LECTURE EXAM 2
1/190
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
191 Terms
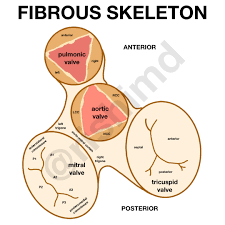
what is the fibrous skeleton of the heart?
cardiac skeleton of the heart
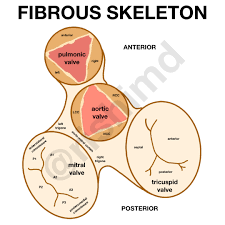
Fibrous Skeleton of the Heart (function #1)
Separates atria & ventricles
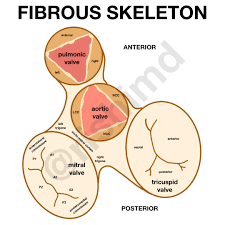
Fibrous Skeleton of the Heart (function #2)
Anchors heart valves
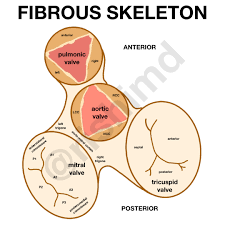
Fibrous Skeleton of the Heart (function #3)
Provides electrical insulation between atria & ventricles
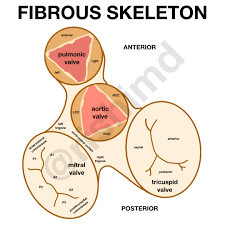
Fibrous Skeleton of the Heart (function #4)
Provides framework for attachment of myocardium
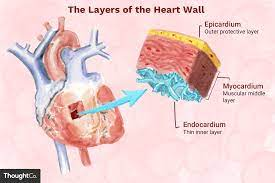
what is the Heart Wall?
thick muscular layer that makes up heart's structure
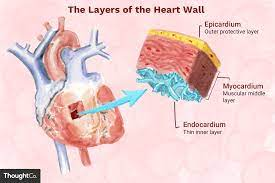
Heart Wall (layer #1: epicardium)
Pericardium - outermost later (thin)
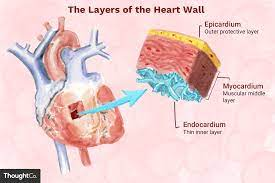
Heart Wall (layer #2)
Myocardium - middle layer
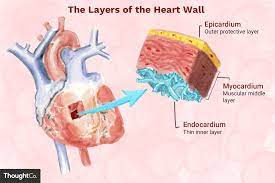
Heart Wall (layer #3)
Endocardium - innermost layer (thin)
layer 1: Pericardium (function #1)
membrane that surrounds and protects the heart
layer 1: Pericardium (function #2)
It ANCHORS heart to diaphragm with fibers
what part of the Pericardium anchors the heart?
Fibrous layer of Parietal
layer 1: Pericardium (function #3)
Outer and is tough tissue
what is the Serous layer of Pericardium
inner part secretes pericardial fluid to reduce friction
what is the Pericardial cavity
contains about 30 ml of pericardial fluid
what is the Visceral Pericardium
(aka epicardium) directly attached to myocardium deep to pericardial cavity
layer 2: Myocardium function
responsible for pumping action
what are the two layers of muscle of Myocardium?
Superficial and Deep
what percentage of Myocardium makes the heart wall?
95%
layer 3: Endocardium function
continuous with the endothelium of blood vessels
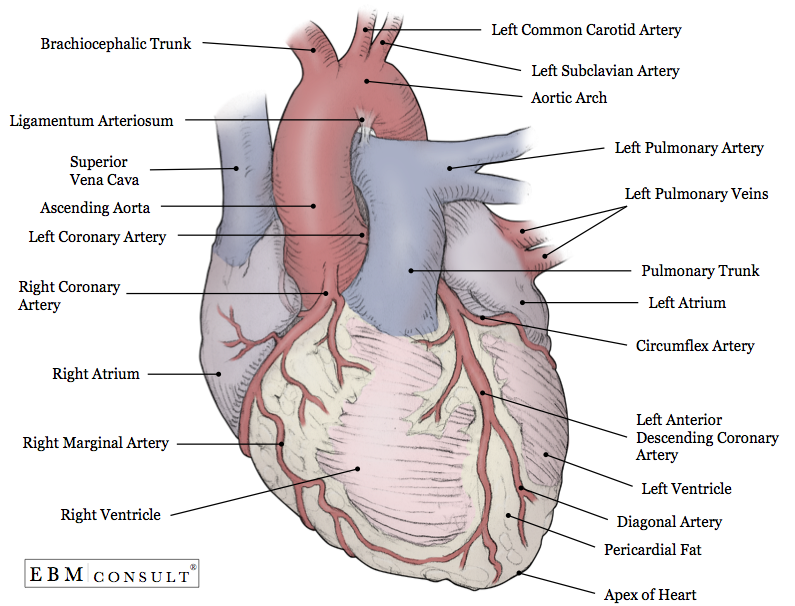
what is the External Surface of the Heart?
portion of the heart that’s visible when looking at the heart from the outside.
