The Endocrine System Outline Part 1
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
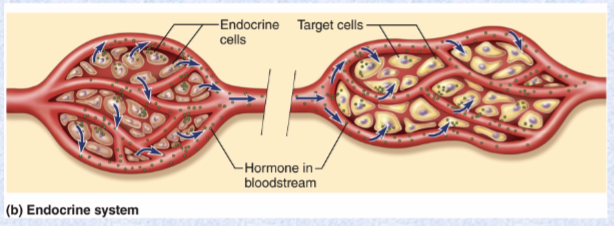
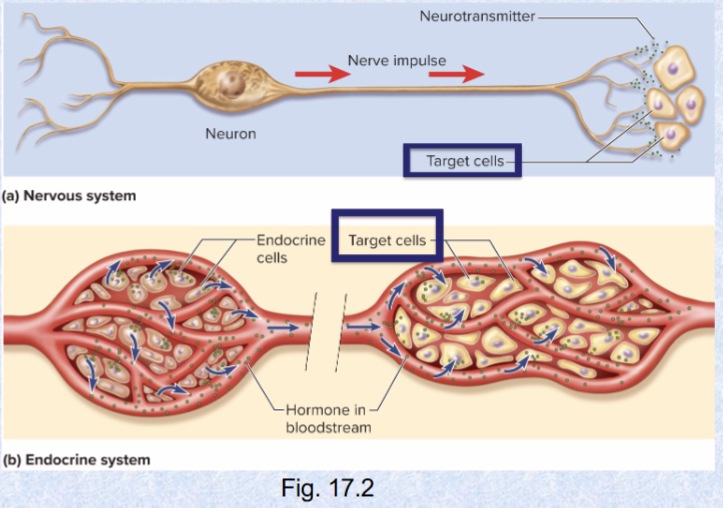
communication system for nervous and endocrine systems
neurotransmitters and hormones
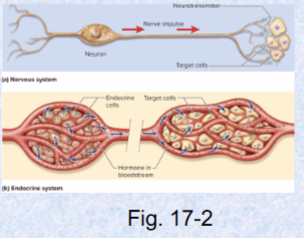
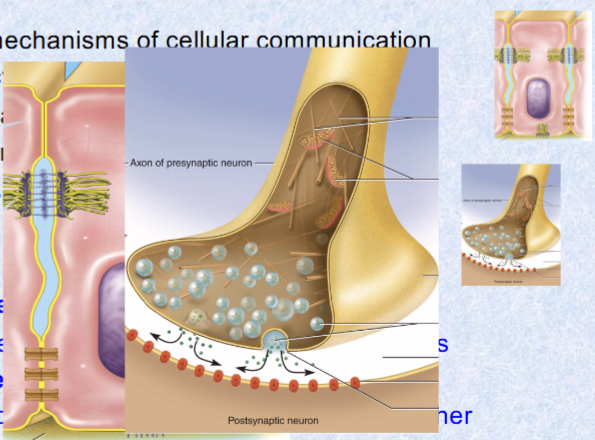
4 principal mechanisms of cellular communication
Gap junctions: tiny channels
Neurotransmitters: across synaptic cleft
Paracrine (local) hormones: secreted into tissue fluids, affect NEARBY cells
Hormones (far away): chemical messengers travel via blood to other tissues and organs
hormones
chemical messengers transported via blood; stimulate physiological responses in another organ, often considerable distance away
exocrine vs endocrine glands
DUCTS carry secretions to epithelial surface (ex: sweat glands)
EXTRACELLULAR effects (food digestion)
vs
NO ducts
dense, hole-y, capillary networks allow easy uptake of hormones into blood
INTRACELLULAR effects (altering target cell metabolism)
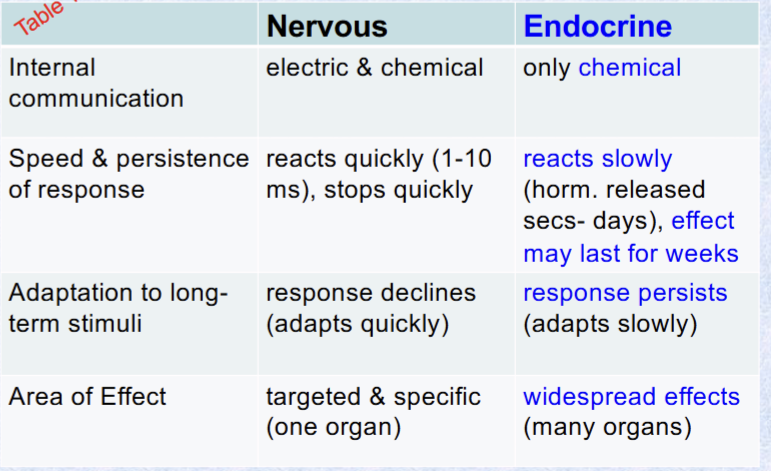
Both are involved in communication but contrast nervous and endocrine system based on internal communication, speed and persistence of response, adaptation, area of effect
chemicals that function as both hormones and neurotransmitters
