6.4- Nuclear Fission & Fusion
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
nuclear reactions (fission, fusion, radioactive decay) can be a source of…
energy (used for electricity, transport, etc)
advantages of nuclear power
produces no polluting gases e.g. carbon dioxide
require far less fuel than fossil fuels (produce more energy)
highly reliable (unlike some renewable resources)
disadvantages of nuclear power
produces radioactive waste which is very dangerous and expensive to deal with
risk: in the event of an accident e.g. a nuclear meltdown such as Chernobyl, can have catastrophic consequences on the environment and to the people in the surrounding area
public perception is generally negative, people are very wary of nuclear power
expensive to set up + shut down
nuclear fission
the splitting of a large unstable nucleus into two smaller nuclei
a neutron collides with an unstable nucleus, it splits, and emits 2 or 3 neutrons + gamma rays
the process behind nuclear power stations (usually uses Uranium-235 and Plutonium-239)
all products of nuclear fission are… so have to be…
RADIOACTIVE so have to be stored underground until they aren’t any more
fission of Uranium-235
used as a fuel in nuclear reactors
slow neutrons absorbed by nucleus (fast-moving e- just pass through), becoming an unstable U-236 nucleus
this splits into 2 smaller nuclei and emits 2 or 3 neutrons, releasing energy
products move away at high speed (high KE)
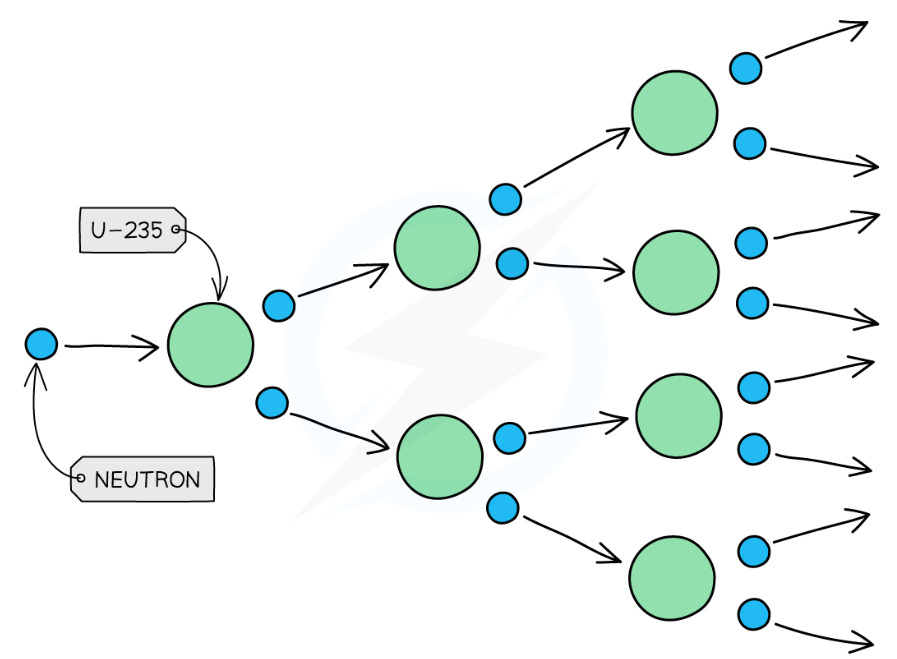
nuclear chain reaction
only 1 extra neutron is needed to induce U-235 fission
each fission produces 2 or 3 neutrons which move away at high speed
each neutron produced can start another fission reaction, again creating further excess neutrons, which go on to induce further fission reactions
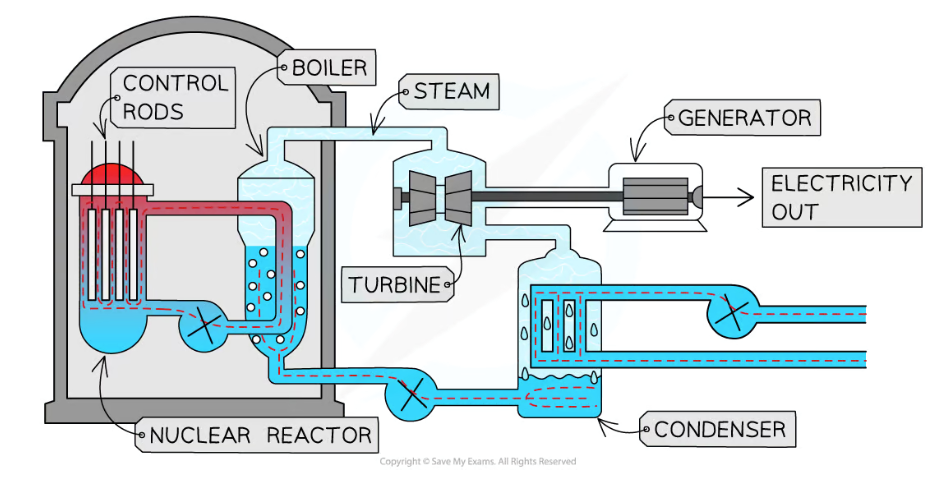
control rods (purpose in controlling nuclear chain reactions in a reactor)
Purpose: absorb neutrons
made of a material that absorbs neutrons without itself becoming unstable
number of neutrons controlled by varying depth of control rods in the fuel (lowering = decreased rate of fission, more neutrons absorbed)
adjusted automatically so only 1 fission neutron goes on to cause another fission
control rods lowered completely to shut down reactor
moderator (purpose in controlling nuclear chain reactions in a reactor)
purpose: slow down neutrons
material that surrounds fuel rods + control rods in core
fast moving neutrons produced by fission reactions slow down by colliding with the molecules of the moderator
slowed neutrons are in thermal equilibrium with moderator, ensuring they can react efficiently with U-235 fuel
how is thermal energy from chain reactions used to generate electricity in nuclear power stations?
KE from nuclear fission produces a large quantity of heat which is carried away from reactor by coolant
coolant used to heat a water source + turn it into steam (separate source used to prevent contamination)
steam turns turbines which turn generators, producing electricity
nuclear fusion
two light nuclei join to form a heavier nucleus
requires extremely high temps to maintain, mostly just occurs in stars, which produce energy from it
produces a huge amount of energy which comes from a small loss of mass, as mass is conserved as energy (according to e=mc2)
conditions for nuclear fusion
very high temp of fuel (millions of degrees C)
very high KE of nuclei to overcome repulsion
very high density/pressure to increase possibility of suitable collisions
why does nuclear fusion not occur at lower temps?
fusion requires the fusion of 2 nuclei, which contain protons (no e-) so are positively charged
protons repel each other as they are both +vely charged
very high KE (therefore extremely high temperature) required to overcome repulsion
why is fusion not used as a power source on Earth?
it is extremely difficult to achieve & maintain high temps + pressures needed for fusion
where these conditions have been achieved, they are hard to maintain, so only a small rate of fusion is produced
this is not useful for current energy needs
Fusion vs Fission
Fission is process of breaking apart
Fusion is process of joining together
fission produces energy in nuclear reactors
fusion occurs in the cores of stars
fission uses large nuclei e.g. Uranium, produces smaller
fusion uses small nuclei e.g. Hydrogen, produces larger
fission provides less energy per kg of fuel than fusion
fission products are radioactive + very dangerous
fusion products are not radioactive + safer
fission requires high temps + neutron to induce
fusion requires extremely high temps