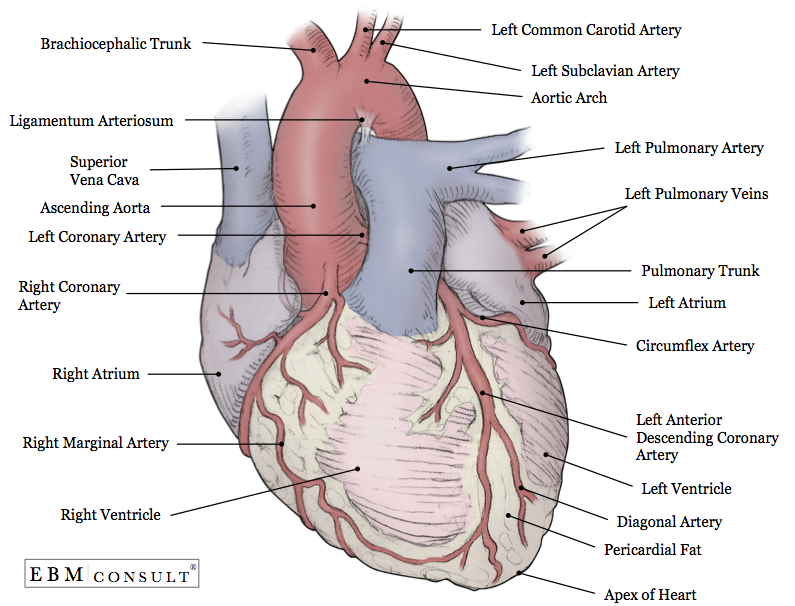
External Surface of the Heart (Part #1)
Coronary
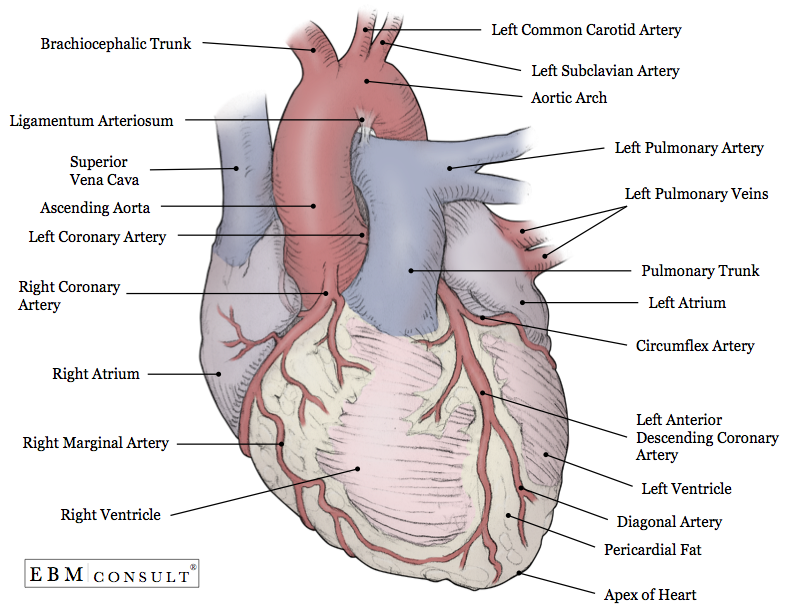
External Surface of the Heart (Part #2)
Ant and Post Sulci
External Surface of the Heart function
Has fat and blood vessels
Part 1: Coronary (function #1)
a large groove and deep on the outside of heart
Part 1: Coronary (function #2)
has fat that separates atria from ventricles
Part 2: Ant and Post Sulci (function #1)
has interventricular sulci external boundary that separates RT and LT ventricles shallow
Part 2: Ant and Post Sulci (function #2)
shallow
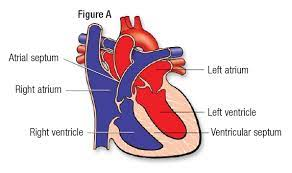
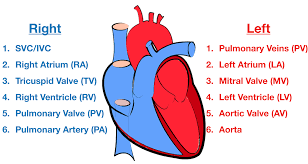
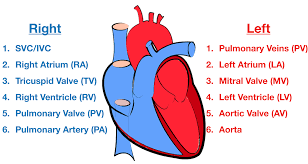
what is the Right Atrium?
one of the four chambers of the heart
where is the right atrium located?
on the right border of the heart
what is the fossa ovalis
a depression/indentation in the right atrium
fossa ovalis (foramen oval) before birth?
the foramen oval is found before birth and allows blood to bypass lungs
fossa ovalis (foramen oval) after birth?
the foramen oval closes after birth after baby can breathe
which three sources does deoxygenated blood enter through, in the right atrium?
Superior Vena Cava
Inferior Vena Cava
Coronary sinus.
