Quantum Numbers
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Quantum Number
A solution to the Schrodinger equation that specifies the properties of an atomic orbital and the electrons found in that orbital.
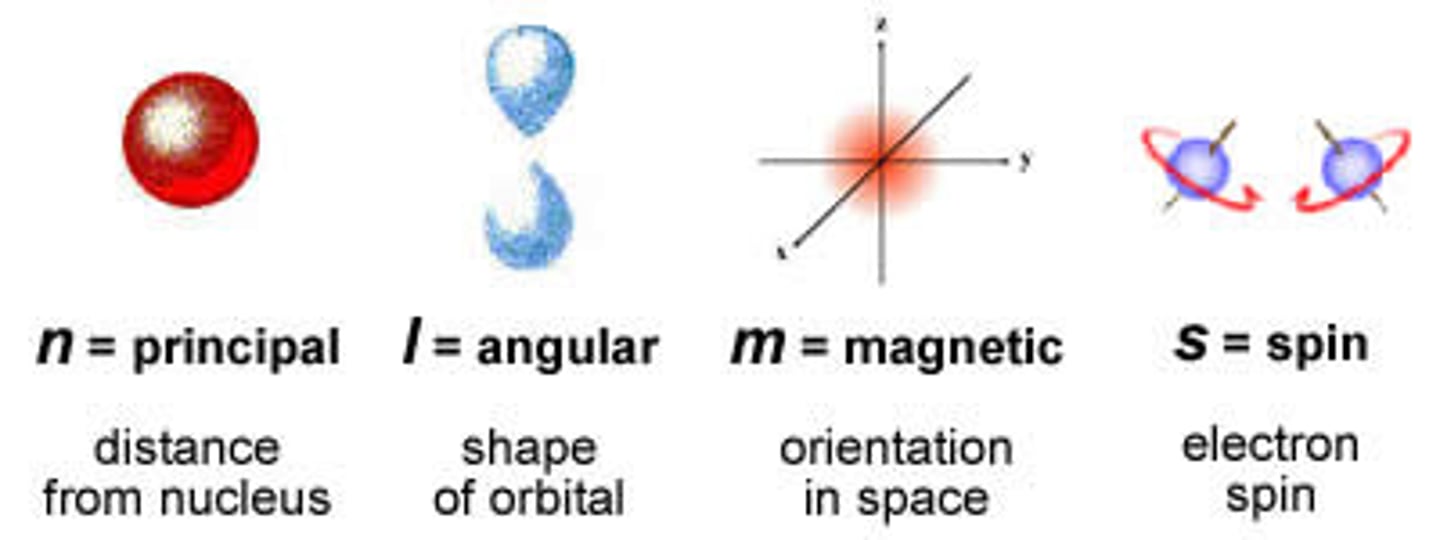
Principle Quantum #
Symbol is n; Indicates the main energy level occupied by the electron.
Angular Momentum Quantum #
Symbol is l; Indicates the shape of the orbital (s,p,d, or f)
What are the different numbers representing the shape of an orbital? (angular momentum quantum)
l=0 is an s-orbital, l=1 is a p-orbital, l=2 is a d-orbital, l=3 is an f-orbital
Magnetic Quantum #
Symbol is ml; indicates the specific orbital within the four types of orbitals.
What does ml equal in correspondance to l?
When l = 0, m l= 0.
when l =1, ml = -1,0,1
when l = 2, ml = -2,-1,0,1,2
when l = 3, ml = -3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3
Spin Quantum # (symbol)
Symbol is ms; Indicates the direction an electron rotates in its orbital.
What are the allowable values for n?
Any positive integer, from 1 to n.
What are the allowable values for l?
Any positive integer in the range [0, ..., n-1].
What are the allowable values for lm?
Any integer in the range [-l, ..., +l].
What are the allowable values for ms?
-1/2 and +1/2 only.
Orbital
A three-dimensional region around a nucleus that indicates the probable location of an electron, defined by specific values of n, l, and m.
Sublevel/Subshell
All similarly shaped orbitals that share the same values for n and l.
Energy Level/Shell
All orbitals that share the same value for n only.
