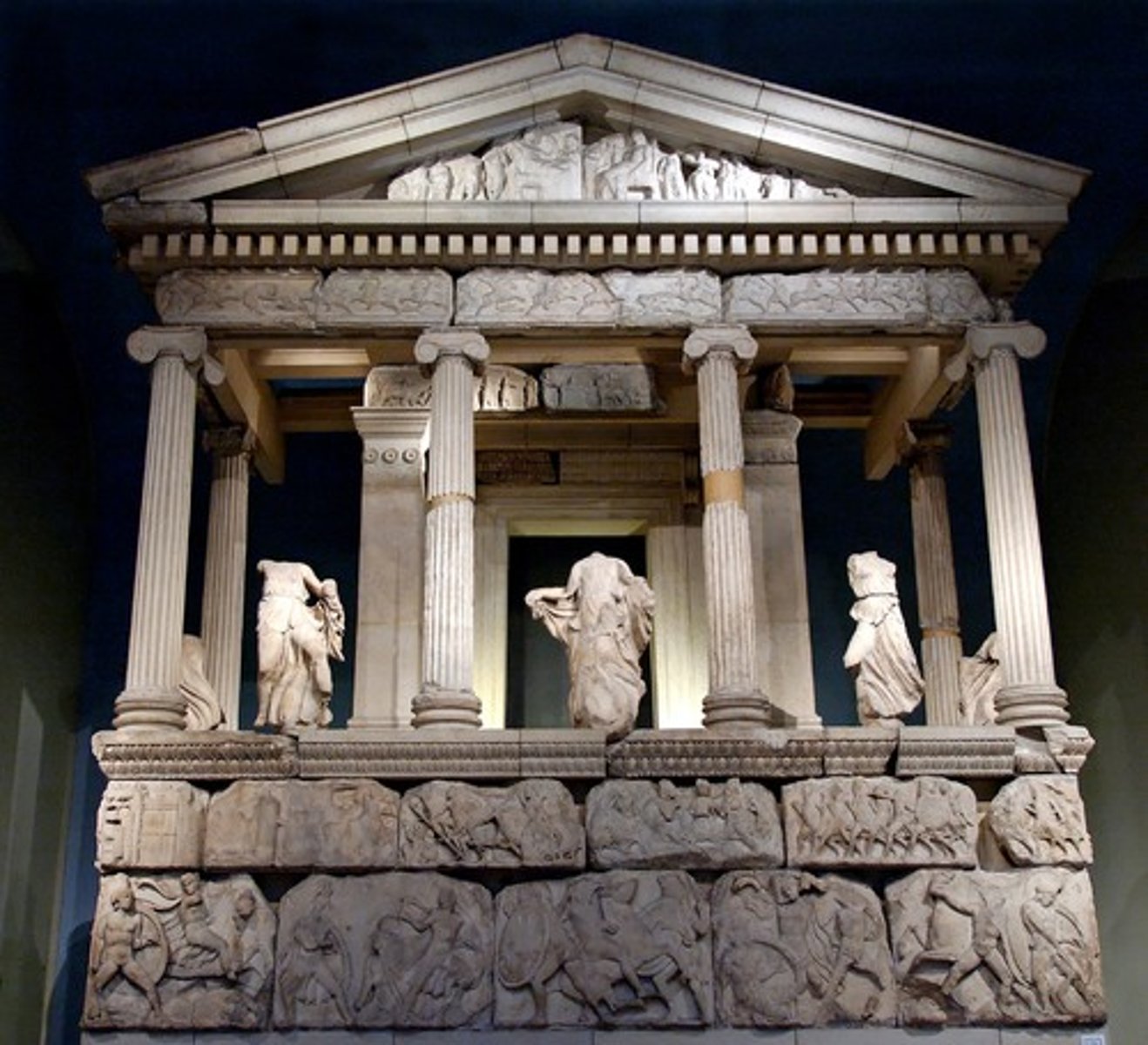

Pergamon Altar: Case Study
- Built on the acropolis of Pergamon, thought to have been designed by sculptors from Rhodes
- ca. 180-160 BCE
- Depicts a Gigantomachy on the exterior, local hero myth on the interior
- Key example of baroque style typical of Hellenistic sculpture (very expressive faces and bodes, dynamic postures, lots of drilling to create light and shadow)

Agora of the Italians on Delos
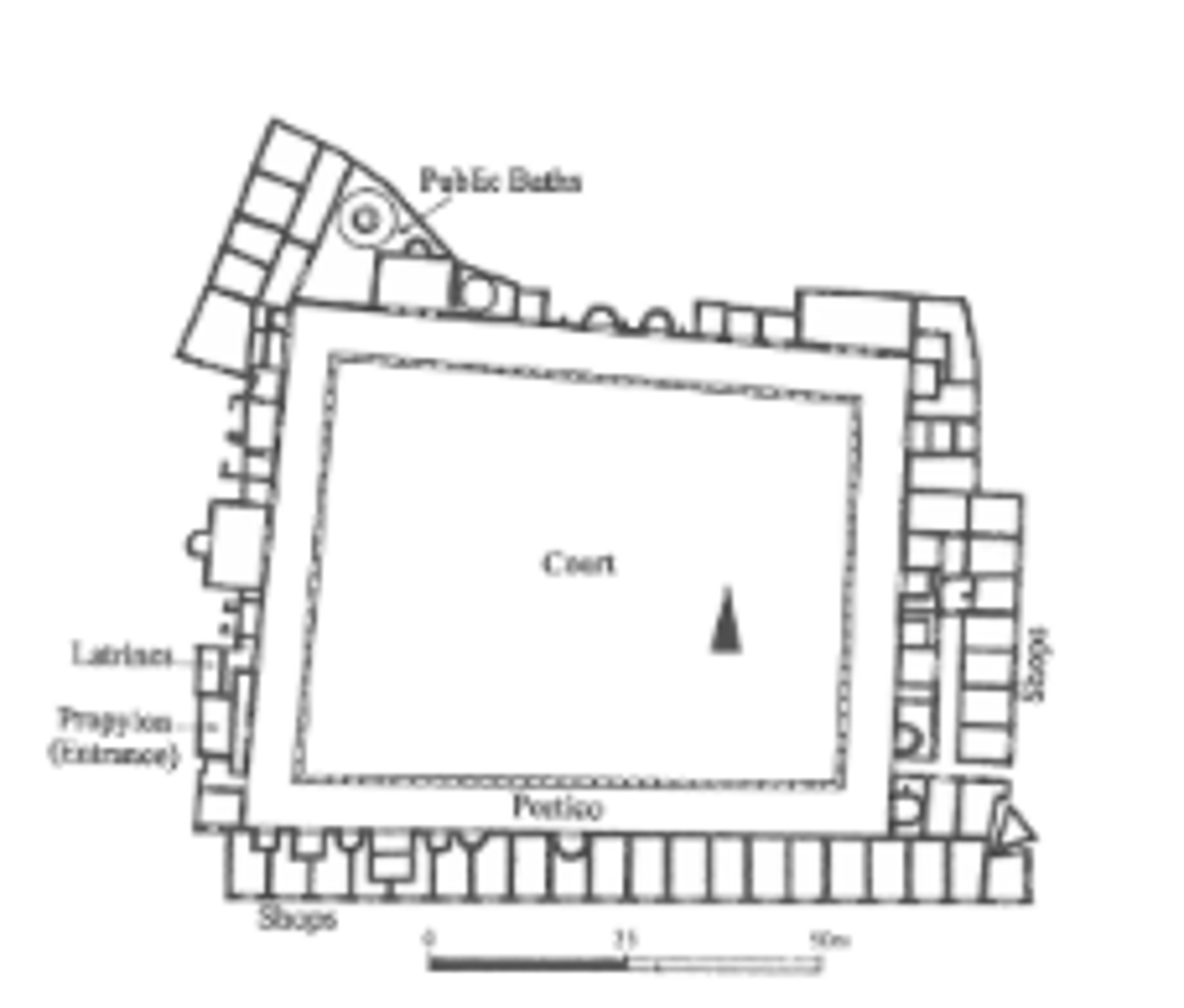
Pastas house
Greek house with separate room leading off from courtyard into one main room in back, the oikos or living room; was semi-enclosed. (Priene)
Kerameikos cemetery
Athens' main cemetery during Archaic and Classical periods
Dexilaos monument
Portrait of Demosthenes from Athens

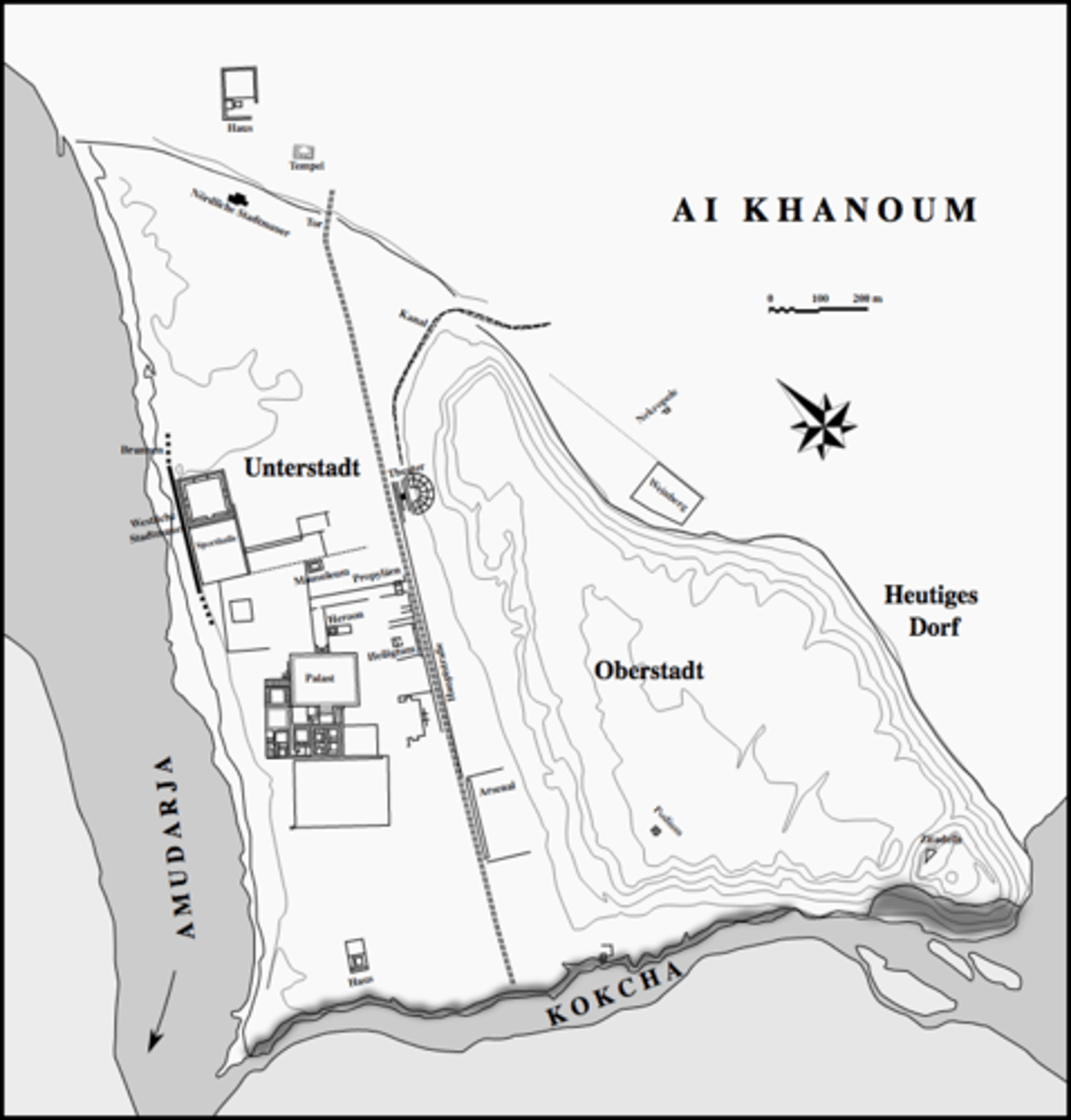
Ai-Khanoum (Case Study)
- One of the Alexandrias, founded by Hephaestion (replacement of earlier Persian City?)
- Colony of veterans
- Several aspects follow Greek norms: gymnasium, roughly Hippodamian plan, theater
- Key stop on overland trade routes, market for luxury goods (e.g. "The Silk Road")
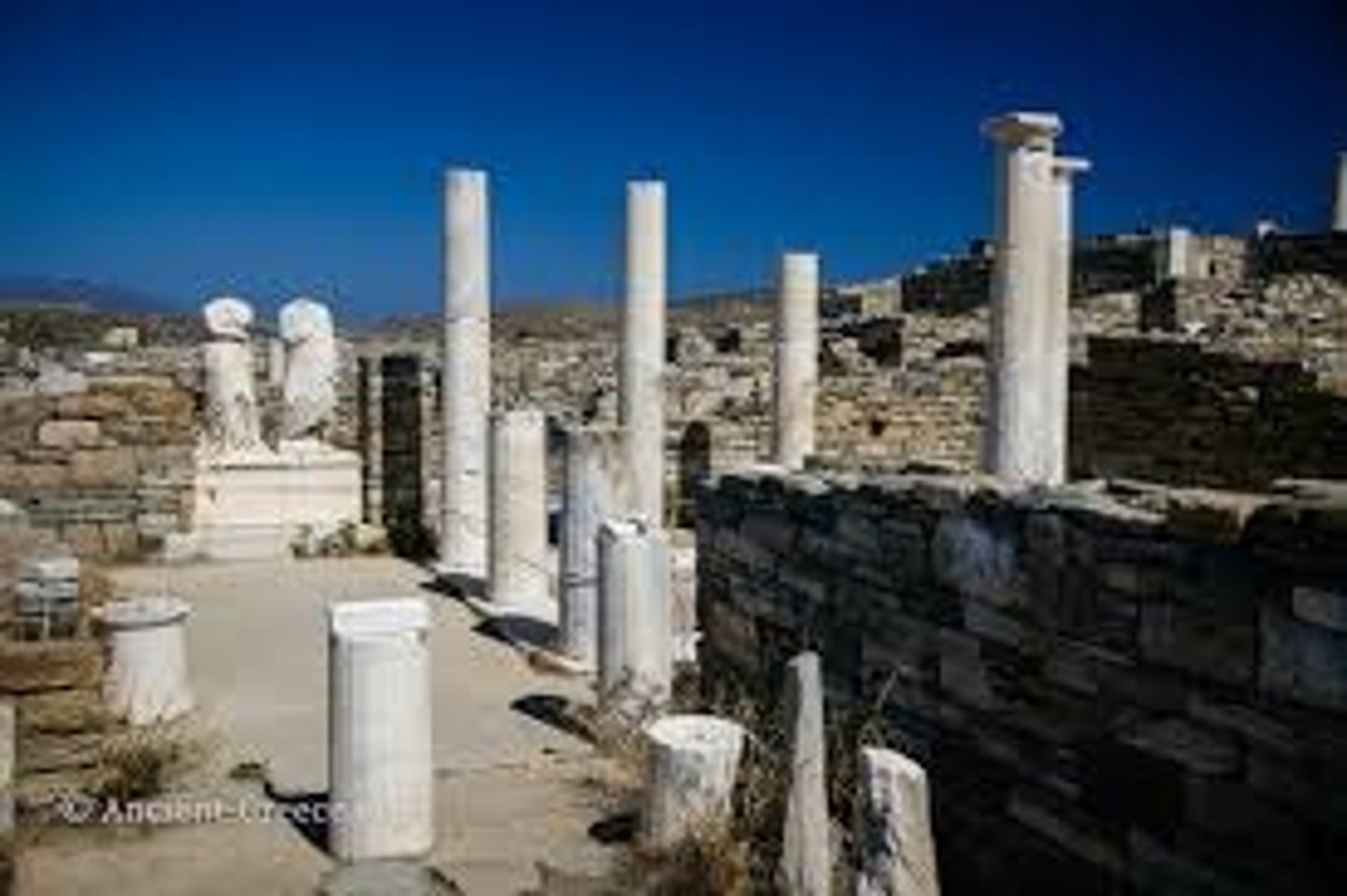
Hellenistic Delos Case study
- Famous panhellenic sanctuary to Apollo and Artemis, but also a major commercial center from the 5th-1st centuries BCE
- Governance:
- Colony of Athens, brief period of independence from 314-167 BCE
- Rome colonizes in 166 BCE, but Athens administers the city
- Two pirate sacks (88 BCE and 69 BCE) lead to massive depopulation
- Key monuments: ethnic clubhouses, sanctuaries to foreign and Greek deities, huge numbers of houses

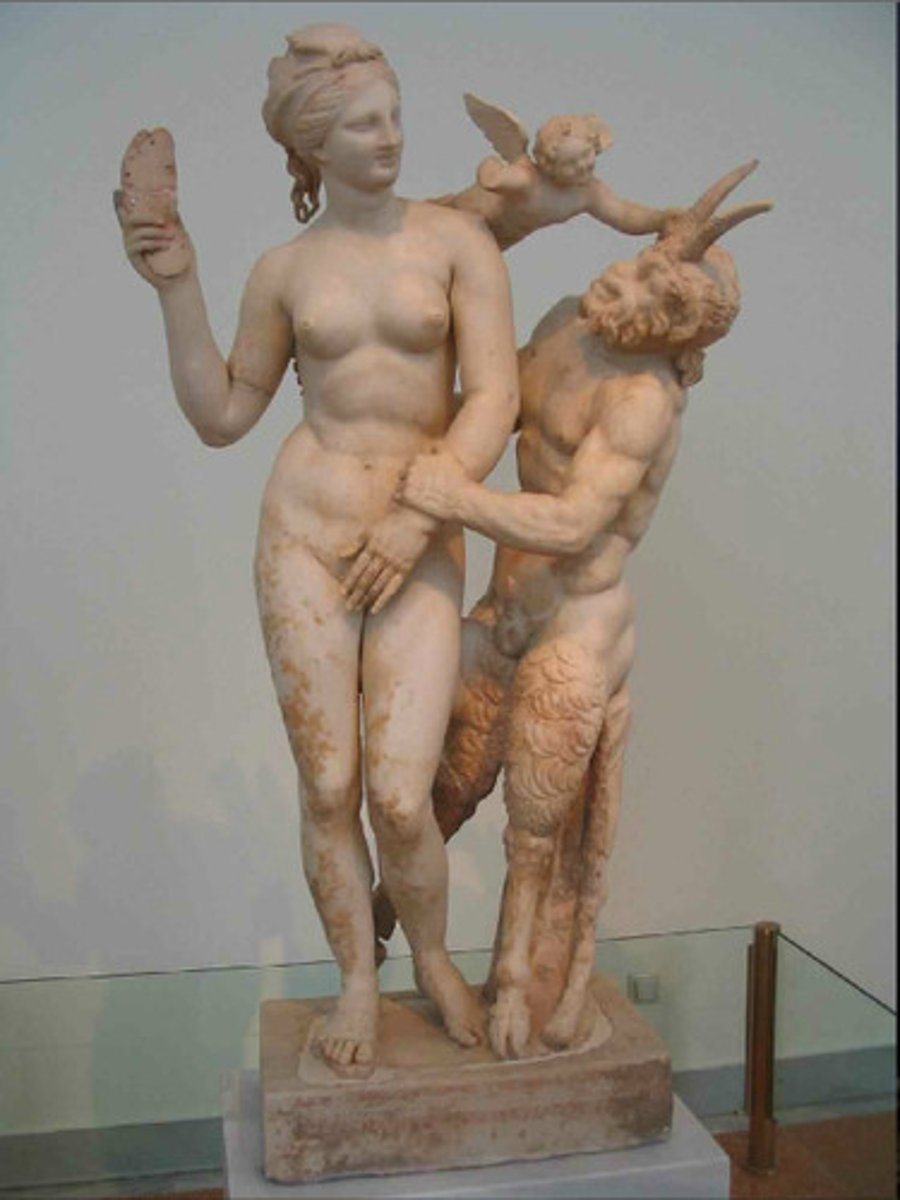
"Slipper Slapper"
- Ca. 100 BCE
- Eclectic mythological group of Aphrodite, Pan, Eros
- Rebecca Martin: Phoenician mythology, Hellenized?