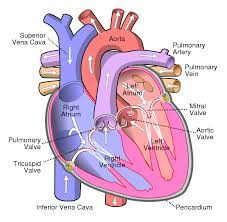
describe the blood flow into the right atrium
deoxygenated blood is sent to right atrium through tricuspid valve
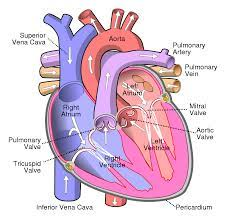
what is the tricuspid valve?
right atrioventricular valve
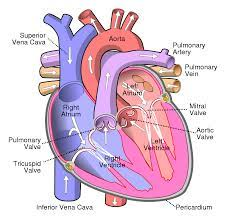
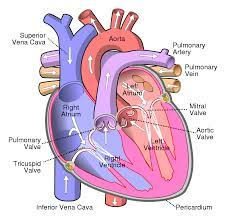
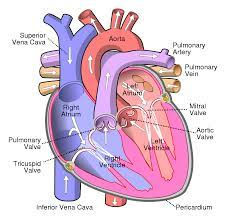
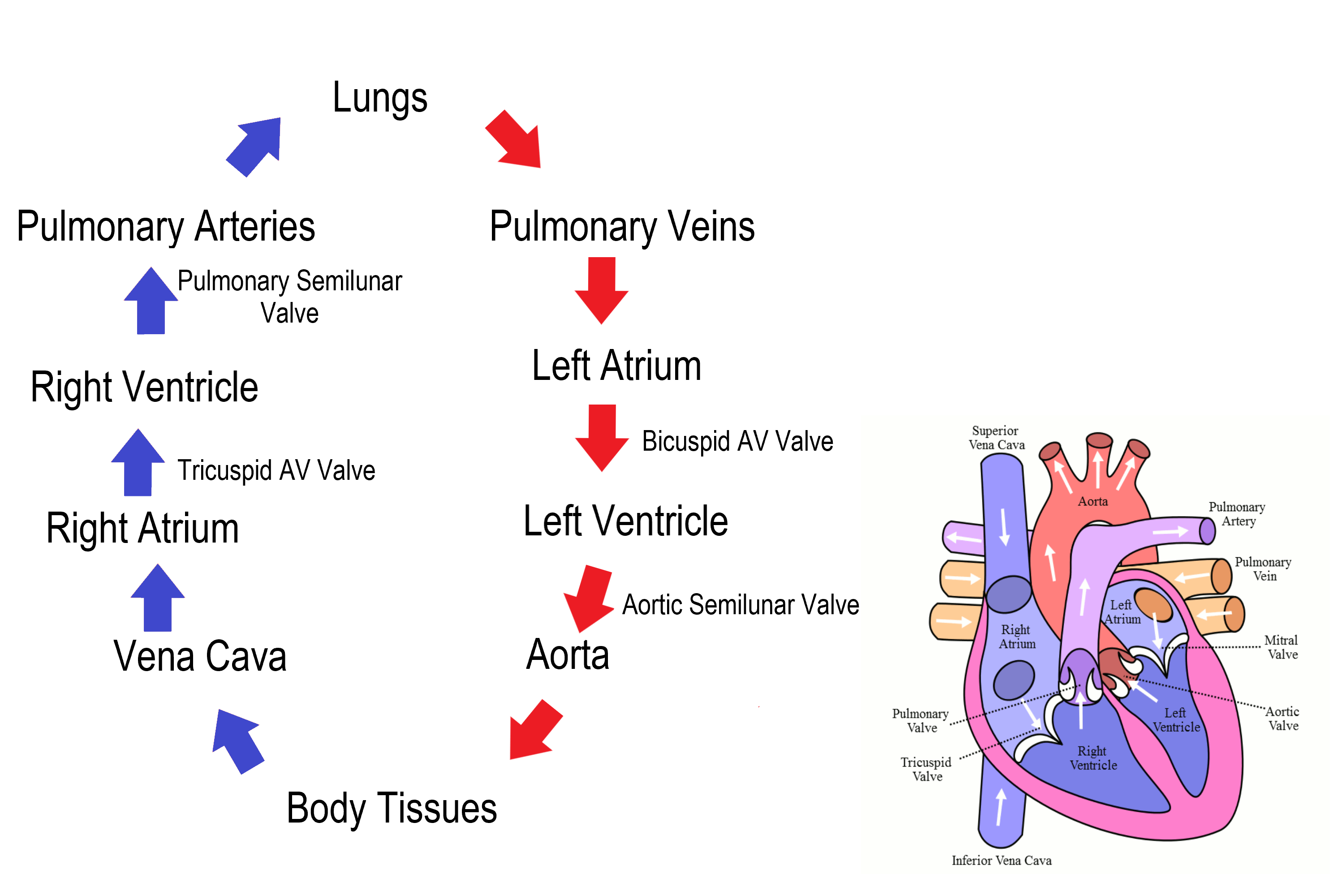
Blood flow through the Heart (step #1)
Superior or Inferior vena cava - deoxygenates blood enters through the cava
Blood flow through the Heart (step #2)
Right Atrium - right atrium receives the deoxygenated blood
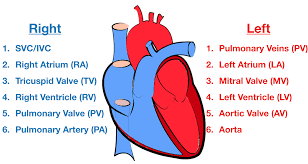
Blood flow through the Heart (step #3)
Tricuspid Valve (RT AV valve) - Valve opens to allow blood flow into right ventricle
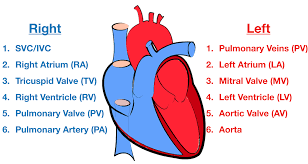
Blood flow through the Heart (step #4)
Right Ventricle - right ventricle receives blood and contract
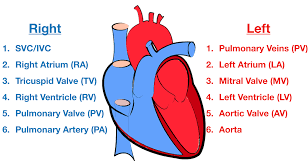
Blood flow through the Heart (step #5)
Pulmonary Semilunar Valve - Valve opens to allow blood to enter pulmonary arteries
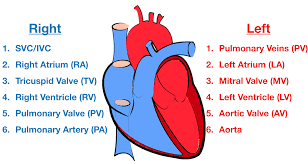
Blood flow through the Heart (step #6)
Pulmonary Trunk and Arteries - deoxygenated blood is carried by the trunk and valves
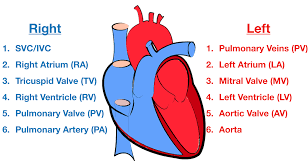
Blood flow through the Heart (step #7)
Lungs - deoxygenated blood becomes oxygenated
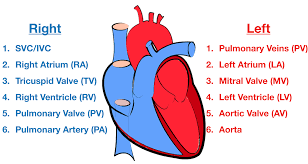
Blood flow through the Heart (step #8)
Pulmonary Veins - the oxygenated blood returns to heart through the veins
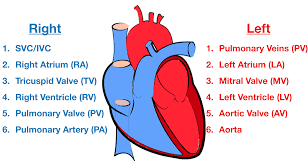
Blood flow through the Heart (step #9)
Left atrium - receives oxygenated blood from pulmonary veins
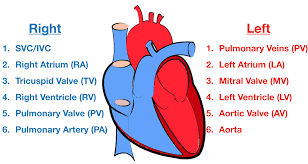
Blood flow through the Heart (step #10)
Bicuspid Valve (Mitral/Left AV Valve) - Opens to allow oxygenated blood to flow into left ventricle