norepinephrine, dopamine (also some chemicals share same target cells and regulate each other)
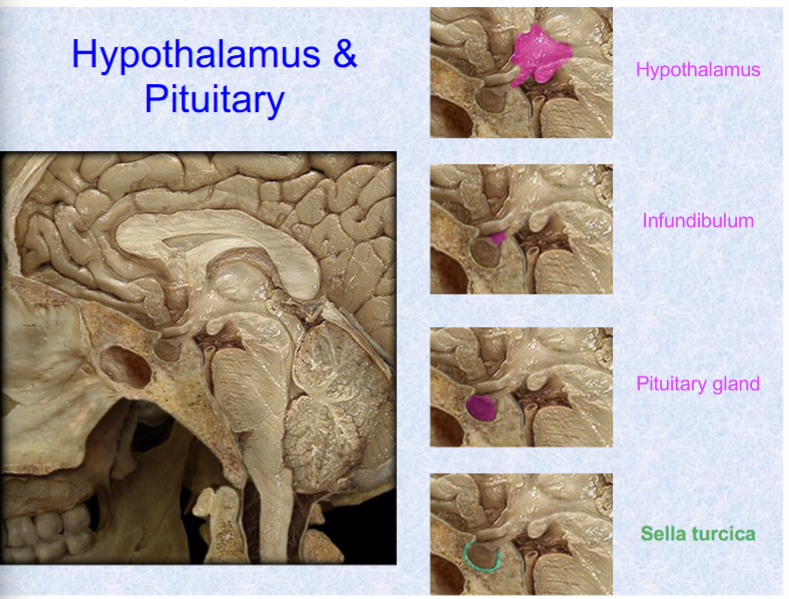
How is hypothalamus related to the pituitary gland?
hypothalamus acts as the master controller, sending hormonal signals to the pituitary (the “master gland”) to regulate other glands like the thyroid, adrenals, and reproductive organs, controlling functions from growth and metabolism to stress response and fluid balance
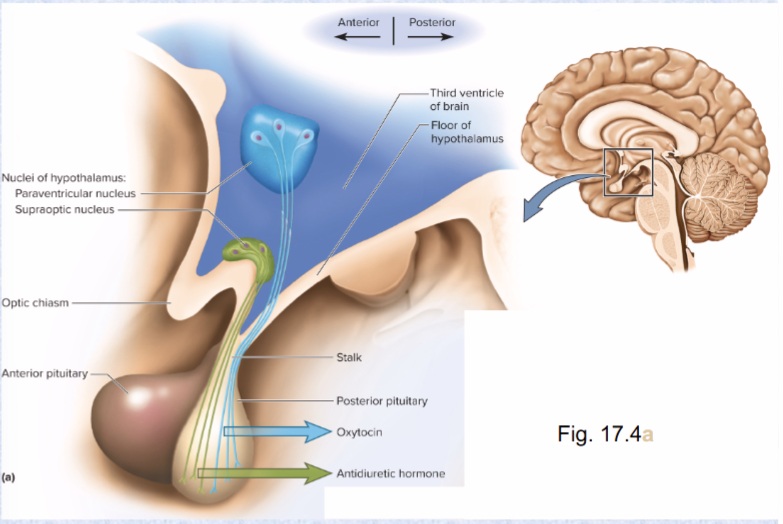
infundibulum
suspended from hypothalamus by stalk
pituitary gland is housed in …. of sphenoid bone
sella turcica (very well protected)
pituitary gland has the size and shape of a
kidney bean
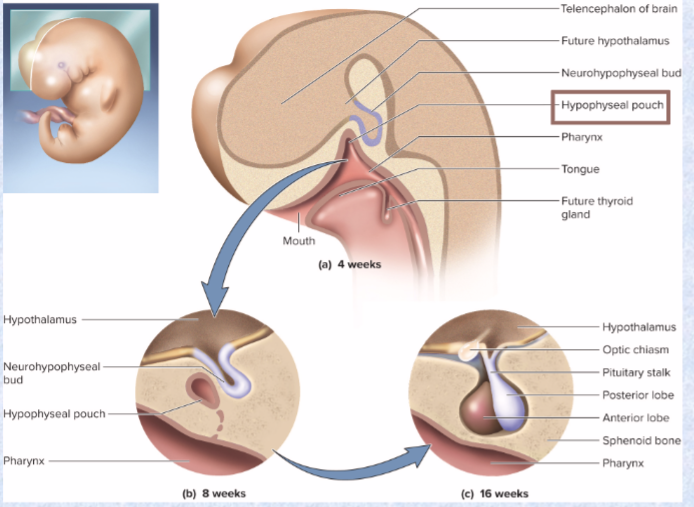
adenohypophysis
(anterior pituitary)
- from hypophyseal pouch - outgrowth of pharynx
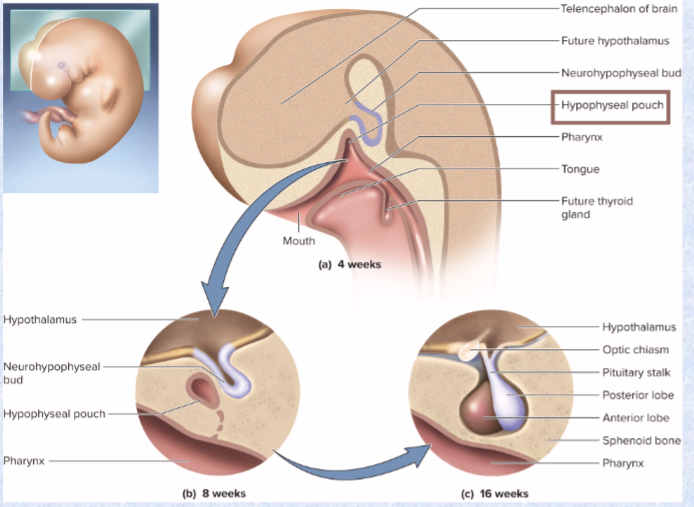
neurohypophysis
(posterior pituitary)
downgrowth from brain
adenohypophysis linked to hypothalamus by…
hypophyseal portal system (vascular connection)
primary capillaries in hypothalamus connected to secondary capillaries in adenohypophysis by portal venules
hypothalamic releasing-hormones (RH) regulate adenohypophysis
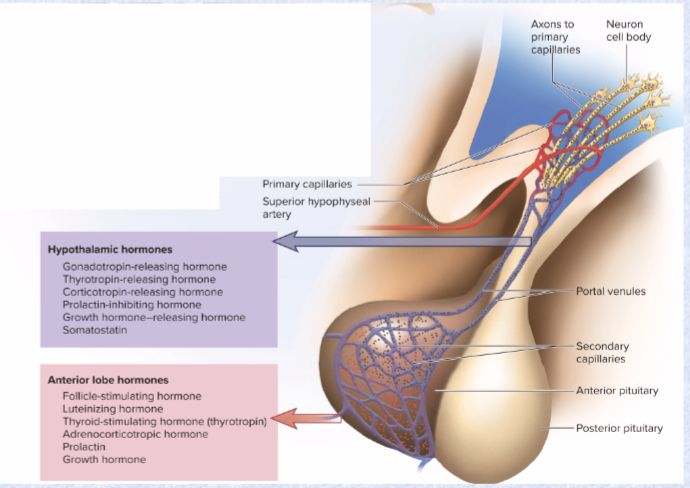
neurohypophysis connected to hypothalamus by…
hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract (neural connection/ nervous tissue! not a true gland)
hypothalamic neurons secrete hormones; stored in neurohypophysis until released into blood (oxytocin and ADH)
4 releasing hormones only…
ONLY goes from hypothalamus to anterior pituitary (RH) (hypothalamic hormones)
TRH (PRL and TSH), CRH (ACTH), GnRH (LH, FSH), GHRH (GH and IGF)
these affect anterior pituitary secretion of TSH, PRL, ACTH, FSH, LH, and GH
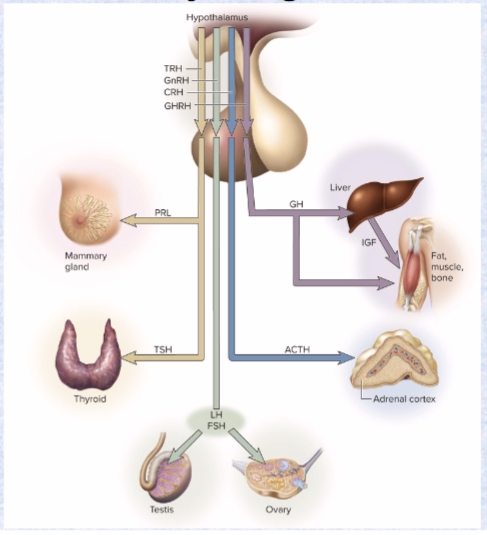
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) (targets and effects)
ant. pit
target: ovaries/testes
effects: ovarian s3x hormones, development of ovarian follicles, sperm production
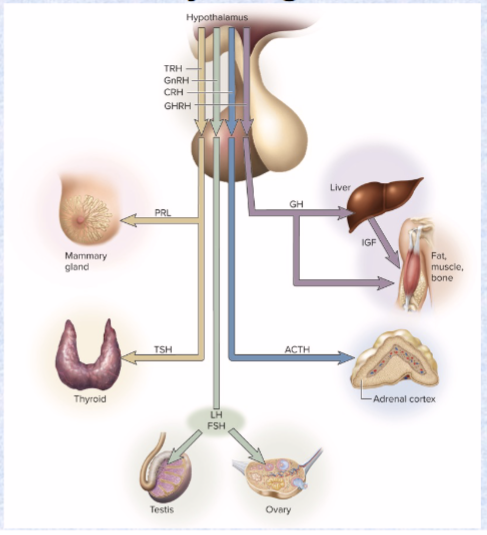
Luteinizing hormone (LH) (targets and effects)
ant. pit
target: ovaries/testes
effects: stimulates ovulation, secrete progesterone and testosterone
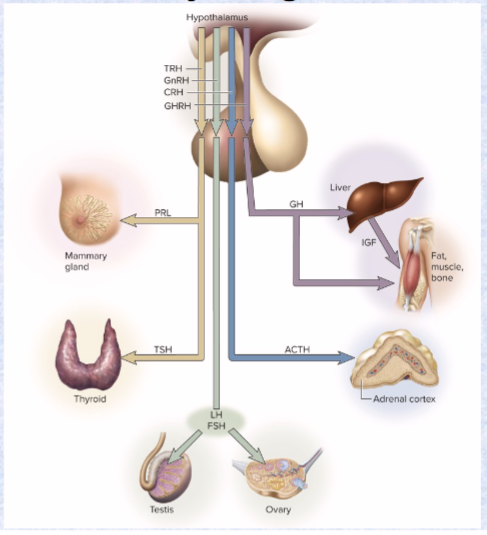
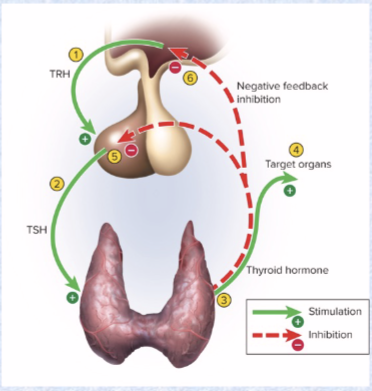
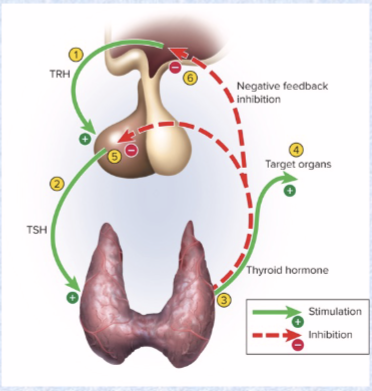
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) (target and effects)
ant. pit
target: thyroid
effects: stimulates secretion of thyroid hormone (metabolism, T3, T4, temperature)
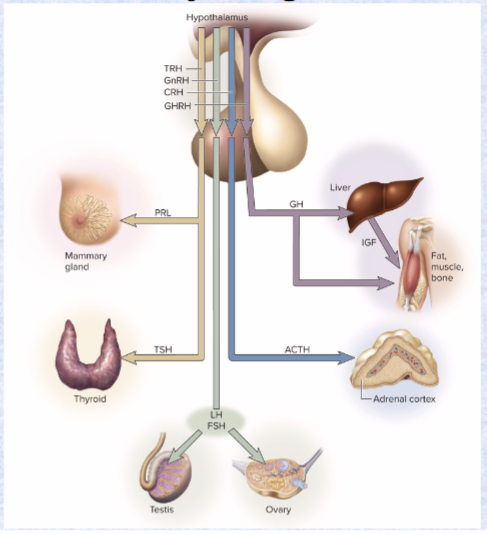
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) (target and effects)
ant. pit