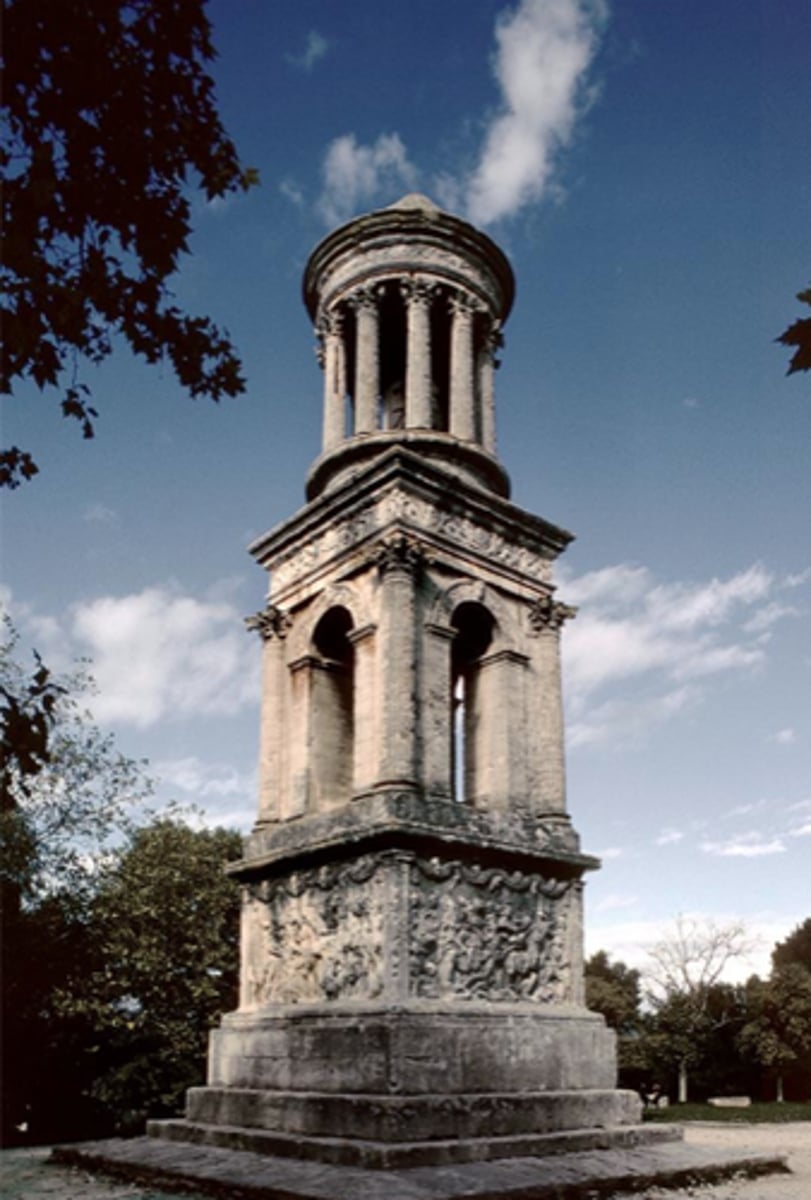
Mausoleum of the Julii at Glanum
It has been interpreted as a cenotaph erected in memory of a man of the Julii family, who would have been granted citizenship and his name by Julius Caesar for his service in the Roman army, following the conquest of Gaul. Henri Rolland, left to suggest that it was a mausoleum dedicated to the memory of Caius and Lucius Caesar, grandsons of the emperor Augustus.

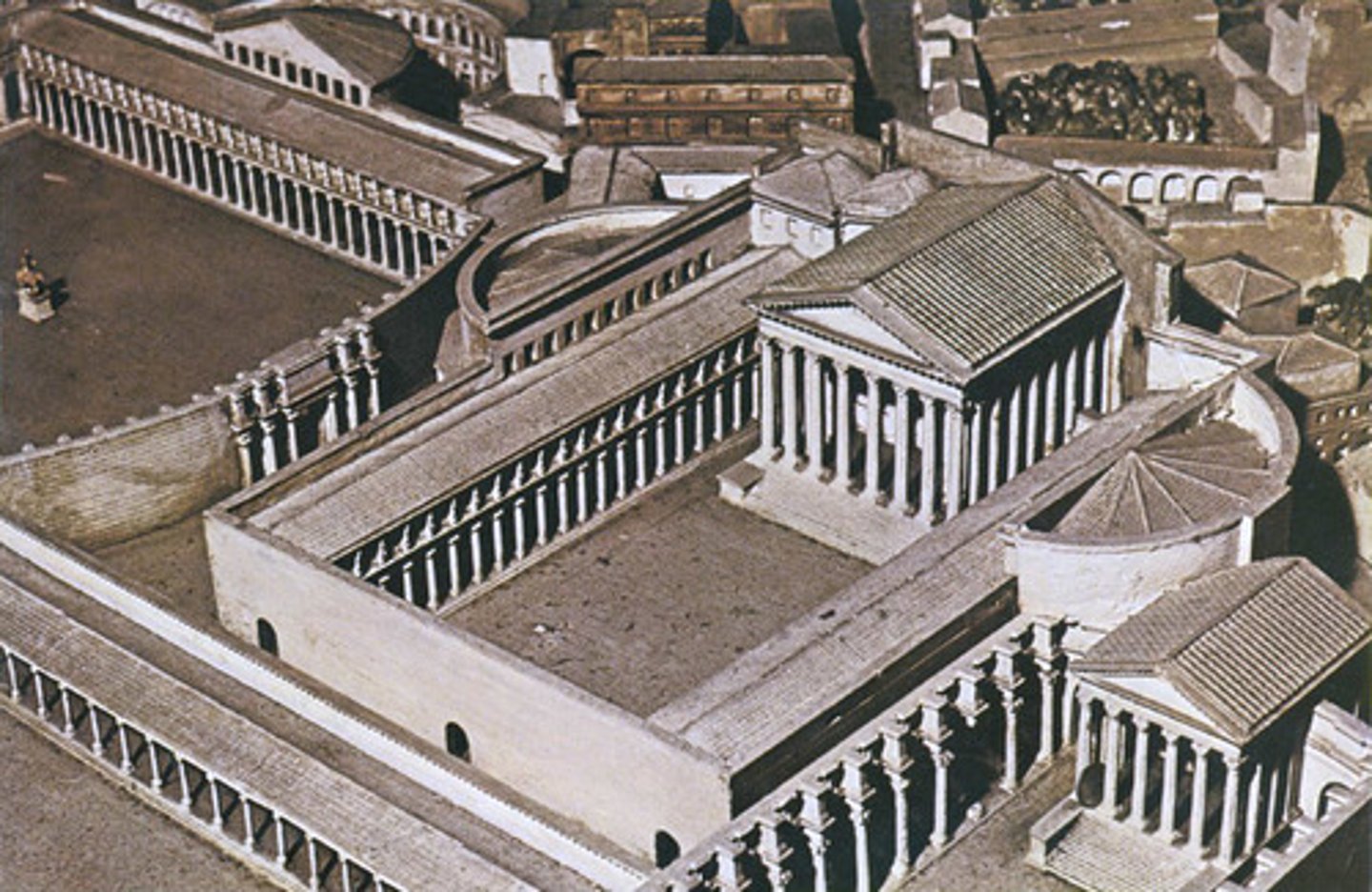
Forum of Augustus at Rome
-A place where elections, public speeches and gladiator matches took place
-Built by Augustus adjacent to the Forum of Caesar

Ara Pacis
- Commissioned by the Roman Senate in 13 BC to honor Augustus' return from campaigns in Hispania and Gaul; consecrated January 30, 9 BC
- Set up outside the pomerium on the pomerium on the Via Appia, in a region called the Campus Martius
- Sculpted in Luna Marble; exterior frieze depicts a large ritual procession
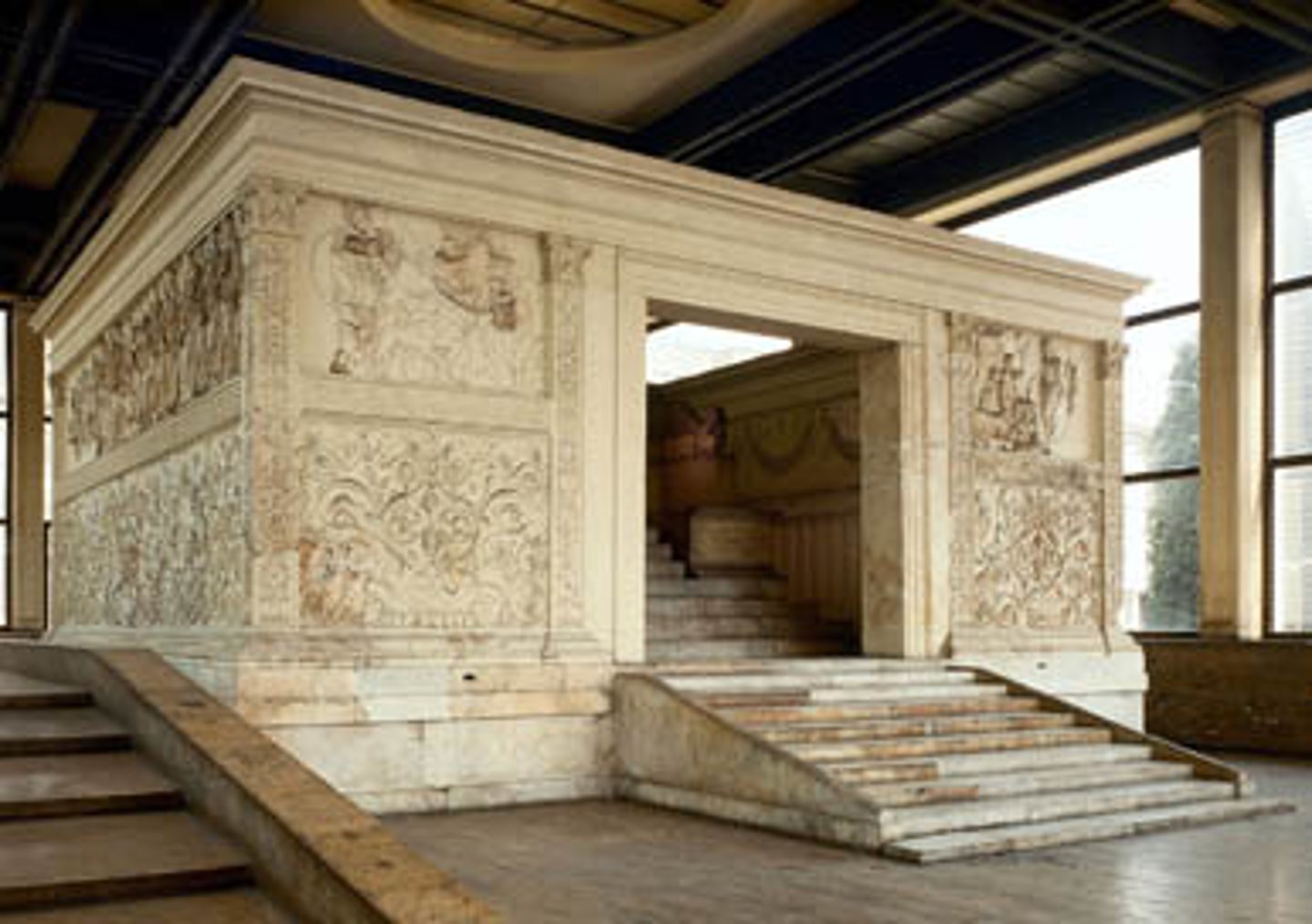

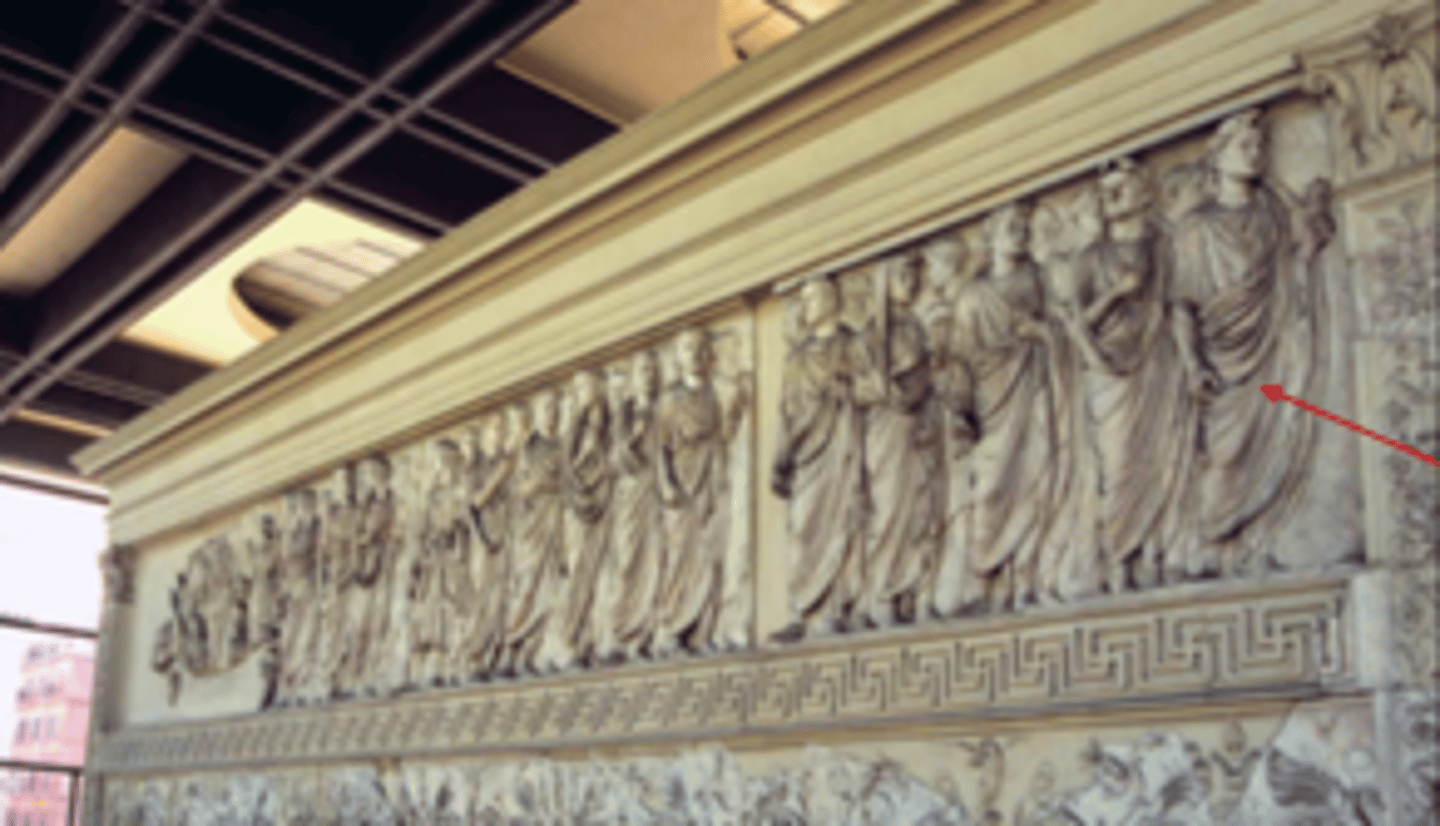
Ara Pacis: North side frieze
Senators or Lictors

Ara Pacis: South side frieze
imperial family
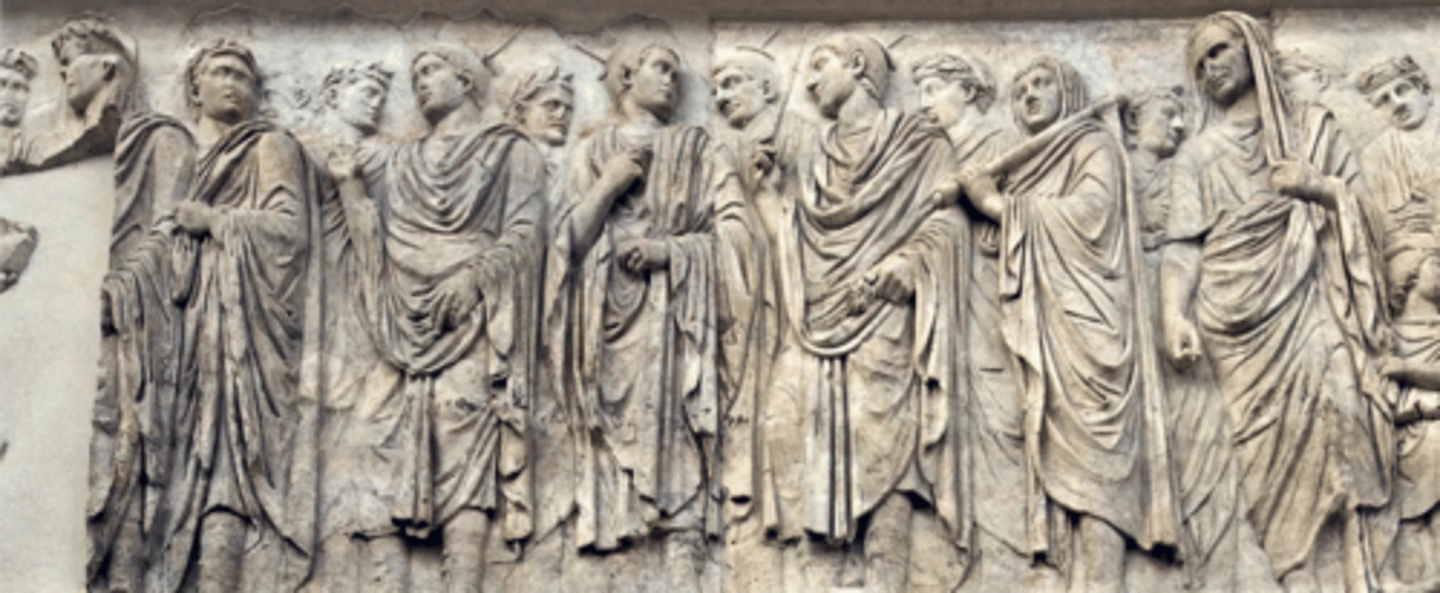

