Physics Paper 1 Summary
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
8 energy stores
-Kinetic
-Thermal
-Chemical
-Gravitational Potential
-Elastic Potential
-Nuclear
-Magnetic
-Electrostatic
4 Energy Transfers
-Mechanically
-By heating
-Electrically
-Radiation
Ways to Generate Electricity
Non Renewable and Renewable Resources
Non Renewable Resources: Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels are made out of remains of living organisms that died millions of years ago
Advantages of Fossil Fuels
They are reliable and release a great deal of energy, they are also abundant and relatively cheap and they are extremely versatile
Disadvantages of Fossil Fuels
Produces carbon dioxide which is a greenhouse gas which leads to global warming
Nuclear Energy
Releases energy form nuclear reactions
Advantages of Nuclear Energy
It is extremely reliable and does not release carbon dioxide therefore does not contribute to climate change
Disadvantages of Nuclear Power
Contains highly dangerous radioactive material and dismantling a nuclear power plant takes many years and is extremely expensive
Advantages of Wind Turbines
Wind is a naturally replenishing resource so it will not run out and they do not produce pollutants
Disadvantages of Wind Turbines
Unreliable as it is dependant on the speed of the wind
Advantages of Solar Panels
Solar panels produce electricity without emitting greenhouse gase , reducing climate change impact.
Disadvantage of Solar Panels
Dependent on the sun, so on cloudy day, its ineffective
Advantages of Wave Power
Uses turbines to produce electricity therefore does not affect climate change
Disadvantages of Wave Power
Could be harmful to marine life
Advantages of Tidal Barriers
Uses turbines that use energy from tides going up and down therefore not affecting climate change.
Disadvantage of Tidal Barriers
Can potentially kill marine life and need a suitable location to construct them
Advantages of Hydroelectric Energy
Uses turbines in a valley to generate electricity therefore not affecting climate change.
Disadvantages of Hydroelectric Power
Can only be built in limited locations and can disrupt the ecosystem by destroying habitats
Advantages of Geothermal Energy
Its renewable and provides a reliable and constant power source
Disadvantages of Geothermal Energy
Can only be used in Volcanic Areas
Advantages of Biofuels
They are produced from plant materials which are burnt however they do not add any extra carbon dioxide to the atmosphere therefore it is carbon neutral
Disadvantage of Biofuels
If we use land to grow crops for fuel, that could increase food prices
Circuit Symbols
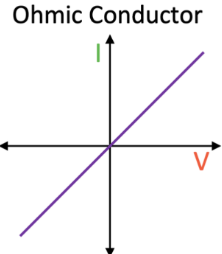
I-V Graph: Ohmic Conductor
The current through an ohmic conductor at constant temperature is directly proportional to potential difference so you get a straight line passing through the origin
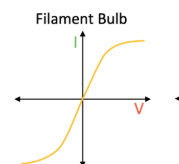
I-V Graph: Filament Lamp
As the current increases, the temperature of the filament increases so the resistance increases. This means less current can flow per unit of potential difference so the graph gets shallower.
I-V Graph: Diodes
Current will only flow in one direction as diodes have a high resistance in the reverse direction.
Thermistors
Decreased resistance when surroundings get hot and increased resistance when surroundings get cold
In series circuits, current is the ? Potential difference is ? Resistance ?
Current is the same everywhere and Potential Difference is shared between the components, Resistance increases as you add more resistors
In Parallel Circuits, the current ? The potential difference ? Resistance ?
The current is shared so it splits between branches and the Potential Difference is the same, Resistance decreases as you add more resistors.
Alternating Current is used in the ?
Uk’s Mains Supply which is 230 Volts and 50Hz
The three core cables
Live wire (Brown) containing 230V, Neutral wire (Blue) which completes the circuit (0V), Earth wire (Green and Yellow) which is for safety (0V)
The Earth Wire
Used when the live wire comes in contact with the metal casing of an appliance
The National Grid
Where electricity leaves power stations and passes through a step up transformer which increases potential difference and decreases current so that less energy is lost due to heat at the transmission cables, it is then distributed around the country and goes through a step down transformer which reduces the potential difference to 230V and increases the current in order to be passed to homes
Solid Particles
Are closely packed and are arranged in a regular pattern and vibrate and have a medium density
Liquid Particles
Are closely packed but are arranged in a irregular pattern and slide past each other
Gas Particles
Are loosely packed, not arranged in a pattern and move rapidly, they have low density
Gas Particles in a Container
The particles collide with each and the walls of the container, which creates a pressure on the container and as the temperature increases the speed of the particles increase which causes the gas particles to hit the walls of the container more often with a greater force which creates more pressure
Internal Energy
is the total energy of all the particles in a substance, including both kinetic and potential energy. It influences temperature changes.
Internal energy= ?
Kinetic Energy + Potential Energy
What is Specific Latent Heat
The energy required to change the state of 1kg of a substance without changing its temperature
What is Specific Latent Heat of Fusion
The amount of energy required to change 1kg of a substance from a solid to a liquid with no change in temperature
What is Specific Latent Heat of Vaporisation
The amount of energy required to change 1kg of a substance from a liquid to a vapour with no change in temperature.
When the state changes are happening, the temperature of the substance ?
Stays the same
When changing states, energy is used to ?
Energy is used to break bonds rather than raising the temperature
John Dalton Believed ?
Atoms are spheres where each element have different types of atoms
JJ Thompson
Discovered the electron and came up with the Plum pudding model, which contained embedded electrons in a positive sphere
Ernest Rutherford
Conducted the Gold Foil Experiment. He fired alpha particles at a thin gold foil and resulted that since most of the alpha particles passed through the foil while a few were deflected and some bounced back, the atom is mostly empty space, it is has a positive charge in the centre of the atom, the mass is concentrated in the centre known as the nucleus
Niels Bohr
Discovered that the electron orbits around the nucleus at specific distances. We call the ‘orbits’ energy levels or shells. The model was called The Planetary Model
James Chadwick
Discovered that the nucleus also contains neutrons, these have no overall charge meaning they are neutral. He came up with the modern nuclear model that we use today containing protons, neutrons and electrons
The electrons can go ?
Up energy levels by absorbing electromagnetic radiation and go down by emitting electromagnetic radiation
Mass number (Top number of element)
contains number of protons and neutrons
Atomic Model (Bottom Number of Element)
Contains number of protons and electrons
Unstable Nucleus become stable by ?
Giving off Radiation, which is known as Radioactive Decay and is a random process
Half Life
The time it takes for the number of undecayed nuclei to halve
How to measure Half life on a graph
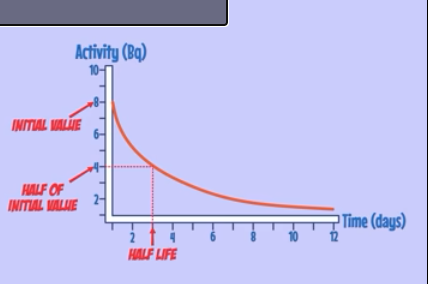
Half life is measured using a ?
Geiger-Muller Tube and is measured in becquerels (Bq)
Contamination
when radioactive particles come into direct contact with materials
Irridation
When an object or a person is exposed to radiation
Alpha particles have a very high risk of ? and have a very low risk of ?
High risk of contamination as it is highly iosnising and low risk of irradiation as it cant travel far into air
Gamma has a high? and low ?
high irradiation risk and low contamination risk