b8
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
what type of circulatory system do humans have
double circulatory system
pacemaker cells
in right atrium, sends electrical impulses that causes the walls of the heart to contract
order of blood flow
body-vena cava-RA-RV-valve-pulmonary artery- valve-lungs- pulmonary vein- LA-LV-valve- aorta- body
vein
carries blood to heart
artery
carries blood away from the heart
capillaries
exchanges nutrients and waste with the tissues
blood travel from atrium to ventricles process
atrium wall contracts and pushed blood into relaxed ventricle, ventricle wall contracts and pushed blood out of the heart, more blood flows into the relaxed atrium
arteries structure
high pressure blood, thick walls, thick muscle and elastic tissue, narrow lumen, high speed blood
veins structure
low pressure blood, thin walls, thin muscle and elastic tissue, wide lumen , valves to stop back flow , slow blood
capillaries structure
permeable walls, one cell thick walls, tiny lumen, low blood pressure
red blood cell function
carries oxygen to cells for cellular respiration
red blood cell adaptation
no nucleus- carries more oxygen, biconcave disc shape - absorb more oxygen, haemoglobin to bind to oxygen - has a red pigment
white blood cell function and structure
fight pathogens, has a nucleus
white blood cells 3 tasks
produce phagocytes to do phagocytosis ( engulf pathogens ) , produce lymphocytes which produce antibodies and antitoxins
platelet function and definition
cell fragments produced by giant cells in bone marrow, clot blood when bleeding
platelet 2 adaptations
secretes proteins that result in chemical reactions which clots the blood, proteins on their surface allow them to clump together and stick to block breaks in a vessel
plasma
carries all blood components
what does plasma carry
glucose, amino acids, hormones, carbon dioxide, urea
cardiac output
The volume of blood pumped through each ventricle per minute
Stroke volume
volume of blood pumped out of each ventricle each time the heart beats
Heart rate
number of beats per minute
cardiac output formula
cardiac output (ml/m) = stroke volume (ml) x heart rate (bpm)
aorta
carries oxygenated blood to the body
vena cava
carries deoxygenated blood from body to the heart
pulmonary artery
carries deoxygenated blood towards the lungs
pulmonary vein
carries oxygenated blood from lungs to heart
What is metabolism?
The combination of all chemical reactions in an organism
What is the word equation for aerobic respiration?
Glucose + oxygen ➔ carbon dioxide + water
What is glucose converted to during anaerobic respiration in animals?
lactic acid
word equation for anaerobic respiration in plants and fungi:
Glucose ➔ ethanol + carbon dioxide
what is the energy from respiration used for
chemical reactions to build larger molecules from smaller ones
muscle contraction to allow movement
Keeping warm and maintaining a constant temperature
anaerobic respiration reaction
glucose —> lactic acid
what is anaerobic respiration in yeast cells called
fermentation
when does the body anaerobically respire
anaerobic respiration takes place in muscles during vigorous exercise
difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration
anaerobic respiration doesn’t fully break down glucose so releases less energy
what is oxygen debt
amount of oxygen needed to break down the built up lactic acid
investigating respiration experiment
put hydrogen carbonate indicator in boiling tube
place a layer of cotton wool
add 10 seeds
seal the tube with a bung
use glass beads as a control
observe after a few hours. Respiration produces CO2 which makes the solution more acidic
main components of blood
red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, plasma
how does the structure of the artery help its function
thick muscular walls and elastic fibres can withstand high pressure blood and maintain the blood pressure. A narrow lumen maintains high pressure
how does the veins structure adapt it to its function
large lumen reduces resistance to blood flow under low pressure, valves to prevent back flow
how does the structure of the capillaries adapt it to its function
one cell thick walls and permeable walls for diffusion
label the heart 1-8
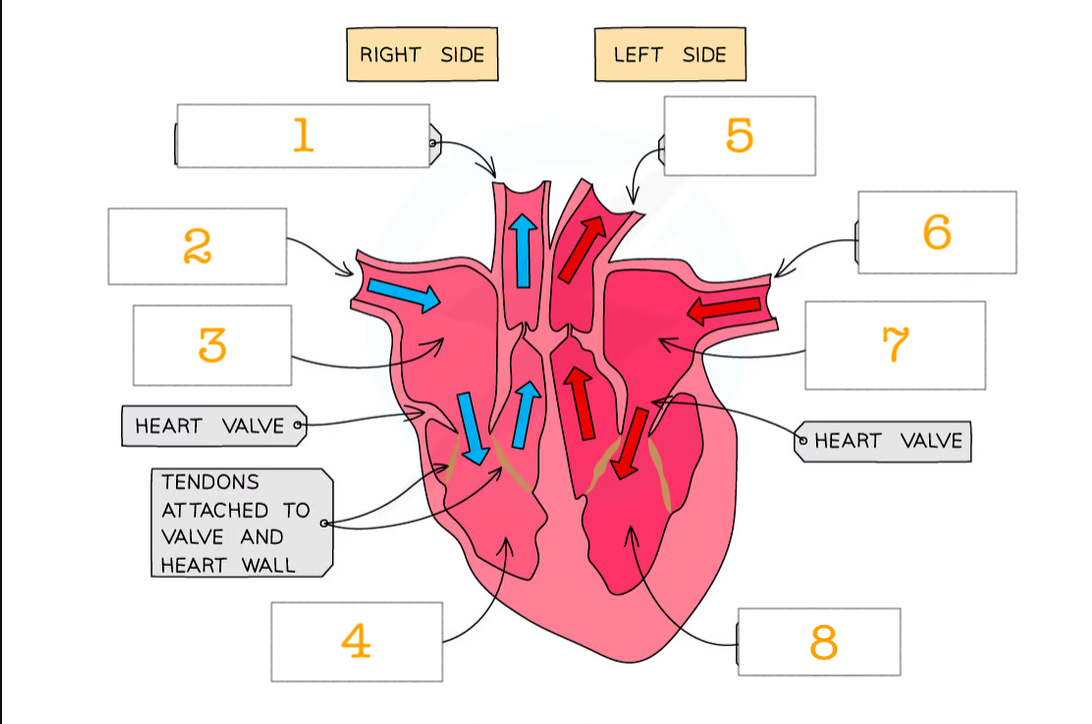
pulmonary artery
vena cava
right atrium
right ventricle
aorta
pulmonary vein
left atrium
left ventricle
diffusion
movement of particles from an area of high concentration to low concentration
why is transport important
organisms need to exchange substances by processes like osmosis , diffusion and active transport
why do multicellular organisms need transport systems
they have large distance from the cell membrane to inside the cell so diffusion wouldn’t be efficient enough for transporting substances