Ara Pacis: small side frieze panel
- Symbolizes the prosperity of the Roman Empire under Augustus's rule due to the elements being on his side
- "Tellus" (the earth goddess) or "Pax" (peace) or "Italia" (Italy) or "Venus"
- Element of water rides a wave while element of air rides a swan and Tellus sits on some type of stone/earth piece
- The babies in Tellus's lap are depicted as...
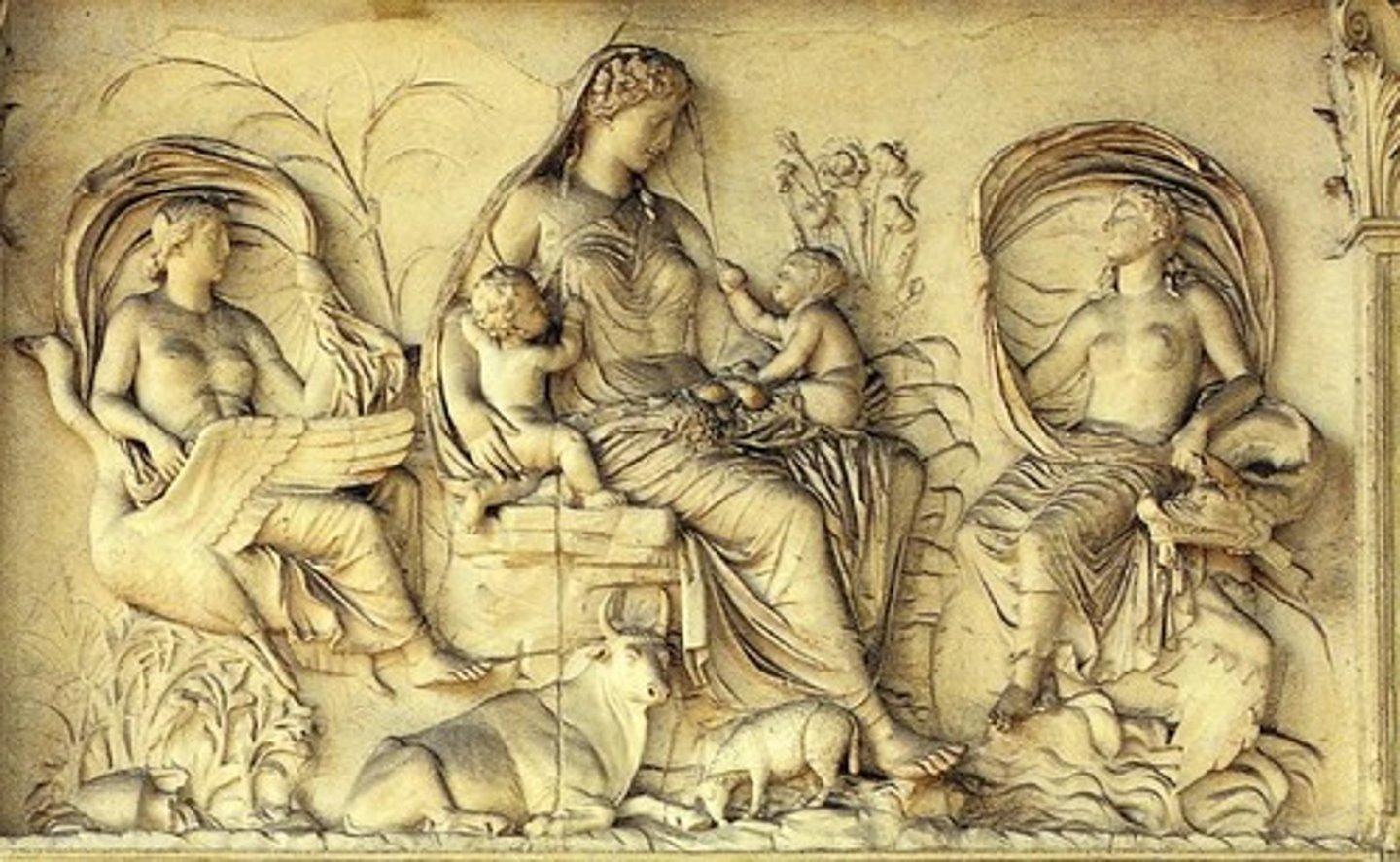

Ara Pacis: South side panel
Aeneas sacrificing to the gods
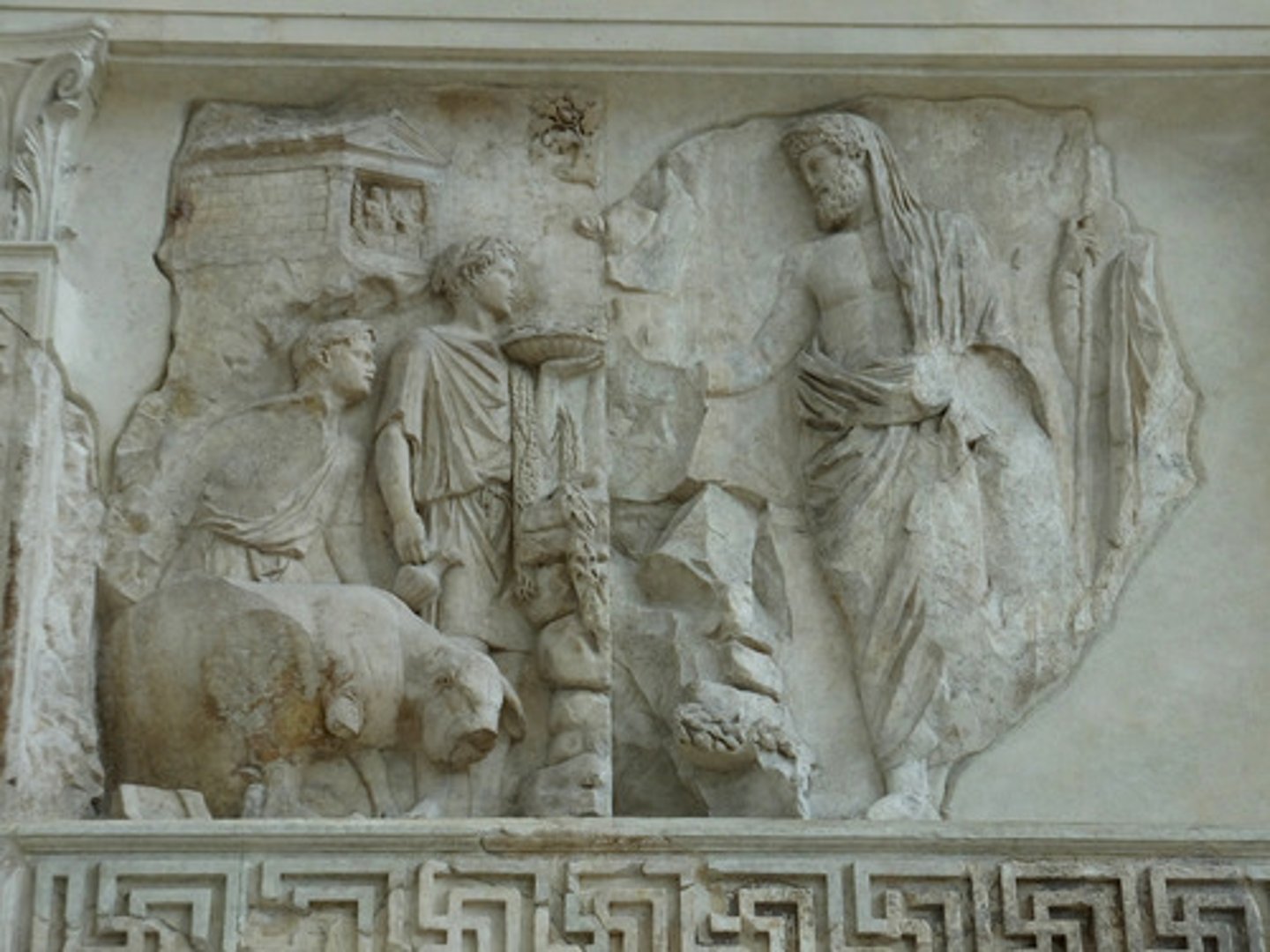

Theater of Pompey
- Built in 55 BCE
- One of the meeting places of the senate
- Julius caesar was killed here
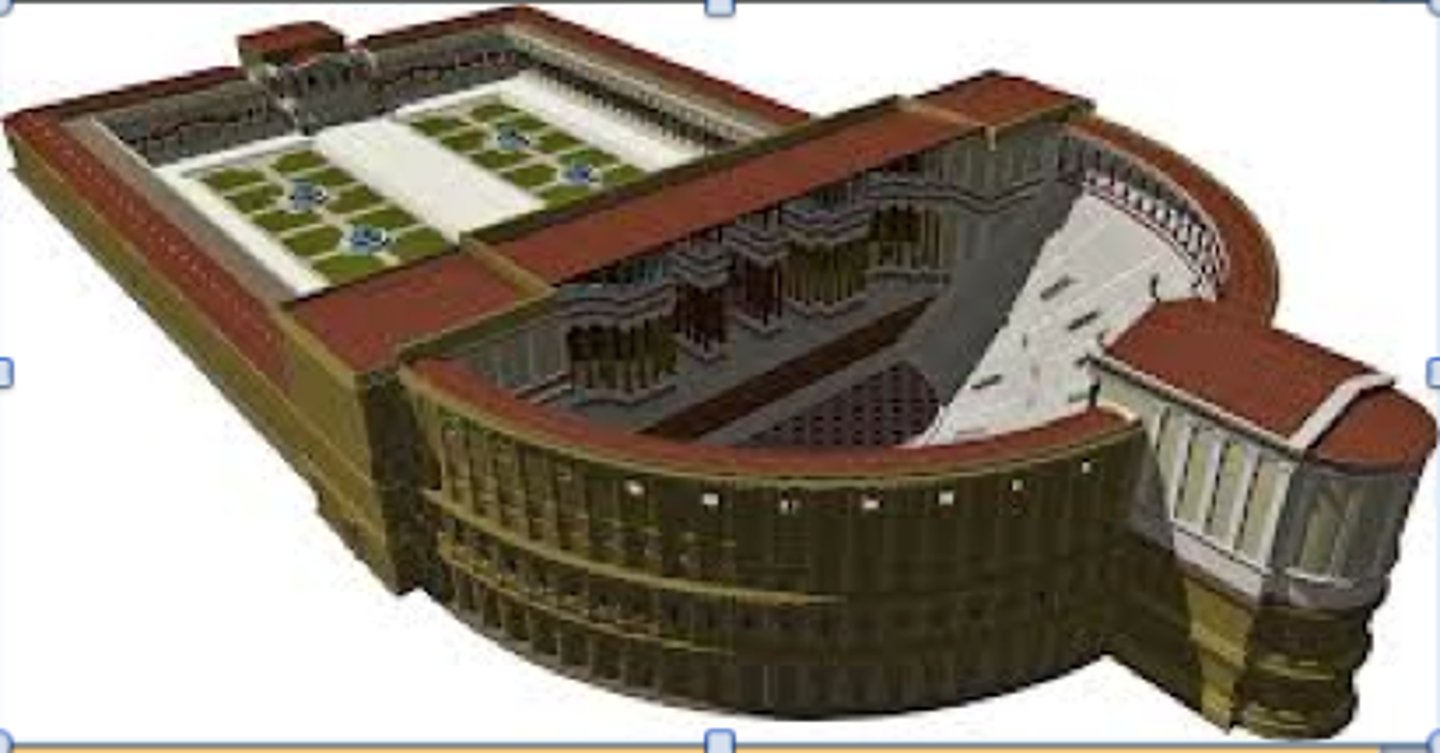
Forum of Caesar, Rome
constructed at end of Caesar's life
served as prototype for all subsequent imperial fora
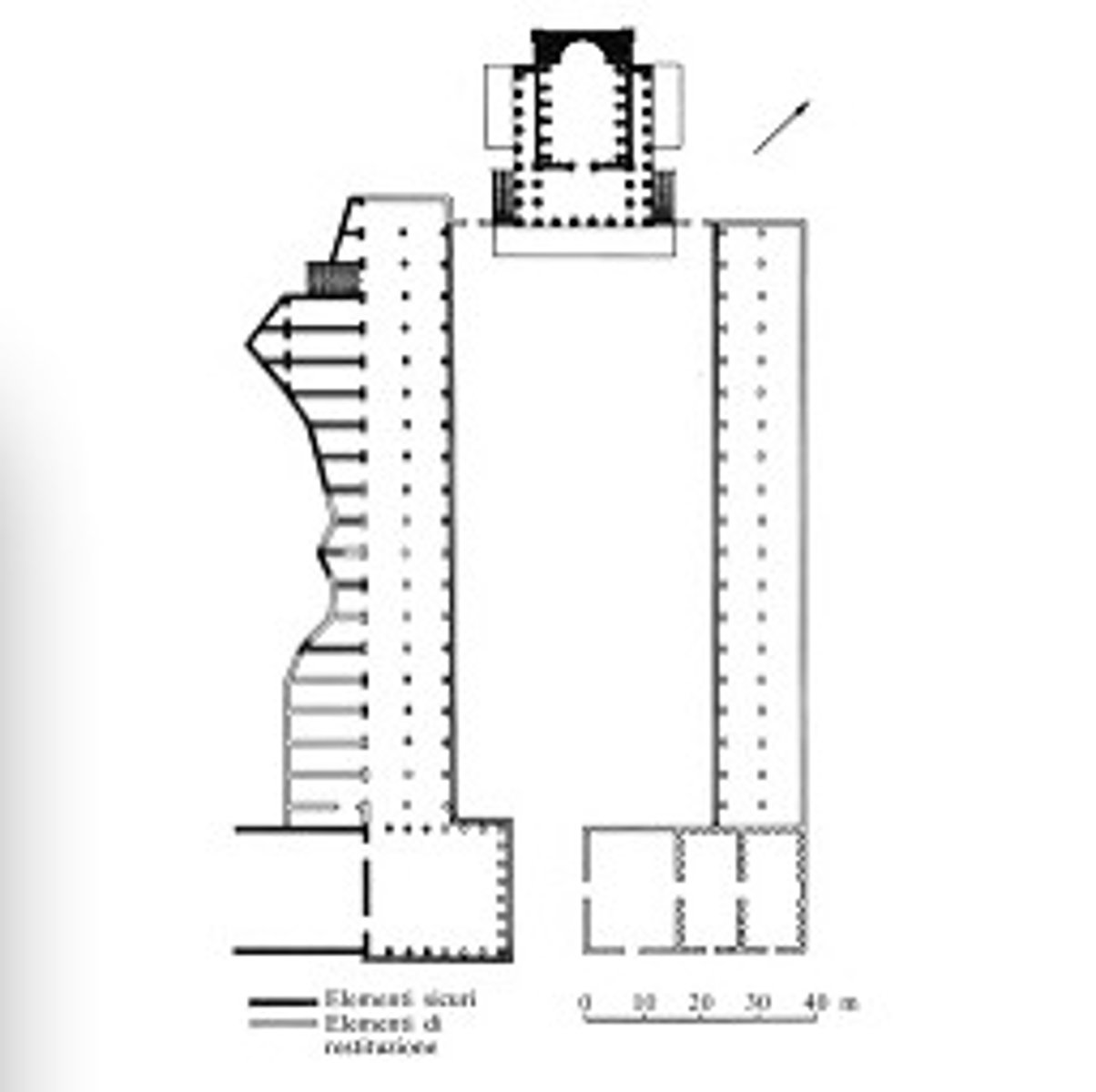
Forum Romanum (curia, rostra, use of space)
market place, business district, senate, public buildings
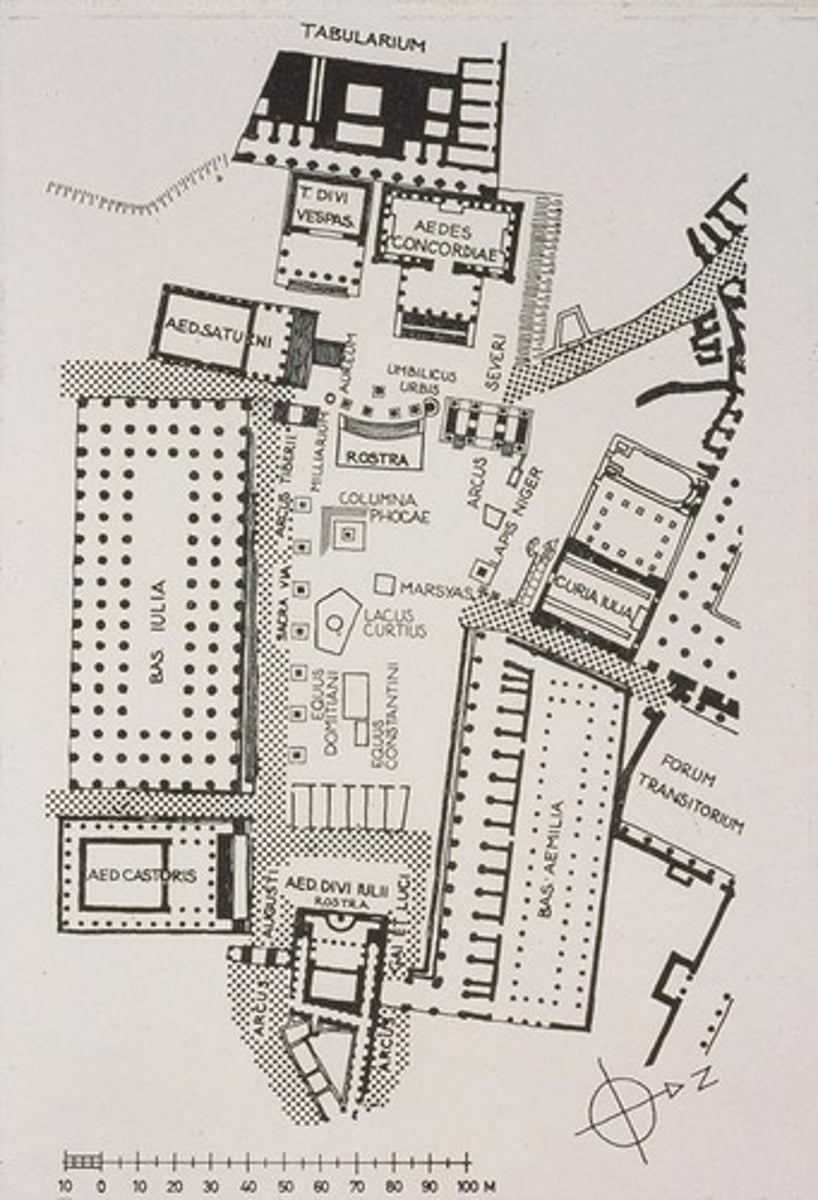
Sant'Omobono sanctuary

