HSC 214: Superior Muscles and Actions 1-41, Integumentary 1-8
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
occipitofrontalis
raises eyebrows, wrinkles forehead
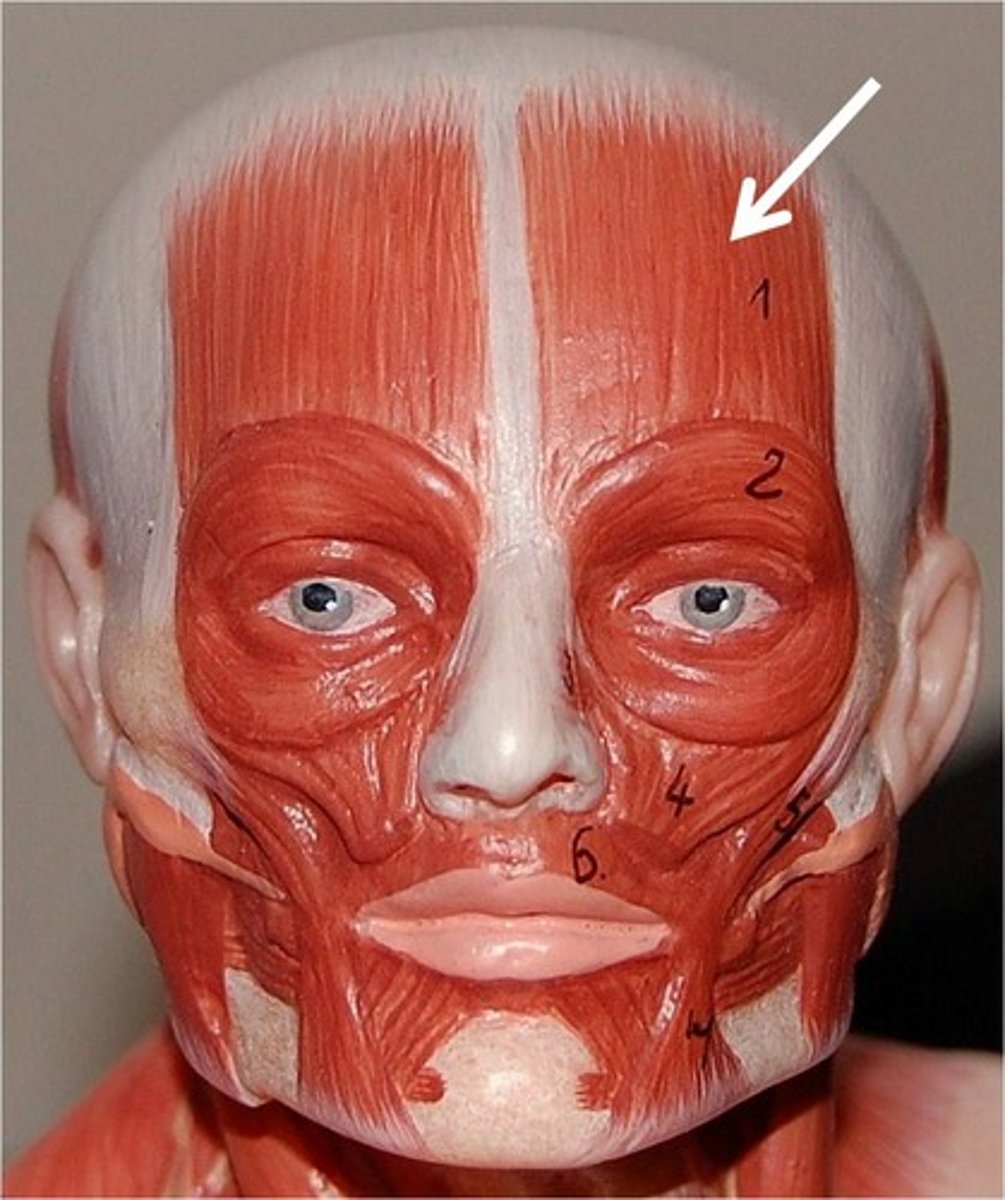
epicranial aponeurosis
Tendon that connects the occipitalis and frontalis muscles
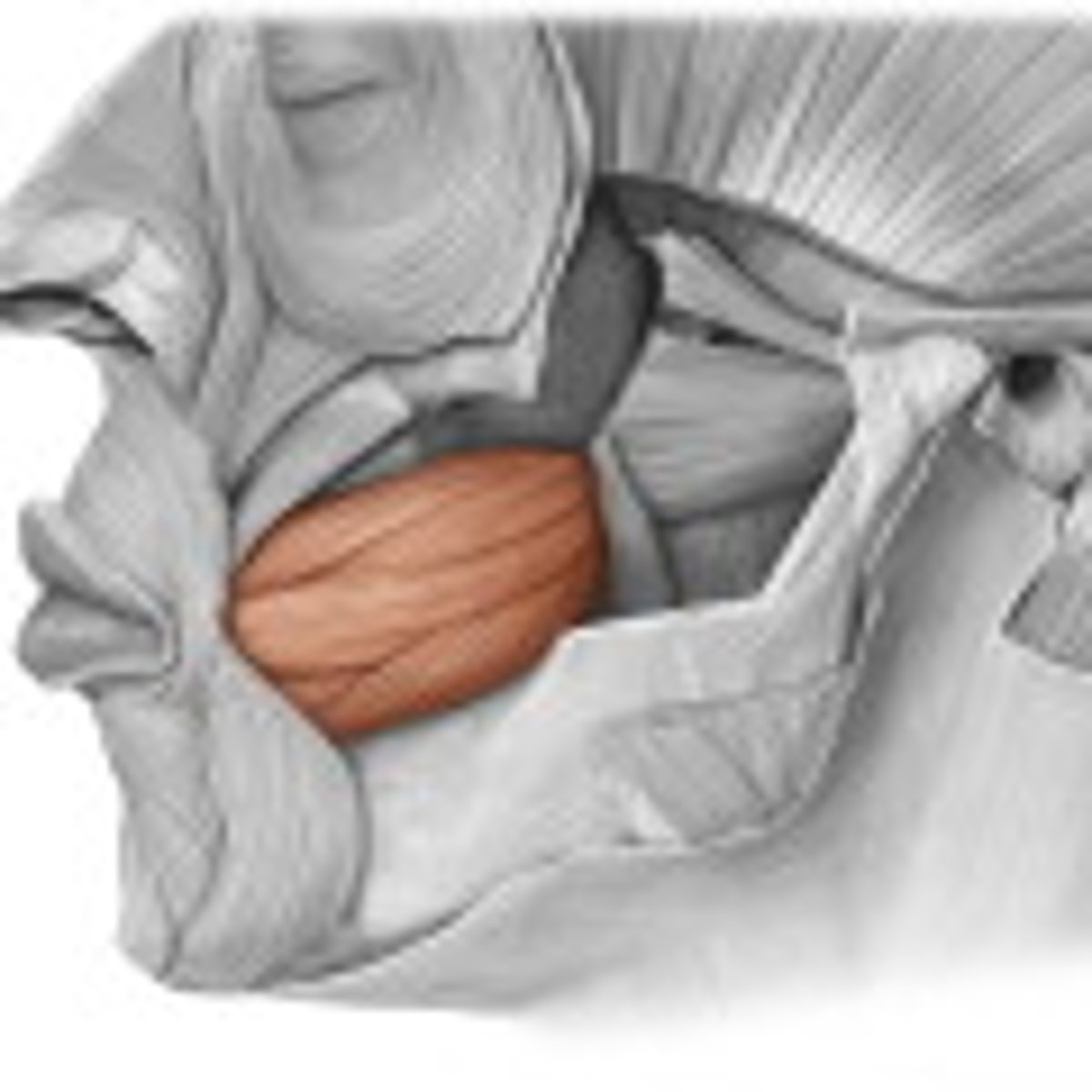
buccinator
compresses cheek
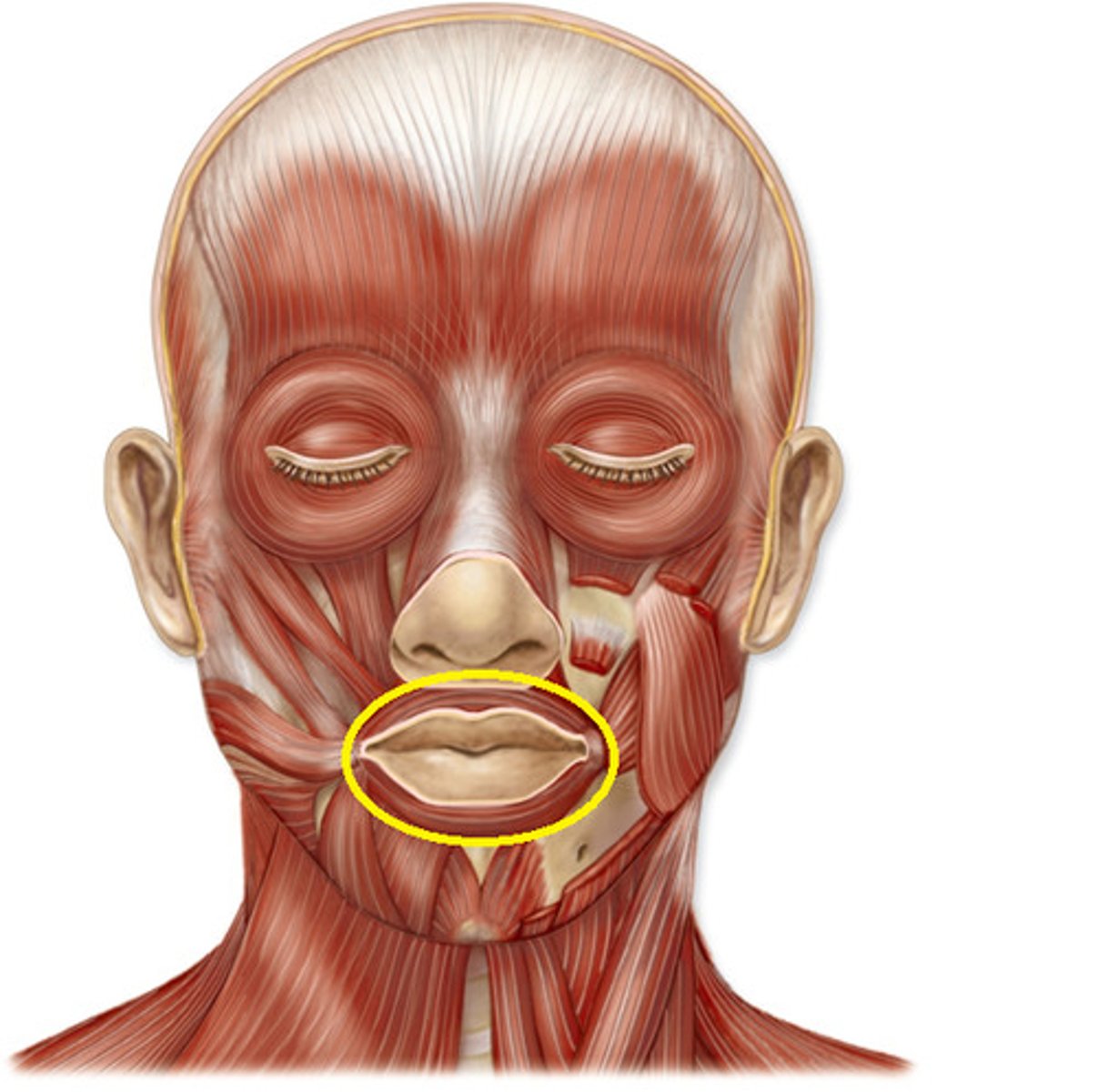
Orbicularis oris
closes lips
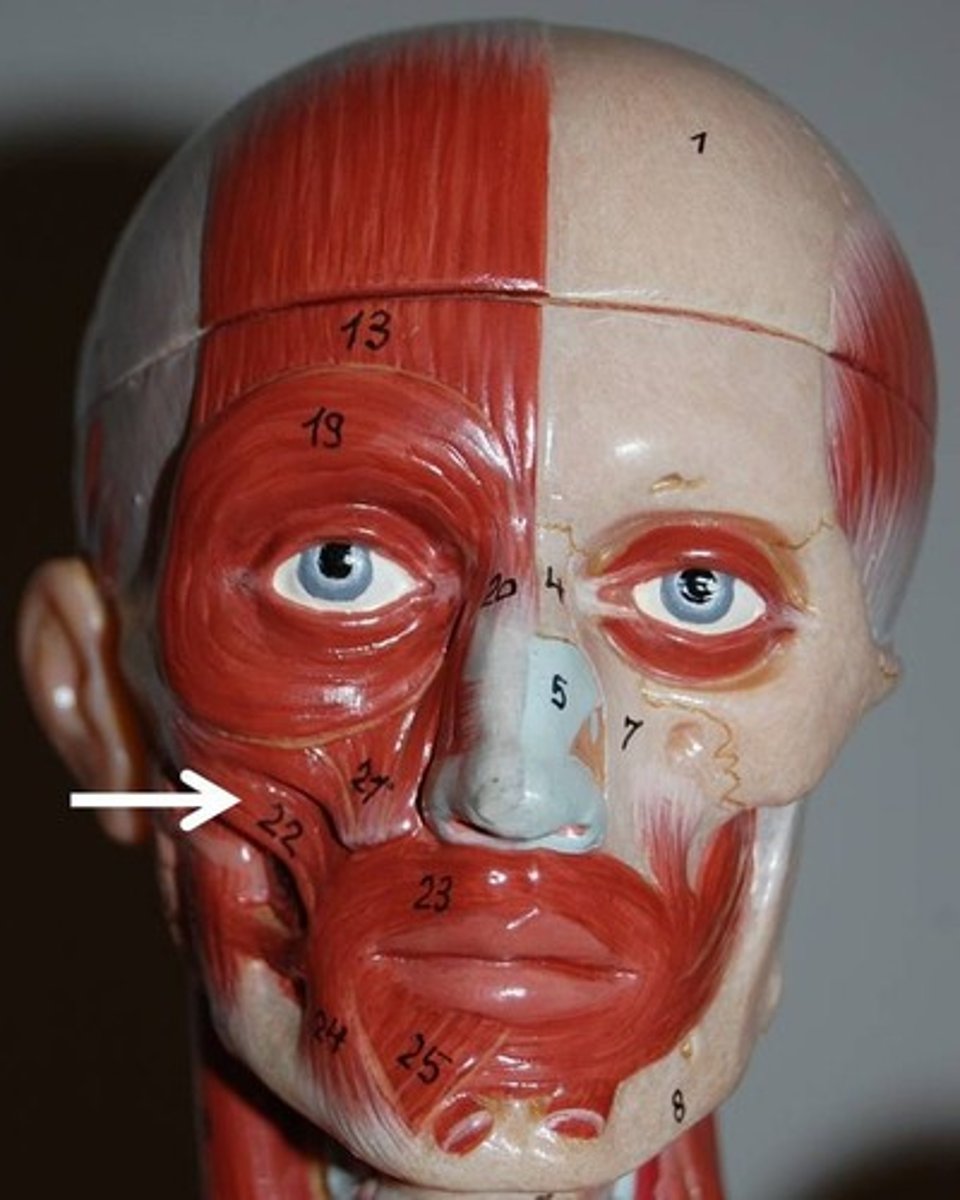
zygomaticus major
retracts and elevates corner of mouth
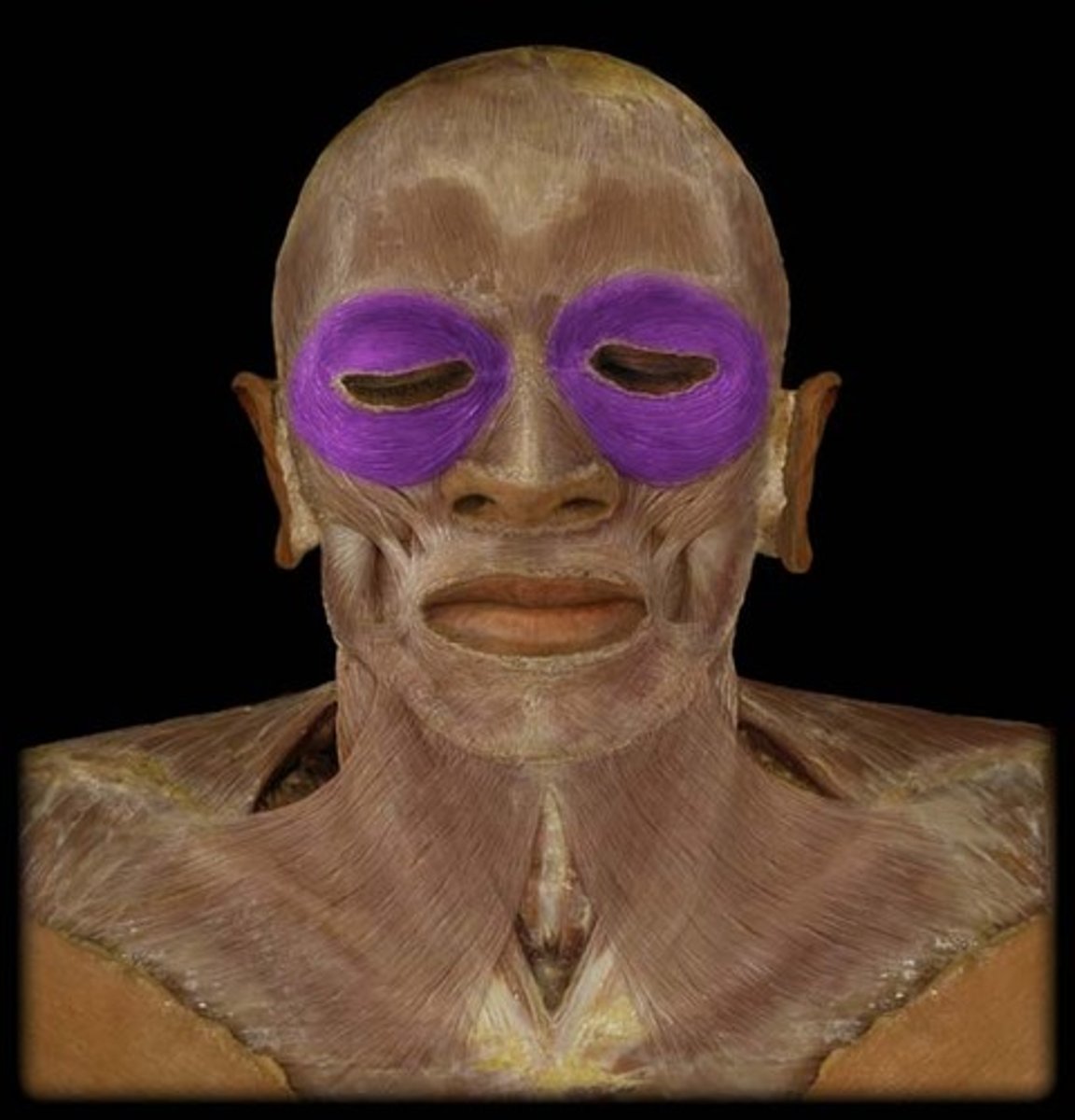
orbicularis oculi
closes eye
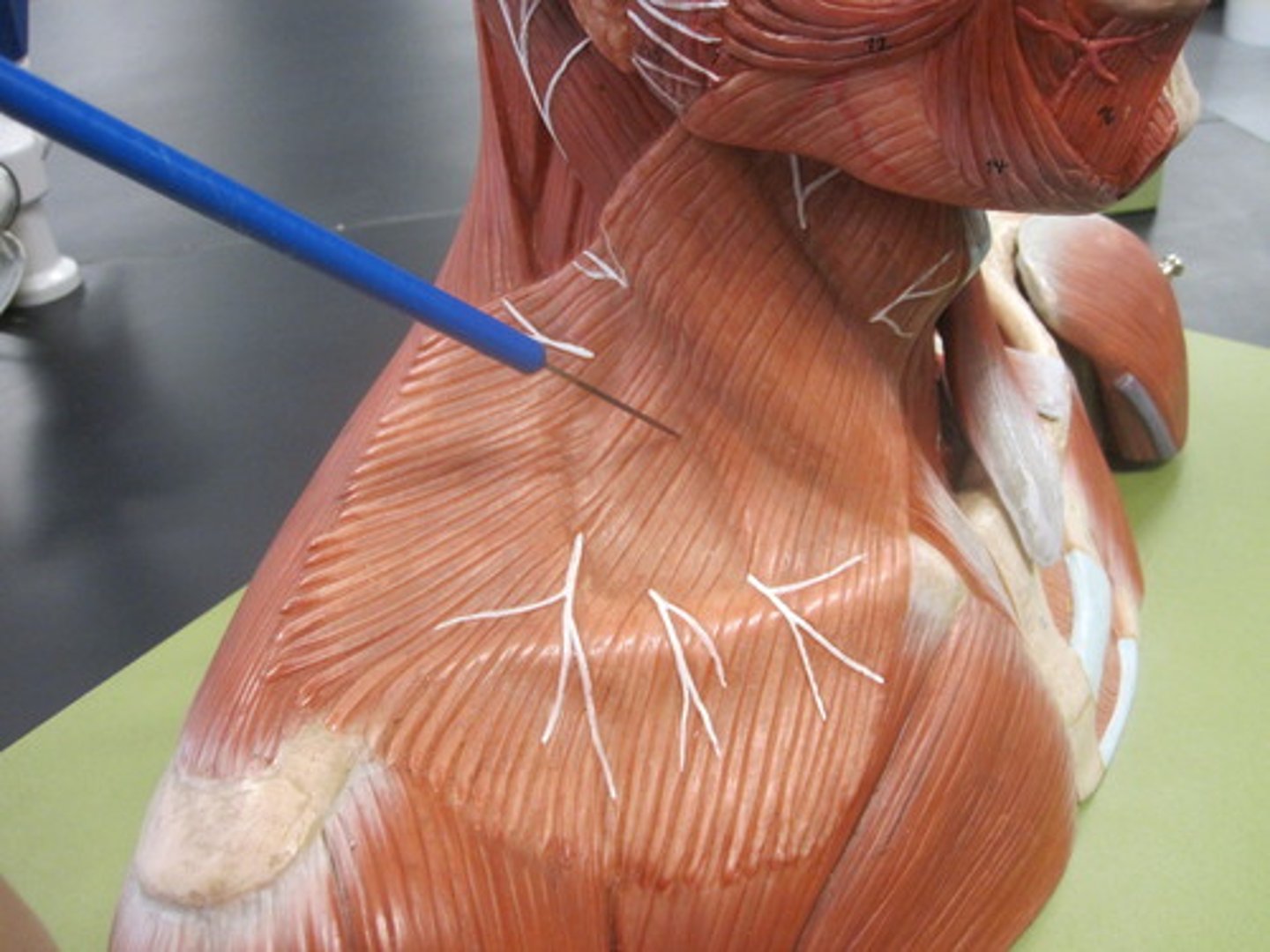
platysma
tenses skin of neck
