Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Anatomy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
31 spinal nerves
8 cervical
12 thoracic
5 lumbar
5 sacral
1 coccygeal
Somatic motor vs Visceral motor
Somatic sensory vs Visceral sensory
Somites
will become body tube (peripheral skeleton, muscles, dermis)
What is responsible for body tube?
somatic nervous system
What is responsible for gut tube?
autonomic nervous system
CNS
brain and spinal cord
formed by neural tube
PNS
spinal nerves and cranial nerves
ganglia formed by neural crest cells
Somatic nervous system
somatic nerves innervate somites and their associated dermis
somatic motor: (efferent) innervates skeletal muscle
somatic sensory (afferent): touch, vibration, proprioception, pain
Somatic nerves
Sensory cell bodies are in a ganglia outside the CNS (DRG for spinal nerves, cranial nerve ganglia for cranial nerves)
Derived from neural crest
Somatic sensory neuron have distal axons that innervate a dermatome and proximal axons that synapse in the CNS
Motor neurons are located in the ventral horn of the spinal (brainstem nuclei for cranial nerves)
Derived from neural tube
Somatic motor neurons in the spinal cord (lower motor neurons) synapse directly on their targets
Somatic sensory
Pseudo-unipolar neurons from in the Neural crest
Cell bodies become the dorsal root ganglia
Proximal axon enters the CNS
Distal axon innervates a dermatome
Somatic motor
Multipolar neuron
Forms in the CNS (Ventral horn)
Distal axon innervates a myotome
Dorsal and ventral root
Dorsal root: sensory, innervates a dermatome
Ventral root: motor, innervates a myotome
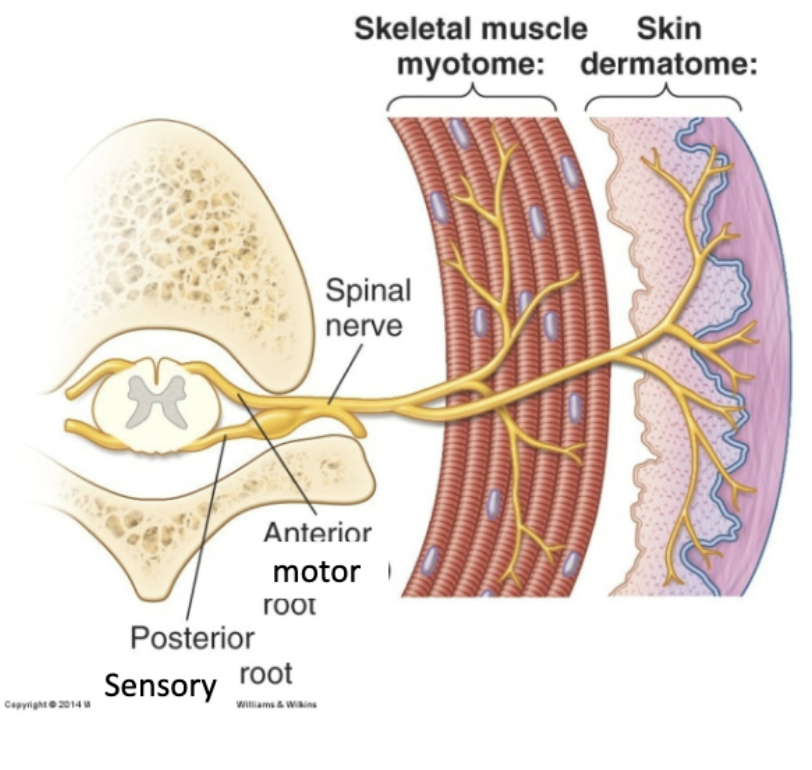
Dermatome
“real estate” on the skin that a particular spinal nerve is responsible for
Myotome
a muscle/muscle group/part of a muscle that a single spinal nerve innervates
migrate during development, but maintain innervation
ANS
Sensory: (Visceral sensory)
These are afferents that provide chemoreceptive, stretch receptive and mechanosensation for the internal body (Gut Tube)