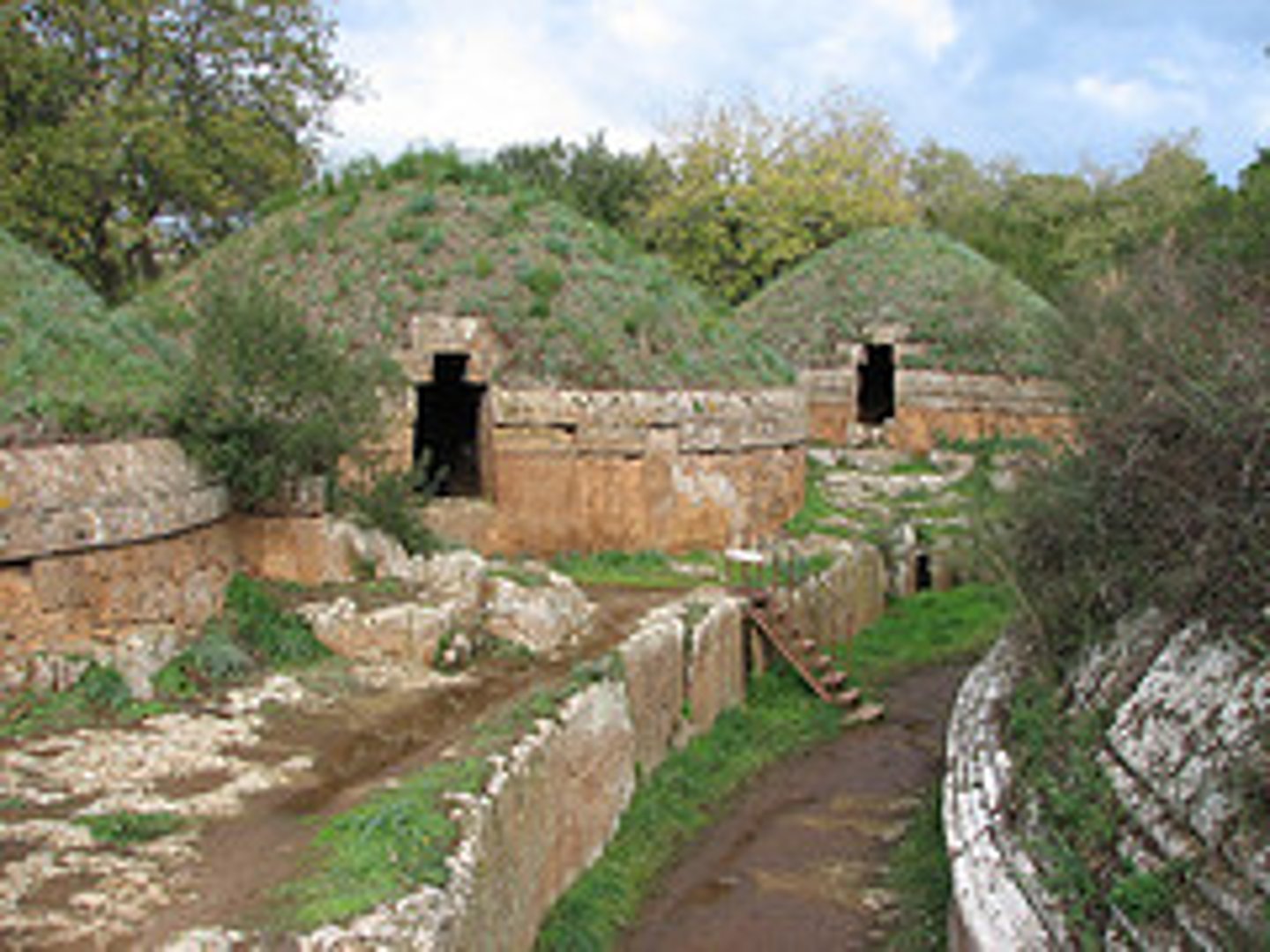
Banditaccia Necropolis at Cerveteri
- Etruscan tombs
-

Pietrabbondante Sanctuary - unfinished
- Troccola necropolis (5th-4th century BCE)
- Bovianum sanctuary: Ionic temple (3rd century BCE)
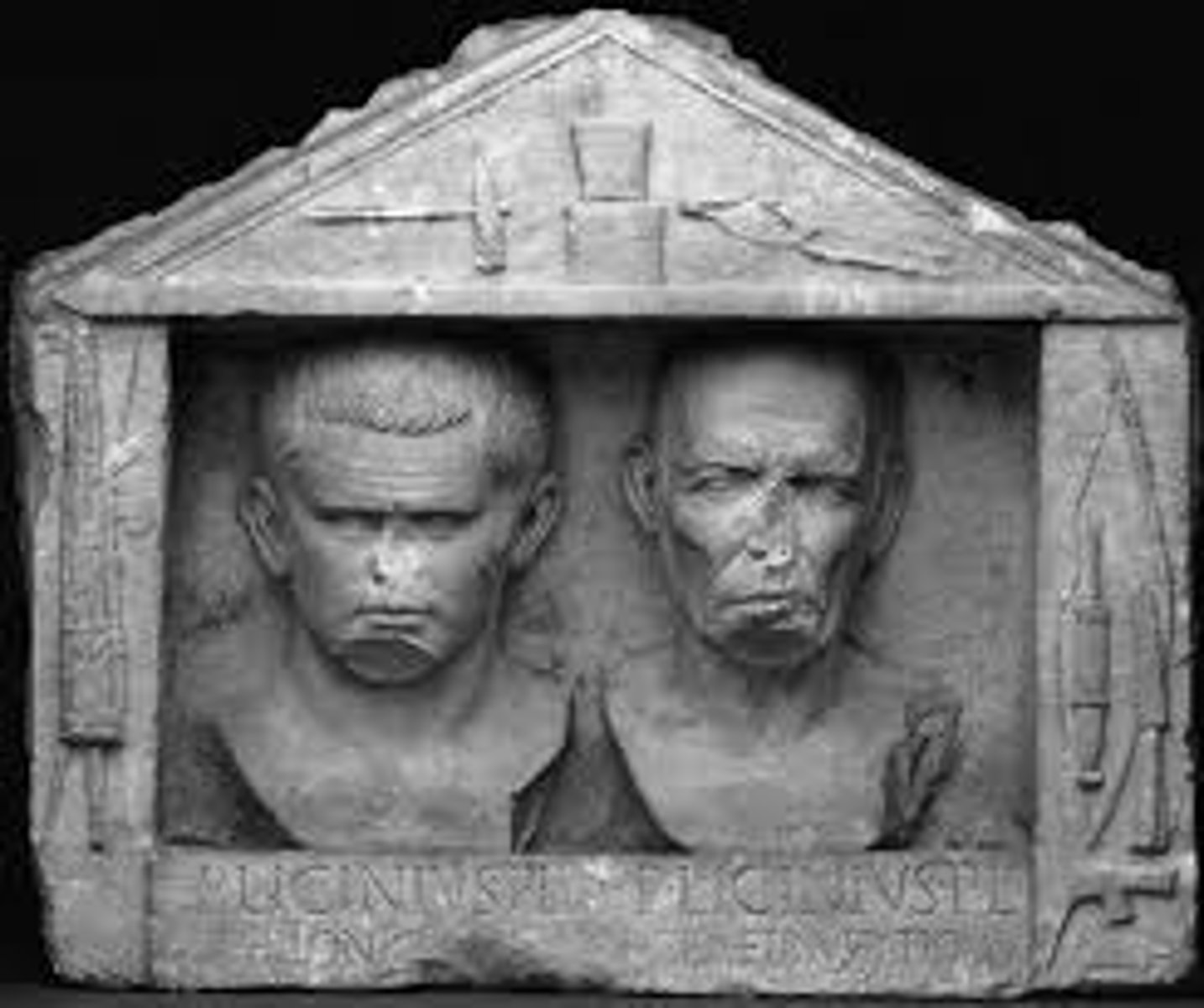
Freedmen's reliefs
This is an example of a portrait of two past slaves who are blacksmiths and sent this to their master
(Publius Licinius Philonicus, freedman of Publius and Publius Licinus Demetrius, freedman of Publius, made this for their master) they could use this when these freedmen would die as their gravestone in the family burial site (Niches).

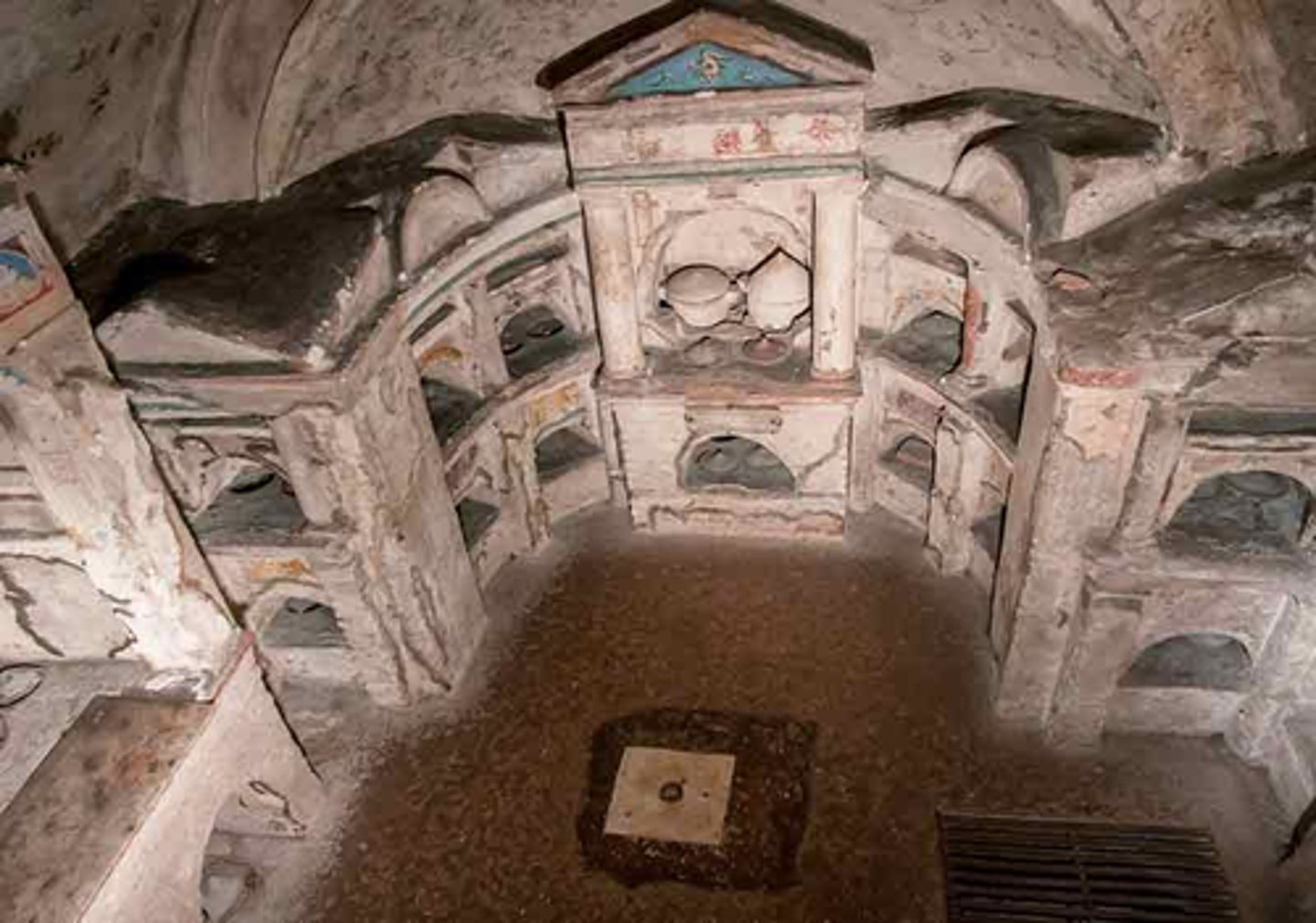
Tombs with Niches
- Tomb of the Flavii: Late Republican, Pompeii
- Niches contain portrait busts, cinerary urns, or sometimes both
- Each niche is labeled with the deceased's name
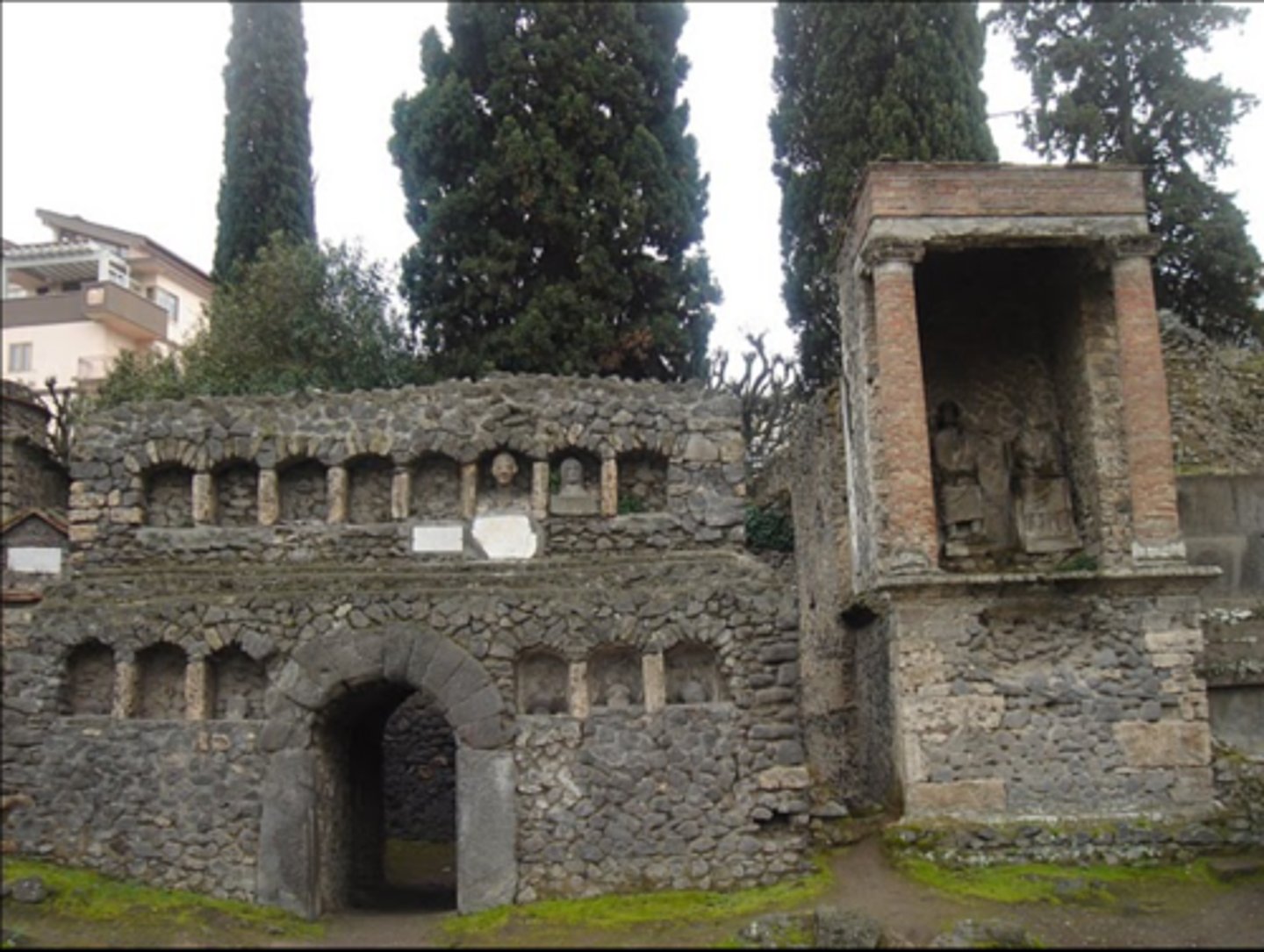

Columbarium of Pomponius Hylax
- On the via Appla, near the Porta Latina in Rome
- Columbaria are associated with slave and freedmen's burial
- usually underground, can contain burials for many people
- Building dates to between 14 and 54 AD (based on the funerary inscriptions inside)
- bought by Pomponius Hylas for himself and his wife in the Flavian period, who added a mosaic panel with their names

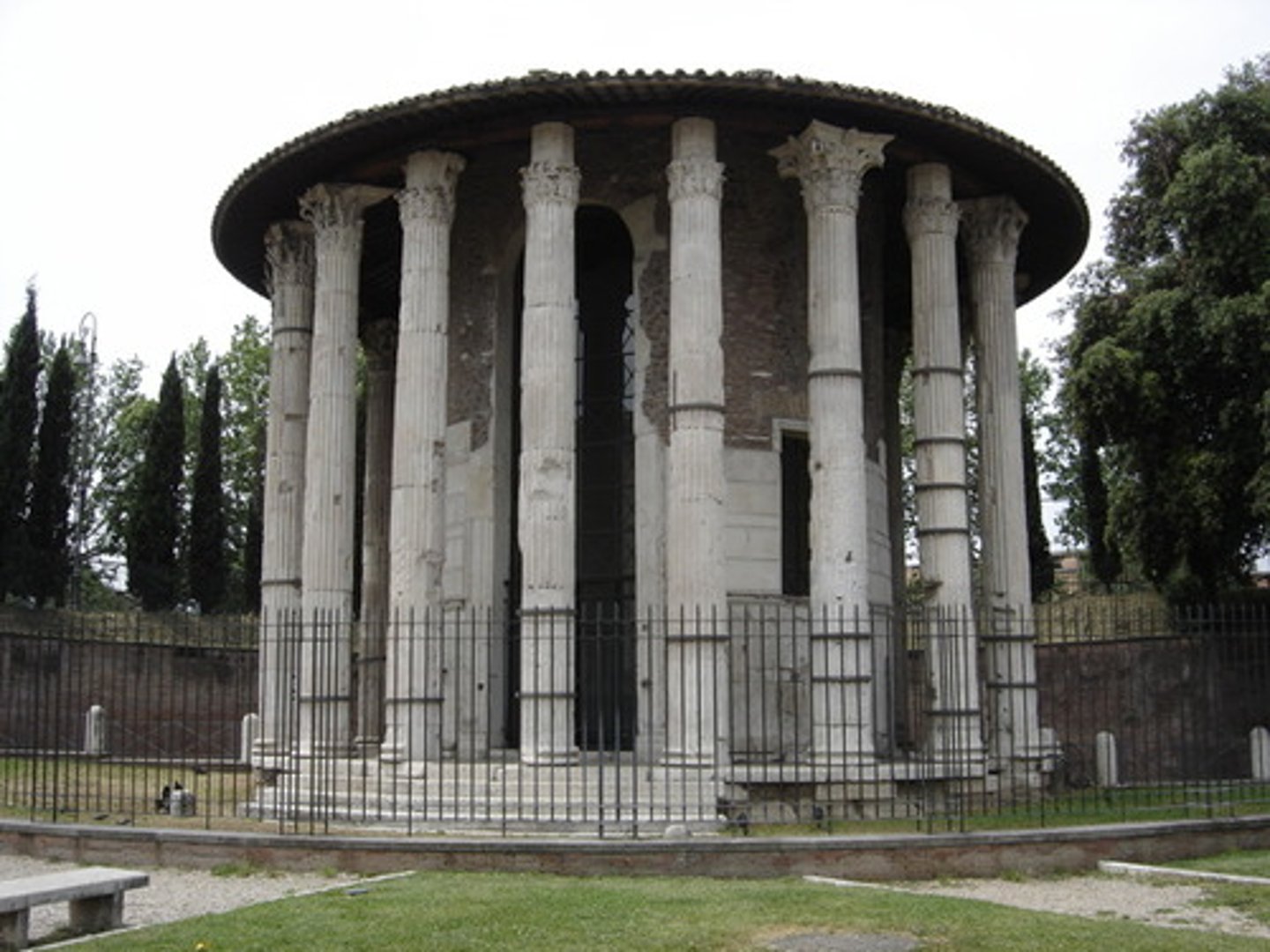
Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus
AKA Temple of JOM. Finished in 509 BC. Big temple dedicated to Jupiter, Juno and Mars on Capitoline Hill. Where Romans went when Gauls sacked Rome in 390 BC.
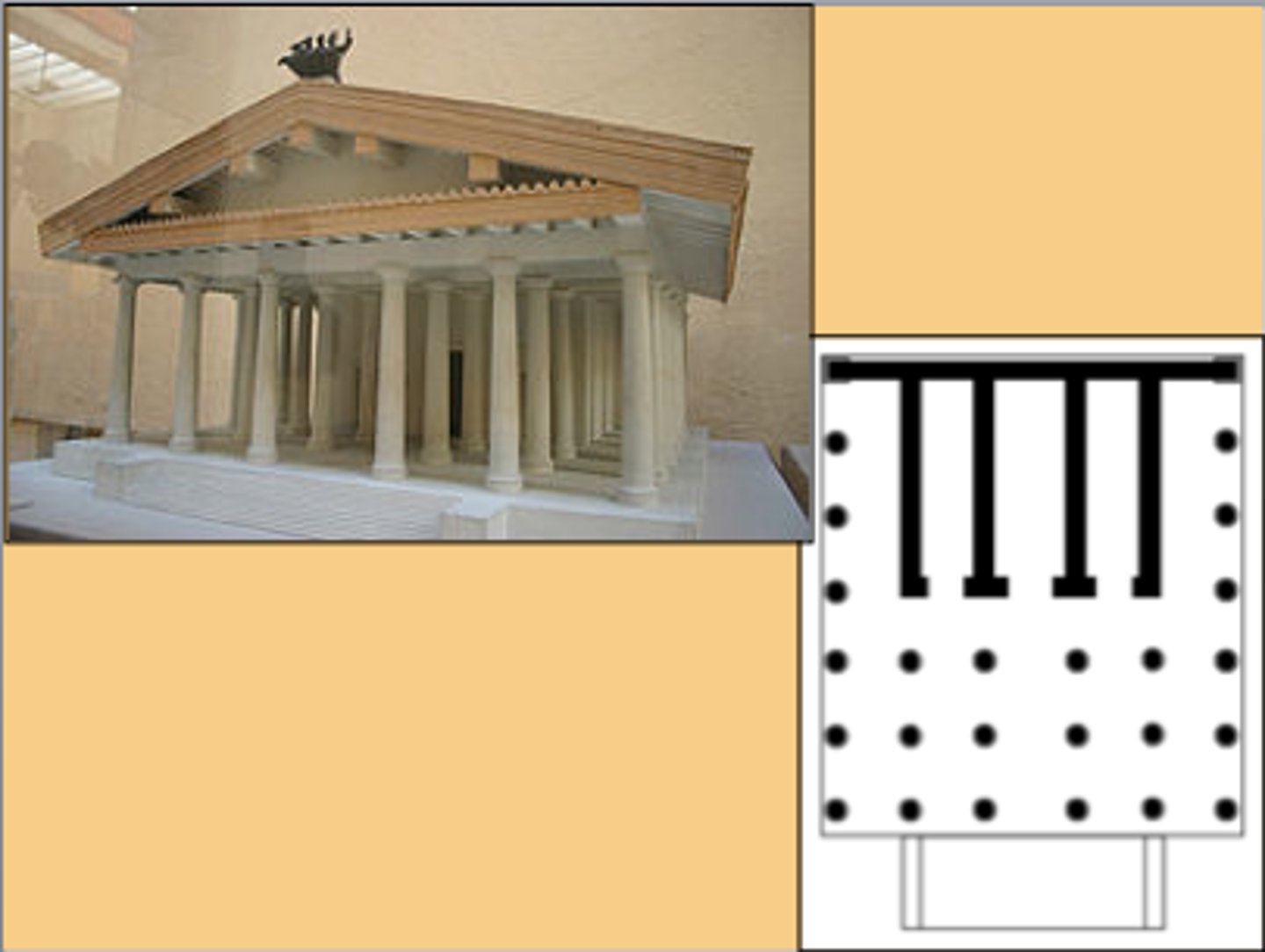
Manubial temple
a temple dedicated from the spoils of war, often by a returning general
- "triumphal booty"