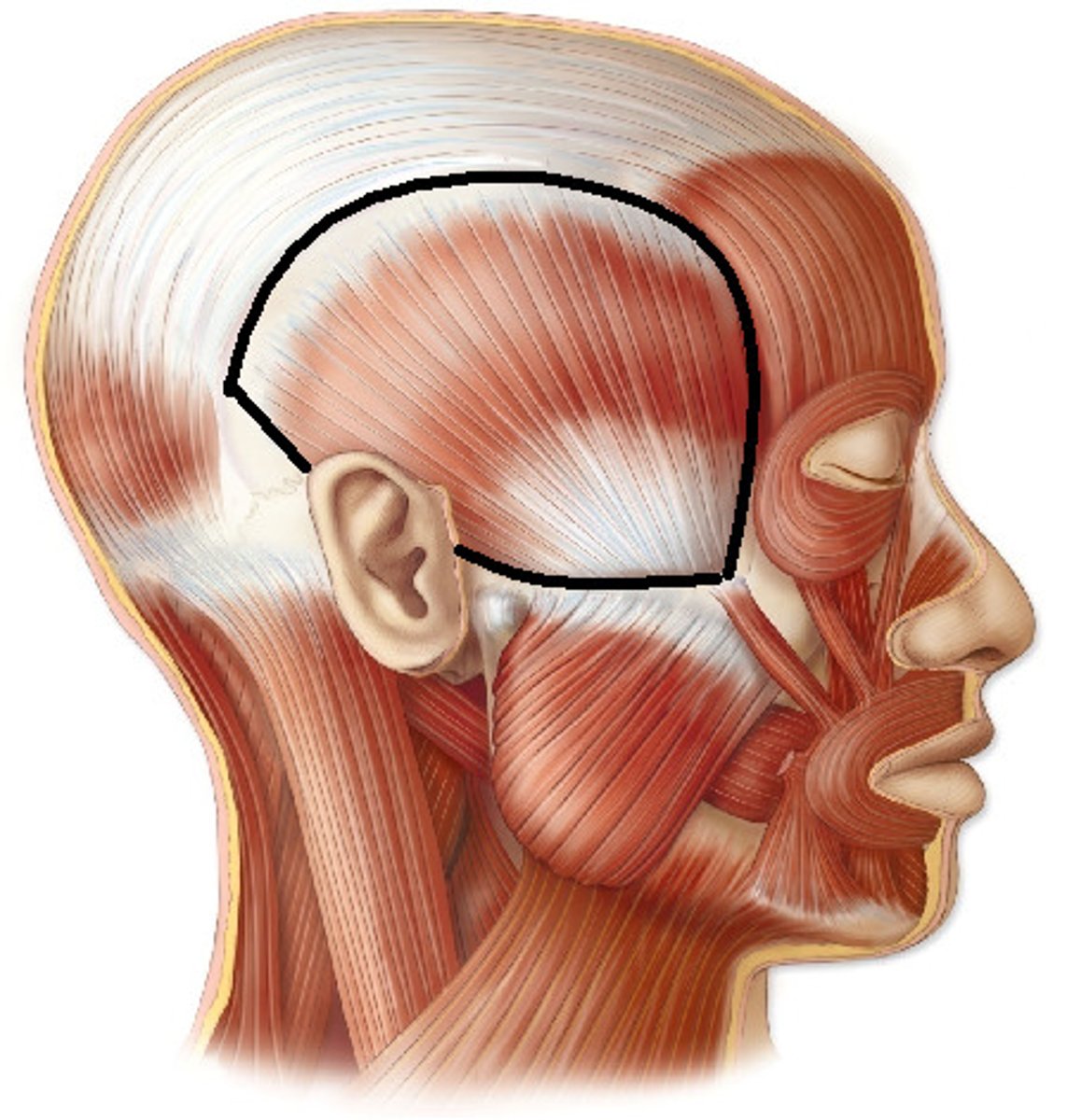
temporalis
elevates and retracts mandible
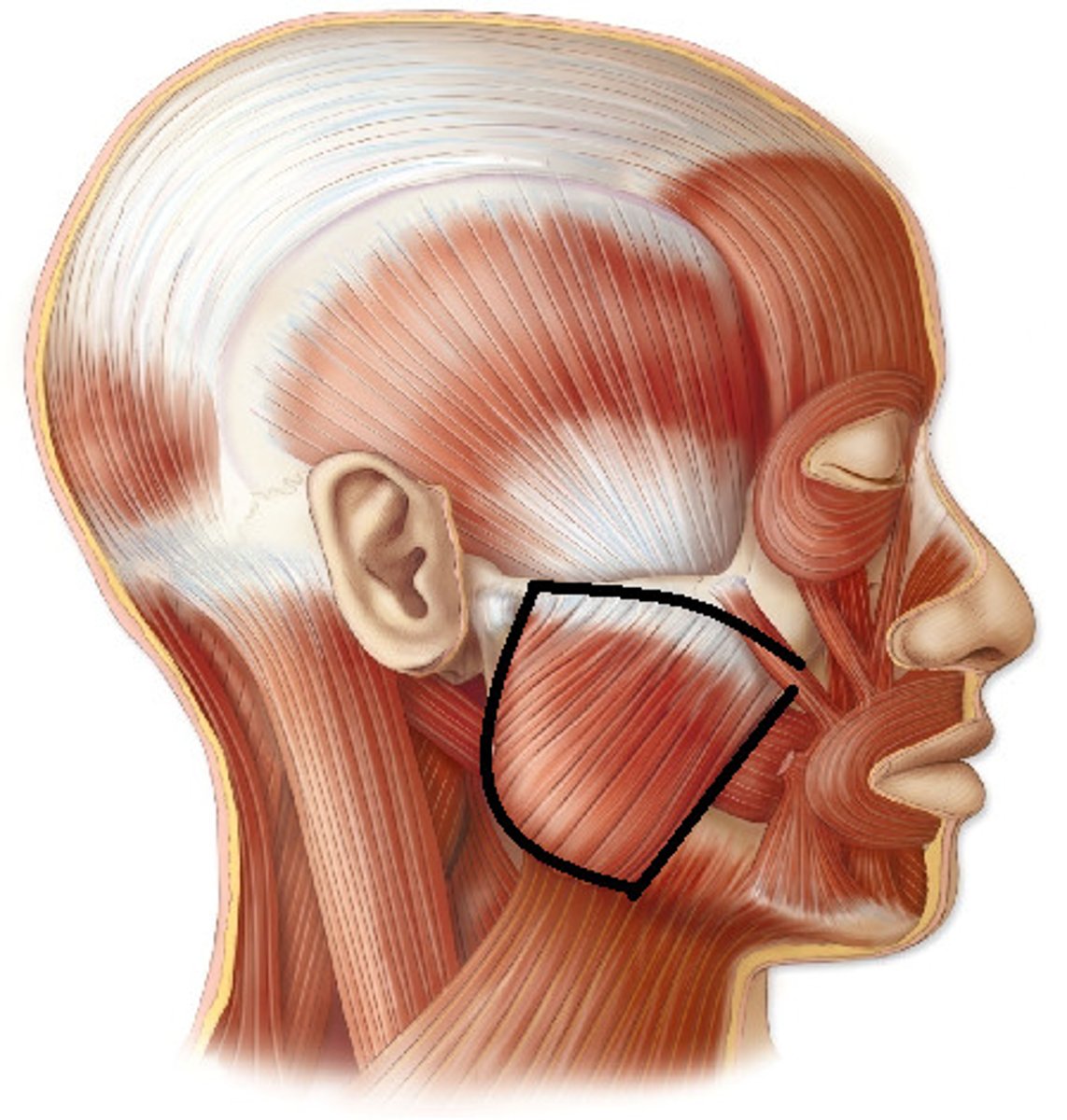
masseter
elevates mandible
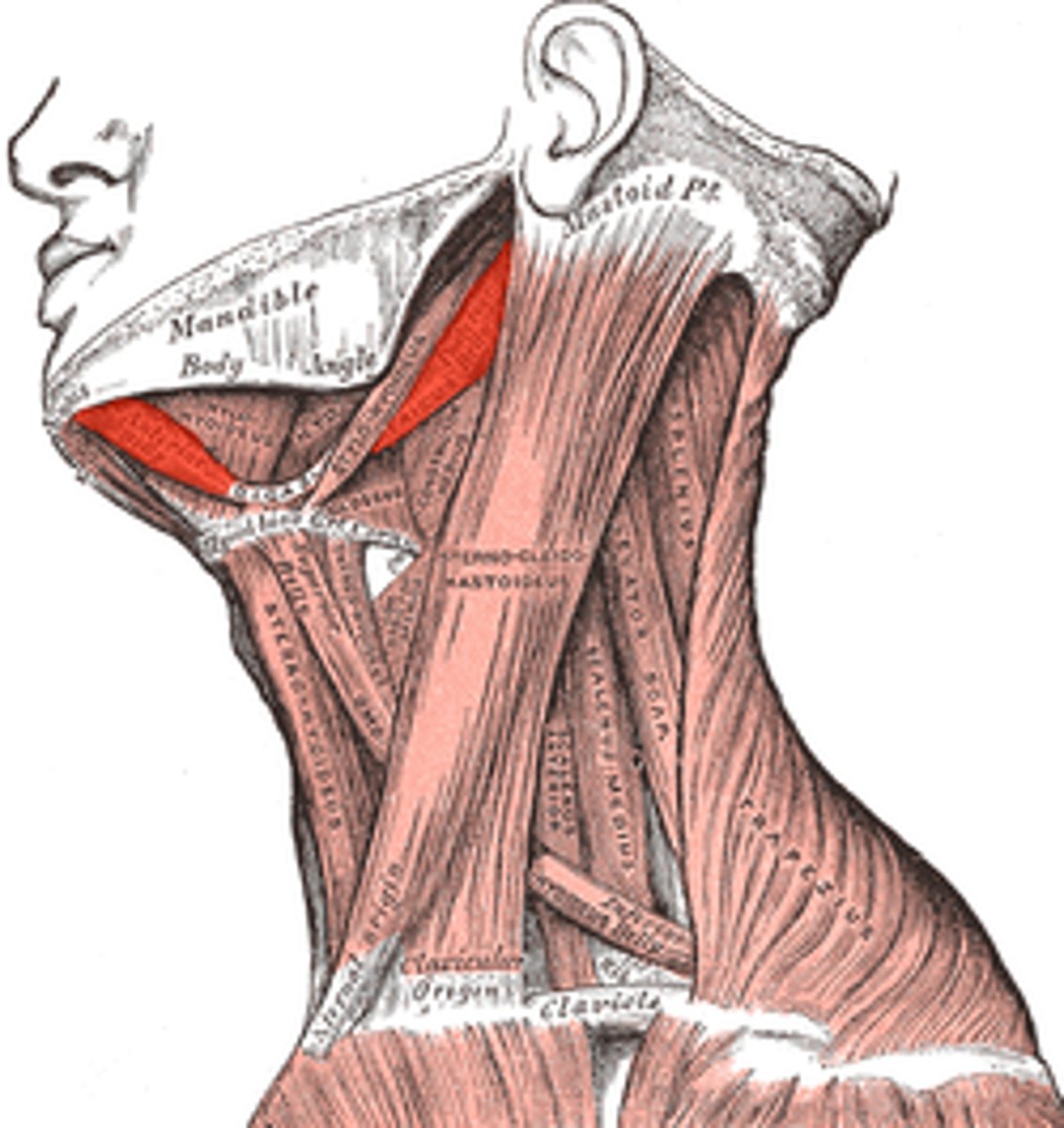
digastric
depresses mandible
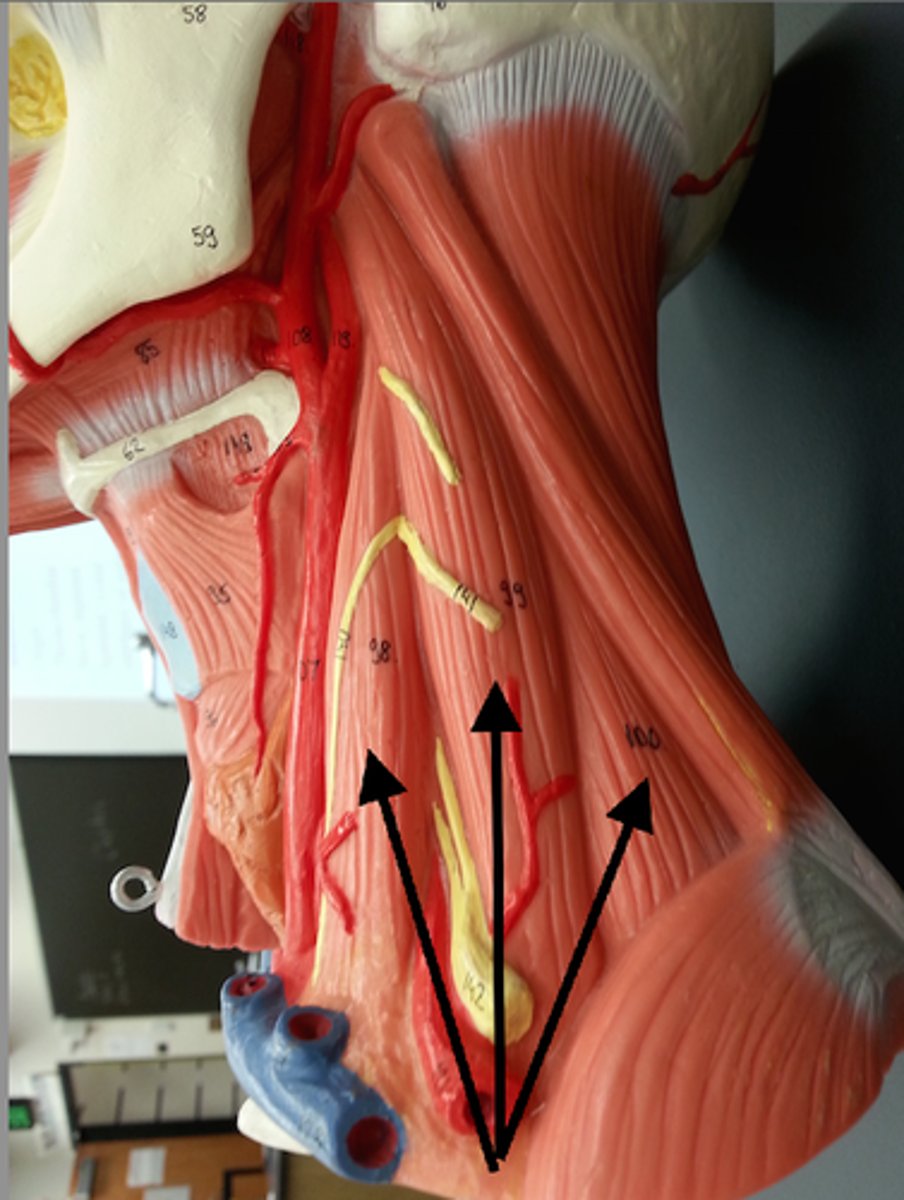
omohyoid
depresses hyoid
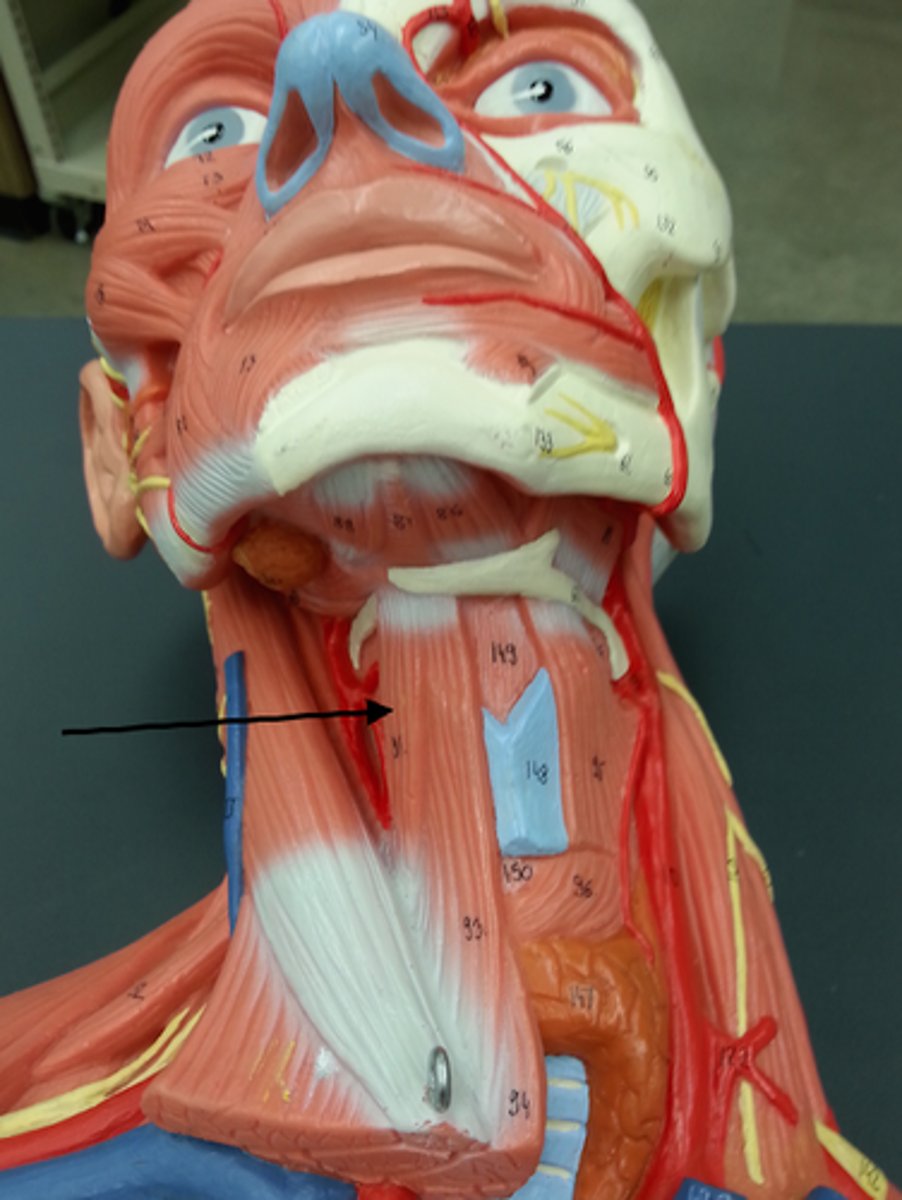
sternohyoid
depresses hyoid
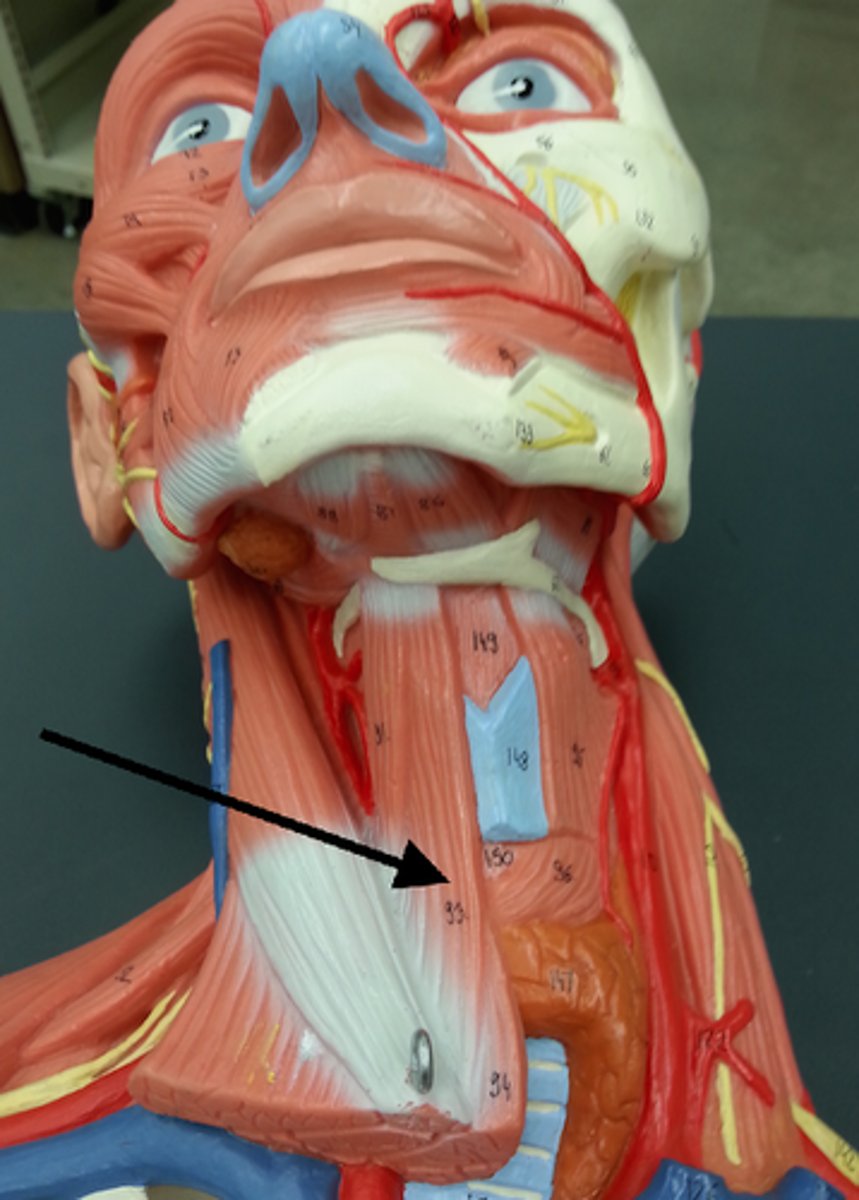
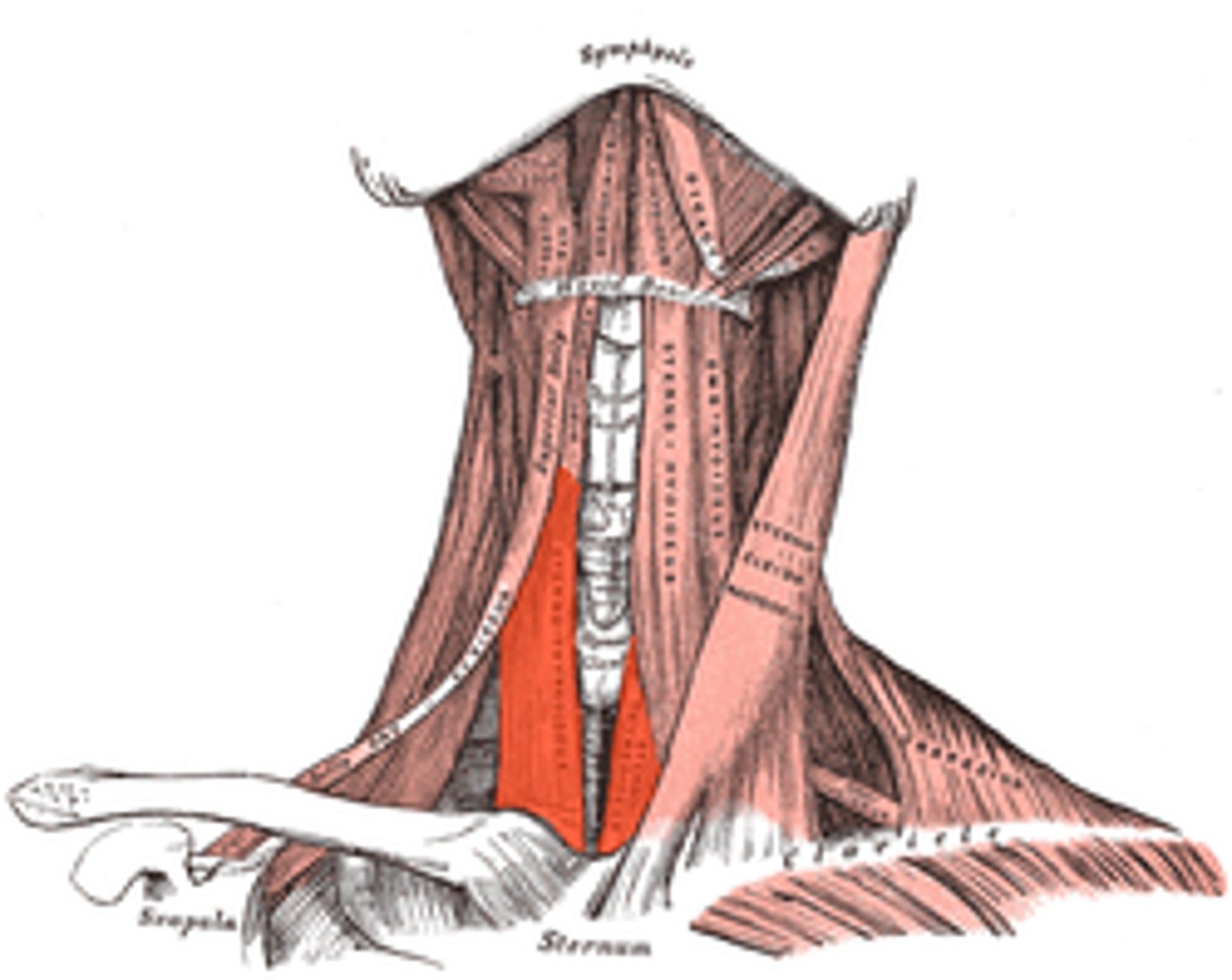
sternothyroid
depresses thyroid cartilage
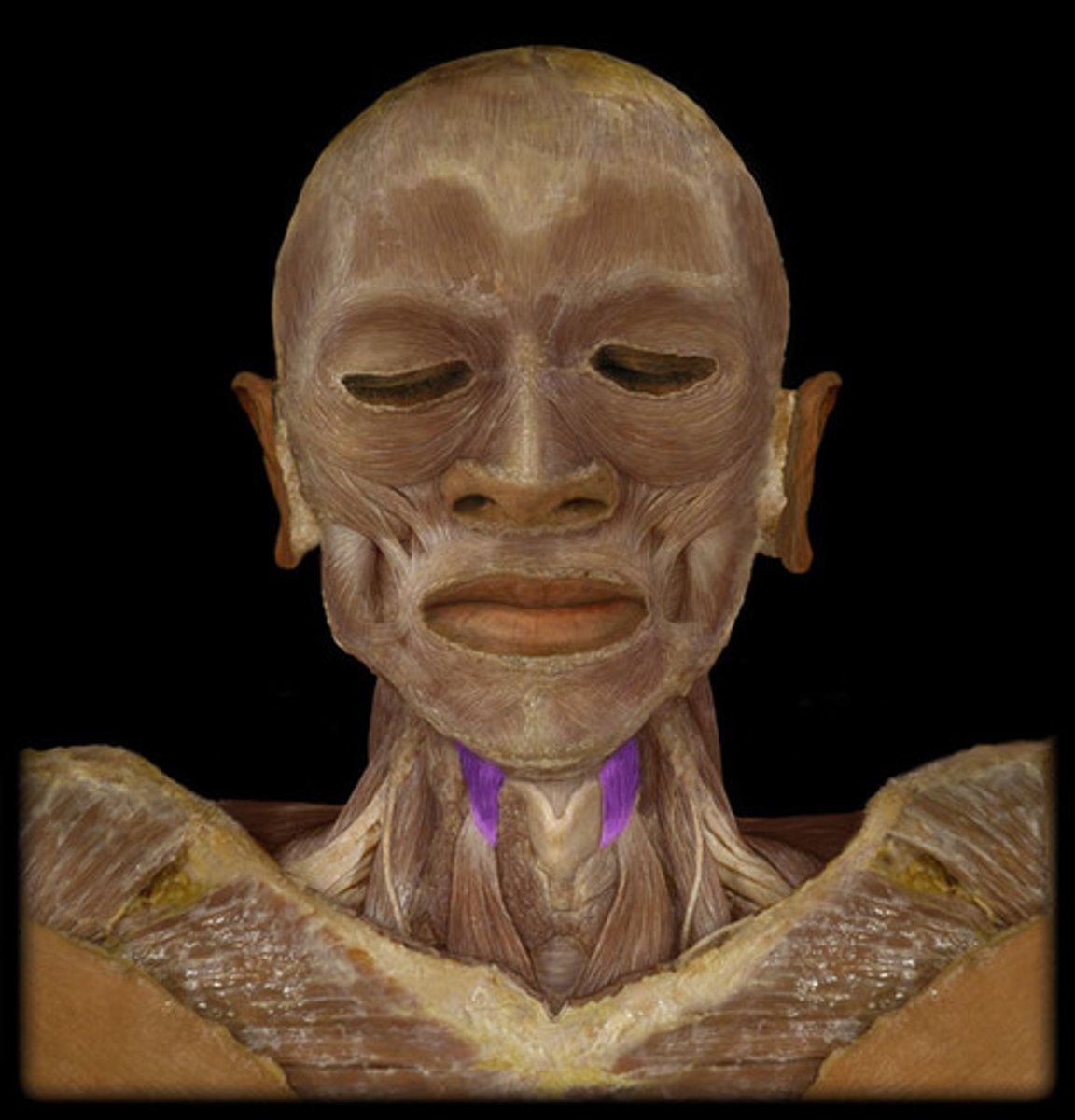
thyrohyoid
depresses hyoid and elevates larynx
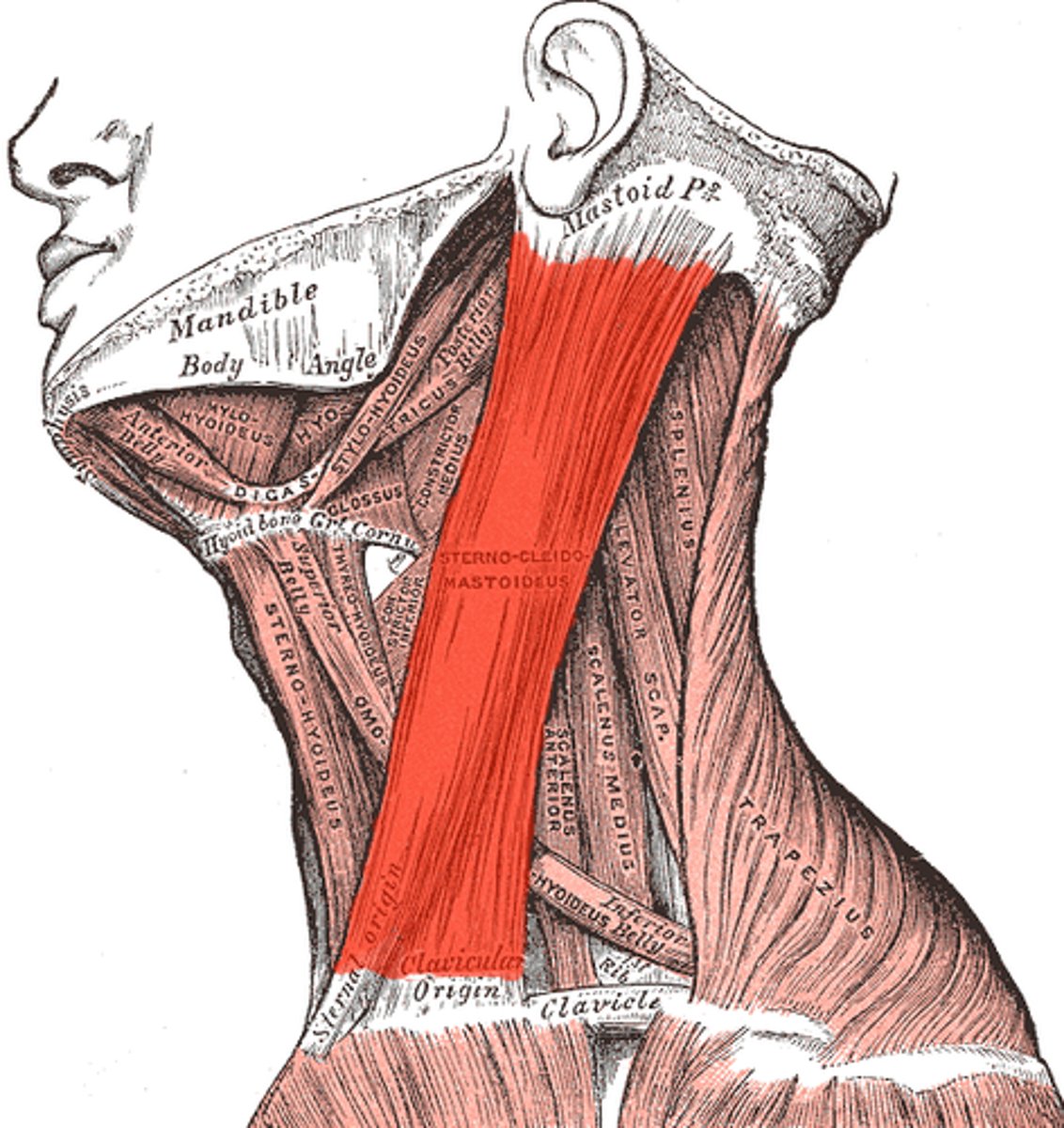
sternocleidomastoid
flexes neck; rotates head