Motor: (Visceral motor)
These are efferents that supply smooth muscle, heart muscle and glands (Gut Tube)
(glands and blood vessels in the skin start as gut tube)
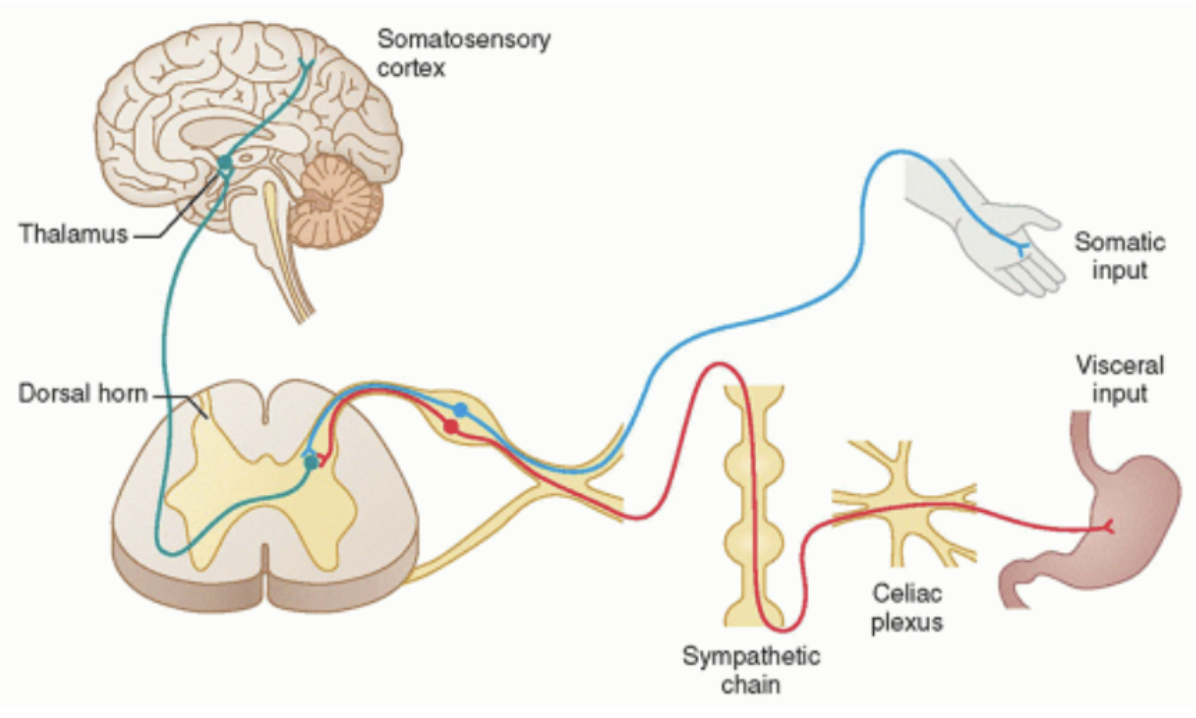
Visceral sensory
psuedounipolar and fibers enter the spinal cord along with their somatic counterparts
pseudo-unipolar cell body in the DRG.
Distal axon in the viscera (either gut tube or cardiovascular)
Proximal axon enters the spinal cord but not necessarily that close to where the distal axon is innervating
Visceral reflex afferent fibers provide input to the CNS for control of glands and smooth muscle
Visceral pain afferent fibers detect distention and pain, however, the pain is generally dull and poorly localized
Visceral motor
controls smooth muscle cardiac muscle and glands are part of a two-neuron system to the gut tube
Preganglionic neurons are in the brainstem or lateral horn of the spinal cord
Postganglionic neurons in a ganglia outside the CNS
Could be sympathetic or parasympathetic
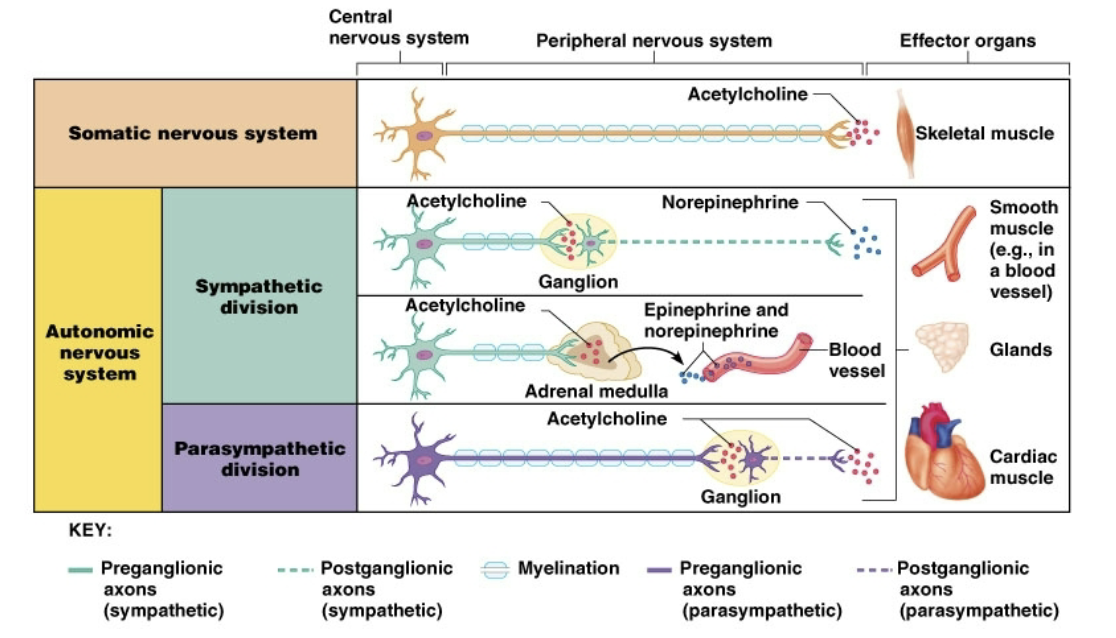