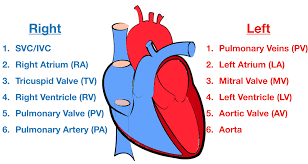
Blood flow through the Heart (step #11)
Left ventricle - receives oxygenated blood and contracts pumping it through aortic semilunar valve
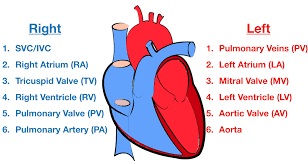
Blood flow through the Heart (step #12)
Aortic Semilunar Valve - opens to allow oxygenated blood to enter the aorta
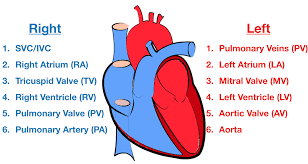
Blood flow through the Heart (step #13)
Ascending Aorta - oxygenated blood is pumped into ascending aorta and travels into arch of aorta
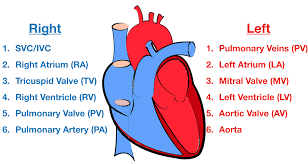
Blood flow through the Heart (step #14)
Arch of Aorta - gives rise to arteries that distribute oxygenated blood to upper body
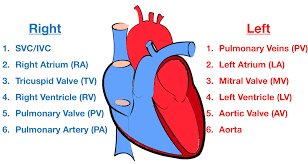
Blood flow through the Heart (step #15)
Systemic Circulation - oxygenated blood is delivered to systemic circulation where it provides oxygen and nutrients to body’s tissues and organs (start over to step 1 RIGHT AFTER)
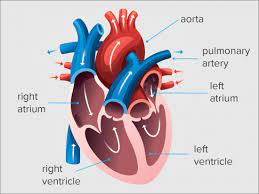
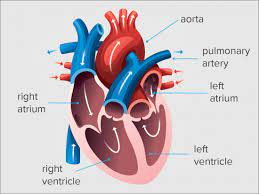
what is the Left Ventricle
one of the four chambers of the heart and helps in circulatory system
Left Ventricle (function #1)
Pumps Blood out to body therefore has Thicker walls
Left Ventricle (function #2)
Has Trabeculae carne
trabecular carne function?
receives blood from LT Atrium
Left Ventricle (function #3)
has Bicuspid valve (mitral)
Bicuspid valve (mitral) function?
has chordae tendineae (fibers) that anchor valve to papillary muscles
Left Ventricle (function #4)
has a CIRCULAR LUMEN
circular lumen function?
pumps blood into aortic semilunar valve against great pressure
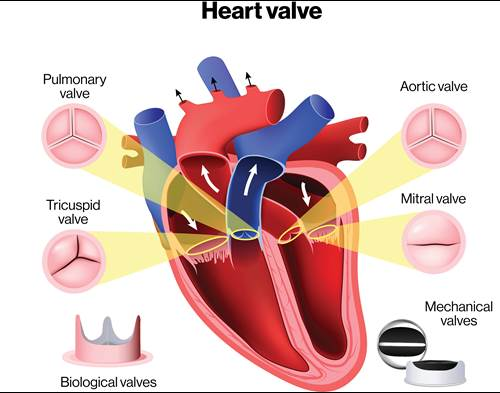
what is Cardiac Valves
Fibrous skeleton around valves
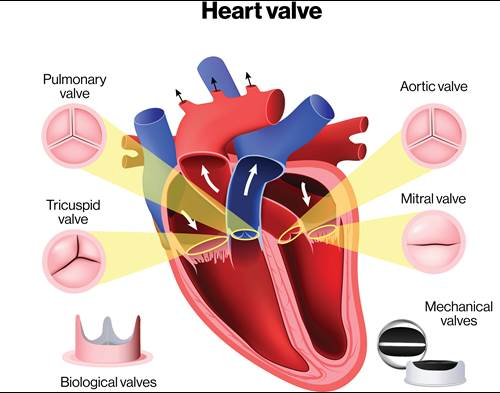
what are all the cardiac valves?