scalene muscles
ORIGIN: transverse processes (C3-C7)
INSERTION: ribs 1-2
ACTION(S): elevates ribs 1-2 during forced inspiration; lateral flexes neck
RELATIONSHIP: consists of three muscles; anterior, middle & posterior
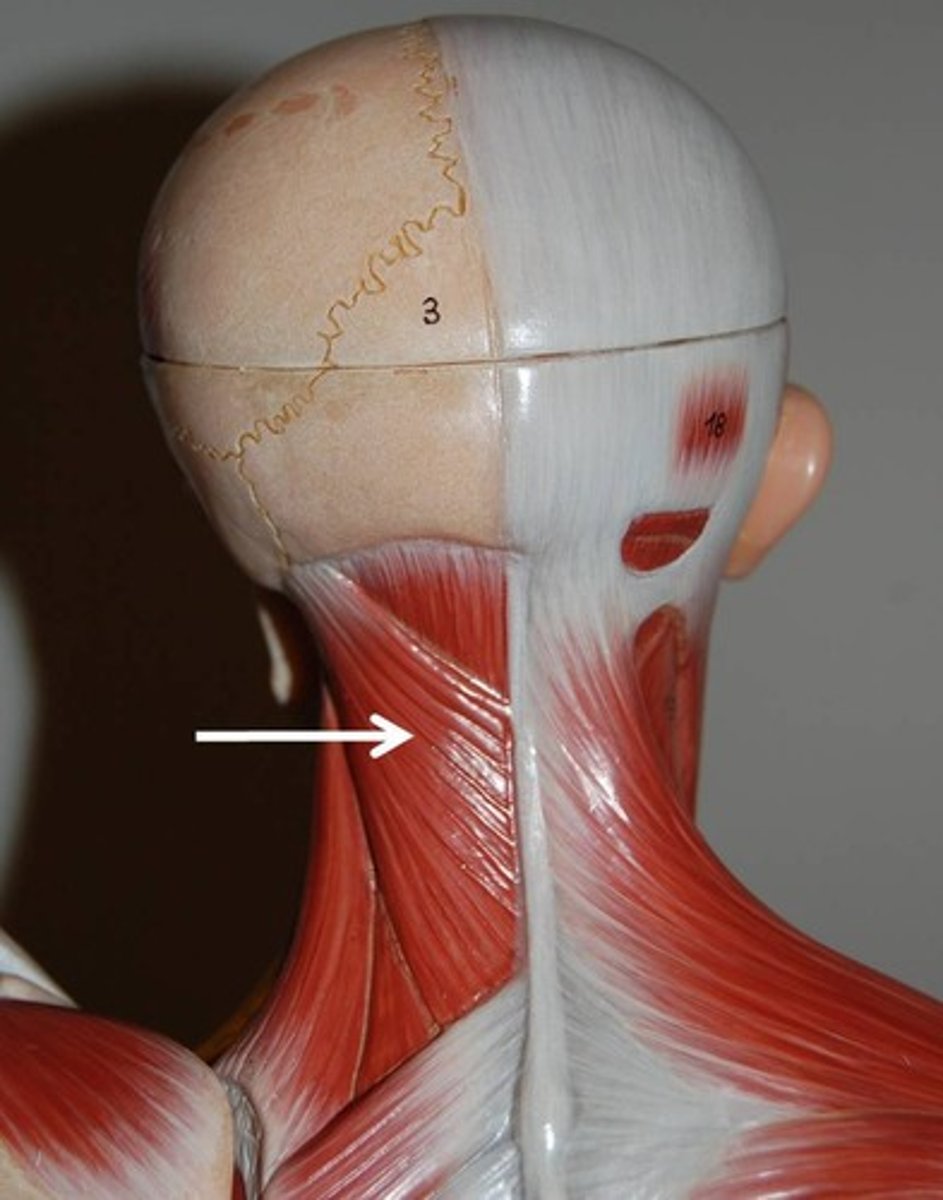
splenius capitis
extends head
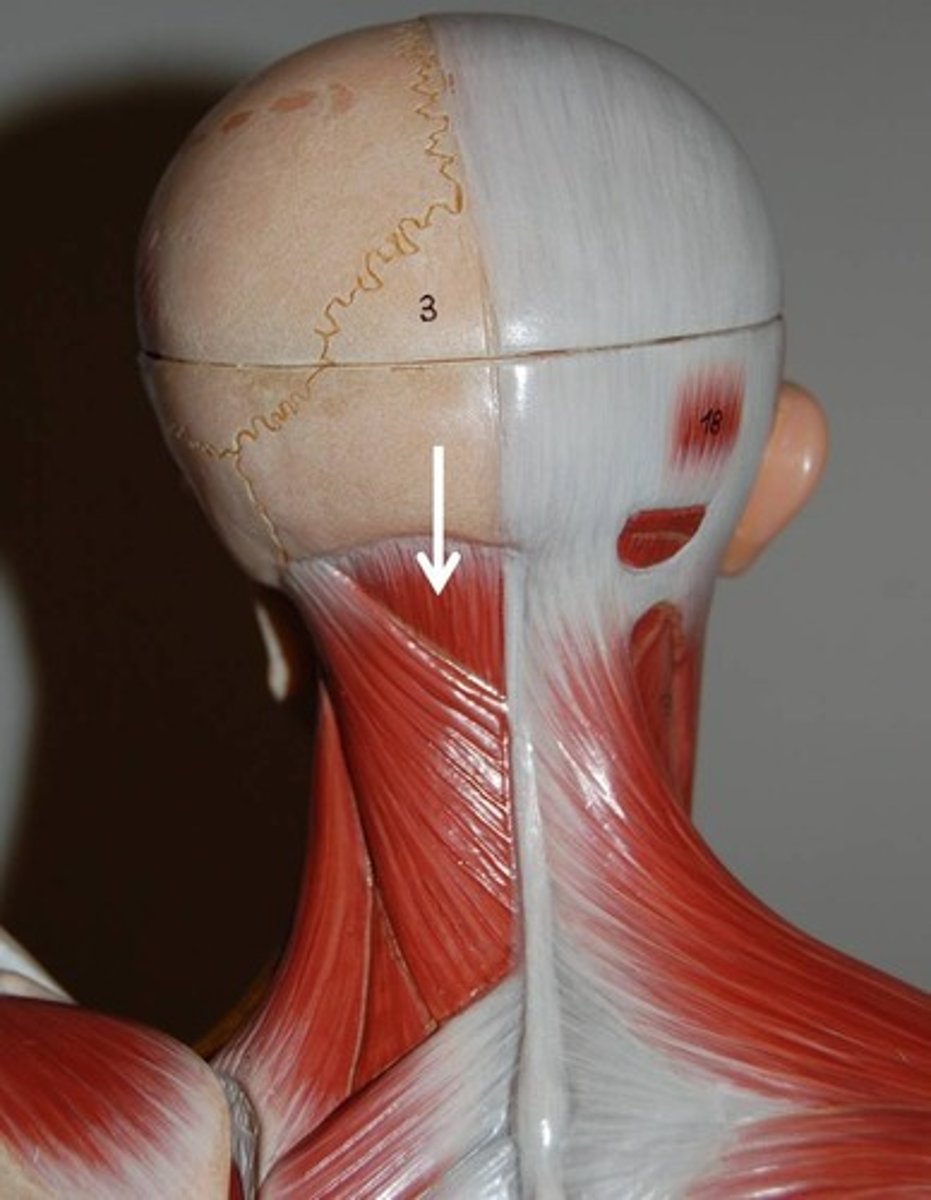
semispinalis capitis
extends head, rotates head
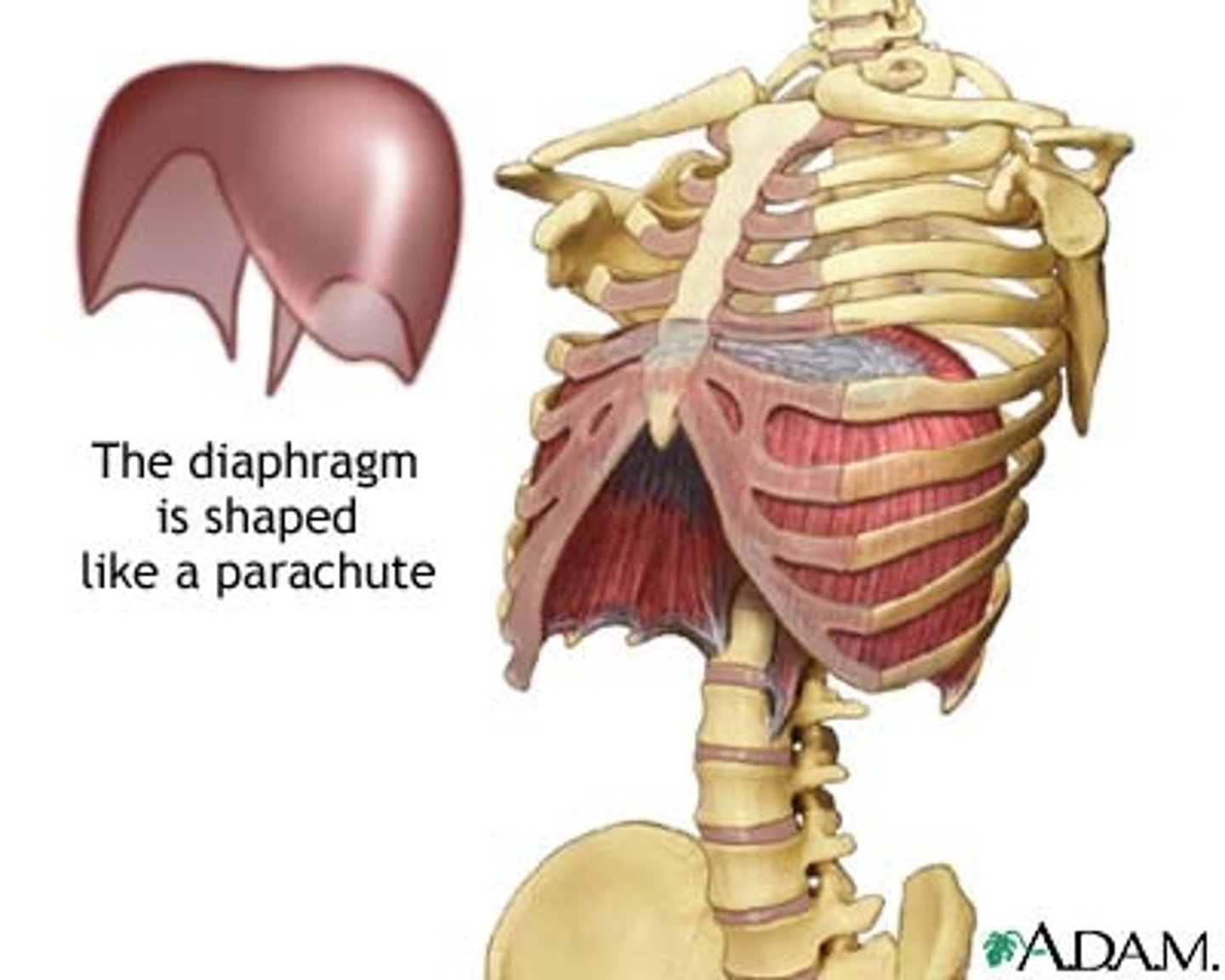
central tendon
muscle fibers of the diaphragm converge from its margins into a central fibrous tendon
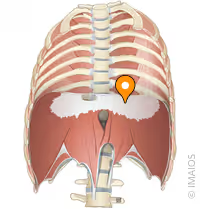
diaphragm
ORIGIN: diploid process, ribs 5-10, and vertebral bodies (L1-L3)
INSERTION: central tendon