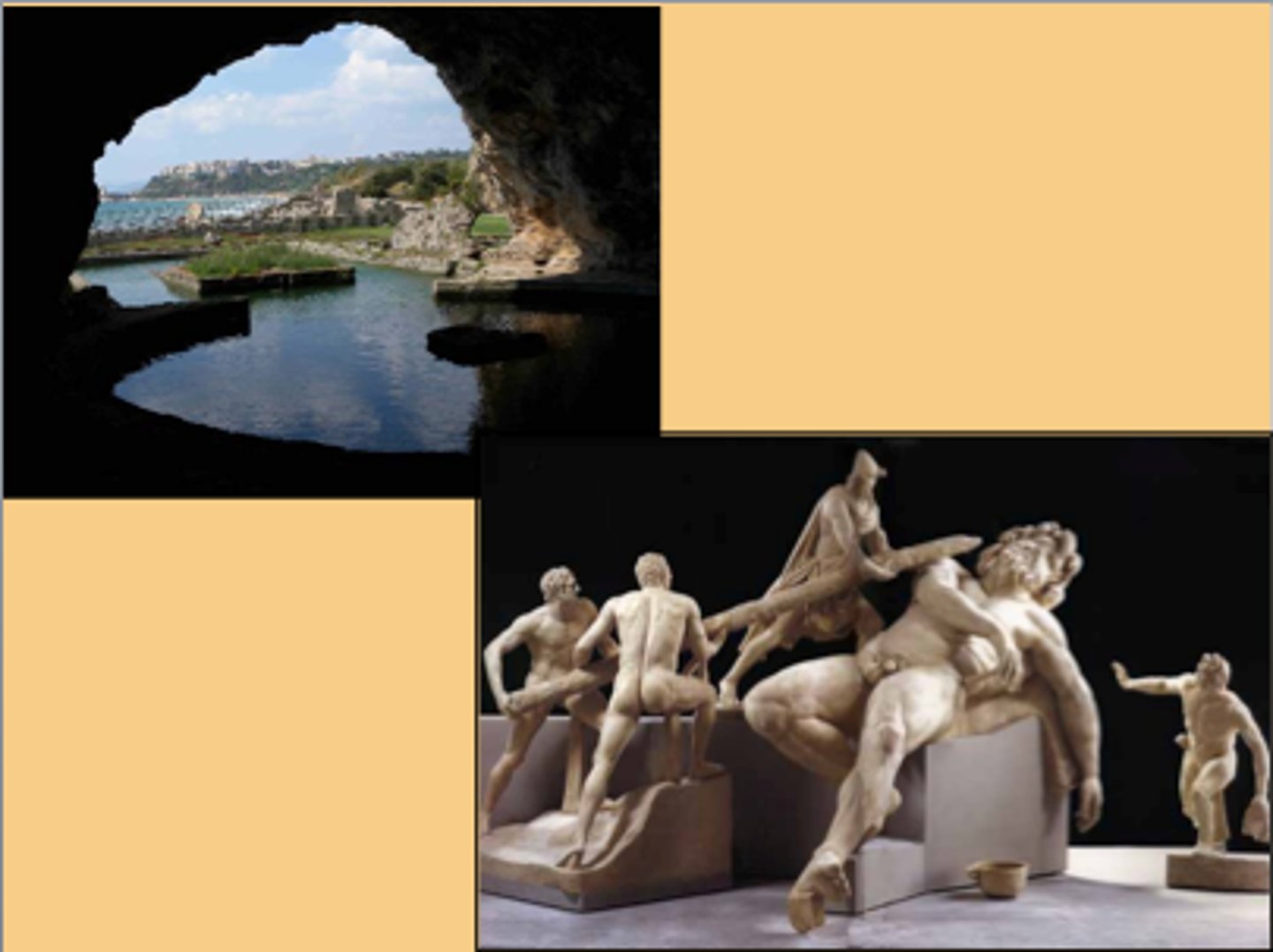
Sperlonga
site of a villa of Tiberius, 75 miles southeast of Rome, famous for the cave that housed large marble statuary depicting scenes from the adventures of Odysseus.

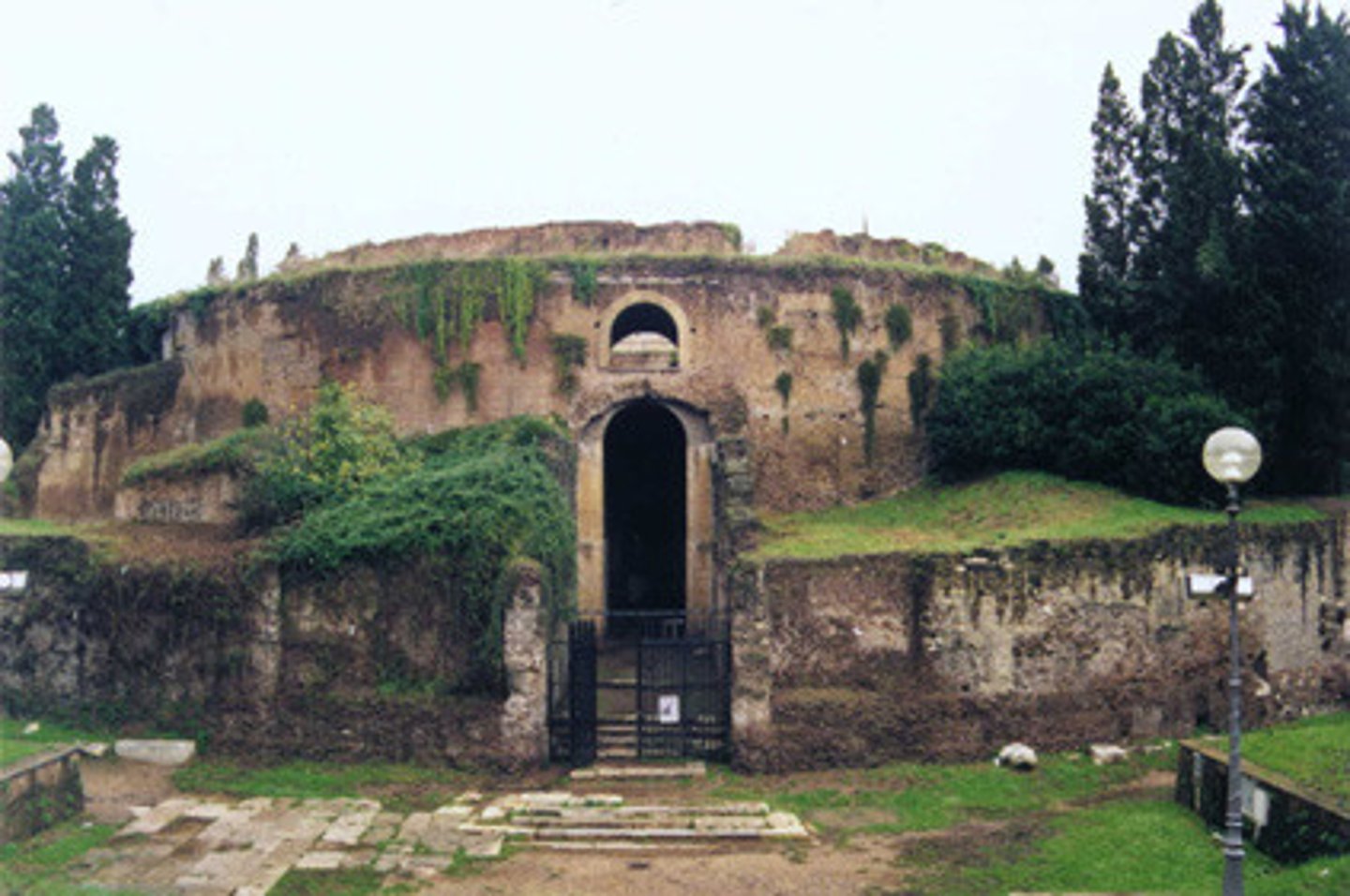
Mausoleum of Augustus
- Familia tomb for the Julio-Claudian dynasty
- Built 28 BCE, dedicated with a bronze copy of Augustus' Res Gestae at the front
- Top: probably meant to imitate an Etruscan burial mound

Arelate
- Modern Arles France, founded as a Roman colony in 46 BCE
- Replaced the town of Theline
- Close to Massalia, a key emporia sit
- Major shipbuilding center
- Major features: Augustan wall, two municipal arches of the Republican period, forum, theater, amphitheater, circus

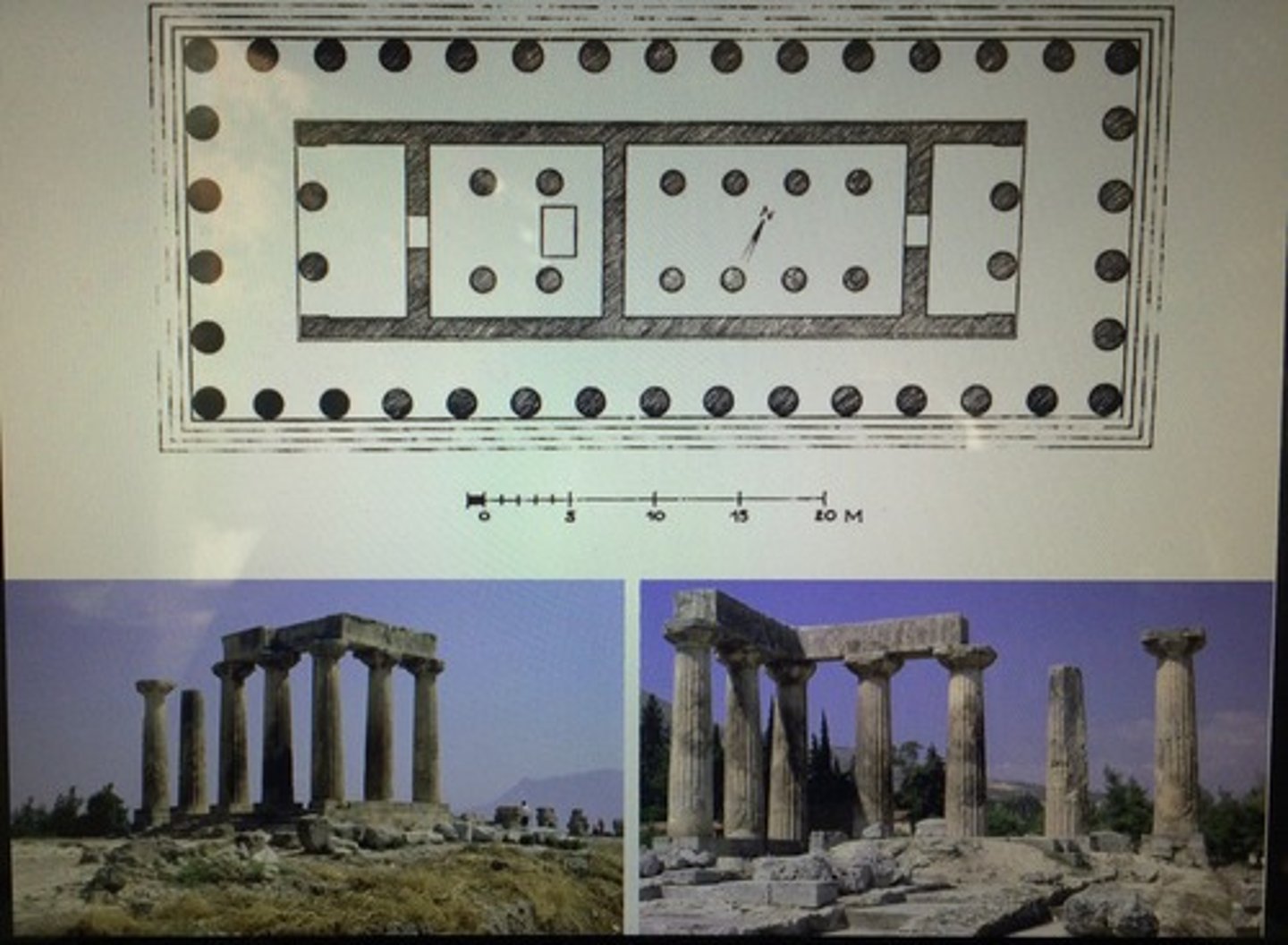
Corinth
a leading city of ancient Greece famous for its architecture, pottery, and shipbuilding
Villa of Prima Porta
One of the "Garden triclinia"

Manumission
- Slaves can buy their own freedom or be freed by their owners (usually in wills)
- Question of marriage
- Freedmen still required to act as clients, pay a portion of earning to former owner
- Augustales
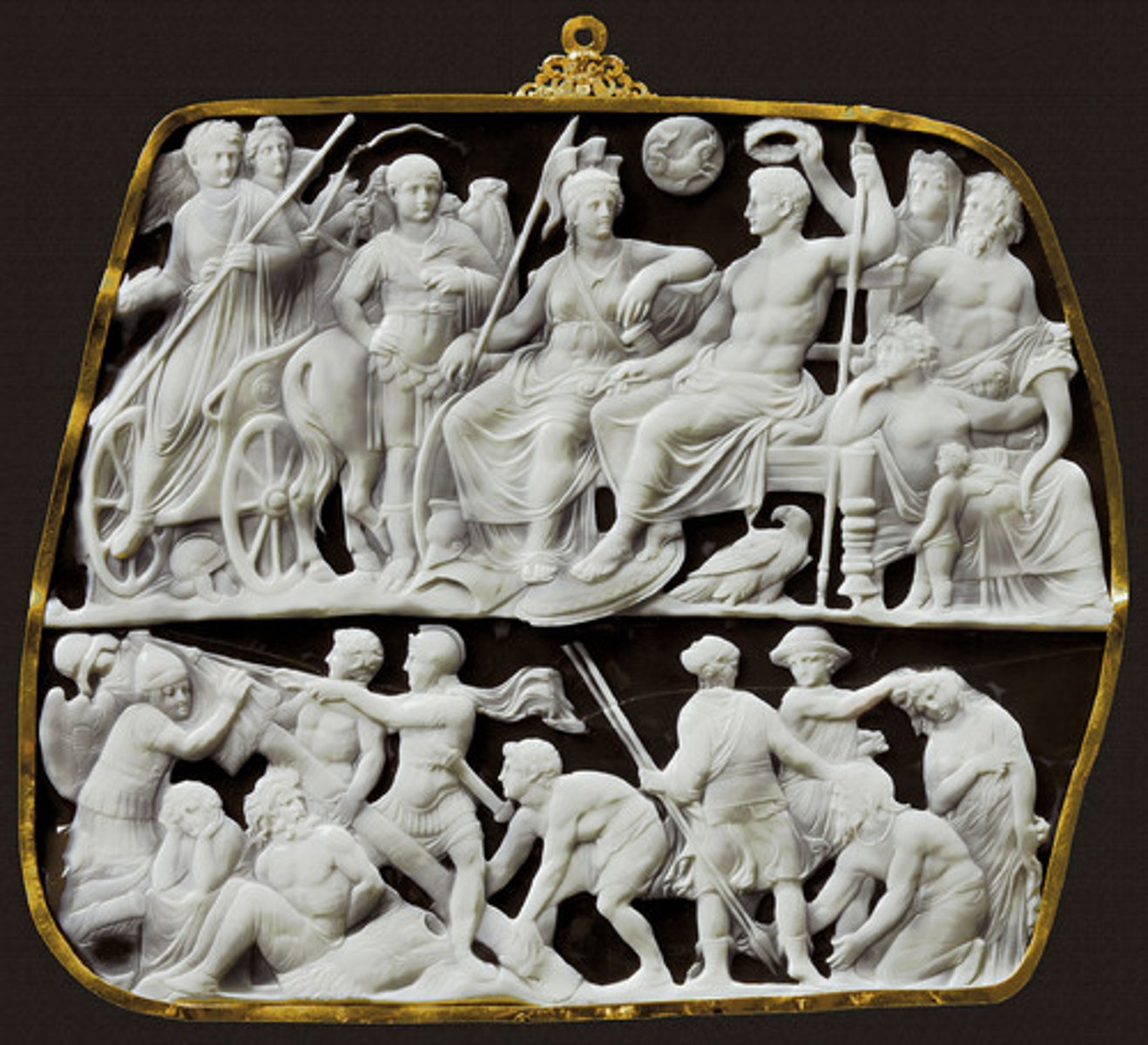
Gemma Augustea
large cameo. Augustus portrayed as Jupiter, seated next to the goddess Roma, the lower scene depicts Roman soldiers erecting a war trophy in the presence of captured barbarians