Generalities of sympathetics
Fight or Flight increase body’s “readiness”
Preganglionic neuron in the lateral horn of spinal cord
Postganglionic neuron in the sympathetic chain (we will learn exceptions here)
Preganglionic neurotransmitter is Ach
Postganglionic neurotransmitter is NE or ACh

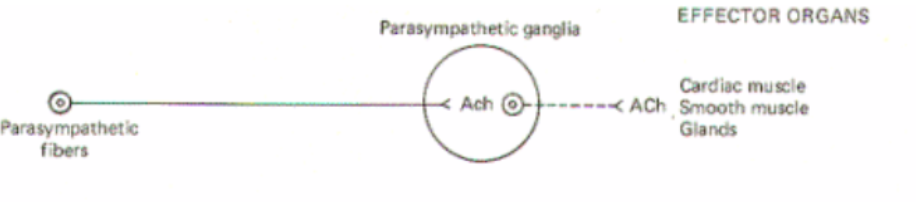
Generalities of parasympathetis
Relaxes most systems in body that sympathetics excite (“rest and digest”)
Preganglionic neurons in the brainstem or sacral nucleus
Postganglionic in ganglia closer to target
Preganglionic neurotransmitter is Ach
Postganglionic neurotransmitter is Ach
Specific sympathetic function
Increases heart rate and blood pressure (increases stroke volume)
Increases respiration
Decreases blood flow to areas not essential for immediate survival (skin and digestive system)
Increases blood flow the muscles, heart and brain
Dilates pupils
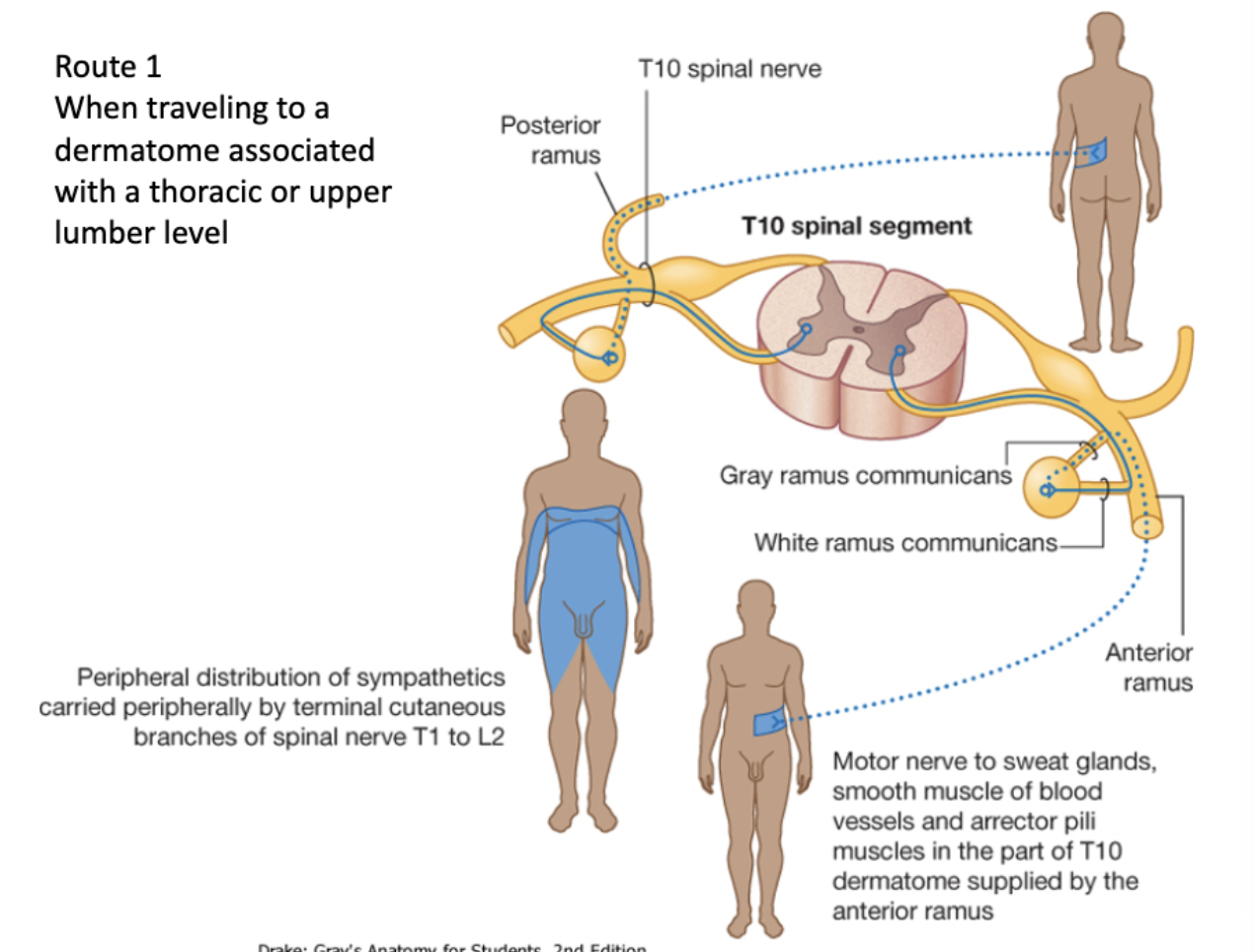
Sympathetic Route 1: When traveling to a dermatome associated with a thoracic or upper lumber level