ACTION(S): increases thoracic cavity dimension during inspiration
RELATIONSHIP: primary muscle of respiration; separates the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
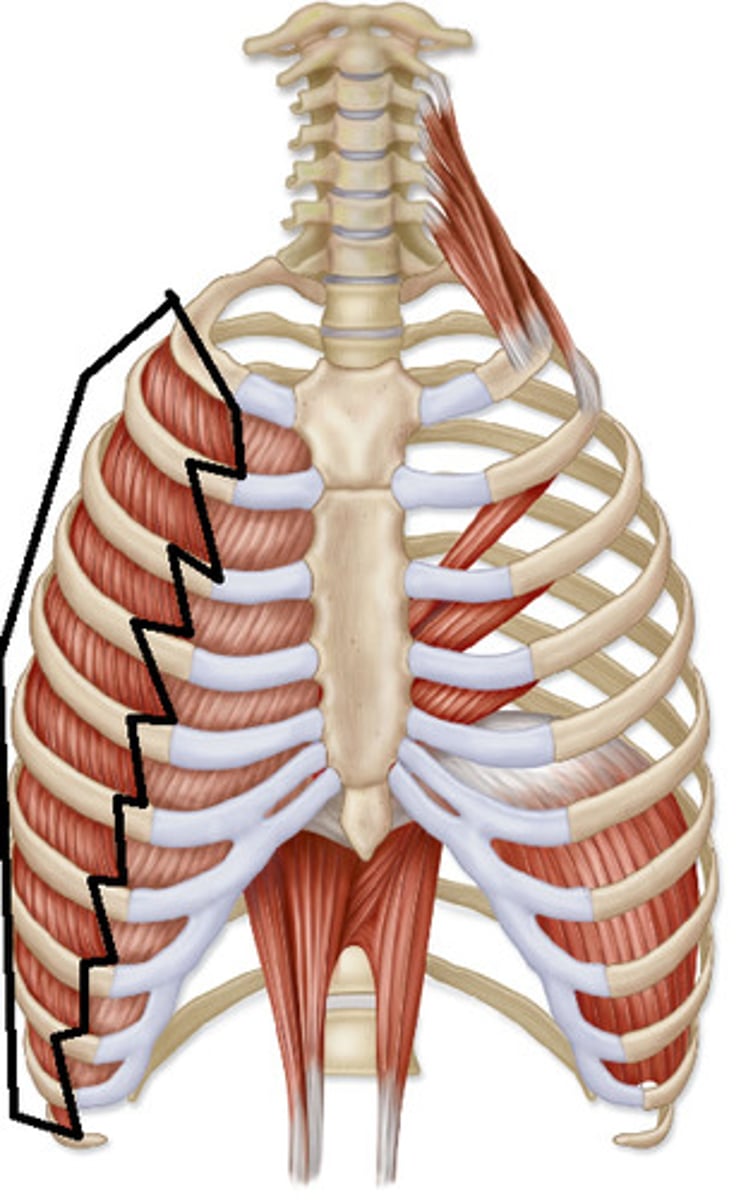
external intercostals
ORIGIN: inferior border of ribs 1-11
INSERTION: superior border of ribs 2-12
ACTION(S): elevates ribs during inhalation
RELATIONSHIP: oblique muscle fibers that run toward the midline of the body (from superior to inferior)
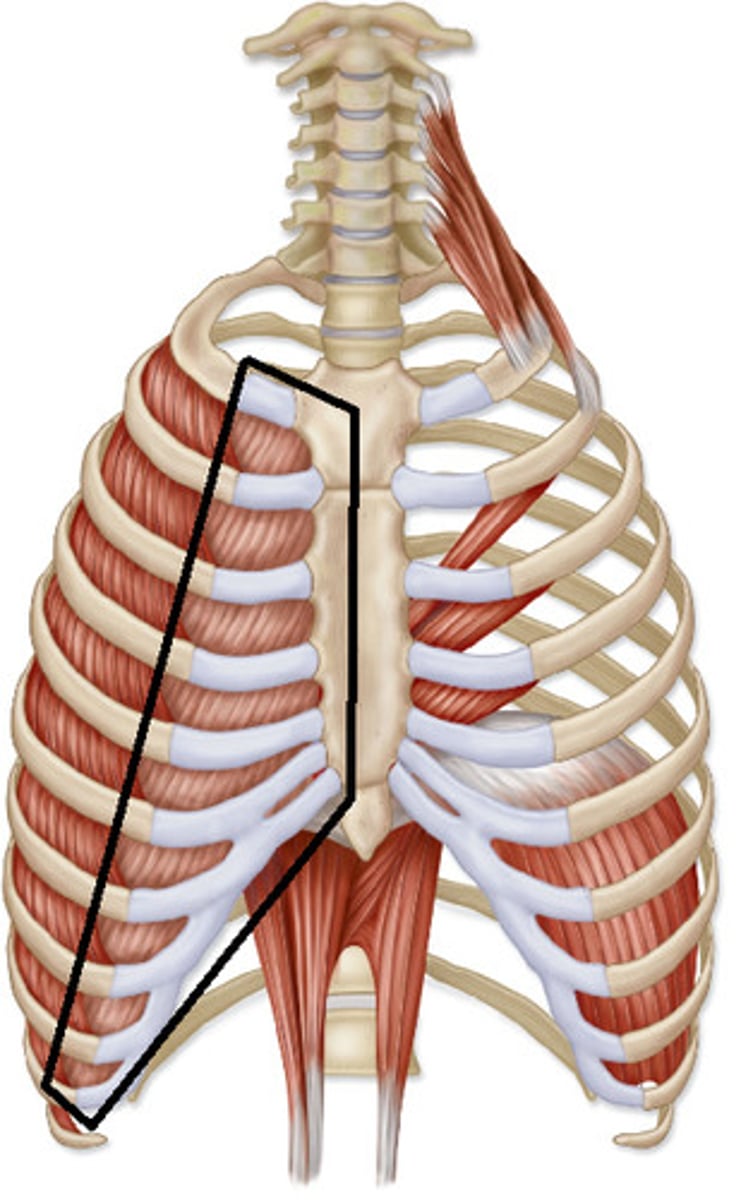
internal intercostals
ORIGIN: inferior border of ribs 1-11
INSERTION: superior border of ribs 2-12
ACTION(S): depresses ribs during forced exhalation