target: adrenal cortex
effect: secrete glucocorticoids (immune system)
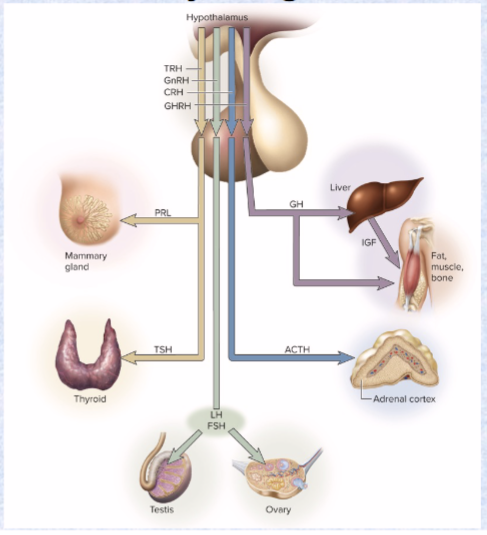
Prolactin (PRL) (target and effects)
ant. pit
target: mammary glands/testes
effect: synthesize milk/secretion of testosterone
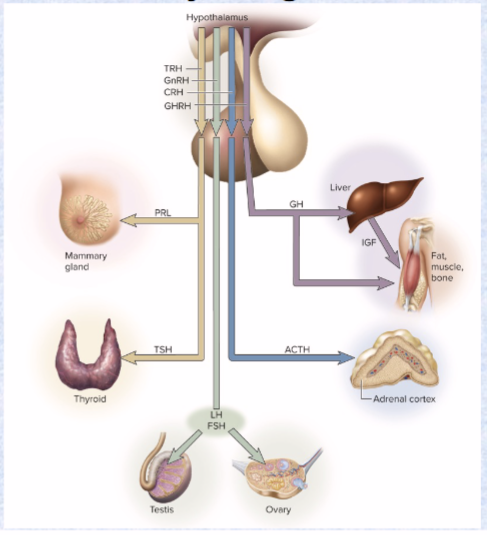
Growth hormone (GH) (target and effects)
ant. pit
target: bones, muscles, liver
effect: stimulates mitosis and cellular differentiation
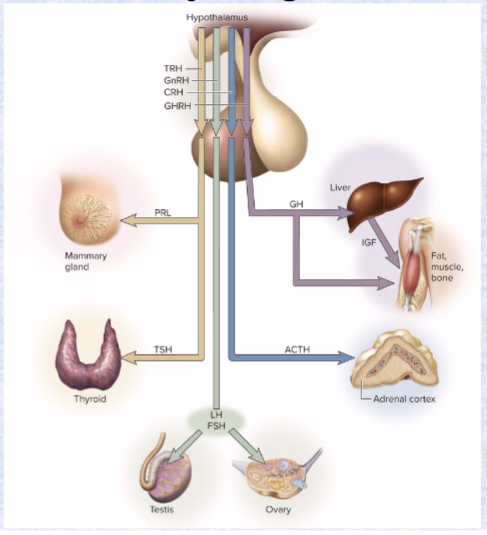
ADH (antidiuretic hormone) (location and effect)
posterior pituitary hormone
increases water retention; reduces urine volume and prevents dehydration
Oxytocin (OT) (location and effect)
posterior pituitary hormones
released during sexual arousal and orgasm, stimulates labor contractions during childbirth, emotional bonding, stimulates flow of milk during lactation
Hypothalamic and cerebral control to respond to cold and stress
HT stimulates anterior lobe to release TSH- generate body heat
ACTH- cortisol- tissue repair
Neuroendocrine reflexes example suckling infant
stimulates nerve endings- HT- posterior lobe- oxytocin- milk ejection
(higher brain centers) Milk ejection reflex can be triggered by
a baby’s cry
Negative feedback
increased target hormone levels INHIBIT further release of hormones
Positive feedback