Augustus achieves these values through his building program
- Piety (pietas)
- Virtue (virtus-gendering is important here)
- Family (Familia)
- Conservatism and continuity
Practice Exam Essay Question
Hellenistic art is often described as culturally eclectic because it incorporates foreign ideas, religions, and ideas into Greek art in creative and surprising ways. Is Hellenistic art still Greek? Discuss key characteristics of Hellenistic culture and 2-3 examples of Hellenistic art and architecture in your answer.
Characteristics for sculptures: more expressive and dynamic styles (baroque)
examples: the case study of the pergamon altar, "Slipper Slapper", Venus di milo, Manubial Temple
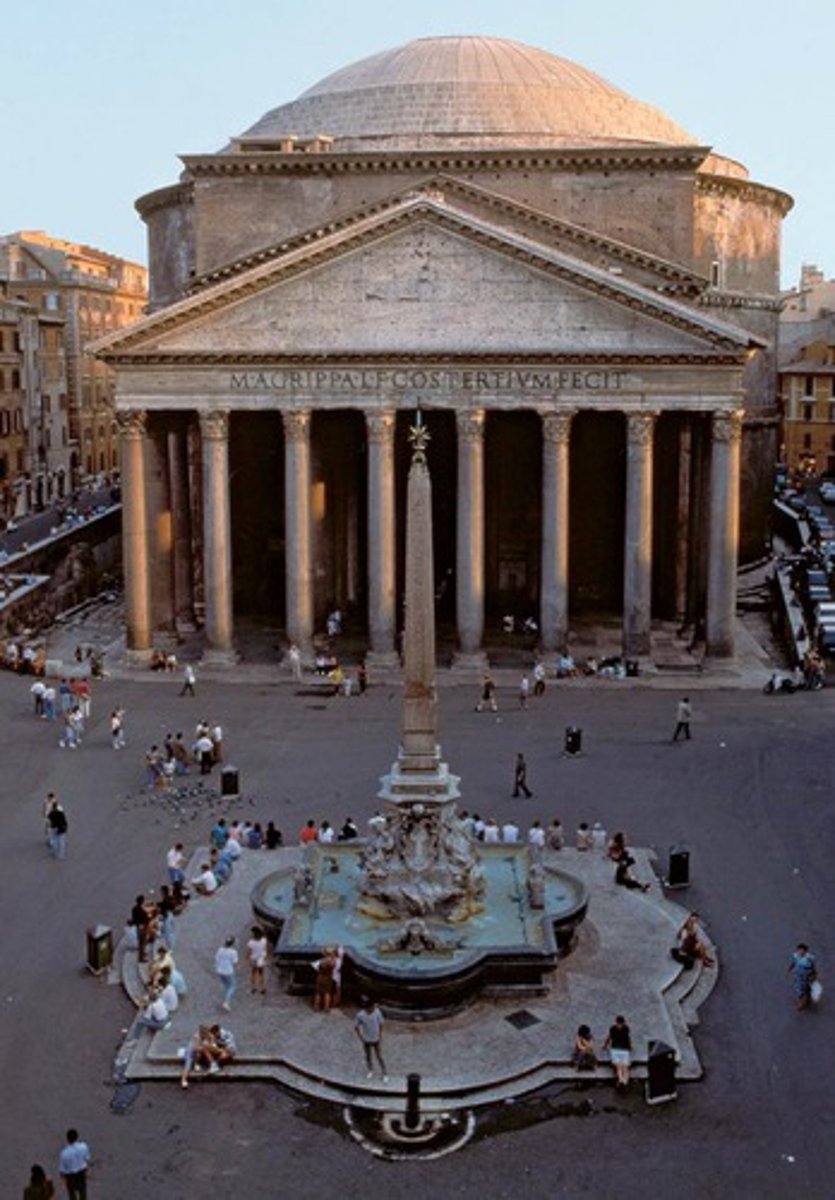
Pantheon
First commissioned by Marcus Agrippa during the reign of Augustus, completed by Hadrian in 128 AD• Part of a complex of buildings with the Baths of Agrippa, Basilica of Neptune• Destroyed in a fire in 80 AD, rebuilt by Domitian, burned again in 110• Largest free dome in the premodern world: height to the oculus and diameter of interior circle are43.3 meters

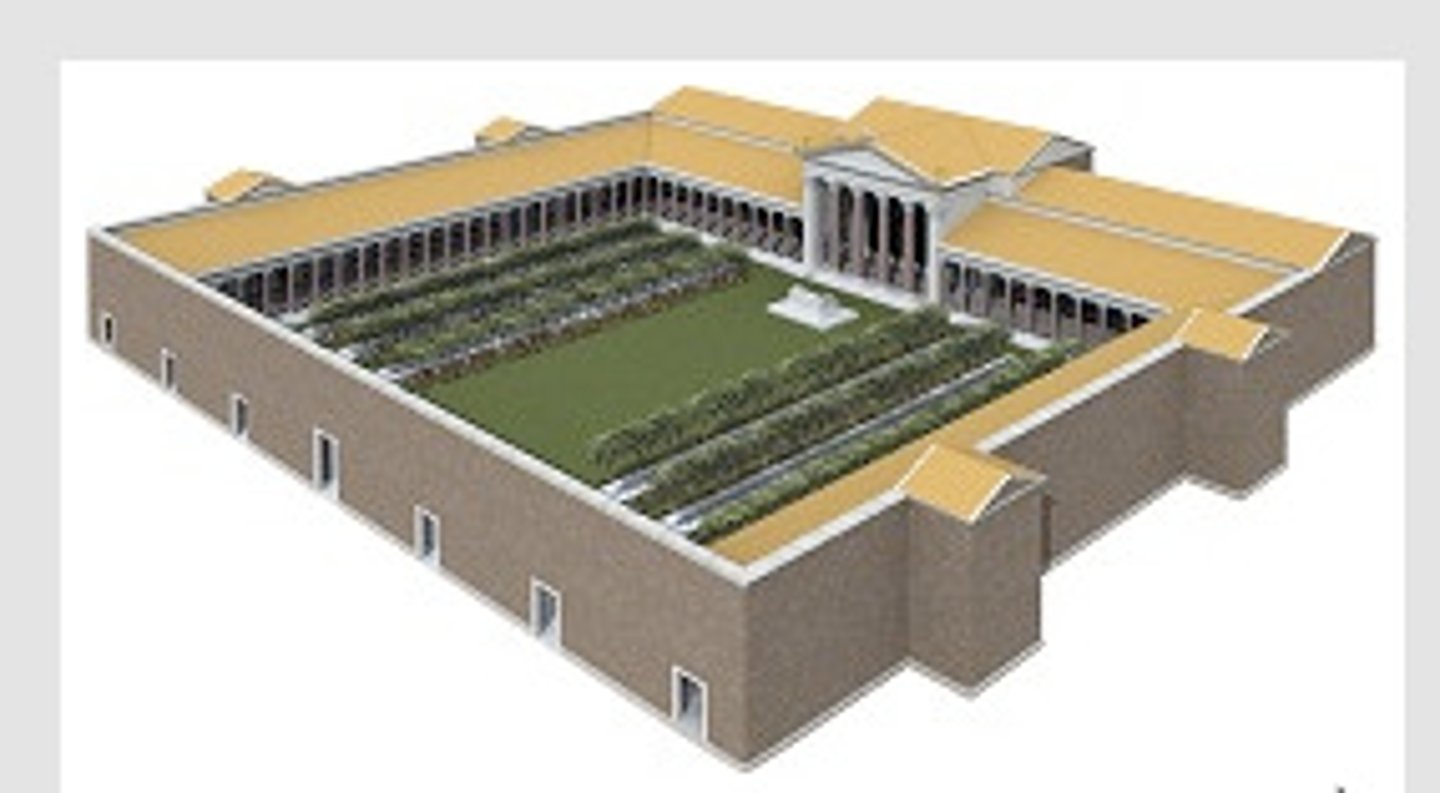
Timgad
Algeria; 100 BCE; Emperor Trajan was the patron; ruins are noteworthy for representing one of the best extant examples of the grid plan as used in Roman city planning
Trajan's Forum (and the buildings/monuments it contains)
Main monuments: equestrian statue of Trajan, Basilica Ulpia
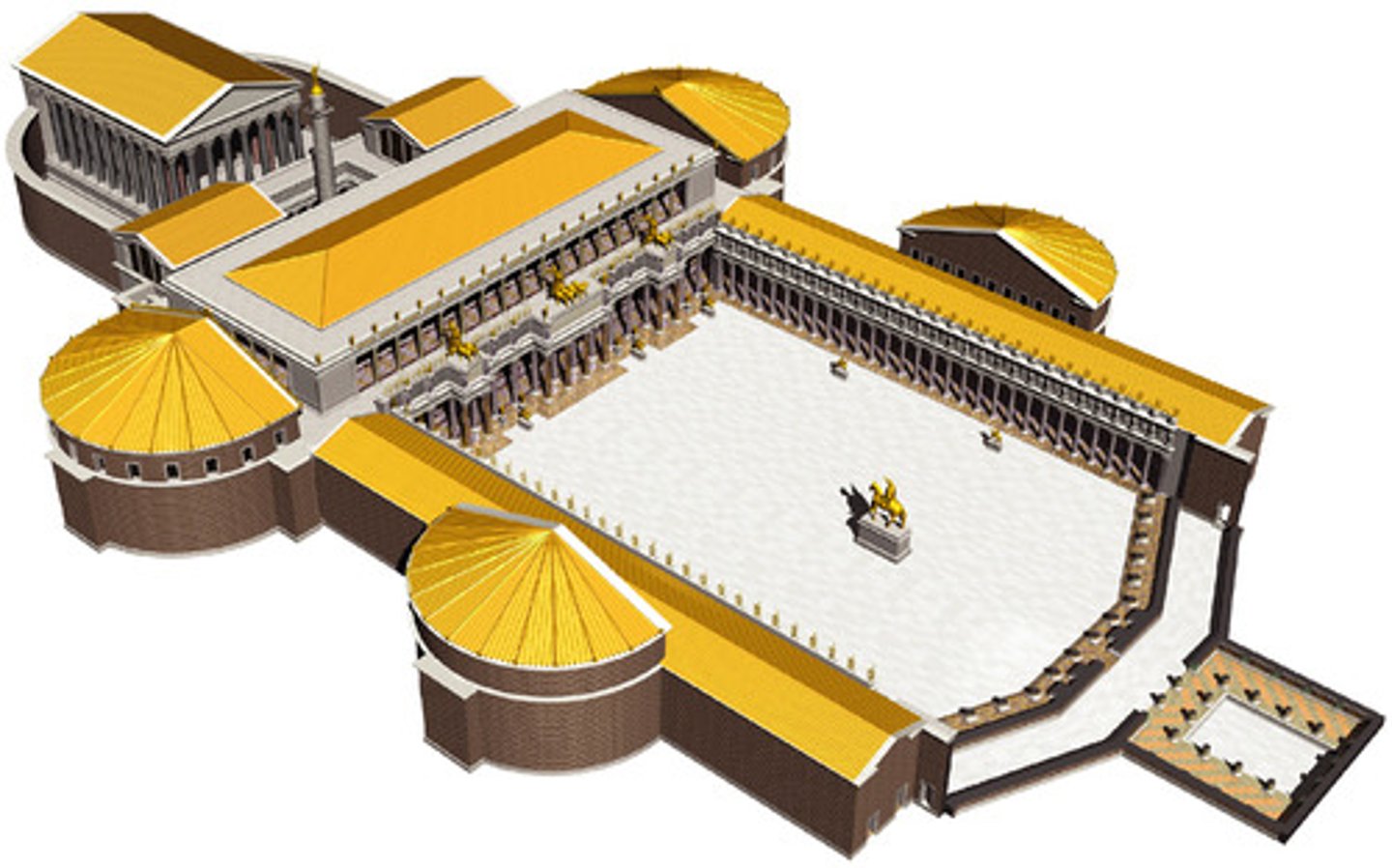
Templum Pacis
Temple of Peace

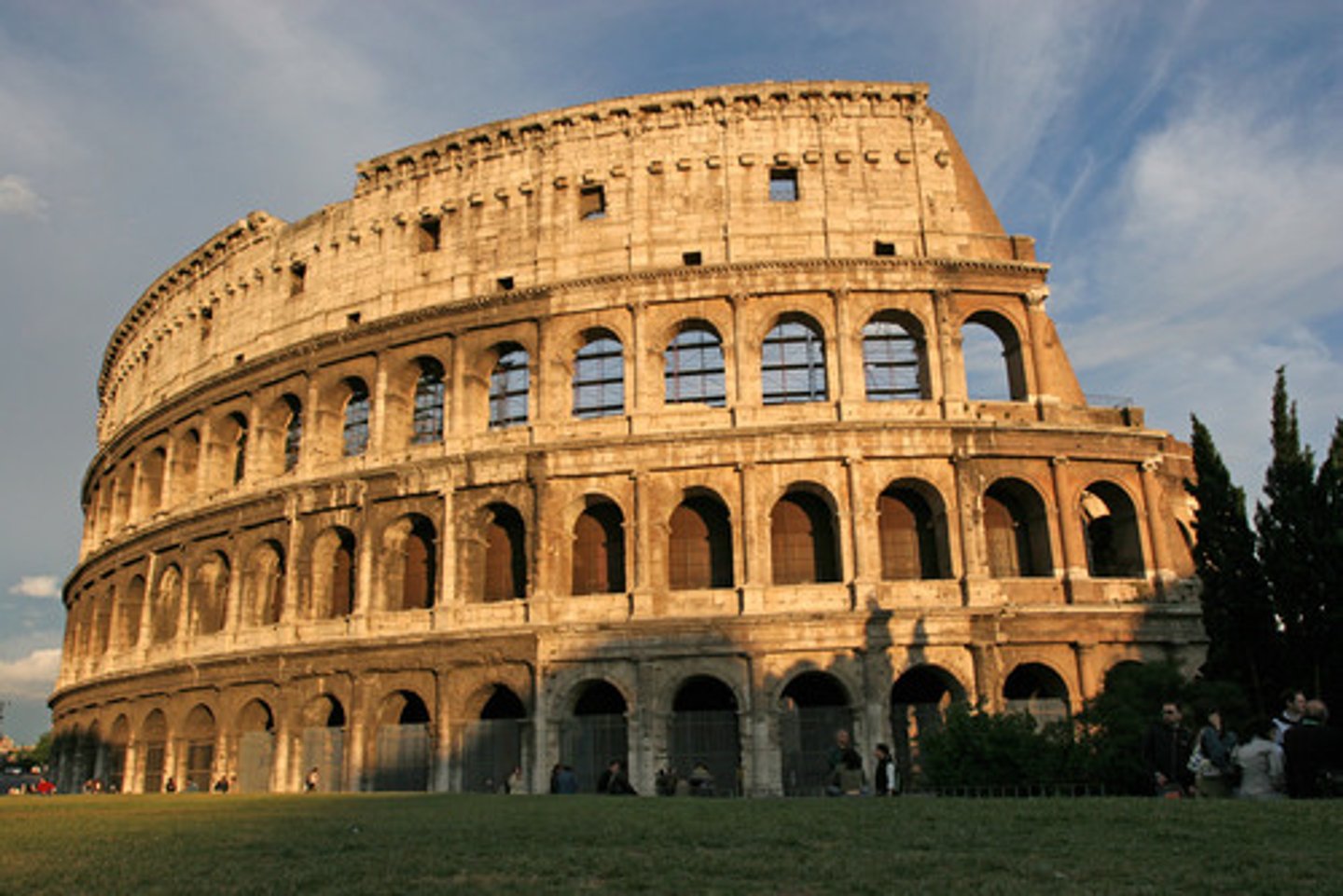
Colosseum
- The first permanent amphitheater in Rome
- Inaugurated by Titus finished by Domitian
- Elaborate social and gender segregation in the seating arrangements