RELATIONSHIP: oblique muscle fibers that run away from the midline of the body (from superior to inferior)
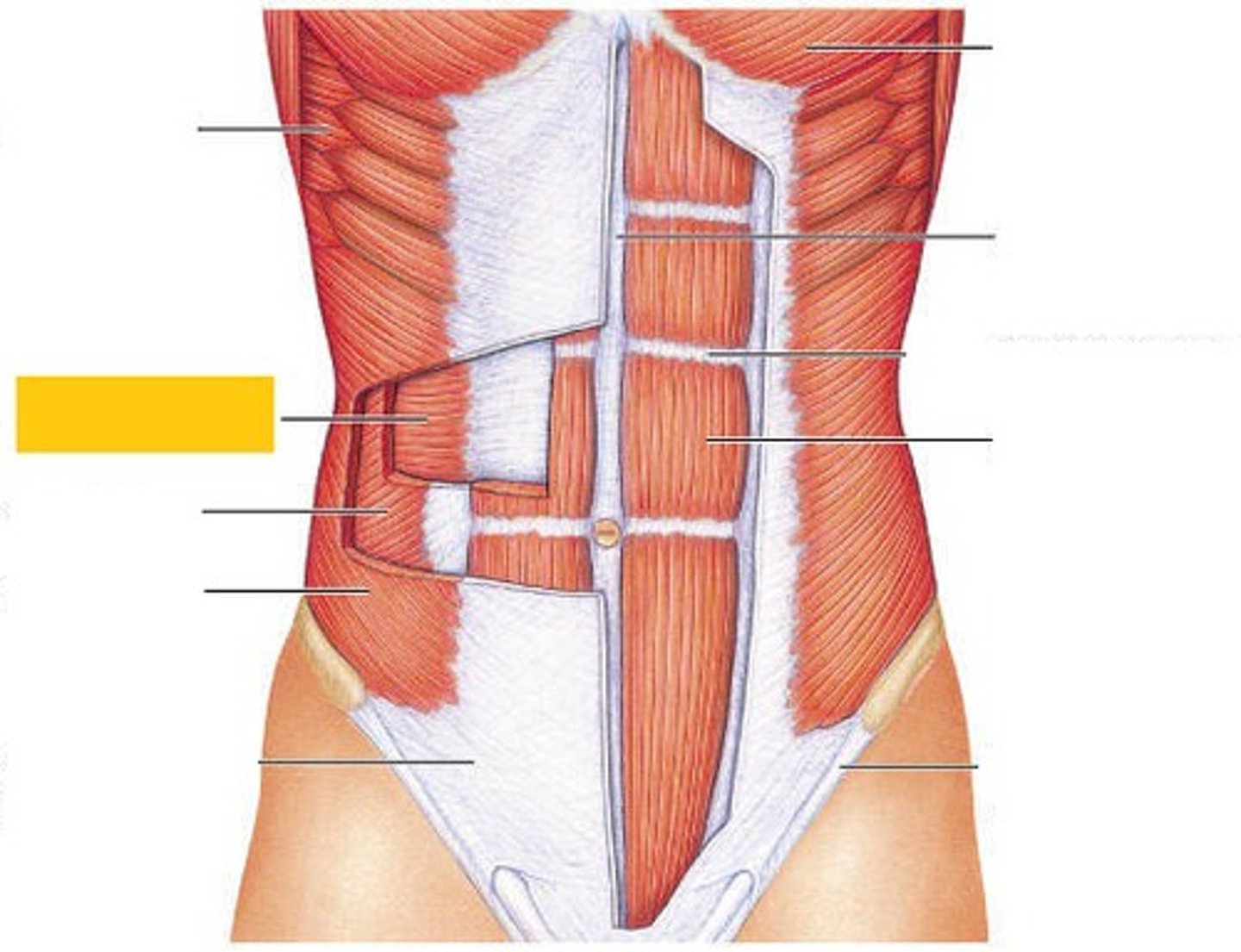
rectus sheath
Fibrous sleeve enclosing the rectus abdominis
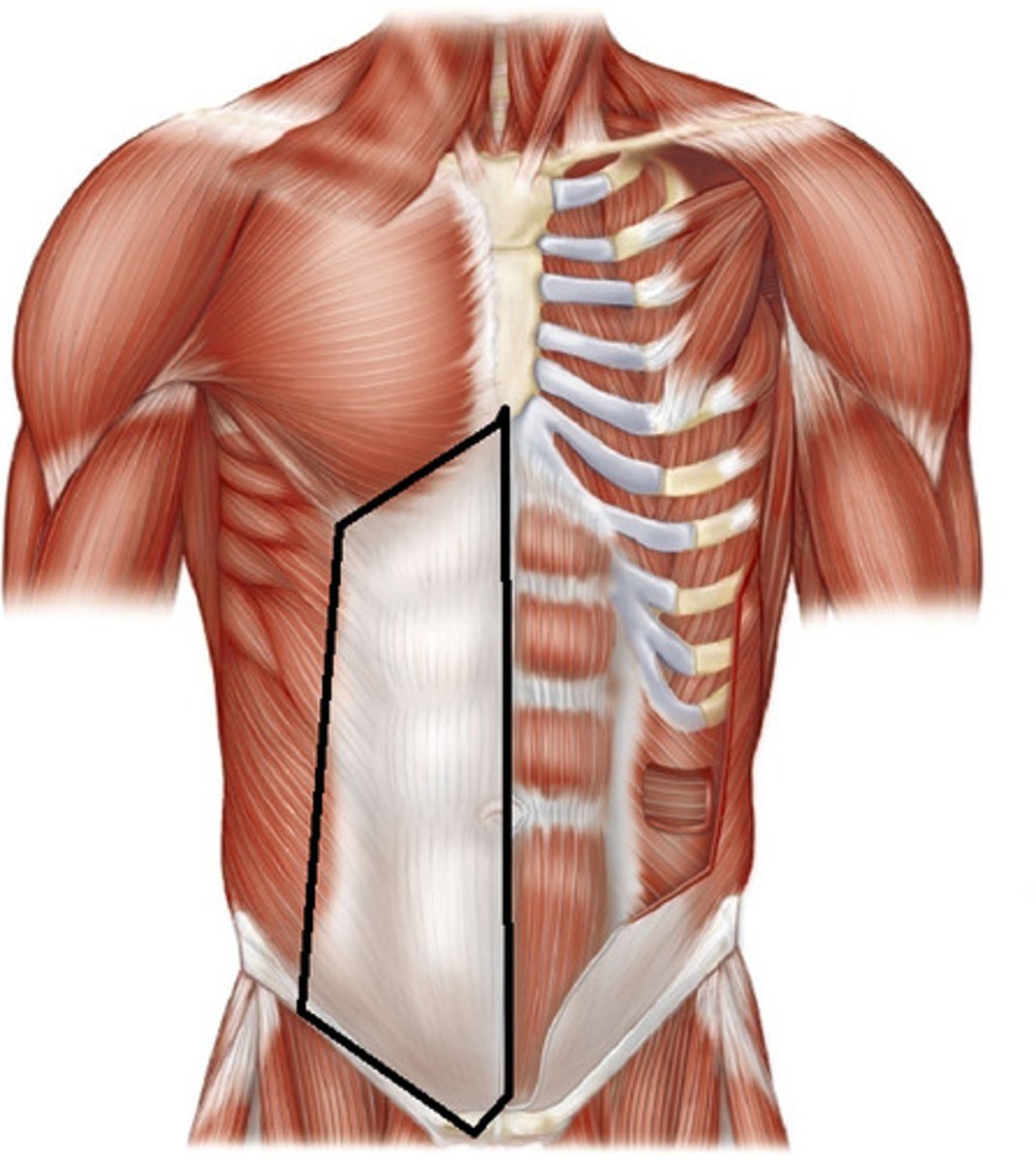
linea alba
midline tendinous seam joining the abdominal muscles
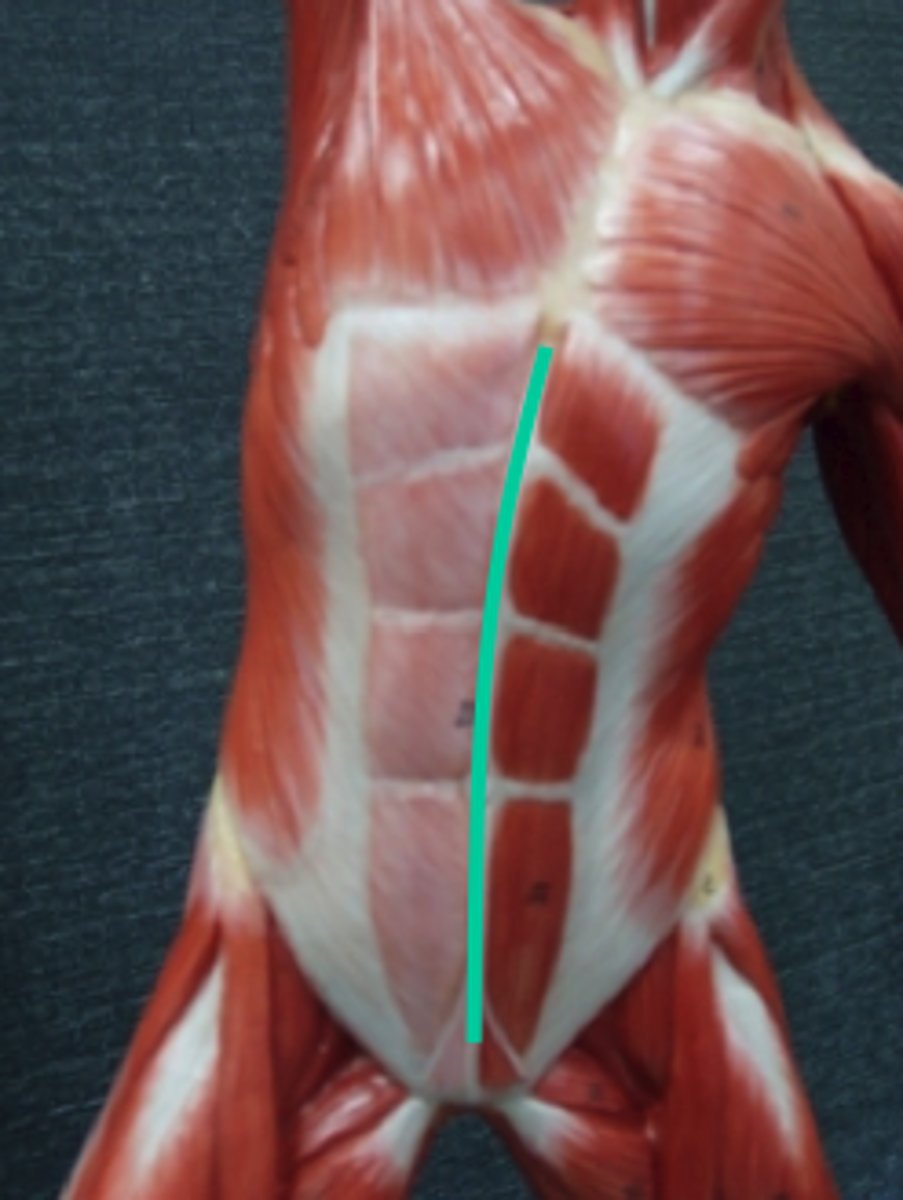
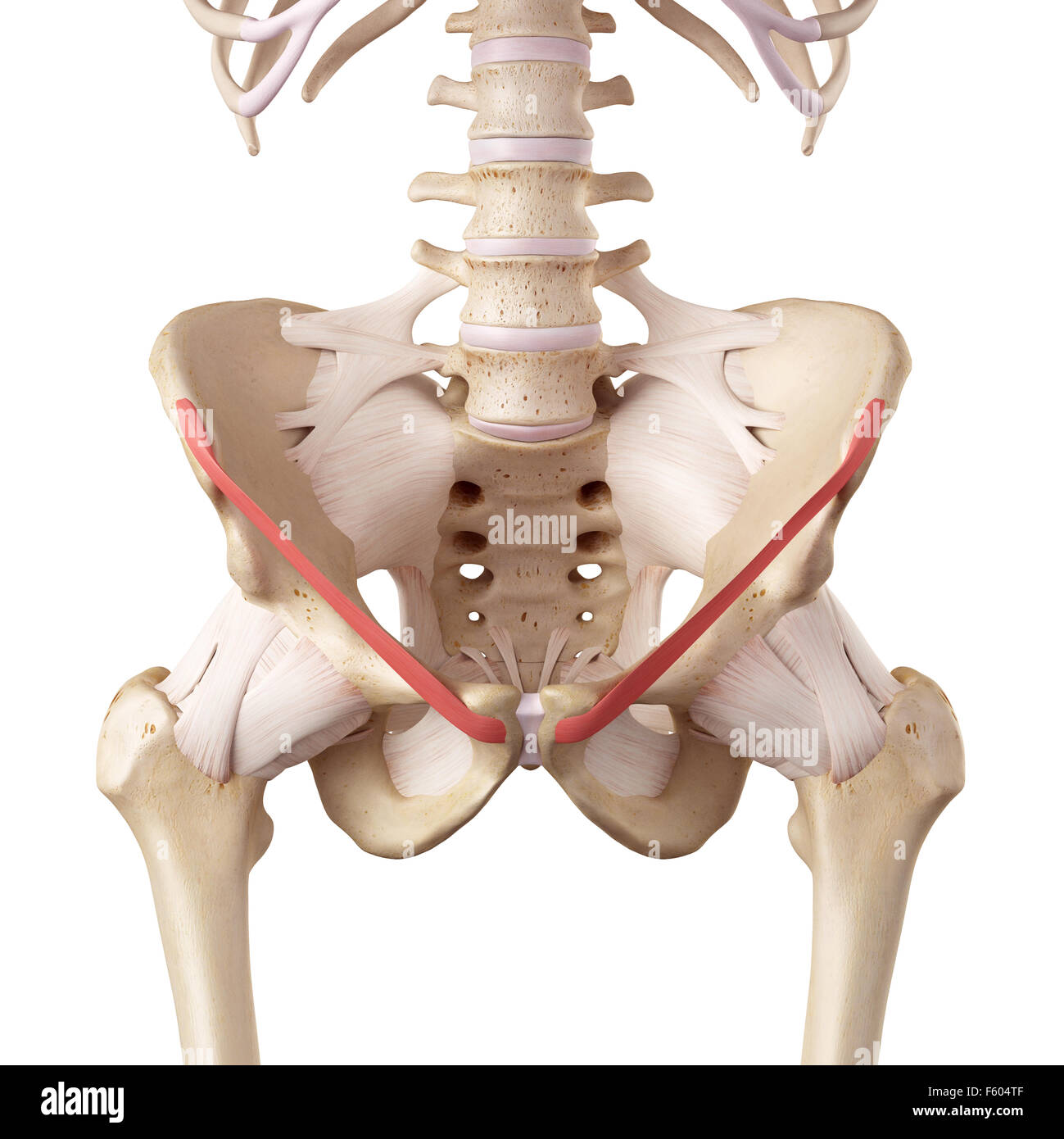
inguinal ligament
a band of connective tissue running from the pubic bone to anterior superior iliac spine
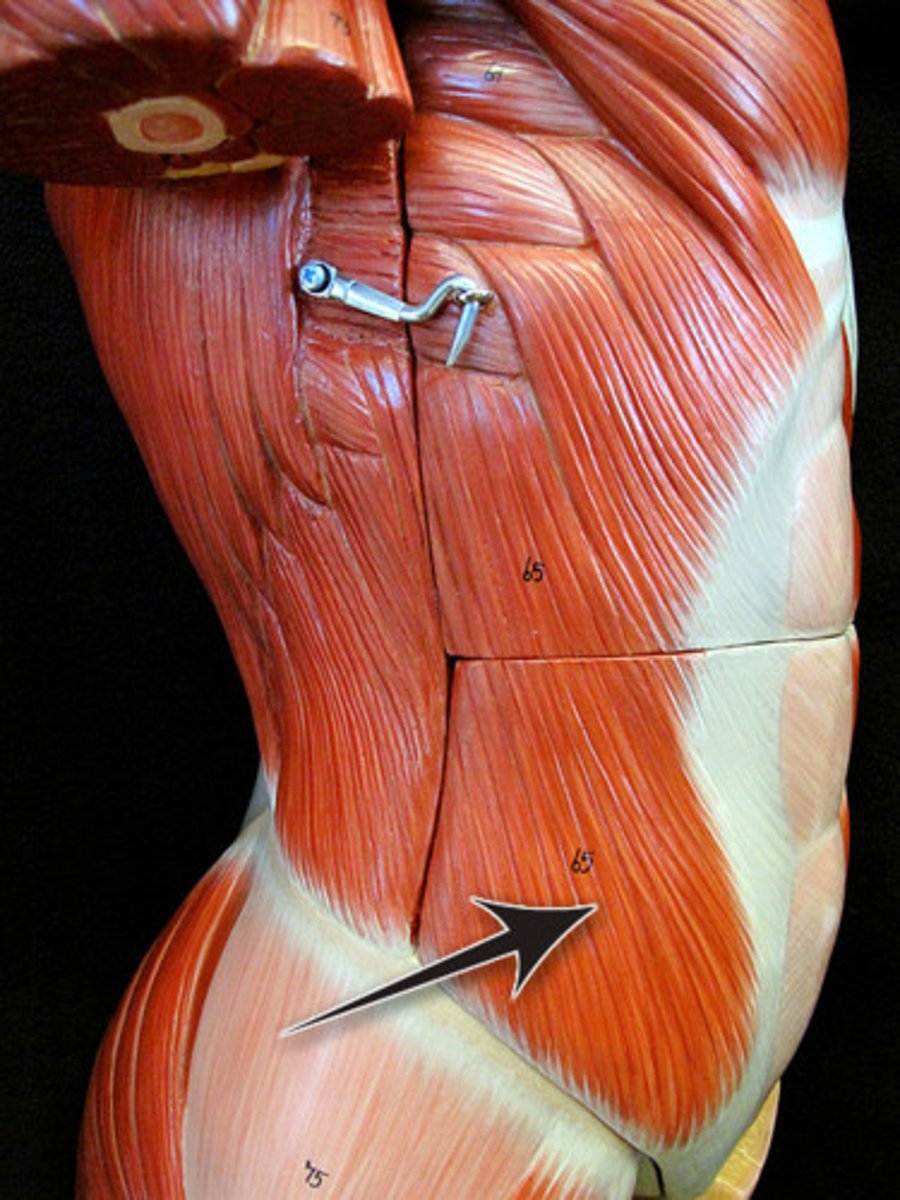
external oblique
compresses abdomen
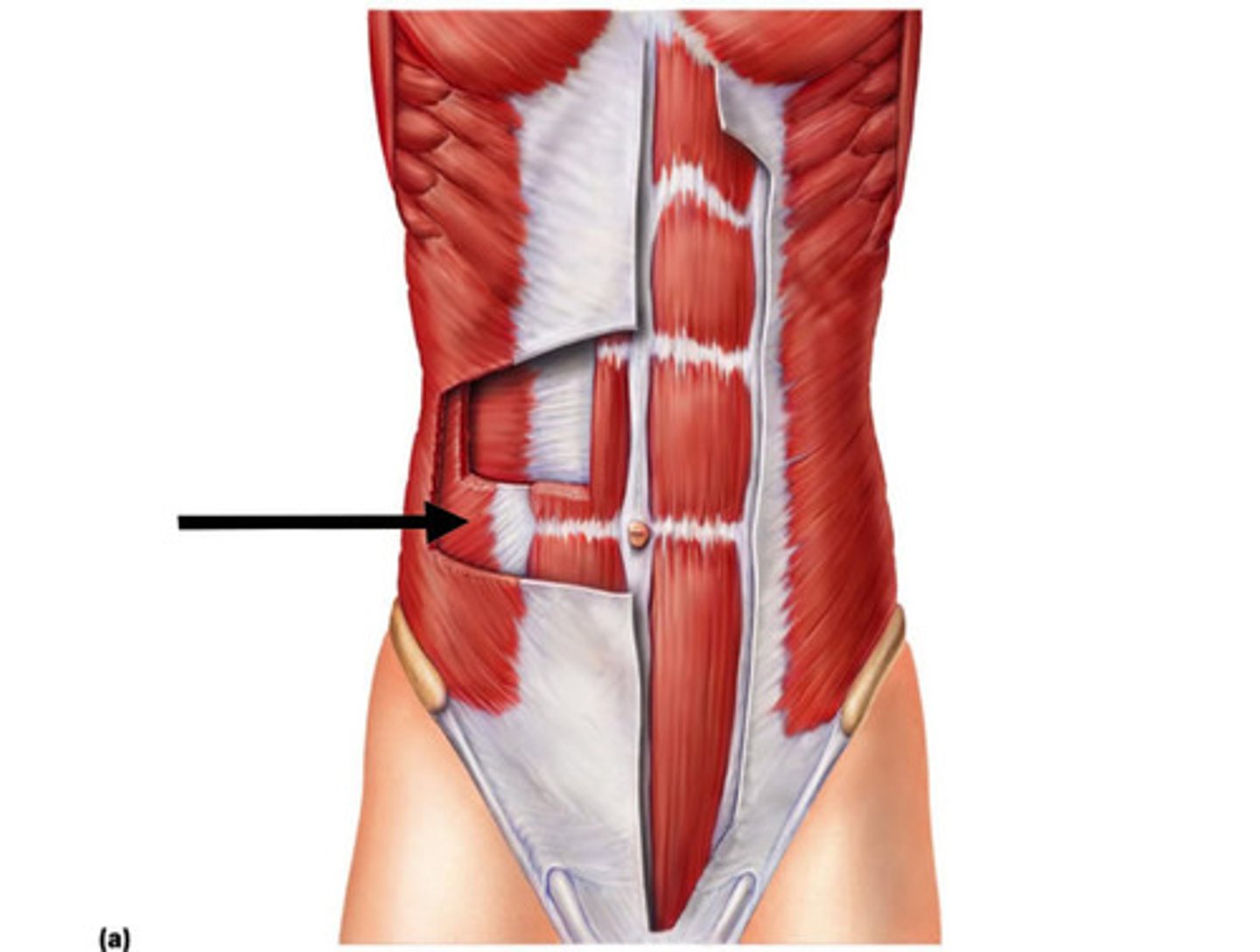
internal oblique
compresses abdomen