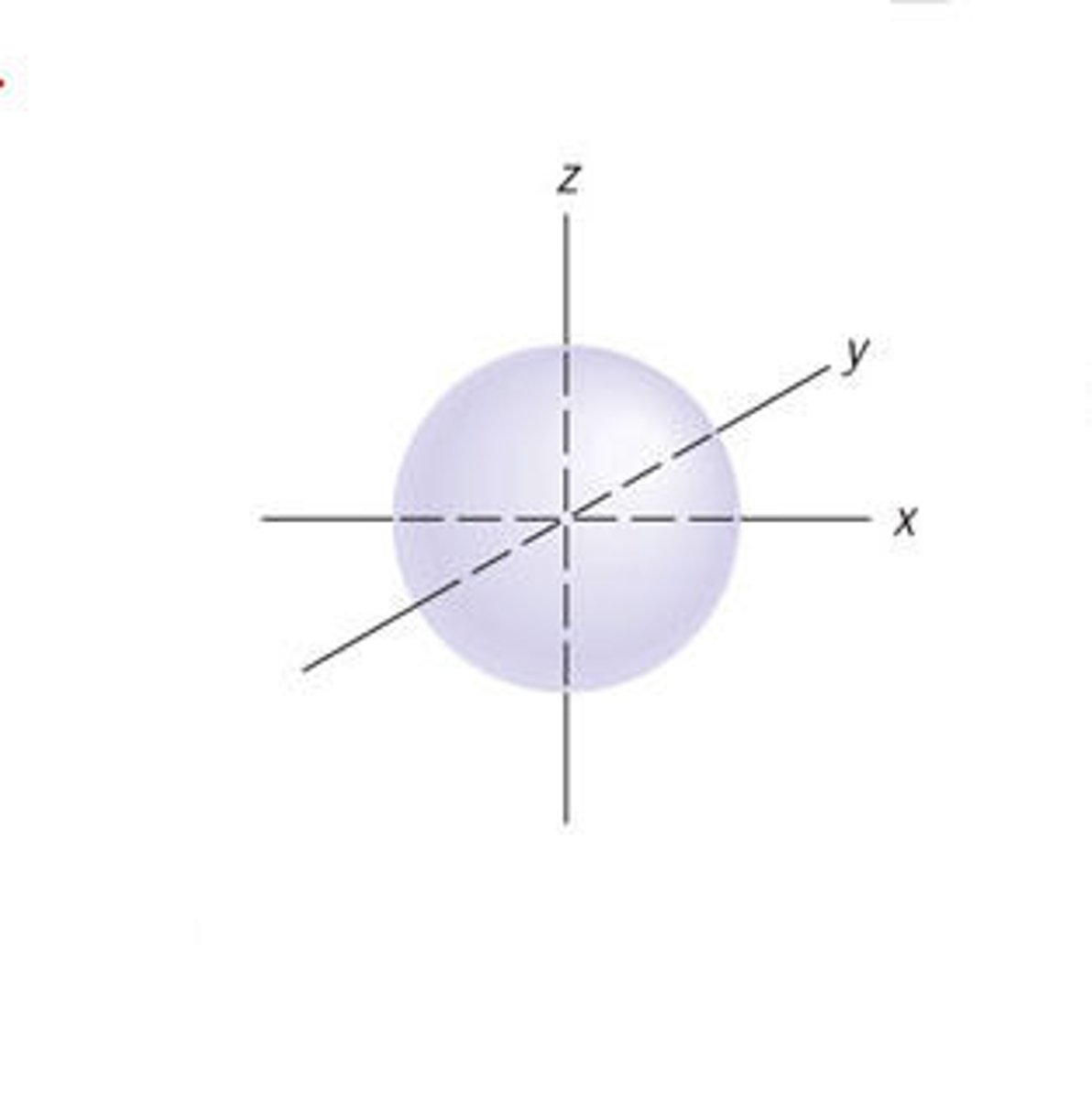
s-orbital
A spherical orbital defined by l=0. There is one orbital within this type.
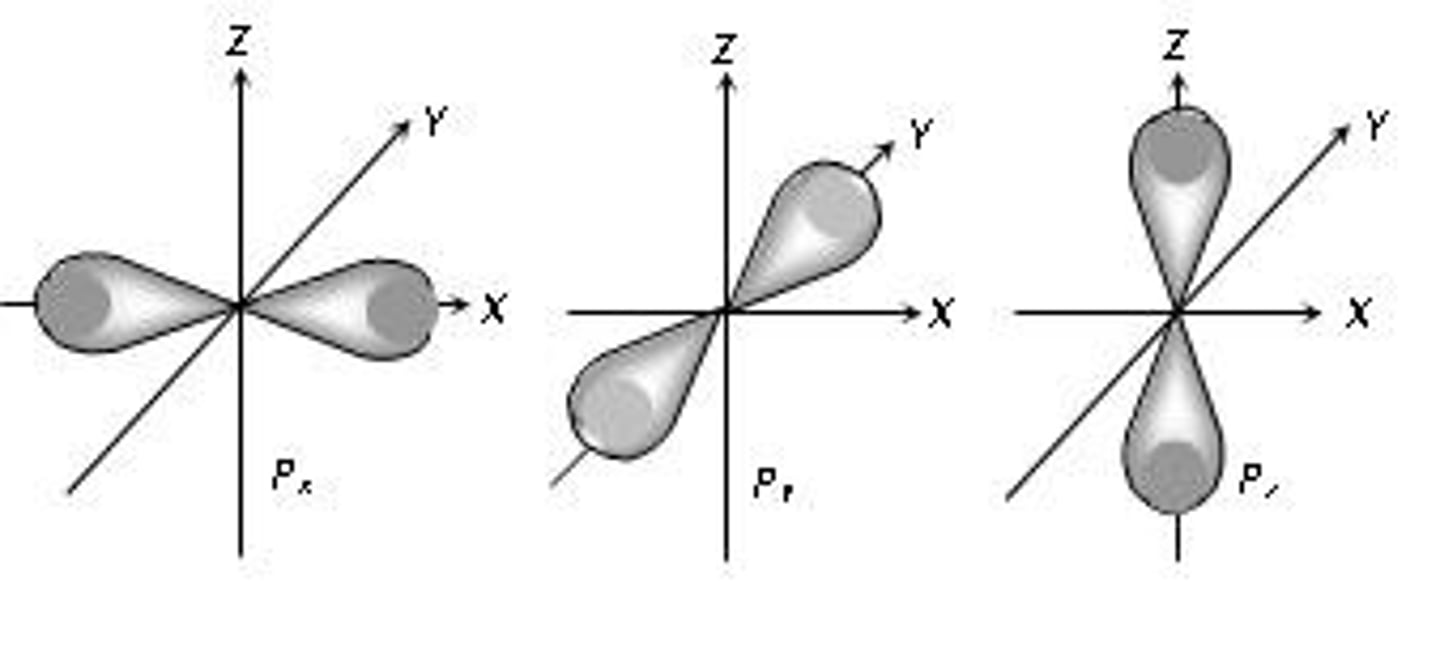
p-orbital
A dumbbell-shaped orbital defined by l=1. There are three orbitals within this type.