Preganglionic cell originates in lateral horn
↓
Leaves via ventral root of spinal cord
↓
Enters white ramus communicans
↓
Enters the sympathetic chain ganglia
↓
Synapses in the post ganglionic cell body
↓
Leaves by gray ramus
↓
To spinal nerve
↓
Travels to effector
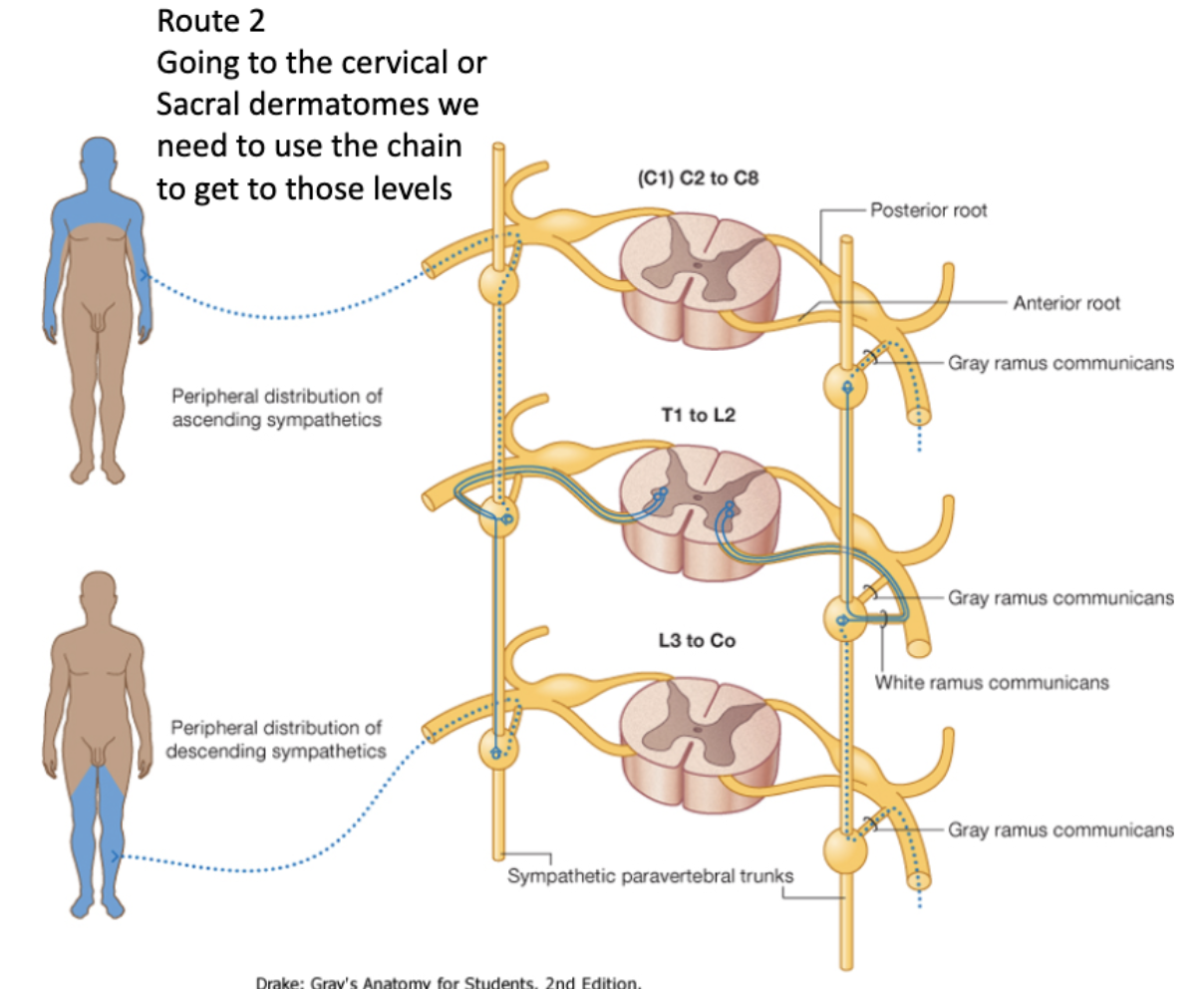
Sympathetic Route 2: Going to the cervical or Sacral dermatomes
Preganglionic cell body originates in the lateral horn
↓
Leaves via ventral root of spinal cord
↓
Goes through white ramus communicans
↓
Enters sympathetic chain ganglia
↓
Travels up/down the chain to its preferred ganglia and synapses
↓
Exits through the cervical gray ramus communicans
↓
Into spinal nerve to effector
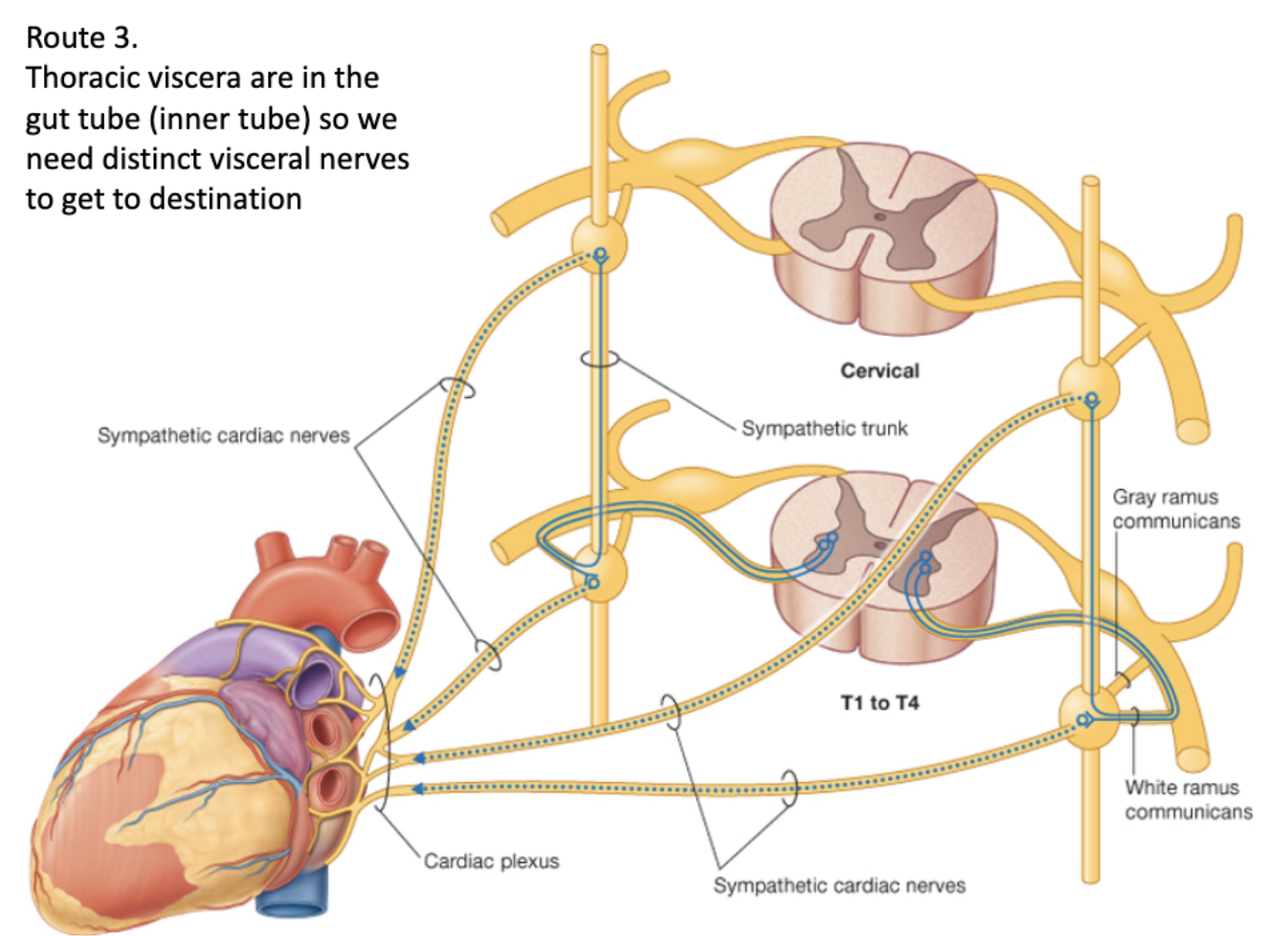
Sympathetic Route 3: Thoracic viscera
Preganglionic cell body originates in the lateral horn
↓
Leaves via ventral root of spinal cord
↓
Goes through white ramus communicans
↓
Enters sympathetic chain ganglia
↓
Travels up/down/lateral chain ganglia
↓
Synapses at desired ganglia
