AP Psych Midterm ALL VOCAB EVER
1/341
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
342 Terms
Psychology
the scientific study of the mind and behavior
Confirmation Bias
the tendency to favor information that confirms existing beliefs
Hindsight Bias
the tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it
Overconfidence
the tendency to be more confident than correct—to overestimate the accuracy of our beliefs and judgments.
Empirical Evidence
information acquired by observation or experimentation
Scientific Method
A systematic approach to research where a problem is identified, relevant data is gathered, a hypothesis is formulated from this data, and the hypothesis is empirically tested
Hypothesis
a testable prediction, often implied by a theory
Falsifiable
capable of being disproved by experimental results
Peer Review
a process by which something proposed (as for research or publication) is evaluated by a group of experts in the appropriate field
Replication
the action of repeating a study, using the same methods to see if the original results can be consistently reproduced
Reliability
the consistency of a research study or measuring test
Validity
the extent to which a test measures or predicts what it is supposed to do
The American Psychological Association (APA)
a professional organization representing psychologists in the United States
*Quantitative Data
information about quantities; that is, information that can be measured and written down with numbers
*Qualitative Data
descriptive information, which often comes from interviews, focus groups, or artistic depictions such as photographs
Likert Scales
A psychometric scale commonly used in questionnaires, and is the most widely used scale in survey research
Structured Interviews
a quantitative research method where the interviewer asks a set sequence of questions
Survey Technique
a research technique that involves the collection of information from a sample of individuals through their responses to questions
Wording Effect
the effect that question phrasing and order have on survey data
Social Desirability Bias
a tendency to give socially approved answers to questions about oneself
*Naturalistic Observation
observing subjects in their natural environment without manipulation or control by the researcher
*Case Study
an in-depth study of a single person, group, event or community
Correlational Research
a type of non-experimental research method, which studies the relationship between two variables with the help of statistical analysis (no manipulation)
Third Variable Problem
A form of confounding in which a third variable leads to a mistaken causal relationship between two others
Scatterplot
a graphical representation of the values of two variables for a set of data
*Positive Correlation
a relationship between two variables in which both variables move in the same direction. For example, as one variable increases, the other also increases, indicating a direct relationship
*Negative Correlation
a relationship between two variables in which the variables move in opposite directions. For example, as one variable increases, the other decreases, indicating an inverse relationship
Correlation Coefficient
a statistical index of the relationship between two things (from -1 to +1)