d-orbital
A cloverleaf-shaped orbital defined by l=2. There are five orbitals within this type.
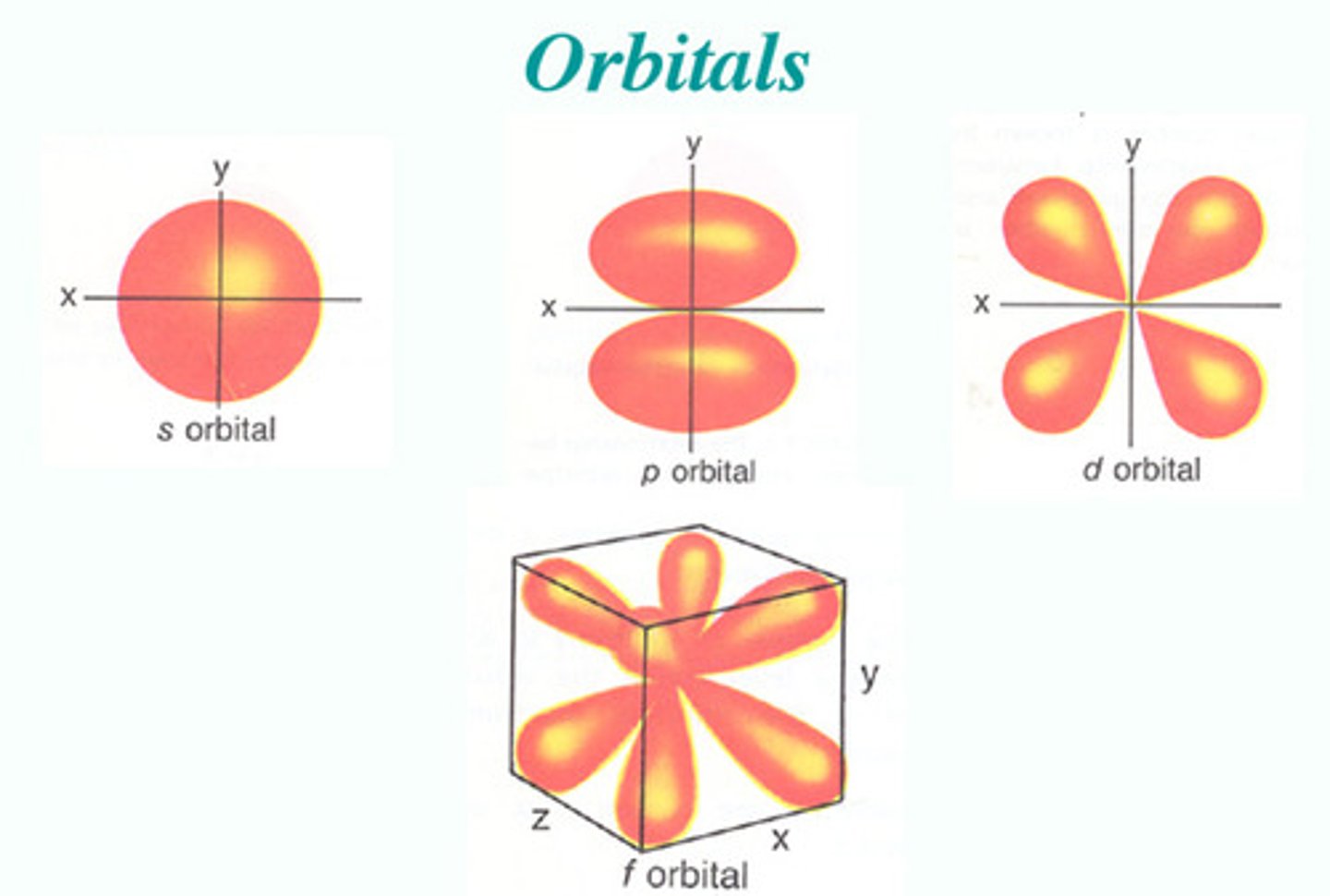
f-orbital
A complex orbital defined by l=3. There are seven orbitals within this type.