↓
Leaves ganglia and enters specialized (does not leave by gray ramus)
↓
Multiple cardiac plexi are created around the organ (forms own specialized cardiac nerves)
Sympathetic Route 4: Abdominal viscera
Preganglionic cell body originates in the lateral horn
↓
Exits via ventral root of spinal cord
↓
Goes through white ramus communicans
↓
Enters the sympathetic chain ganglia (does not synapse in chain ganglia)
↓
Exits into splanchnic nerve (without synapsing)
↓
Travels to vasculature (paraaortic ganglia) and synapses at ganglia (on aorta)
↓
Travels through postganglionic route (blood vessels) to the effector
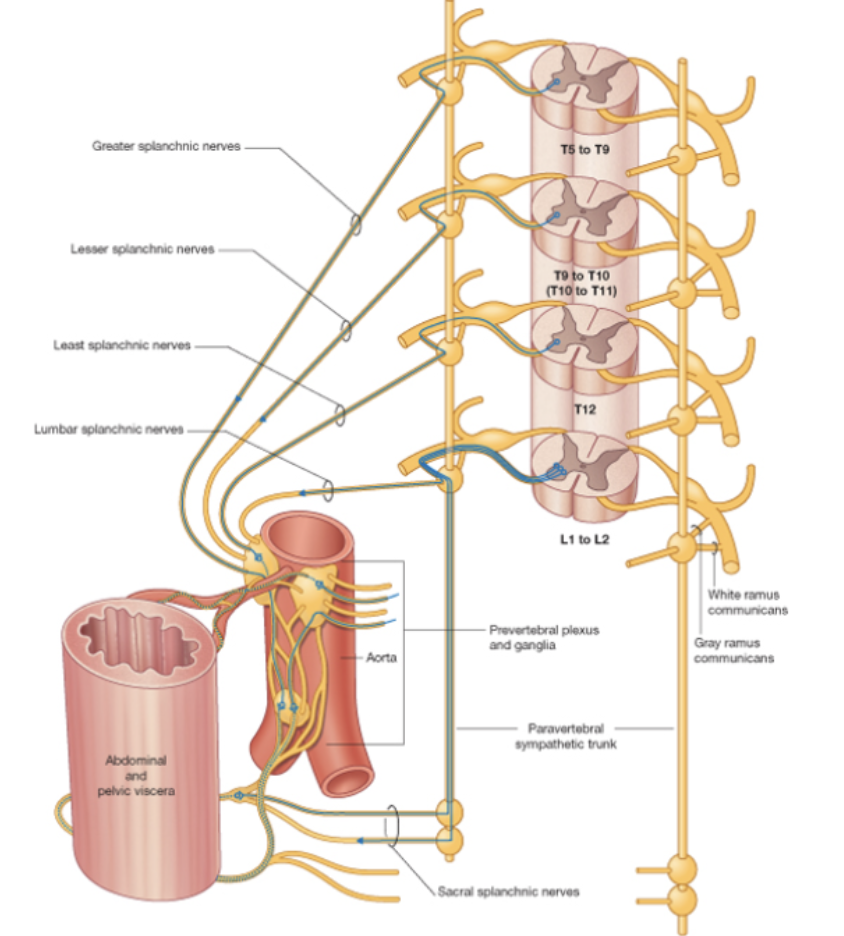
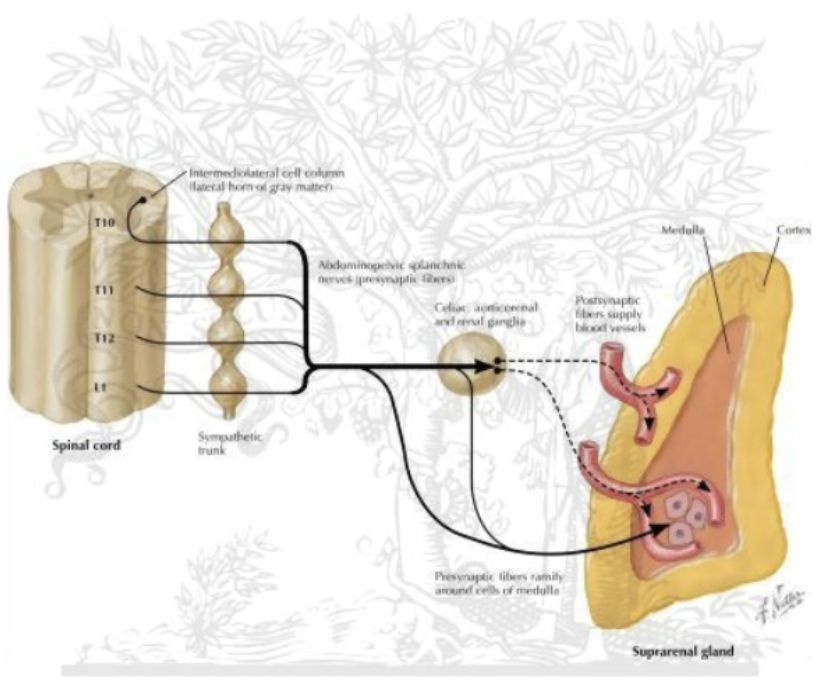
Sympathetic Route 5: Adrenal gland
Preganglionic cell body originates in lateral horn
↓
Exits via ventral root of spinal cord
↓
Goes through white ramus communicans
↓
Enters the sympathetic chain ganglia
↓
Exits into splanchnic nerve
↓
Splanchnic nerve goes directly into adrenal medulla
↓