stretching of uterus increases oxytocin release, MORE contractions, MORE stretching, etc. until delivery
Insulin-like Growth Factors (IGF-I) does what
PROLONGS growth hormone action
LONGER hormone half life- time required for 50% of hormone to be cleared from blood
Prolactin vs oxytocin
milk synthesis vs milk ejection
Growth hormone effects
Protein synthesis increases
Lipid metabolism increases
Carbohydrate metabolism- save glucose for brain
Electrolyte balance- sodium and potassium retention by kidneys, enhances calcium absorption in intestines
pineal gland synthesizes…
MELATONIN (signals body to rest) from serotonin at night- synchronize physiology with 24-hour circadian rhythms of daylight/darkness
Seasonal affective disorder (SAD)
occurs in winter of northern climates
depression, sleepiness, irritability, carbohydrate craving
2-3 hours of exposure to bright light/ day reduces melatonin levels and symptoms (phototherapy)
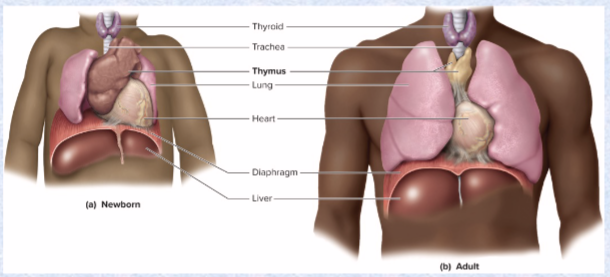
Thymus hormones (3) and effects
site of maturation of T cells- immune defense
hormones: thymopoietin, thymosin, thymulin- stimulates nervous system
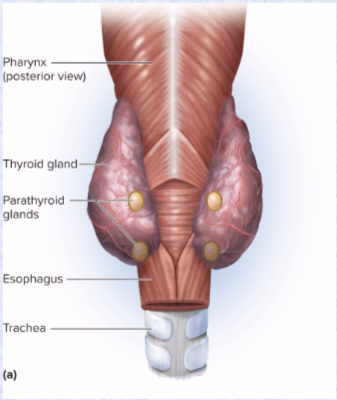
Thyroid gland hormones (3) and effects
hormones: thyroxine (T4 more abundant), triiodothyronine (T3 more potent)