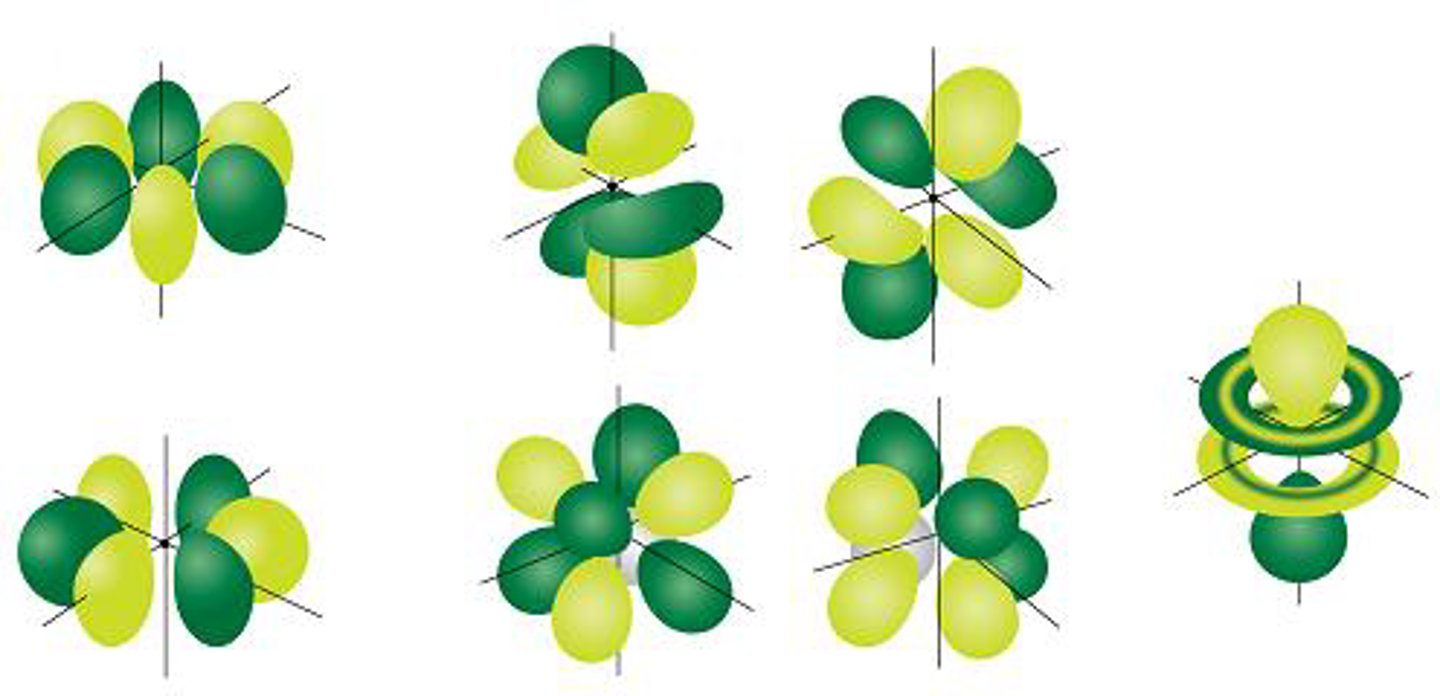
Rank the different quantum representations from general to specific:
n (principal) , l (angular momentum), ml (magnetic), and ms (spin)
Hund’s Rule
When electrons enter degenerate orbitals, they enter singularly with the same direction of spin before they pair up with opposite spins
Aufbau’s Princple
Electrons enter the atom filling up the lowest energy level before going to a higher energy level.
Pauli’s Exclusion Prinicple
Every electron in the atom must have a unique set of quantum numbers (QN).