No synapse because there is no postganglionic neuron; preganglionic releases
achetylcholine which result in immediate release of norepinephrine and epinephrine from adrenal medulla (adrenal medulla releases directly into blood stream)
(*uses blood instead of fibers to get to its destination)
Parasympathetic Route: Cranial nerves except Vagus nerve
Preganglionic neurons are located the brainstem for cranial nerves
↓
Brainstem parasympathetics travel with cranial nerves and act primarily in the head and neck
↓
Postganglionic neurons are located in the walls of the viscera (intramural ganglia) they innervate
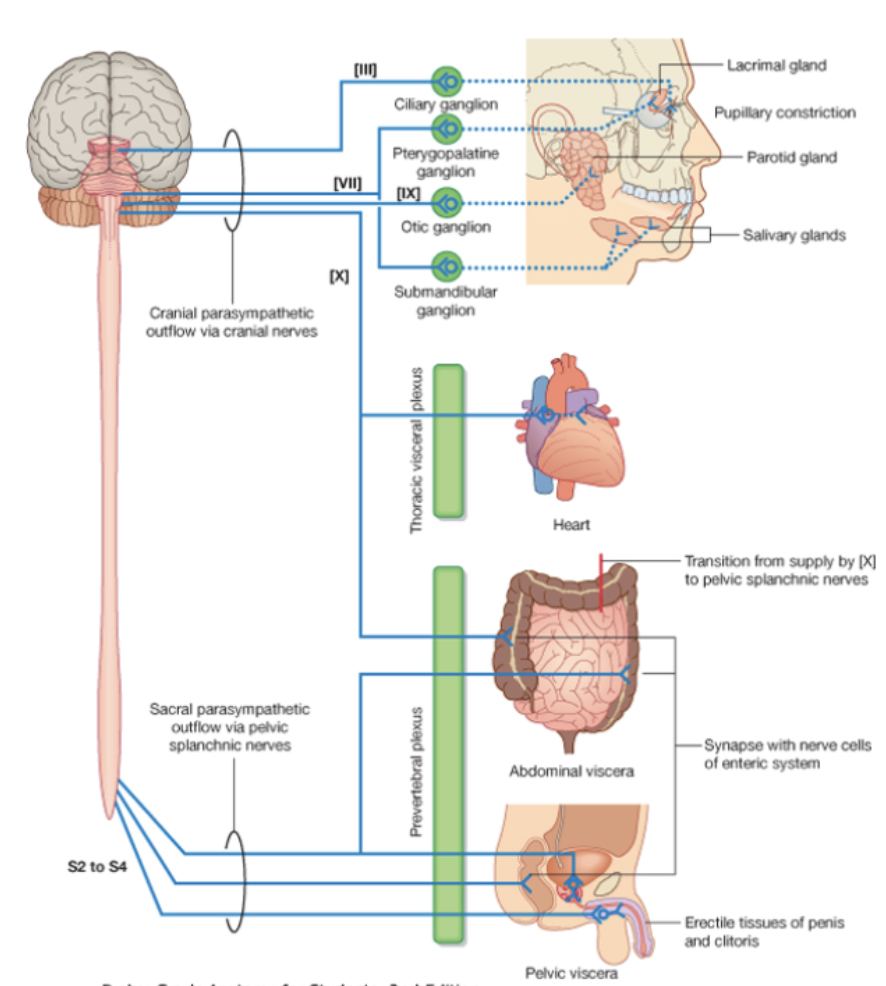
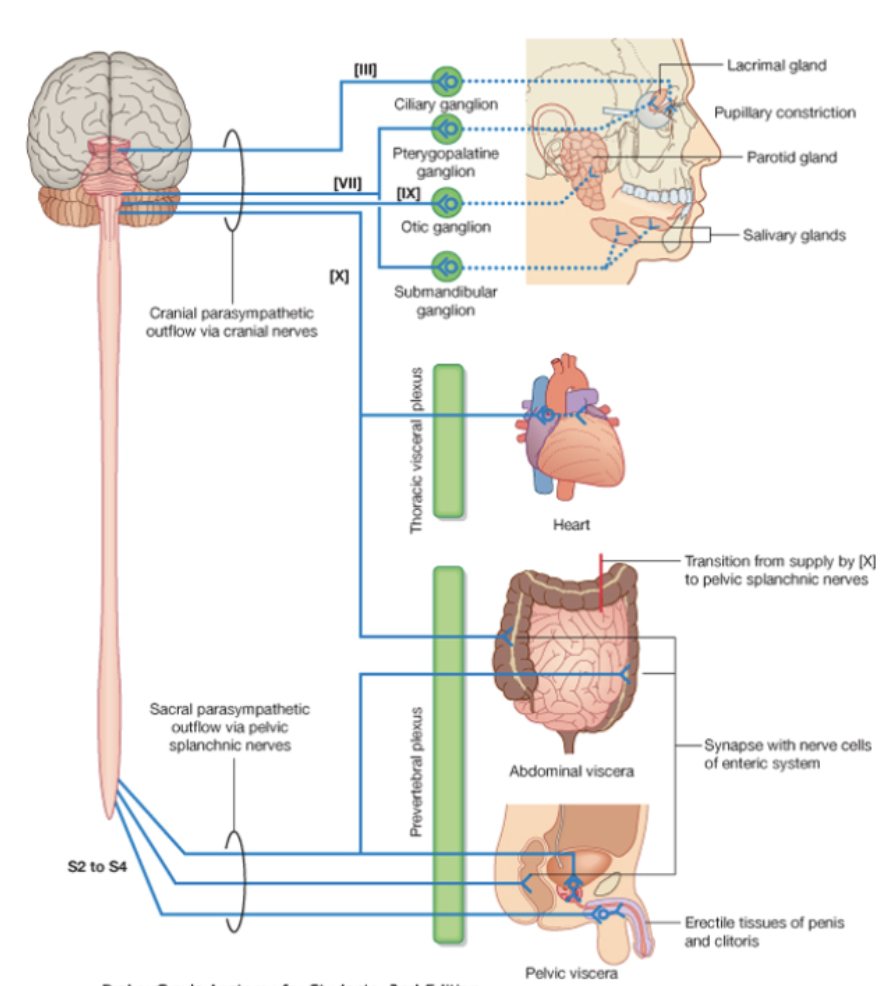
Parasympathetic Route: Vagus nerve
Preganglionic neurons are located the brainstem for cranial nerves
↓
Brainstem parasympathetics travels down head and neck, until end of hind gut (innervates thoracic and abdominal viscera), gives off branches to plexuses in the organs it innervates
↓
In the sacrum preganglionic parasympathetics can be found in the lateral regions of S2-S4 spinal segments which