Semilunar valves (aortic and pulmonary)
Bicuspid valves
Tricuspid valves
Cardiac Valves function
Prevent backflow of blood to ensure a one-way flow
not all cardiac valves have?
strings or chords (chordae tendineae)
semilunar valves have no?
chordae tendineae (no chords)
what are the two semilunar valves?
Aortic Semilunar and Pulmonary Semilunar
Bicuspid (left side) and Tricuspid (right side) valves do have?
chords
Does blood flow back into the vena cavae and coronary sinus during atrial contraction?
no
why doesn’t blood flow back into the vena cavae and coronary sinus during atrial contraction?
The compression of the right atrium during systole prevents this
When the ventricles contract the _____ valve close and the _____ valve are pushed open
Tricuspid Right AV/Bicuspid (Mitral) Left AV
Pulmonary Semilunar/Aortic Semilunar
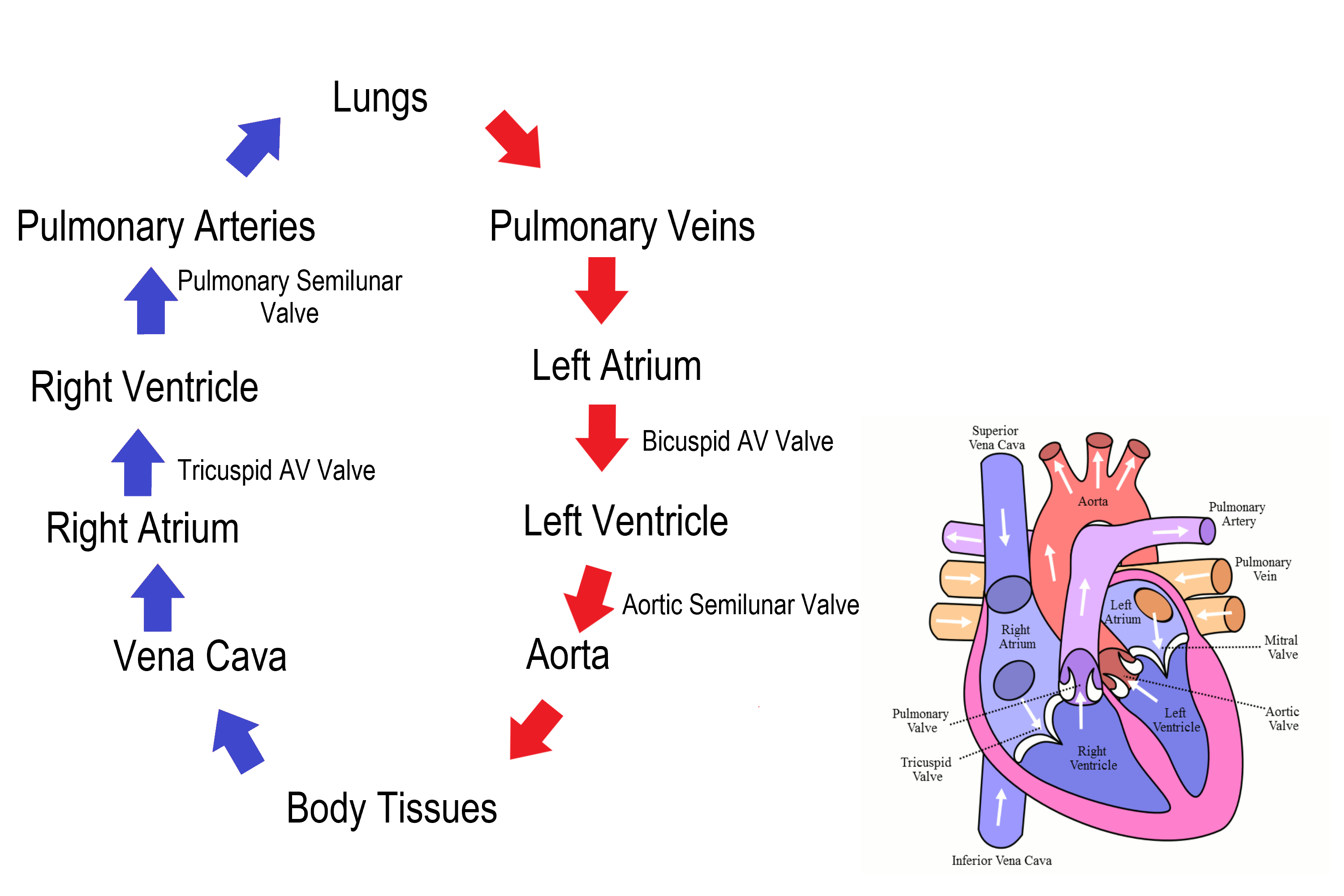
Circulation of Blood (step #1)
The pulmonary circulation transports blood from the heart to the lungs