rectus abdominis
flexes vertebral column
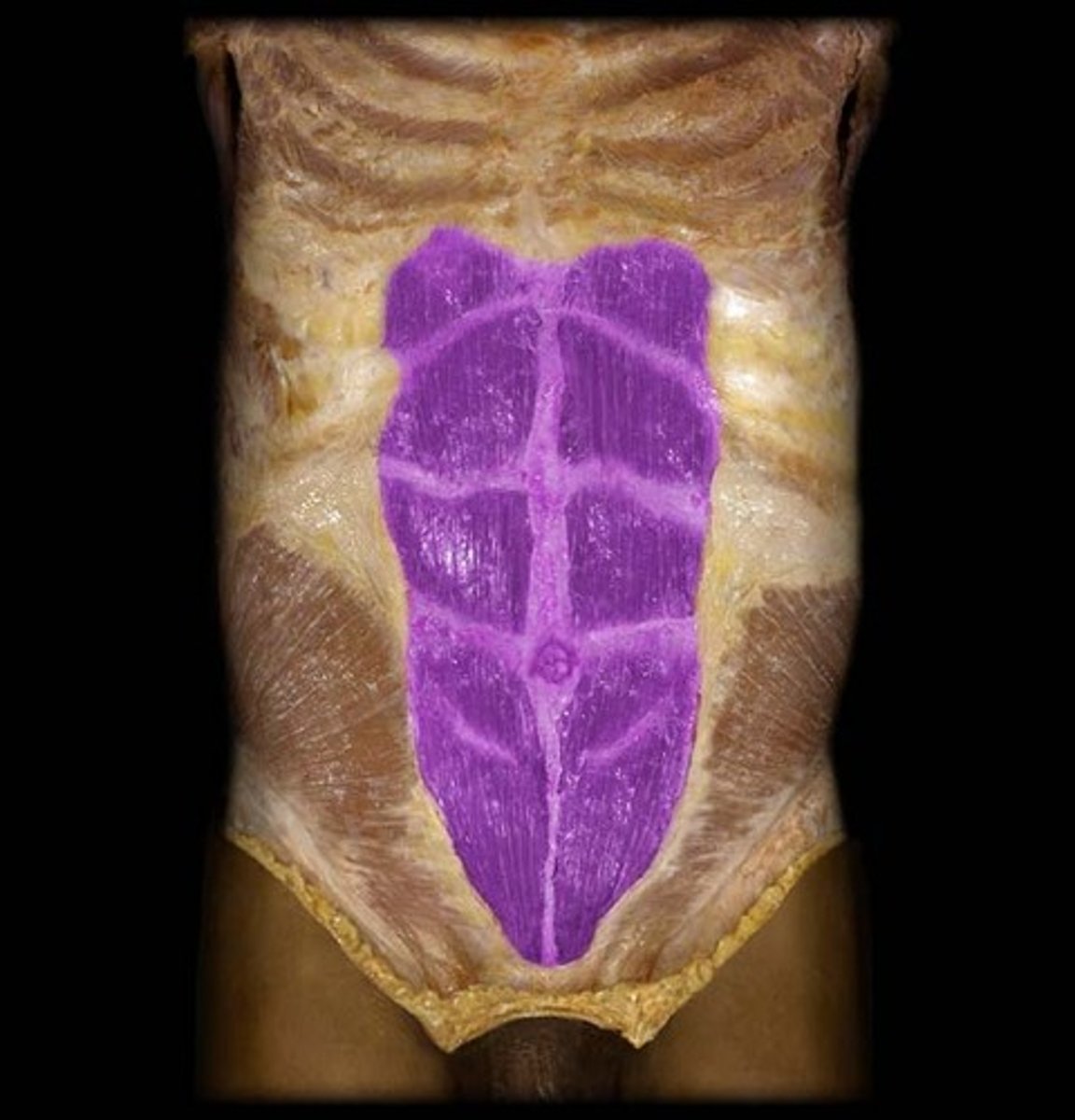
transverse abdominis
ORIGIN: iliac crest, inguinal ligament, and costal cartilage of ribs 7-12
INSERTION: pubis, linea alba, and diploid process
ACTION(S): compresses anterior abdominal wall
RELATIONSHIP: horizontal muscle fibers located deep to the rectus abdominis, external and internal oblique muscles
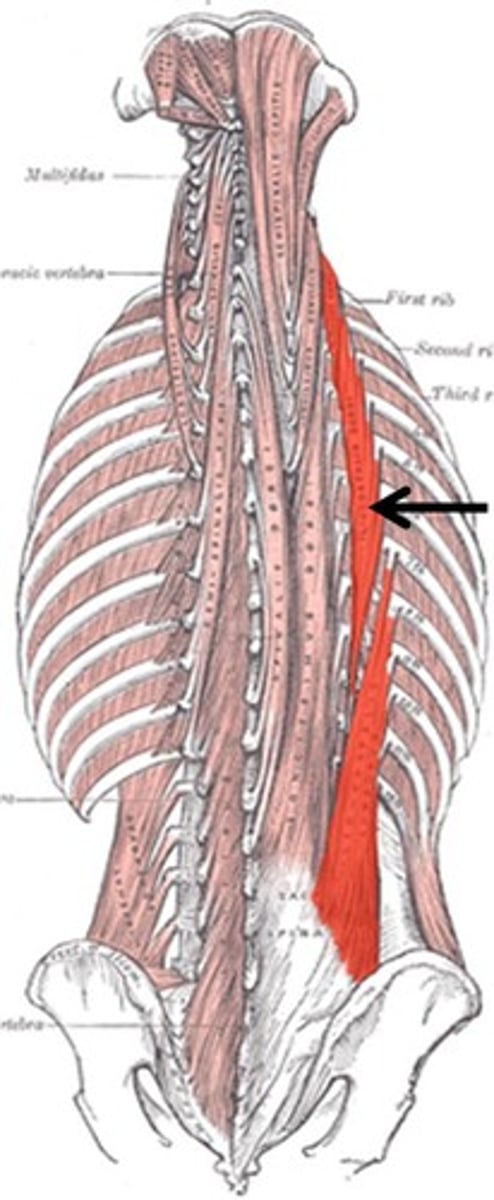
erector spinae
ORIGIN: sacrum, iliac crest, and spinous processes of all vertebrae
INSERTION: transverse and spinous processes of all vertebrae, and occipital bone