↓
Preganglionic fibers exit the ventral horns and travel the ventral rami until they can break off as pelvic splanchnic nerves and follow blood vessels to pelvic viscera to get the rest of the abdomen, since the Vagus nerve stops at the end of the hind gut (Do not travel in the sympathetic trunks)
↓
Postganglionic neurons are located in the walls of the viscera (intramural ganglia) they innervate
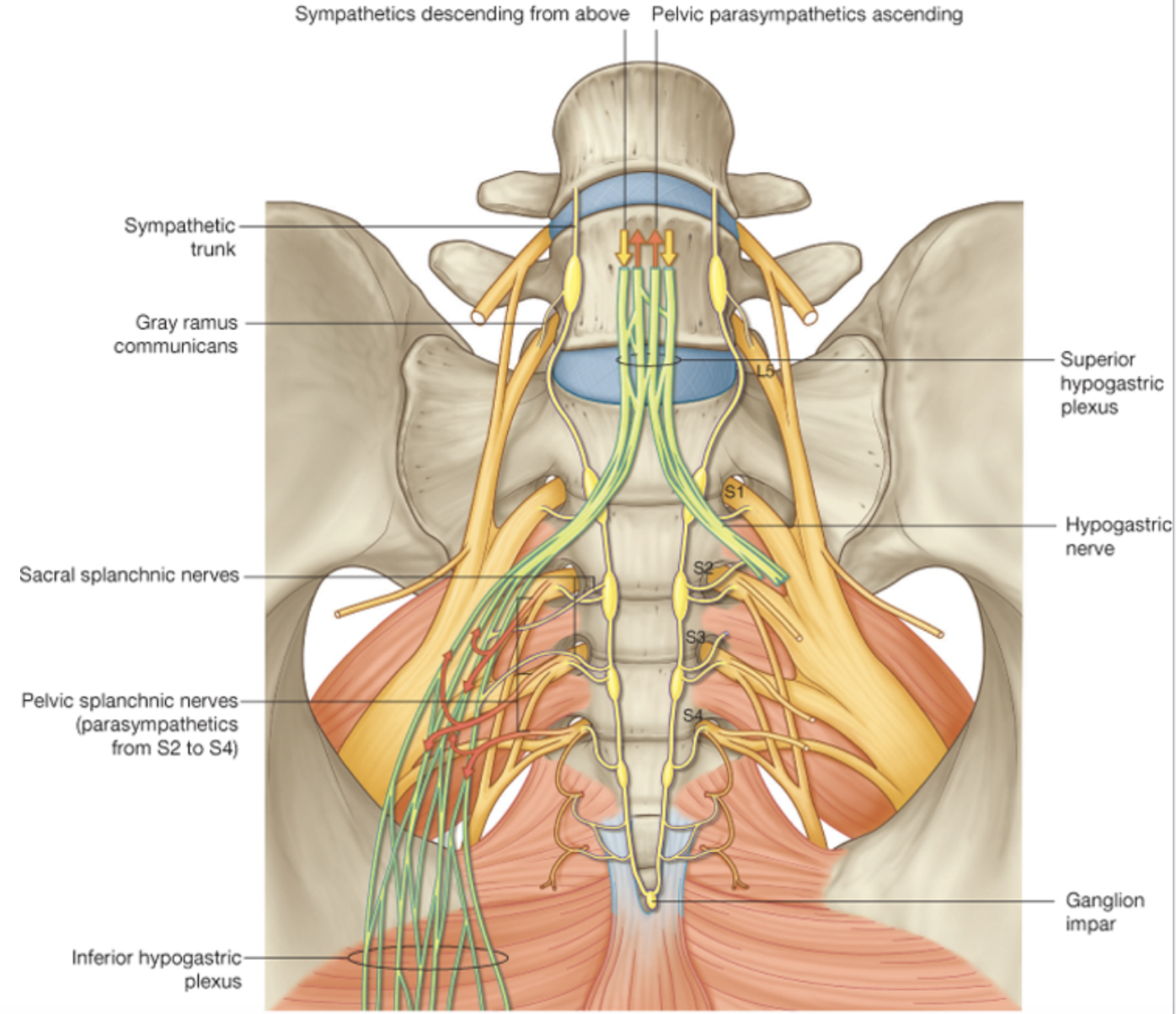
Hypogastric nerve
Sympathetic going to the pelvis need to descend
Parasympathetics going up to the colon need to ascend
Hypogastric nerve is the conduit in and out of the pelvis
Some sympathelics that are paraaortic that reed to make their way down into pelvis to supply pelvic structures, form plexus above pelvis, travel down hypogastric nerve to supply sympathetics to pelvic structures.
At same rate, parasympathetics coming in from S2,S3,S4 form plexus to supply pelvic structures, travel up the abdomen to supply sone of the abdomen viscera (hind gut)