aural rehab
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
where is otitis media?
middle ear
where is the damage in sensorineural loss?
inner ear/auditory/cochlear nerve
what causes conductive hearing loss?
damage in outer/middle ear, or a blockage
what type of hearing loss is noise induced
sensorineural
degrees of loss
-10 to 15= normal
16-25 slight
26-40 mild
41-55 moderate
56-70 mod-severe
71-90 severe
91+ profound
what is mixed loss?
sensorineural and conductive
auditory neuropathy
sound travels through ear fine, but auditory nerve can’t transmit signals to brain
CAPD
sound not processed in cortical areas, but it’s transferred fine
pure tone audiometry testing
identifies type and degree of hearing loss using bone and air conduction
what is speech audiometry testing
establishes thresholds of perception
tympanometry
looks at health of middle ear
OAE otoacoustic emission
inner ear, hair cells wiggle: can indicate sensory hearing loss in newborns
Normal hearing produces OAEs; hearing loss is indicated by
the absence of OAEs
what does ABR do?
can help identify auditory neuropathy
identify retrocochlear hearing issues
used for newborn screening
Tells how inner ear is working
aka auditory brainstem response
auditory training levels
awareness to discrimination to identification to comprehension
help reading audiogram symbols
blue= left ear
red=right
left ear= x
right ear= o
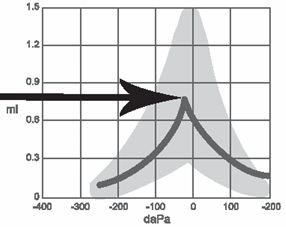
type A tympanogram
normal middle ear
type B tympanogram
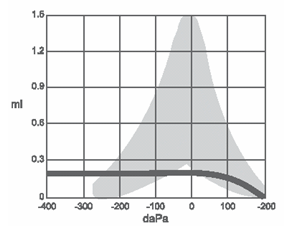
fluid, infection, or hole
type C tympanogram
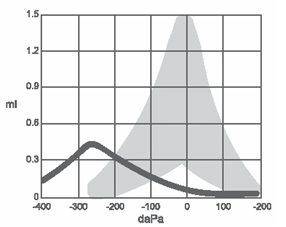
negative pressure, sinus/allergy