why do multicellular organisms need exchange surfaces
they have small surface area compared to their volumes so larger organisms need exchange surfaces within their transport system to carry out diffusion , osmosis and active transport at a sufficient rate
Rick’s law of diffusion
rate of diffusion is directly proportional to ( surface area x concentration gradient ) / thickness of the membrane
factors affecting rate of diffusion
diffusion distance, concentration gradient, temperature, surface area
how does increased surface area increase diffusion rate
more surfaces for the molecules to move and diffuse across
how does greater concentration gradient / difference in concentration on either side affect diffusion rate
substances diffuse faster id there’s larger difference in concentration . If there are more particles, they diffuse faster to try balance the concentration and spread out
how does temperature affect diffusion rate
molecules have more KE and faster movement across membrane
what is the purpose of the alveoli
gas exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide
adaptations of alveoli
thin cell membrane, good blood supply, large surface area, ventilation, layer of moisture
what is the purpose of good blood supply for the alveoli
maintain steep concentration gradients of O2 and CO2 to allow easy gas exchange
what is the purpose of ventilation in the alveoli
creates a steep concentration gradient and mains high levels of oxygen and low levels of CO2 to increase diffusion rate
what does the layer of moisture do in the alveoli
dissolves gases helping them diffuse
what does the large surface area and thin membrane do in the alveoli
increase rate of diffusion
how do receptors on membrane act as an adaptation for wbc
detect pathogens
how does the nucleus/ribosomes act as an adaptation for wbc
make antibodies / antitoxins
how is flexible membrane an adaptation for wbc
to engulf pathogens
ficks law of diffusion
rate of diffusion is proportional to ( surface area x concentration gradient ) / diffusion distance
how can membrane characteristics affect rate of diffusion
thinner and more permeable membrane can increase diffusion rate
how might cell size affect diffusion rate
smaller cells and elongated / irregularly shaped cells increase diffusion due to their higher surface area
how is the small intestine adapted for absorbing dissolved food molecules
villli to increase surface area to volume ratio, good blood supply to maintain concentration gradient
features of efficient gas exchange surface
large surface area, thin membrane, large concentration gradient
what is the rate of diffusion inversely proportional to
membrane thickness
how can steeper concentration gradient increase diffusion
more random collisions against the membrane so faster diffusion
oxygen debt equation
lactic acid + oxygen —> carbon dioxide + water
what is the difference of glucose breakdown in aerobic and anaerobic respiration
in aerobic respiration there is complete breakdown of glucose but not in anaerobic
where does aerobic respiration happen
mitochondria
where does anaerobic respiration happen
cytoplasm
respiration
reacion in cells that releases energy through the breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen.
why does anaerobic respiration occur during intense excersise
the muscles require more energy but aerobic respiration is at its maximum rate and oxygen isn’t supplied fast enough
what 2 industrial processes make use of anaerobic respiration of yeast
bread making, beer making
compare the rate of respiration for germinating seeds and boiled/dead seeds
germinating seeds respire a lot and use energy for growth. boiled seeds have denatured enzymes so cant respire
why is respiration essential for living organisms
releases energy for metabolic processes
why is there more respiration in the roots than leaves
they have more mitochondria
how can anaerobic respiration harm yeast cells
it produces ethanol which can build up and kill yeast cells
what are 2 sources of error
random error, systematic error
what is an example of random error in the respiration experinent
room temperature increase
transport systems in animals
circulatory system
exchange surfaces in animals
lungs and alveoli . small intestine and villi
transport systems in plants
xylem and phloem
exchange surfaces in plants
roots and root hairs , leaves
difference in stroke volume between someone who doesnt excersise frequently and someone who does
person who doesnt excersise has lower stroke volume due to weaker ventricular muscles so his heart pumps less blood per heart beat, so he needs to have higher heart beat to have similar cardiac output and excersise at same intensity