increases metabolic rate, O2 consumption, heat production, appetite, GH secretion alertness
another hormone is calcitonin
lowers blood calcium levels (stimulates osteoblast activity)
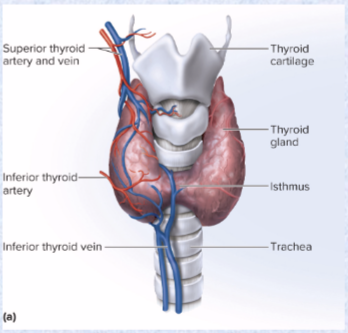
Parathyroid glands hormone (1) and effects
(posterior side of thyroid gland)
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
increases blood calcium levels
increases bone resorption
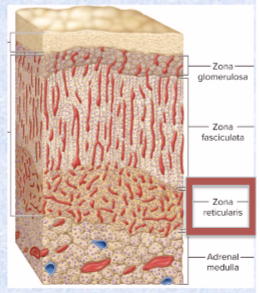
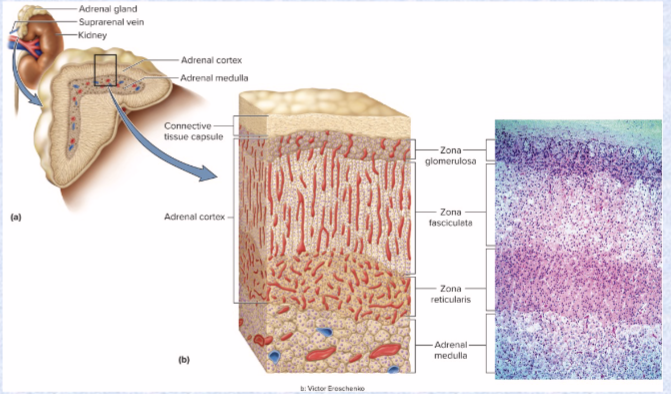
Adrenal glands location and 2 types
on top of kidney
adrenal cortex (3 layers, yellow outside) & medulla (inner core)
Adrenal medulla dual nature and hormones (3)
dual nature: endocrine gland and sympathetic ganglion of sympathetic nervous system
innervated by sympathetic preganglionic fibers
consists of modified sympathetic postganglionic neurons: chromaffin cells
release catecholamines (epinephrine & norepinephrine) and trace of dopamine into blood
effect of adrenal medulla hormones
longer lasting than neurotransmitters
increases alertness, preps body for physical activity
mobilizes high energy fuels, lactate, fatty acids, glucose
glycogenolysis & gluconeogenesis boost glucose levels
glucose sparing effect b/c inhibits insulin secretion
increases blood pressure, HR, metabolic rate, etc.
decreases digestion and urine production