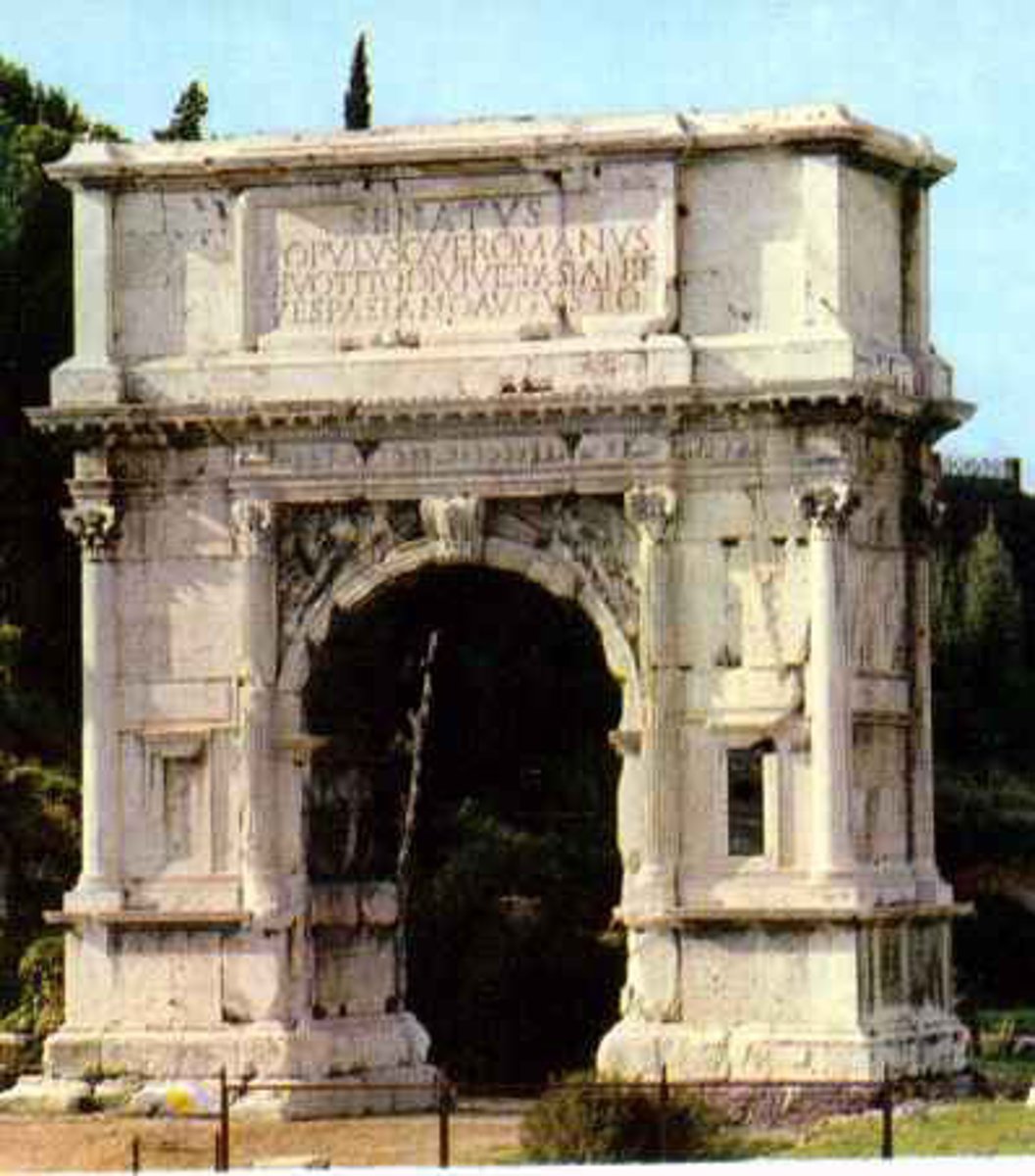
Arch of Titus
81 CE

Forum of Pompeii
regular elongated rectangle, 38 times 142 meters and was built with surrounding colonnades
The lupanar at Pompeii
official brothel
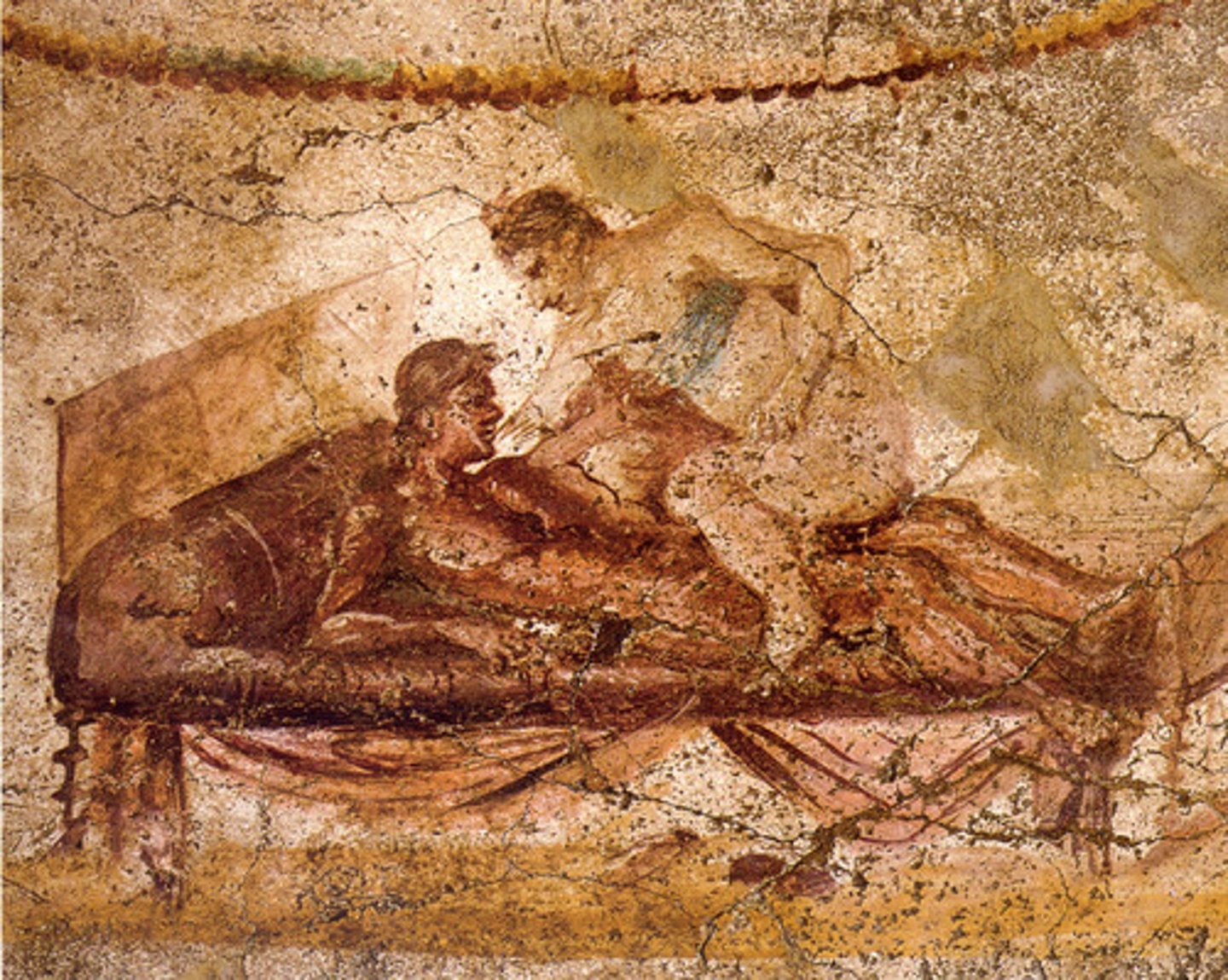

The House of the Faun at Pompeii
-Represents extreme decoration of roman homes
-threshold mosaics spell welcome, depict a dog
-narrative scenes on the walls
-friezes showing figures and landscapes

Ephesus (especially the Library of Celsus and the Terrace Houses)
Founded in the 10th century, becomes a major city in the Hellenistic and Roman periods
Dedicated to Artemis, local cults devoted to founder Androclus
Major city in the Lydian and Persian Empires, part of the Delian League of the early 4th century
Becomes a key center for religious and economic life in the Roman period

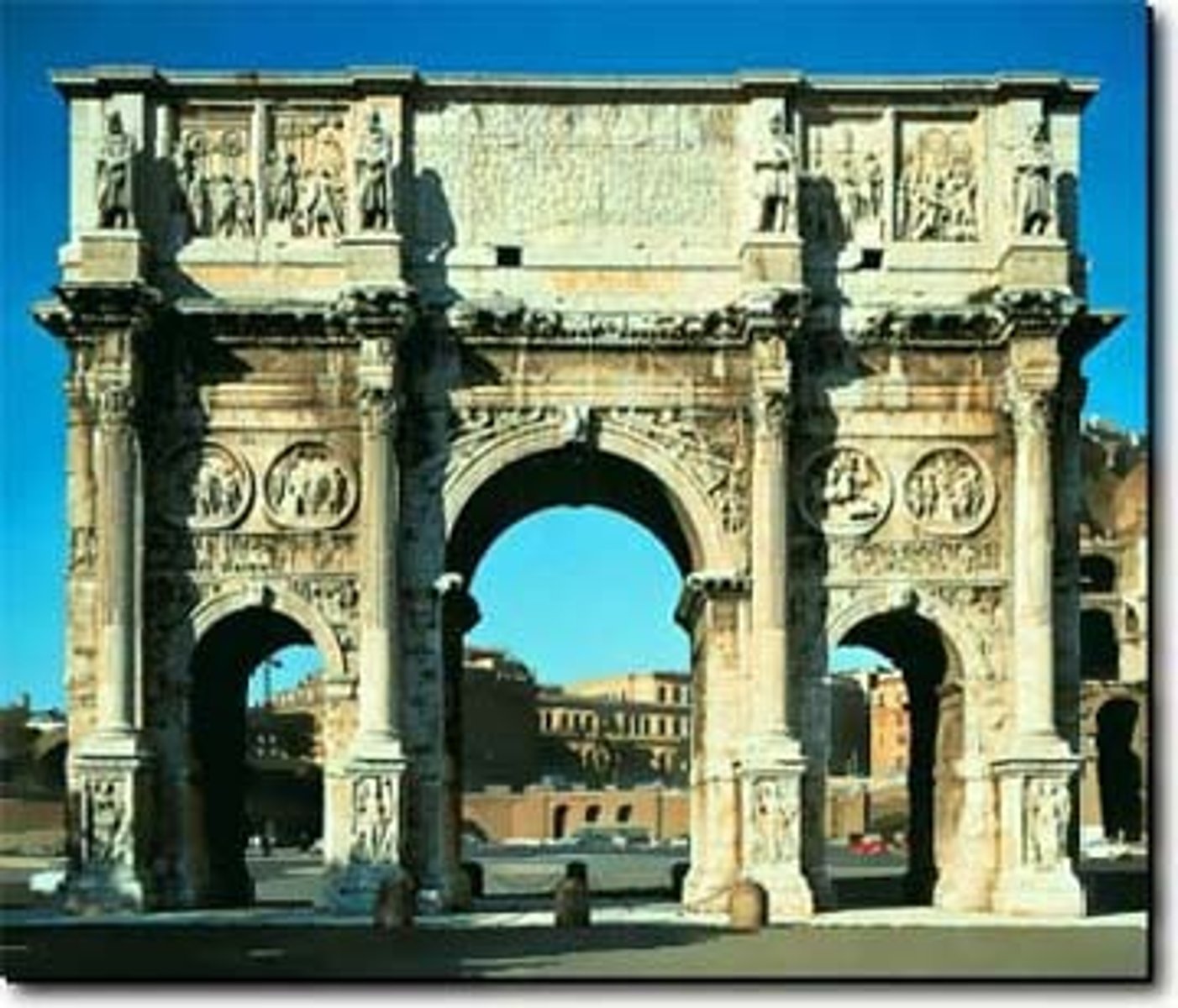
Arch of Constantine
- dedicated in 315 A.D. in honor of his defeat of Maxentius
- Located near the Colosseum, three archways
- Decorated with sculpture taken from earlier monuments (Trajan, Marcus Aurelius, Hadrian)
- Friezes from the time of Constantine - stylistic change, non-naturalistic approach, lacks spatial depth, Constantine is disproportionately large, other figures stumpy, doll-like

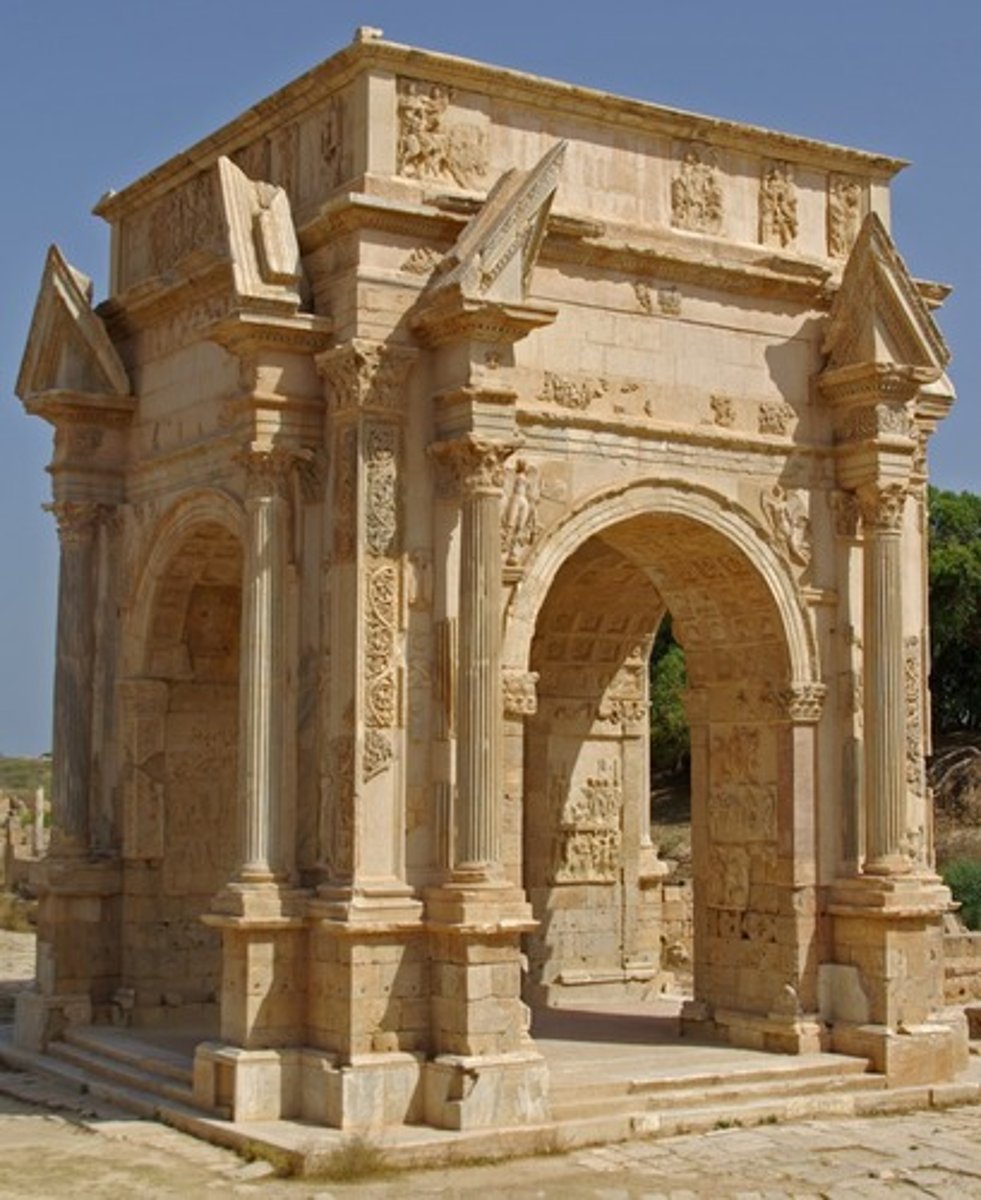
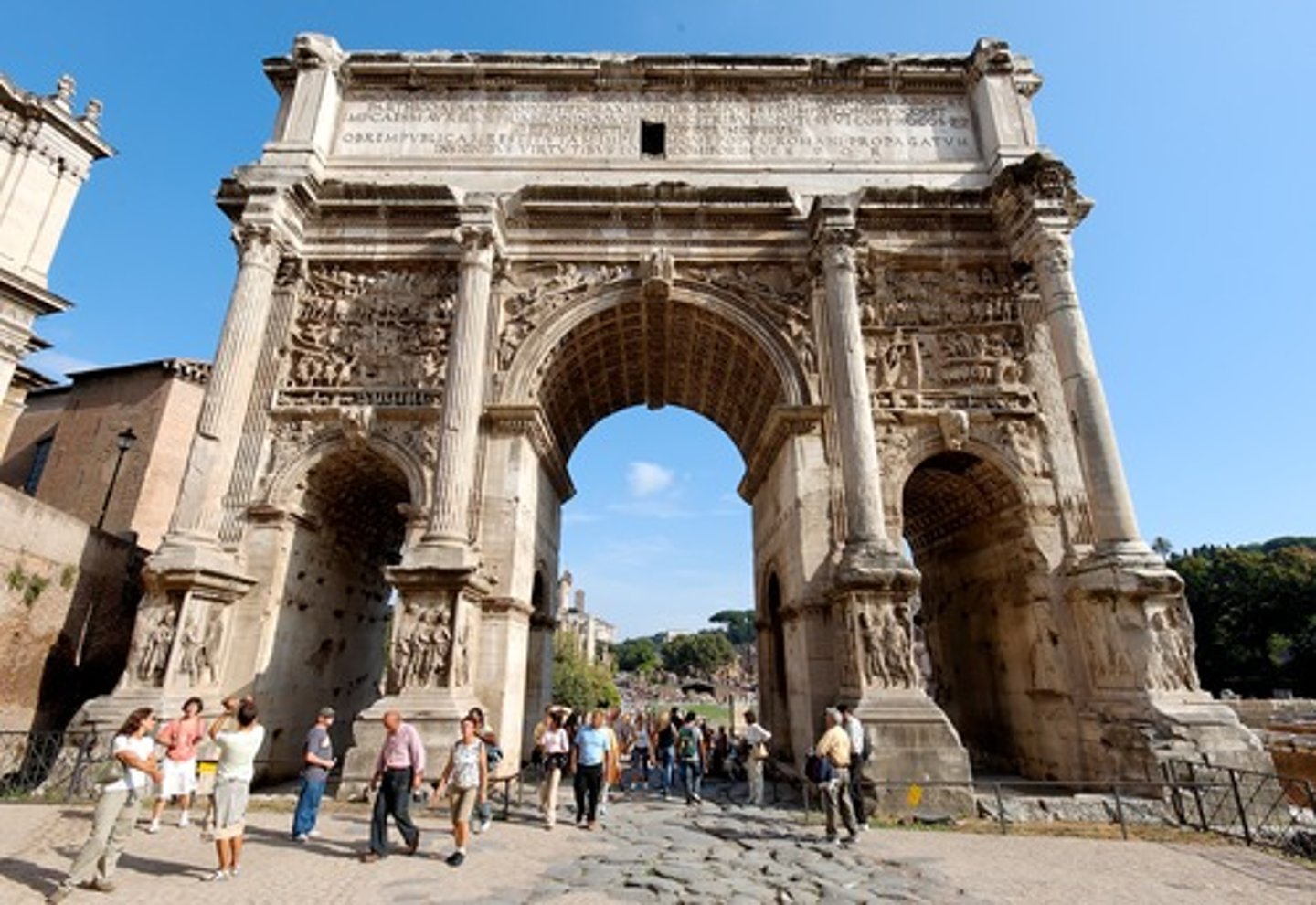
Arch of Septimius Severus
• Dedicated in 203 AD to commemorate Septimius Severus' victory over the Parthians at Ctesiphon in 197 AD • Geta removed from the dedicatory inscription as part of his damnatio memoriae • New style of representation-panels depict multiple aspects of historiated events in one space without clear registers

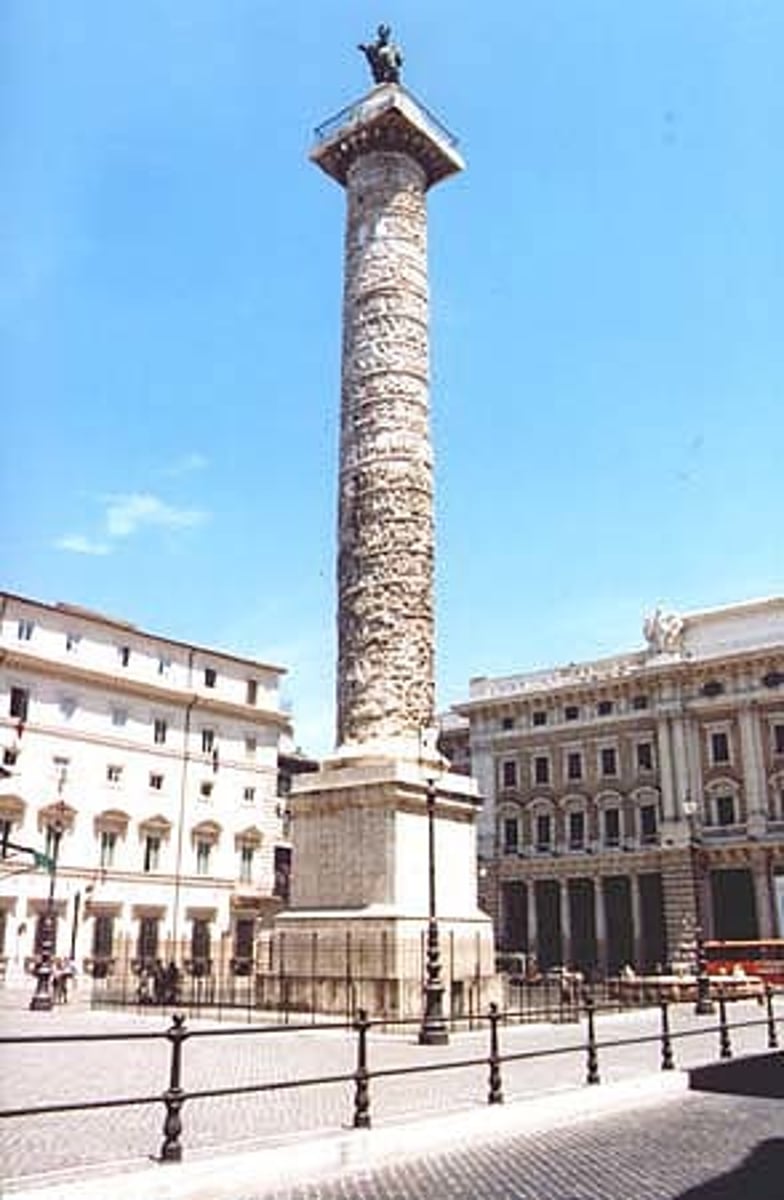
Column of Marcus Aurelius
was carved in the late 2nd century, more stylized and less strictly accurate physical and historical representation became popular, exaggerated gestures and distorted features that were obviously intended to evoke a sense of emotion or horror as might be expected in engaging in a conduct of war