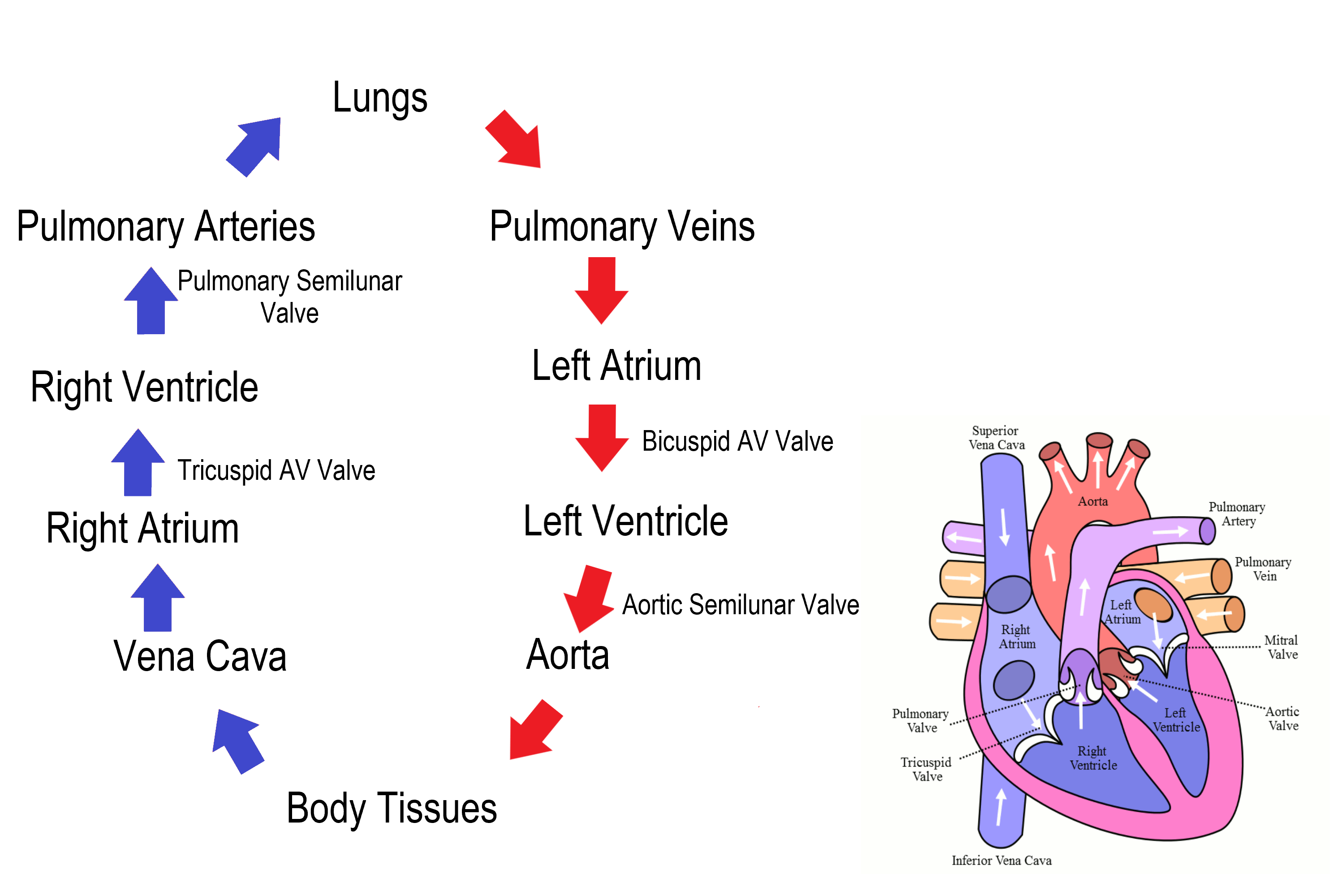
Circulation of Blood (step #2)
blood, from heart to lungs, goes BACK to heart
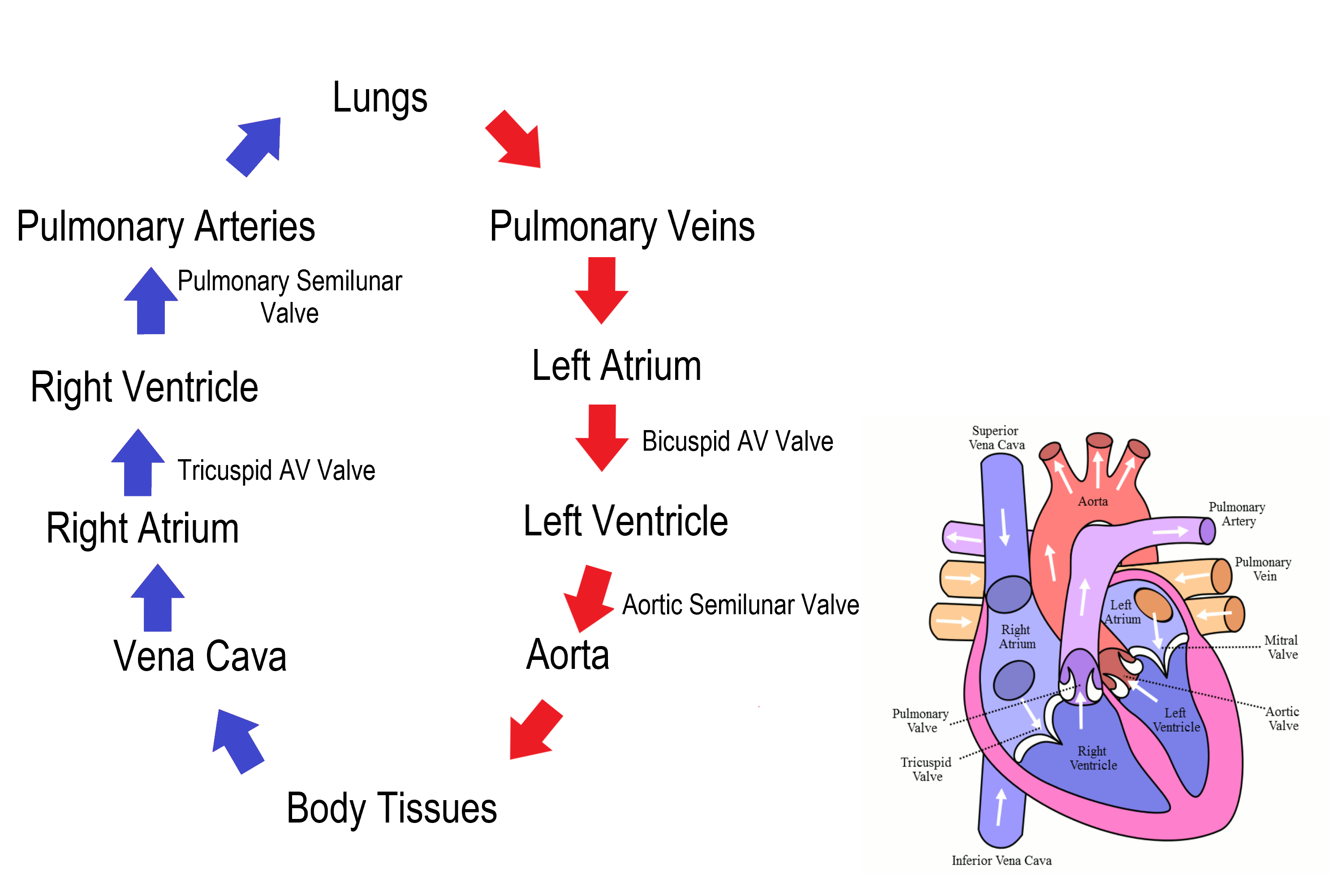
Circulation of Blood (step #3)
The systemic circulation circuit receives blood from the left ventricle
what is the first blood vessel in the systemic circuit?
aorta
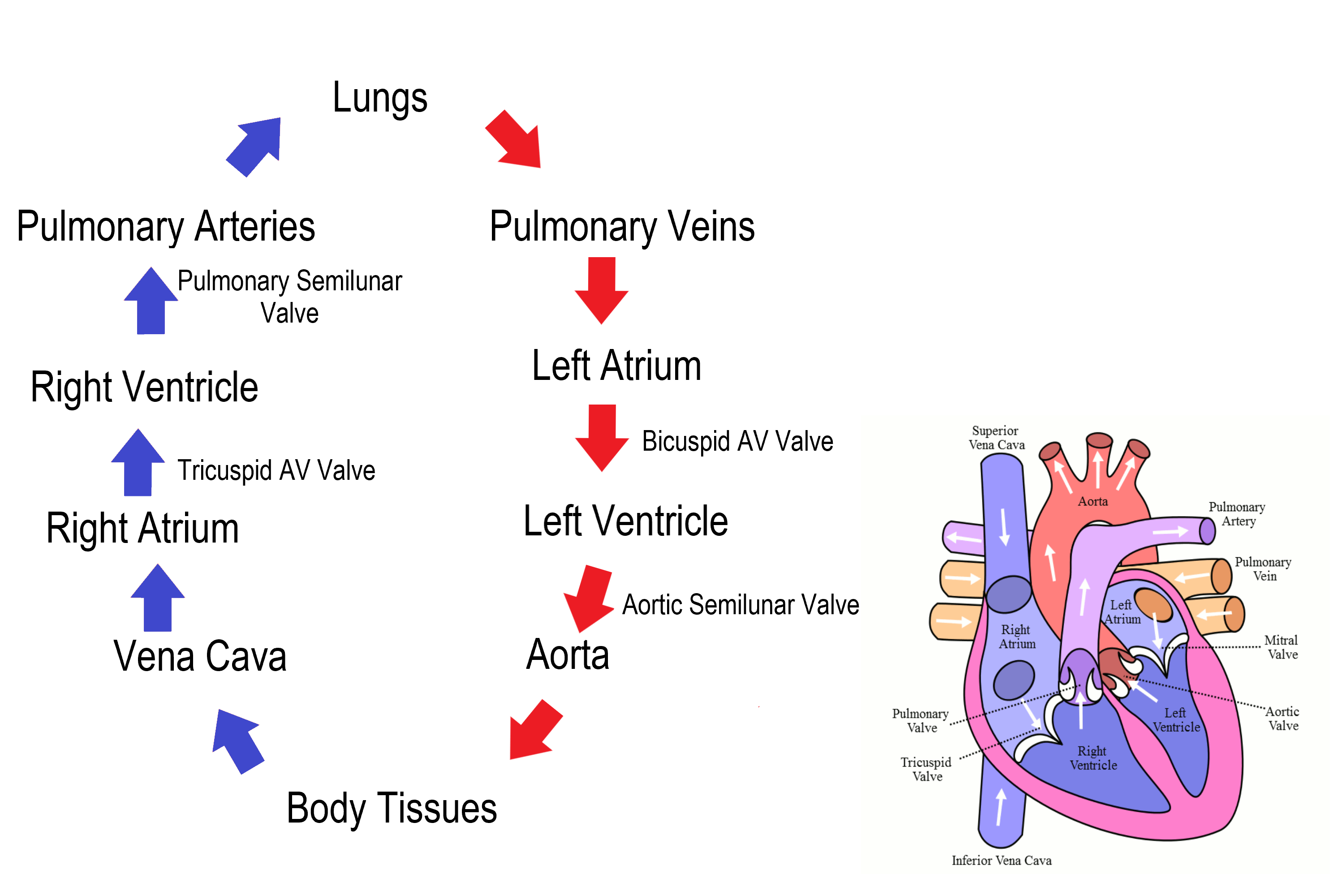
Circulation of Blood (step #4)
The right side of the heart is the pump for the pulmonary circuit
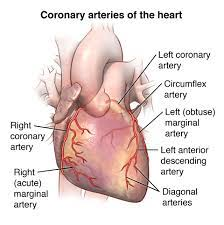
what are the Coronary Arteries?
blood vessels that supply the heart muscle (myocardium) to support its function.
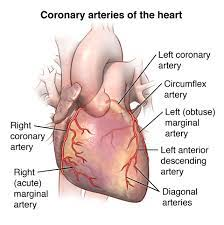
what are the two Coronary Arteries
right and left coronary arteries
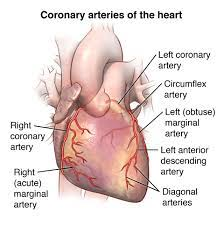
what makes up the right coronary artery?
Posterior interventricular branch
Marginal branch
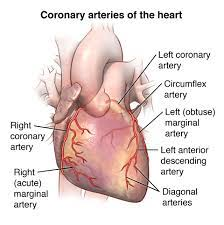
what makes up the left coronary artery?
Anterior interventricular branch