this is a lot like: FIGHT OR FLIGHT
Adrenal cortex secretes…
major steroid hormones from 3 layers of glandular tissue
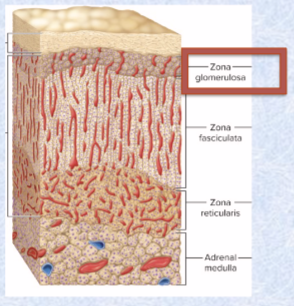
Zona glomerulosa (adrenal cortex thin outer layer) secretes what class of hormones? And what does this class do?
mineralocorticoids
regulates electrolyte balance
Aldosterone (raises BP) stimulates sodium retention and potassium excretion
water retained with sodium by osmosis, so blood volume and BP maintained
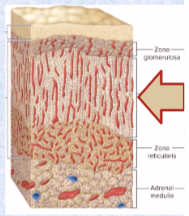
Zona fasciculata (adrenal cortex thick, middle layer) secretes what class of hormones? And what does this class do?
glucocorticoids
cortisol (stress hormone)- stimulates fat and protein catabolism, gluconeogenesis, release of fatty acids and glucose into blood
ACTH makes cortisol
helps adapt to stress and repair tissues
anti-inflammatory effect becomes immune suppression with long-term use
Zona reticularis (adrenal cortex narrow, inner layer) secretes what class of hormones? And what does this class do?
sex steroids (testosterone and estrogen)
androgens: sets libido; important role in prenatal male development (includes DHEA which converts to testosterone)
estradiol: small quantity, but important after menopause for substaining bone mass; fat converts androgens into estrogen