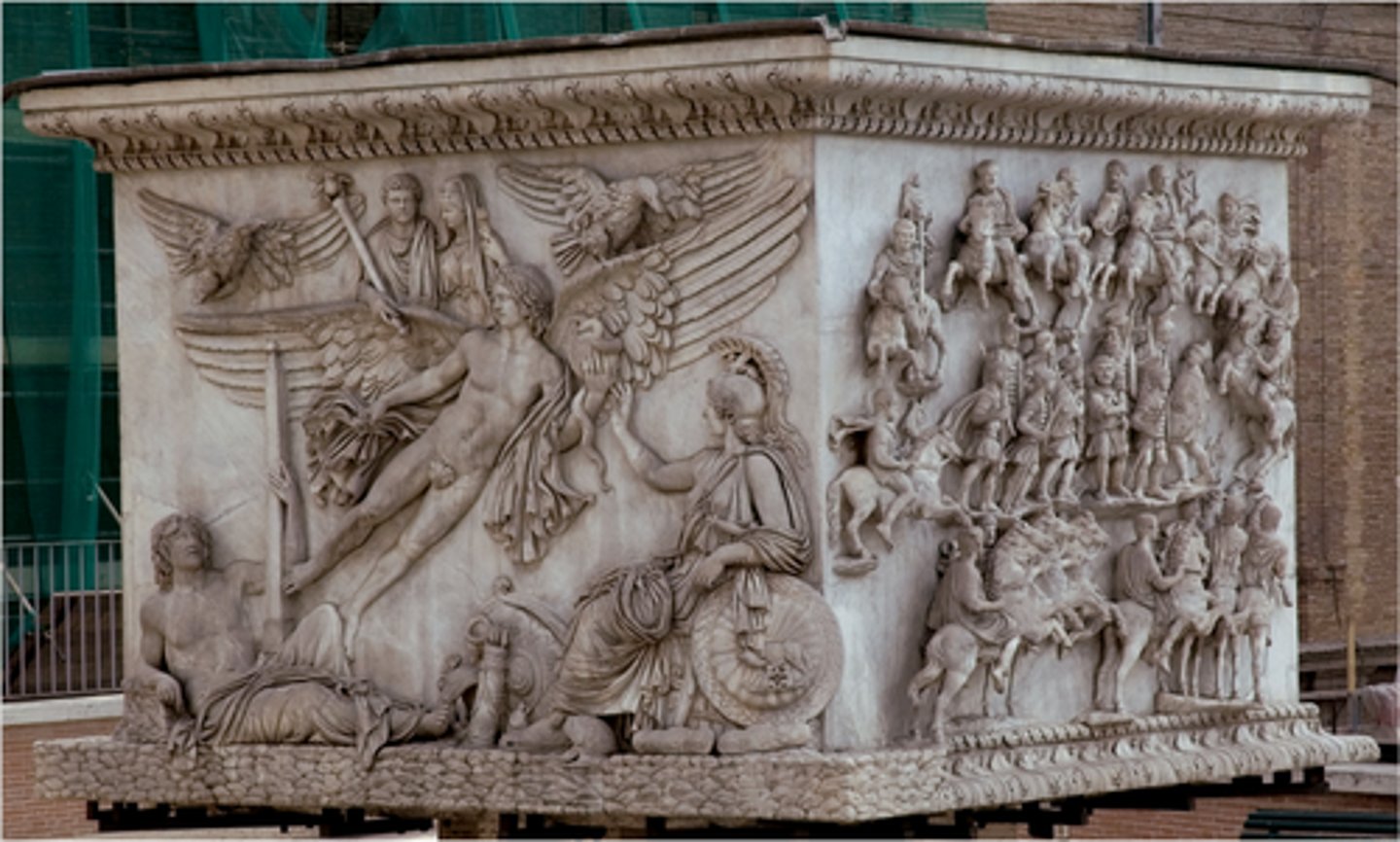
Base of the Column of Antoninus Pius
restored in 1706-08 and erected in the centre of Piazza di Montecitorio

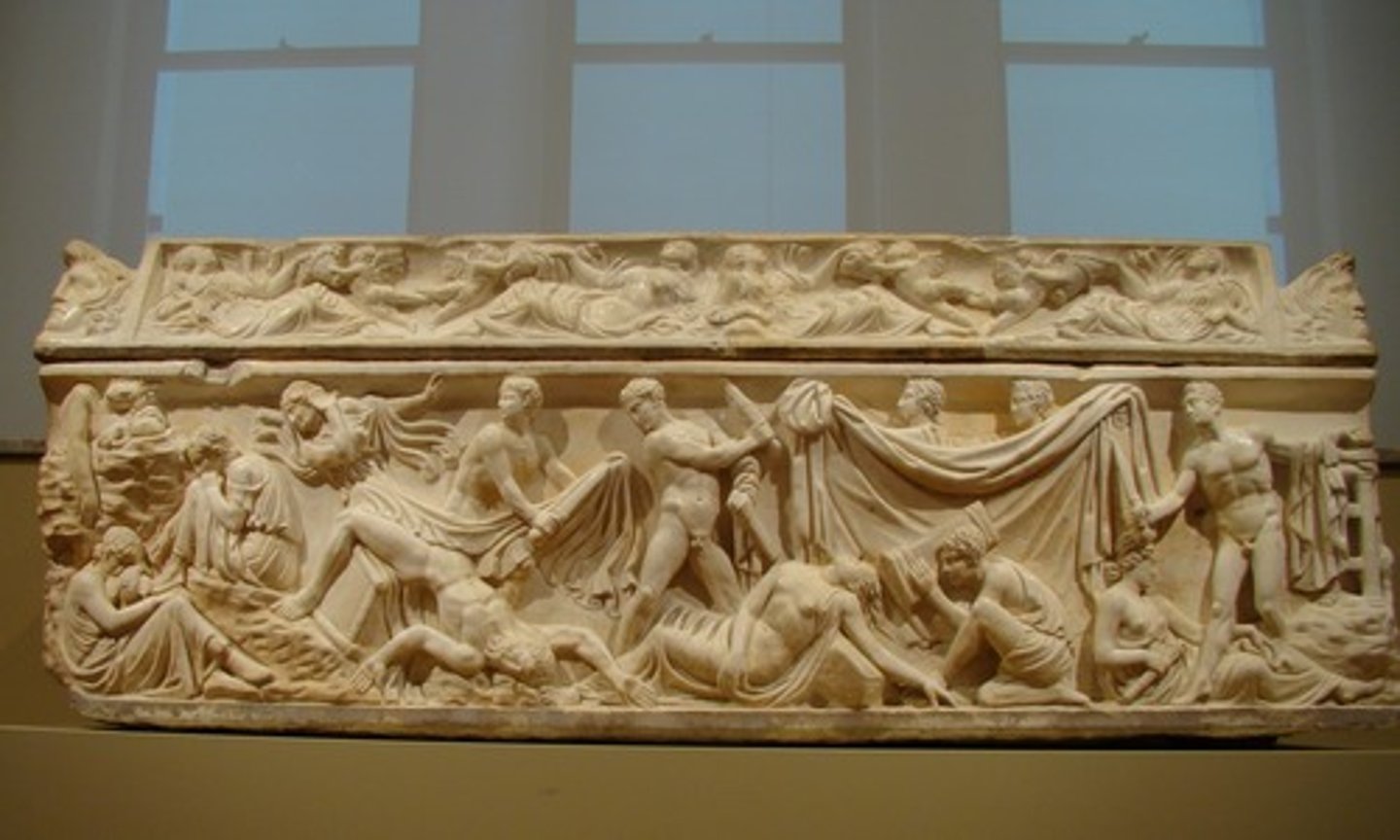
Mythological sarcophagus
heir to a long Roman tradition that celebrated the past by preserving images of the dead

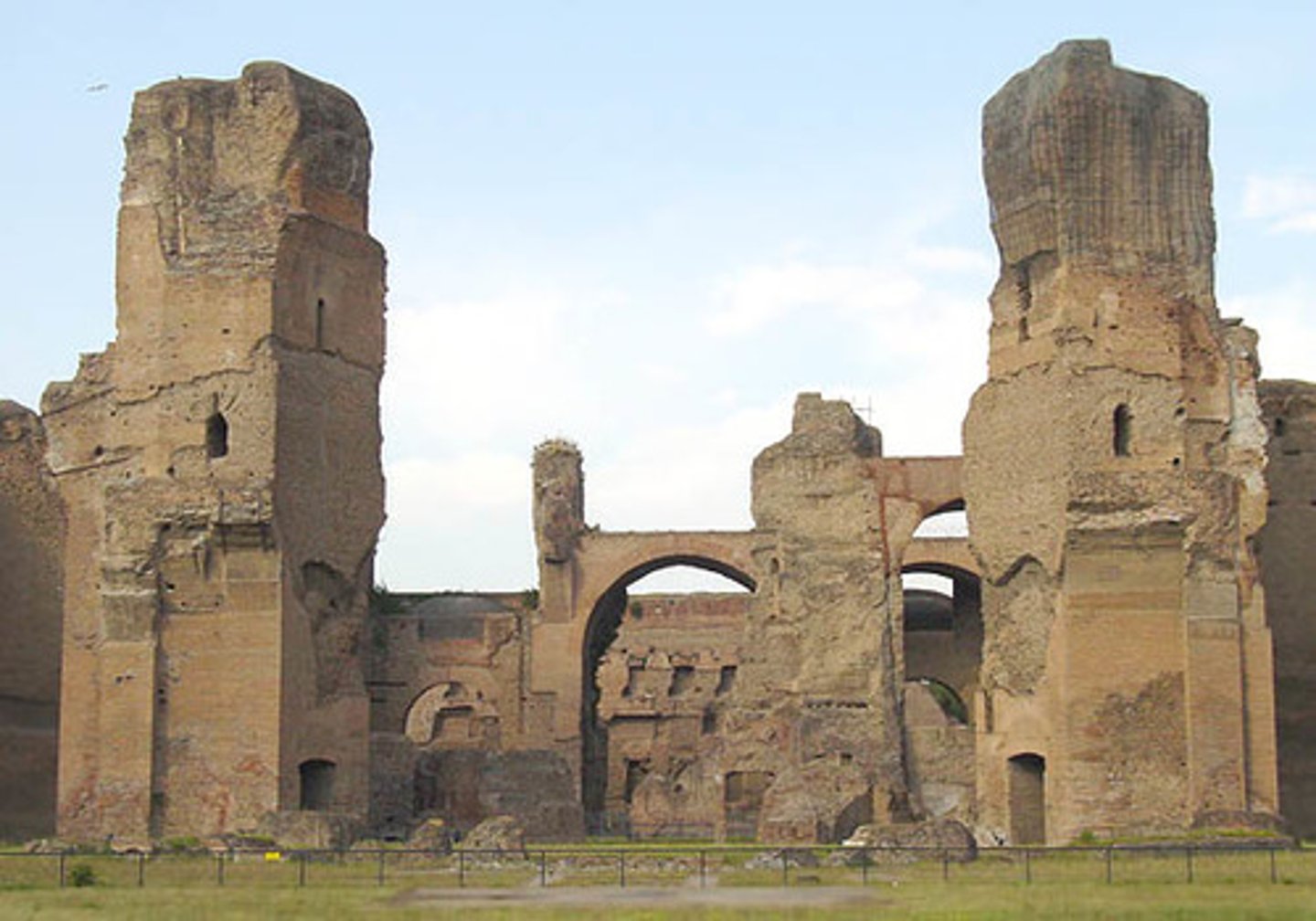
Baths of Caracalla
Built by Emp. Caracalla to please his citizens (vicious ruler) large pools, spas, gym, gardens...basically ancient country clubs for citizens to relax in luxury

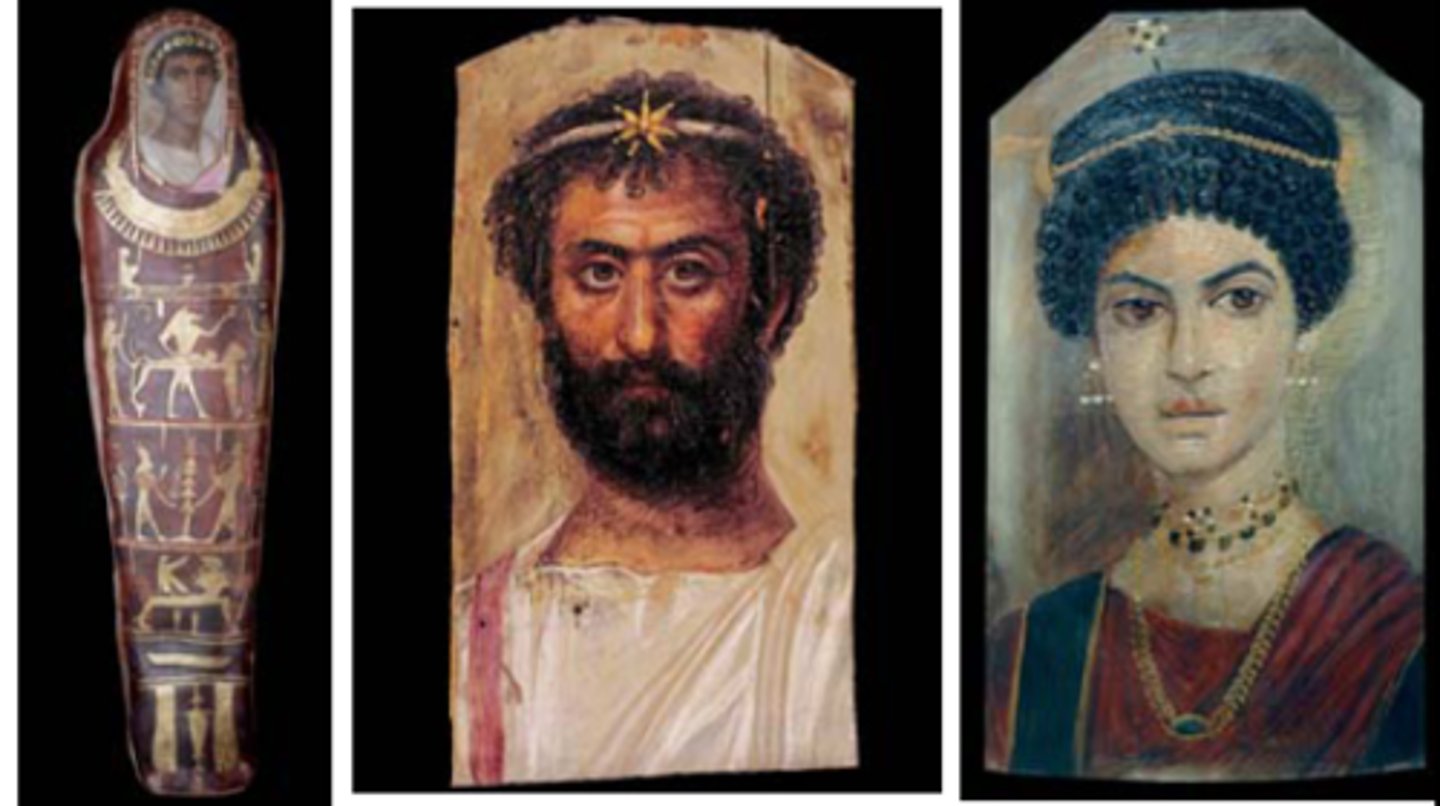
Portrait mummies

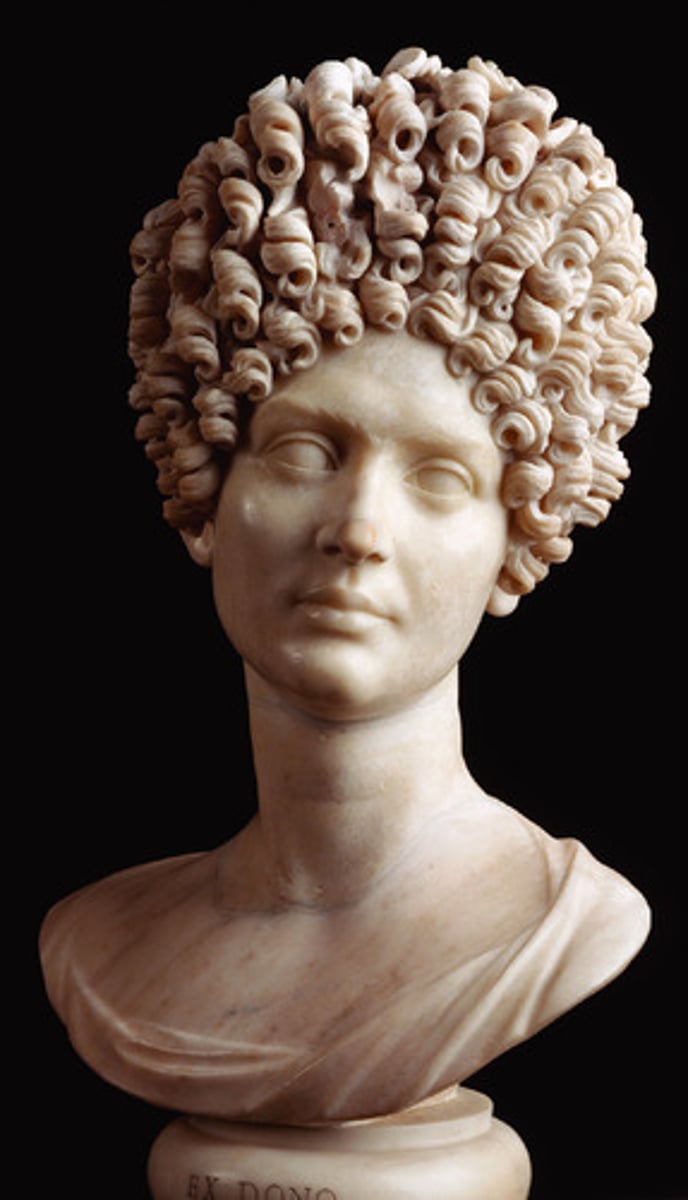
The Flavian Lady
90 C.E., Imperial, idealized beauty with graceful long neck and tilted head, cutting-edge fashionable coiffure, hair creates a dramatic interplay of light and shadow, hair created with a drill

Imperial portraits
Displayed by rulers to assert legitimacy, like in the Ching Dynasty

Leptis Magna
birthplace of Septimius Severus, gets a lot of funding and becomes the most important city in Roman North Africa (modern day Libya)