Circumflex artery
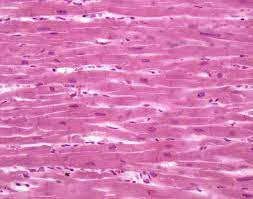
what is Cardiac Muscle Tissue
(myocardium) and responsible for rhythmic contractions of heart, pumps blood throughout circulatory system
Cardiac Muscle Tissue (trait #1)
bifurcated (branched) cells
Cardiac Muscle Tissue (trait #2)
intercalated discs
Cardiac Muscle Tissue (trait #3)
numerous large mitochondria
Cardiac Muscle Tissue (trait #4)
striations
what are Autorhythmic Cells of the Heart
pacemaker cells or cardiac cells that generate electricals impulses (heat beats)
Autorhythmic Cells of the Heart function
depolarize to threshold “spontaneously”
autorhythmic cells depolarize to threshold spontaneously by?
cell’s membrane potential becomes less negative to make a actional potential (cause contractions)
depolarization from autorhythmic cells is caused by?
slow Na+ Channel inflow
what is the primary pacemaker of the heart?
Sino Atrial Node “SA Node”
SA node (function #1)
sets/establishes heart’s basic rhythm
SA node (function #2)
makes cardiac action potentials for heart beats per minute
Cardiac Conduction System (event #1)
SA node
Cardiac Conduction System (event #2)
AV node
Cardiac Conduction System (event #3)
AV Bundle
Cardiac Conduction System (event #4)
Bundle Branches
Cardiac Conduction System (event #4)
Purkinje Fibers
Cardiac Conduction System #1 - SA NODE & AV NODE
The AV node can take over the pacemaking task if the SA node is damaged.
Cardiac Conduction System #2 - AV BUNDLE
The pacemaking ability of the AV bundle alone is not sufficient to maintain homeostasis.
Cardiac Conduction System #3 - Bundle Branches
Ectopic pacemakers may be stimulated by caffeine or nicotine
Cardiac Conduction System #3 - Purkinje Fibers
Ach release by the parasympathetic division of the ANS decreases SA node depolarization
what is the Plateau phase of a cardiac contractile action
a stage in the cardiac action potential of contractile cells in heart