ACTION(S): Bilateral - extends neck and vertebral column; Unilateral - laterally flexes and rotates vertebral column
RELATIONSHIP: largest muscle of back; "antigravity" muscle
iliocostalis
lateral erector of spinae muscle
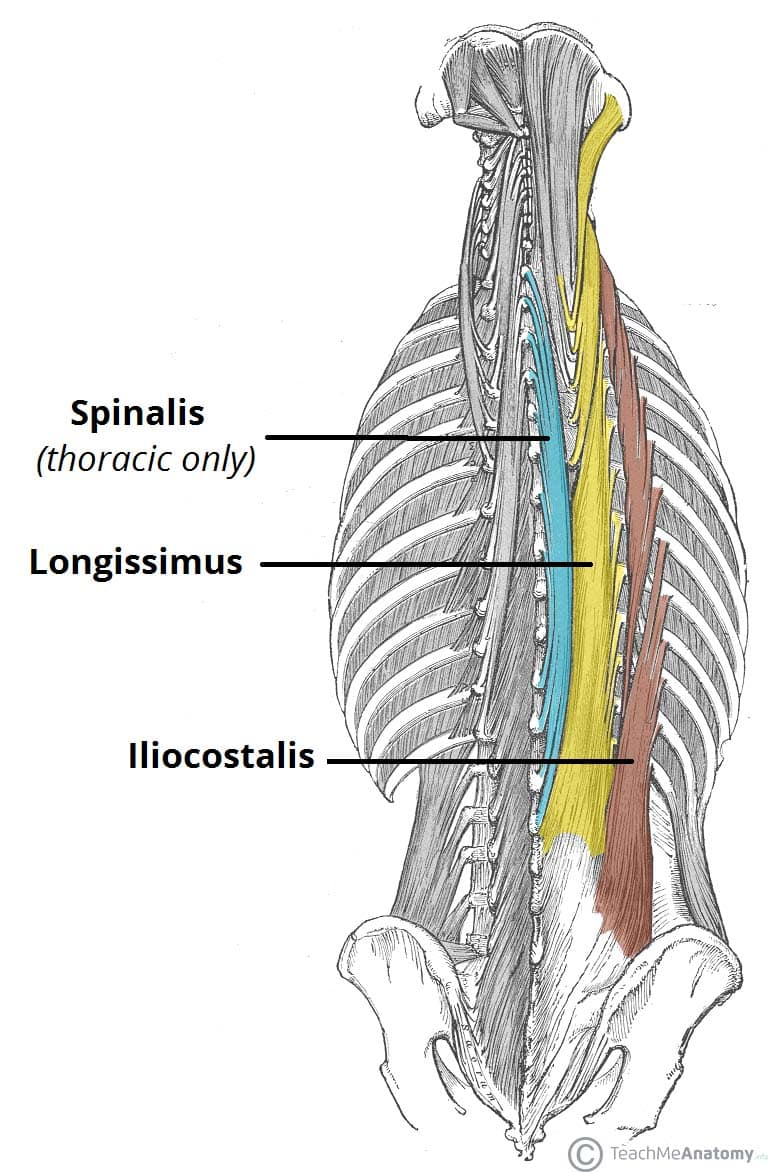
longissimus
middle erector of spinae muscle
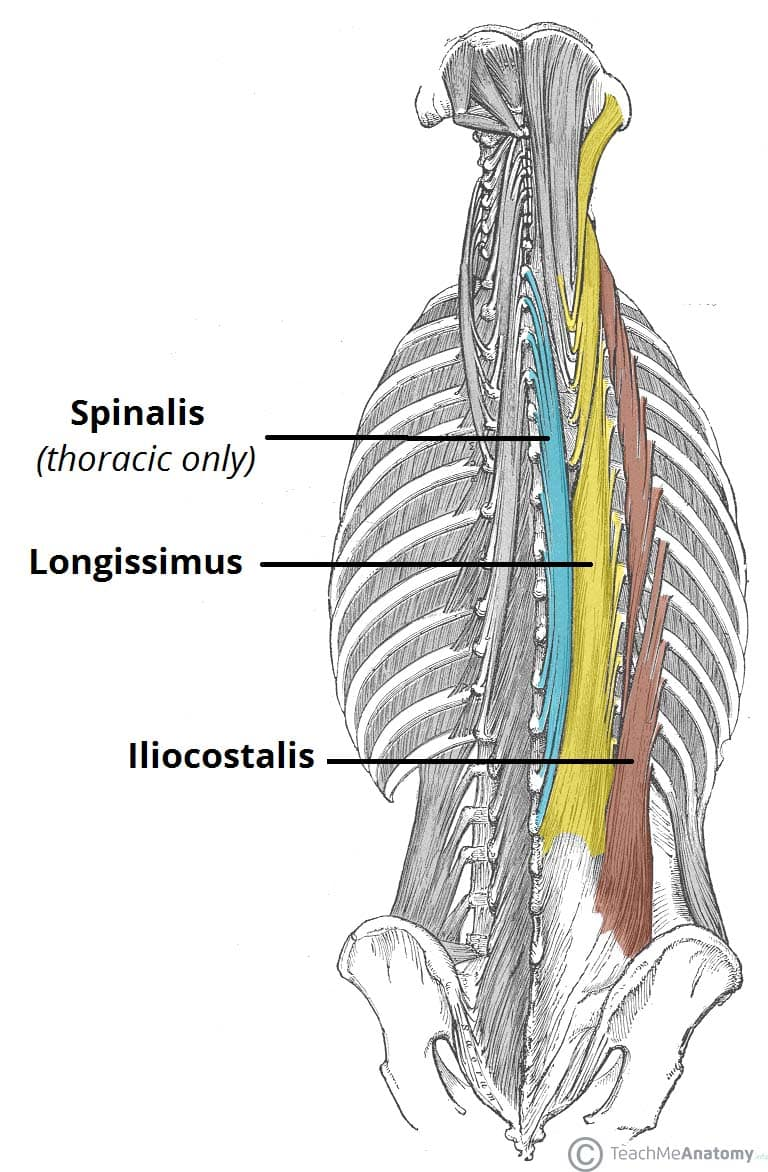
spinalis
medial erector of spinae muscles
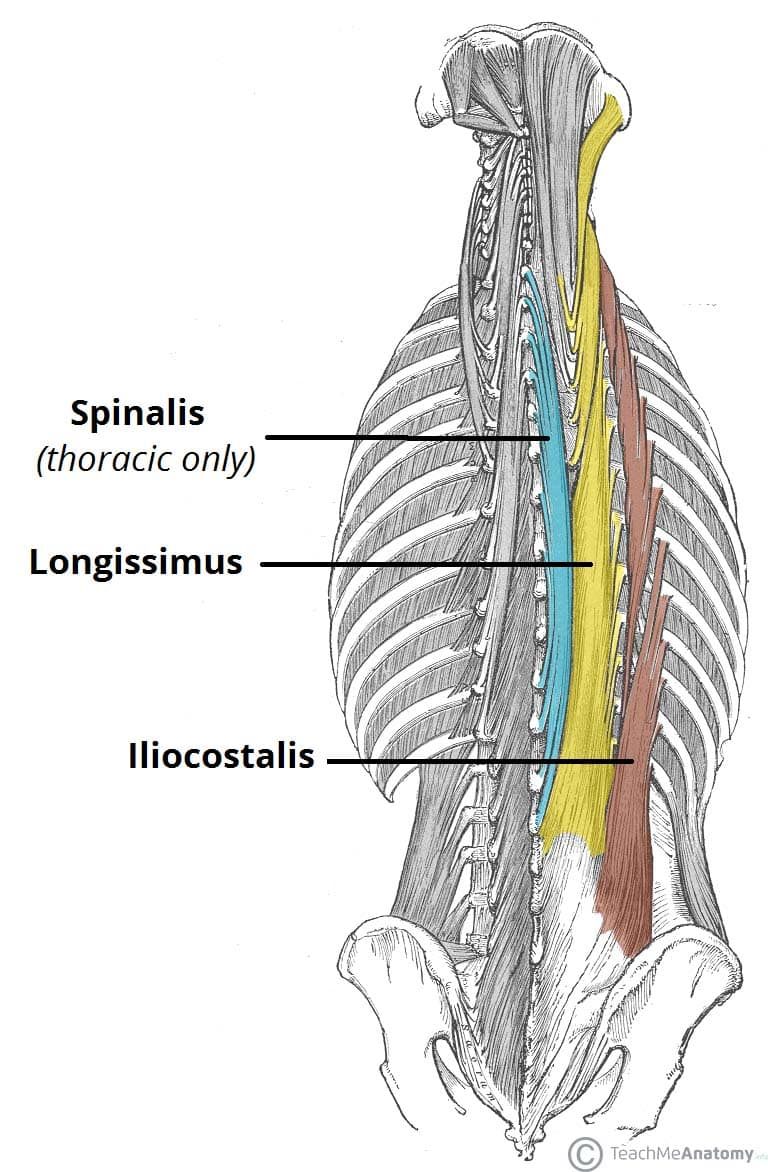
multifidus
acts on both the trunk and lies deep to the erector spinae seen best in the lumbar region
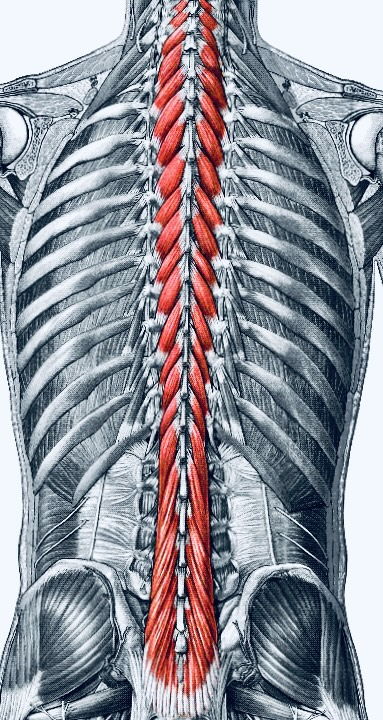
quadratus lumborum
makes up the posterior wall of the cavity
laterally flexes vertebral column
deltoid (anterior fascicles)
flex the GH joint.
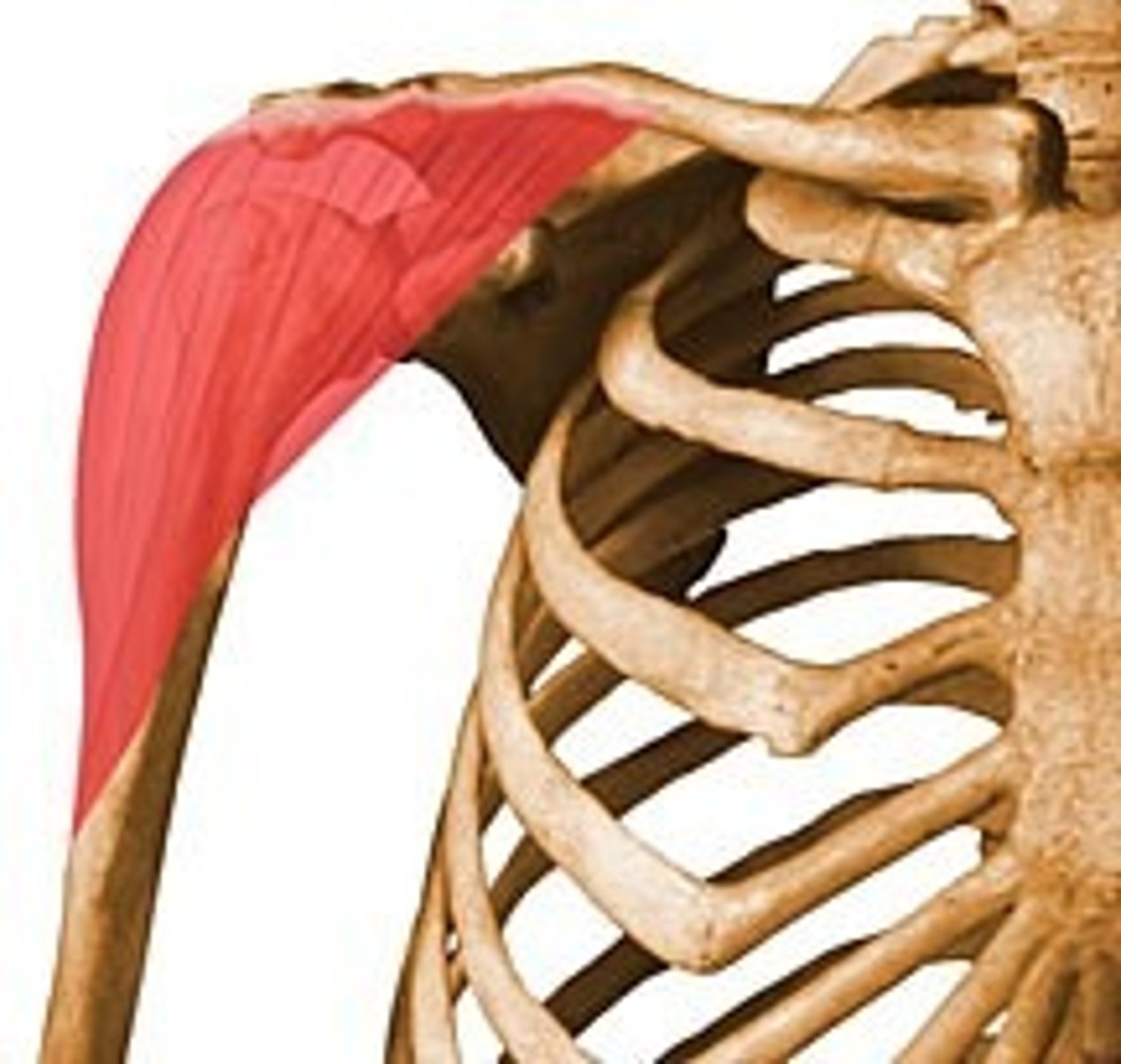
coracobrachialis
adducts GH joint as an additional action
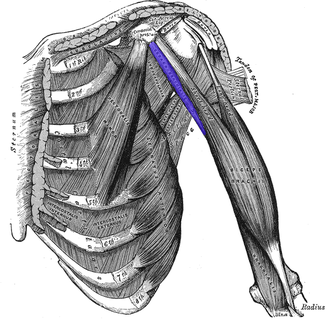
deltoid (posterior fascicle)
extend the GH joint
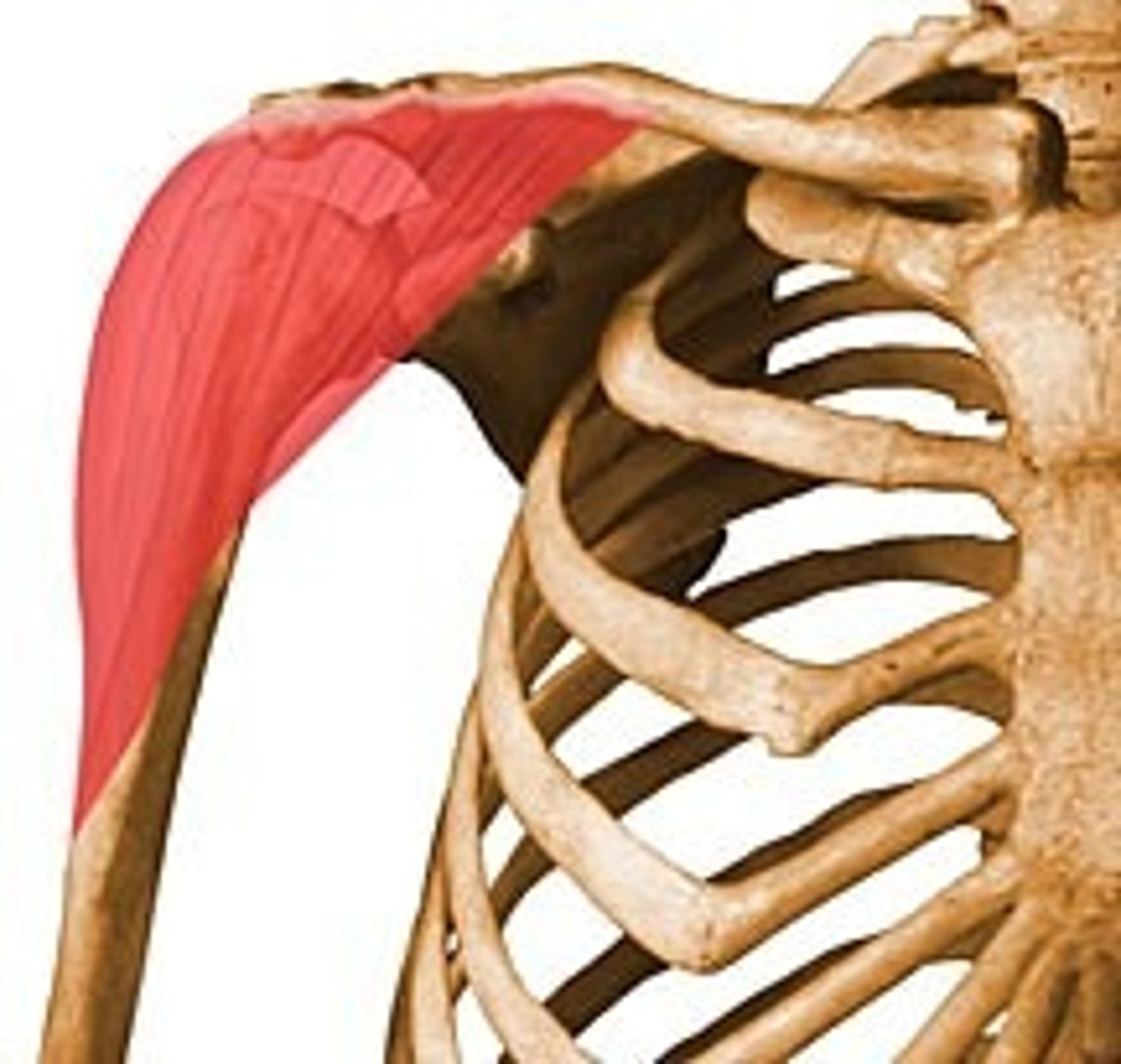
latissimus dorsi
lateral muscle of the chest wall (LATS by body builders)
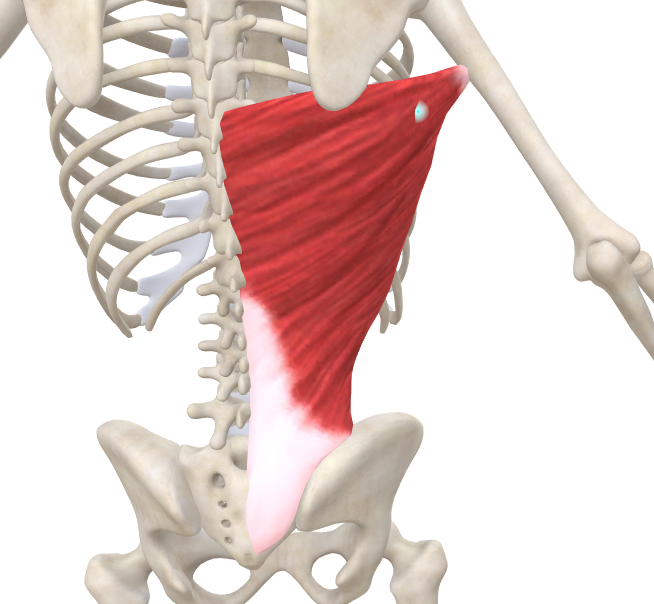
deltoid (middle fascicles)
abduct the GH joint
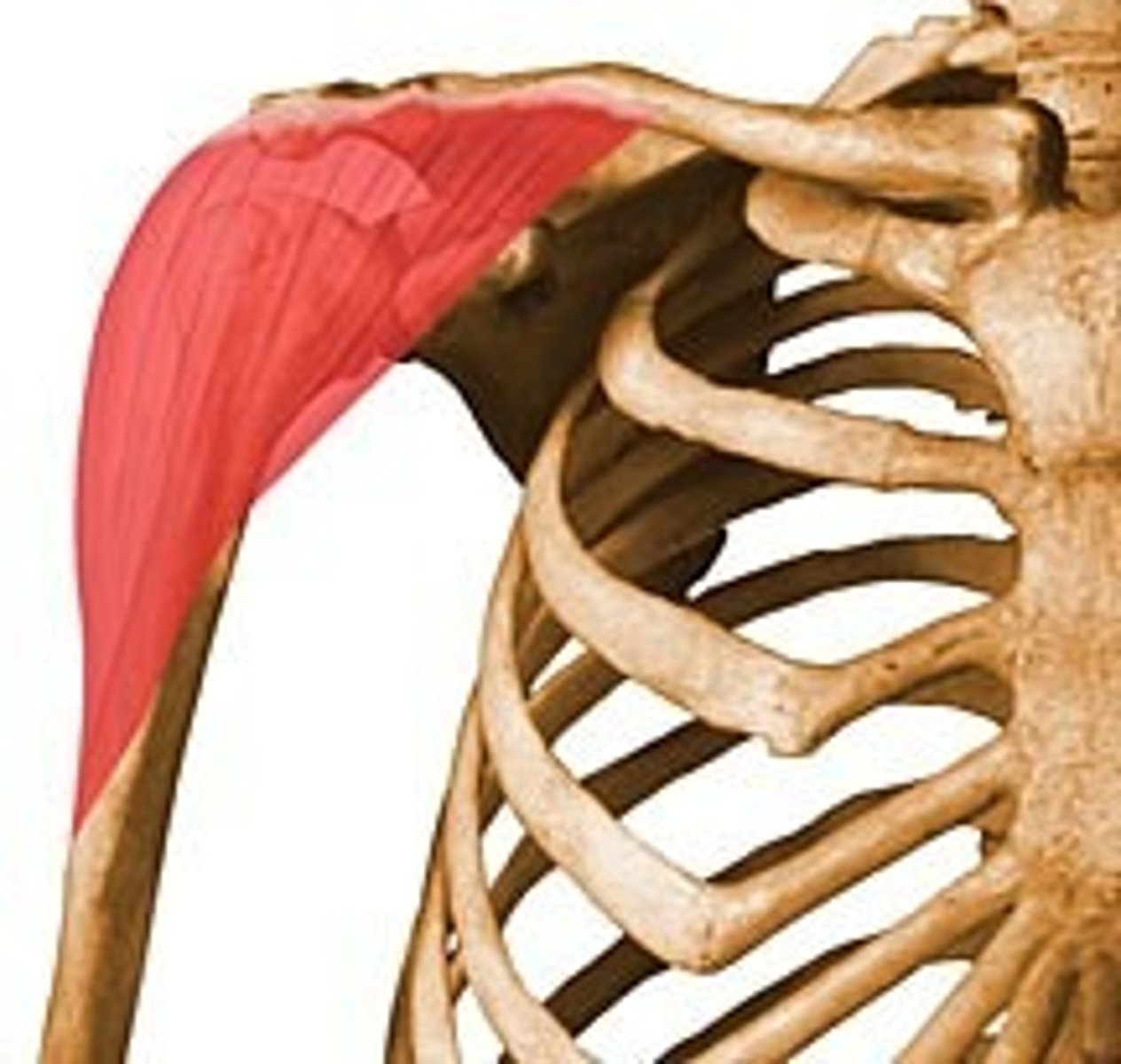
supraspinatus
ORIGIN: supraspinous fossa
INSERTION: greater tubercle
ACTION(S): abducts shoulder
RELATIONSHIP: S in the "SITS" acronym for the rotator cuff muscles
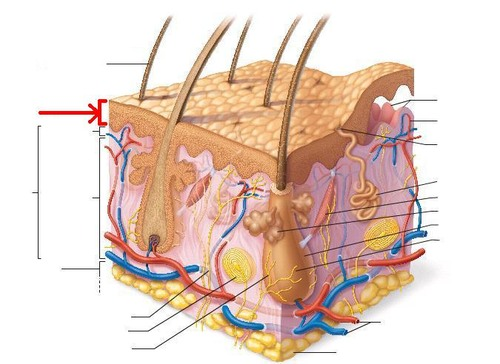
epidermis
most superficial, avascular layer
stratified squamous epithelium
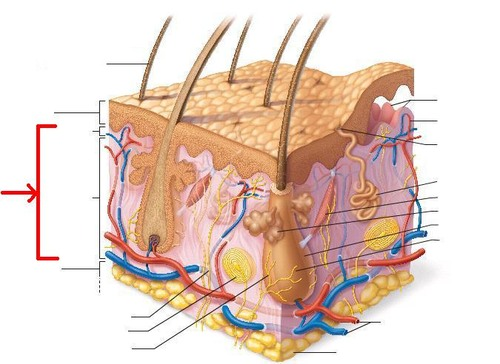
dermis
composed of dense irregular connective tissue
contains appendages of skin
where ink of tattooos is places
dermal papilla
fingerprints
bumps projecting from the dermis into the undersurface of the epidermis
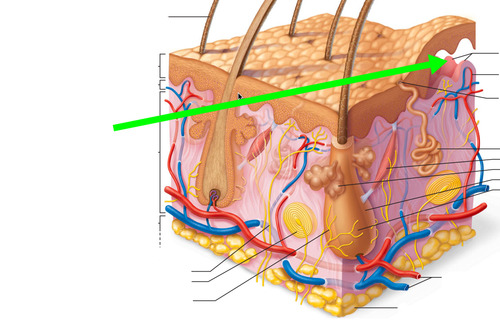
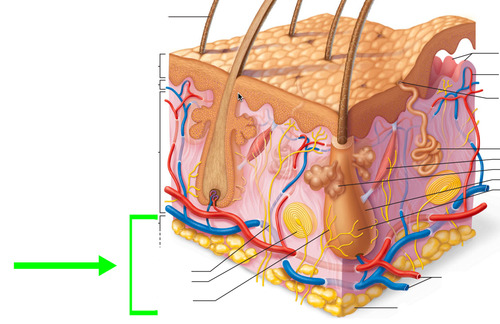
hypodermis
loose connective tissue primarily composed of adipocytes
separates skin from deep fascia
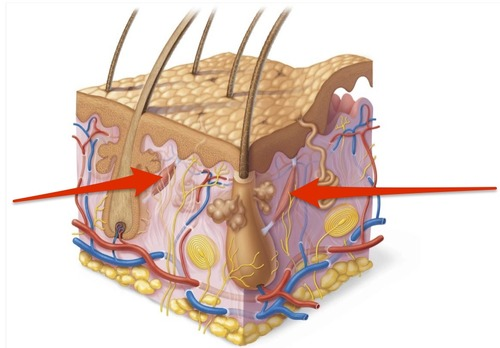
hair follicle
formation of hair below the surface of the skin
decreases heat loss
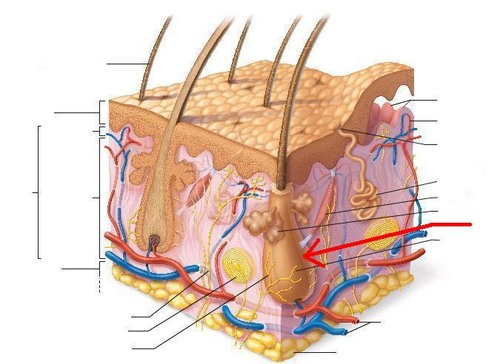
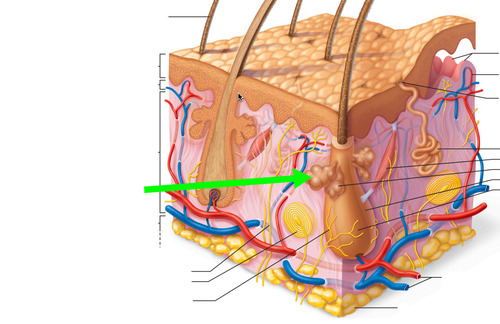
arrector pili muscle
ribbon of smooth muscle extending from hair follicle to the dermal papilla
hair follicles become erect when the body is under stress (goosebumps)
sweat (sudoriferous) gland
gland secreting watery fluid to epidermis
produces sweat in response to heat or stress
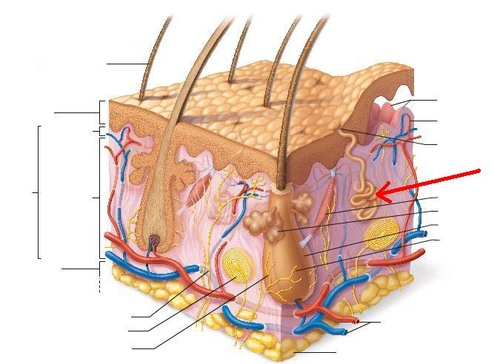
oil (sebaceous) gland
gland secreting sebum to lubricate and waterproof hair shaft and epidermis
not found in skin of palms or soles