-correlation is NOT causation
Experimental Method
A method of research where the researcher manipulates one variable and controls/randomizes the rest of the variables
*Independent Variable
The variable that is manipulated or controlled by the researcher
*Dependent Variable
The variable that is tested and measured in an experiment
*Confounding Variable
a variable that influences both the dependent variable and independent variable causing a spurious association
*Operational Definitions
specifically defining a variable in terms of how it is measured or manipulated in a study (ensures consistency and clarity in research)
Experimental Group
the group in an experiment that receives the variable being tested
Control Group
the group in an experiment that does not receive the test variable
Random Assignment
assigning participants to experimental and control groups by chance, thus minimizing preexisting differences between those assigned to the different groups
Experimenter Bias
a process where the scientists performing the research influence the results, in order to portray a certain outcome
*Single-Blind Study
a study in which the participants do not know whether they are in the control group or the experimental group, but the researchers do
*Double-Blind Study
a study in which neither the participants nor the experimenters know who is receiving a particular treatment
Placebo Condition
a condition in which treatment is not administered but the subject believes that it is administered
Sample
a subset of individuals from a larger population, used to conduct research
Representative Sample
a sample that accurately reflects the characteristics of the population as a whole
Random Sample
a sample that fairly represents a population because each member has an equal chance of inclusion
Sample Bias
A bias that occurs when a sample is collected in such a way that some members of the intended population are less likely to be included than others
Generalizability
the extent to which the results of a study can be generalized or extended to others
Standard Deviation
a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion in a set of values
Percentile Rank
the percentage of scores in its frequency distribution that are equal to or lower than it
Statistics
a branch of mathematics dealing with the collection, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of masses of numerical data
*Descriptive Statistics
statistics that summarize the data collected in a study
*Inferential Statistics
statistics that allow one to make predictions and inferences about a population based on a sample of data
Measure of Central Tendency
a statistical measure that identifies a single value as representative of an entire distribution
Mean
the average of a set of numerical values
Median
the middle value in a list of numbers
Mode
the value that appears most often in a set of data
Range
the difference between the highest and lowest values in a dataset
Normal curve
a bell-shaped curve that represents a distribution of values, frequencies, or probabilities so that most measurements are concentrated around the middle
Positive Skew
This happens when more numbers in a list are on the lower side, but a few really high numbers stretch the average higher
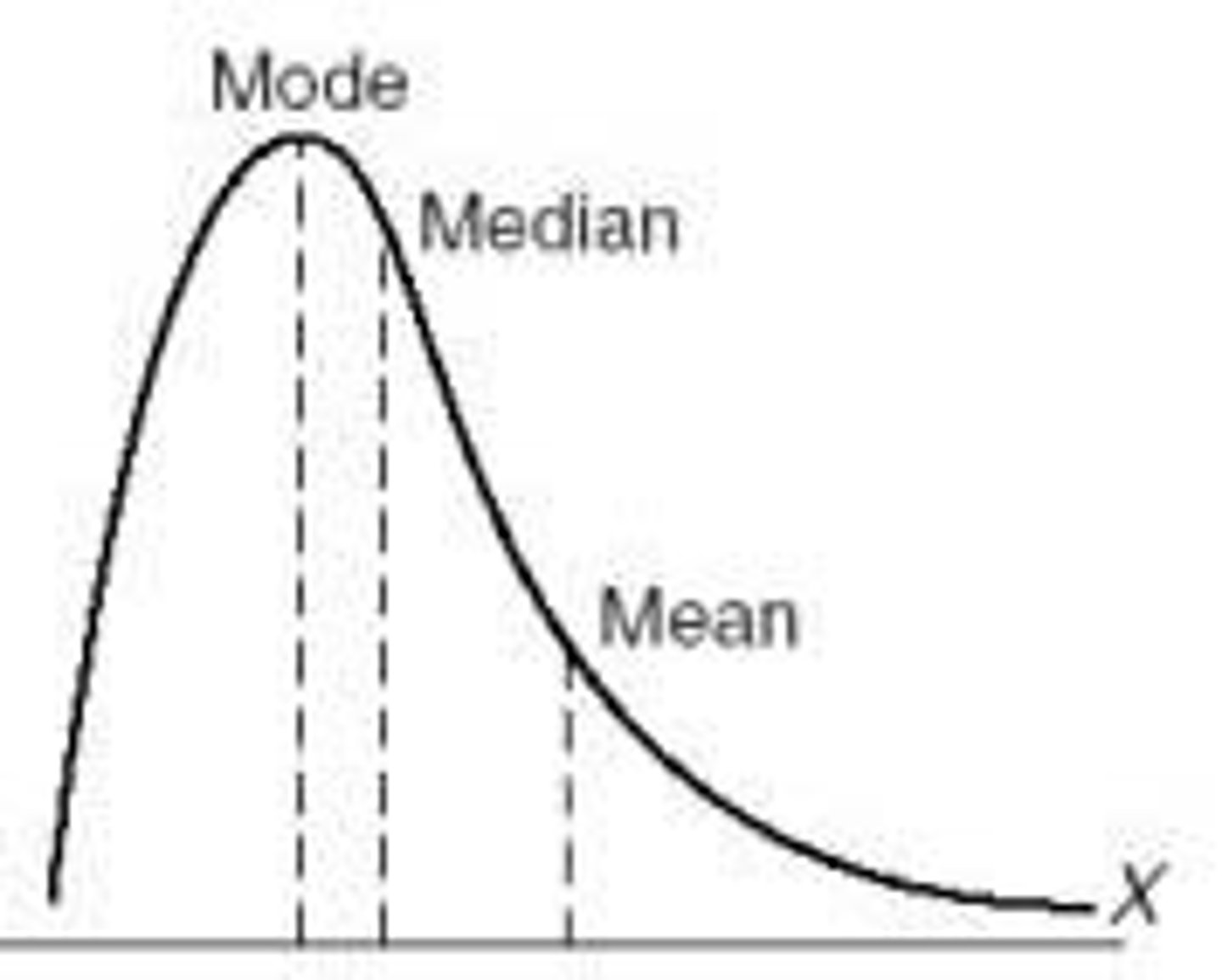
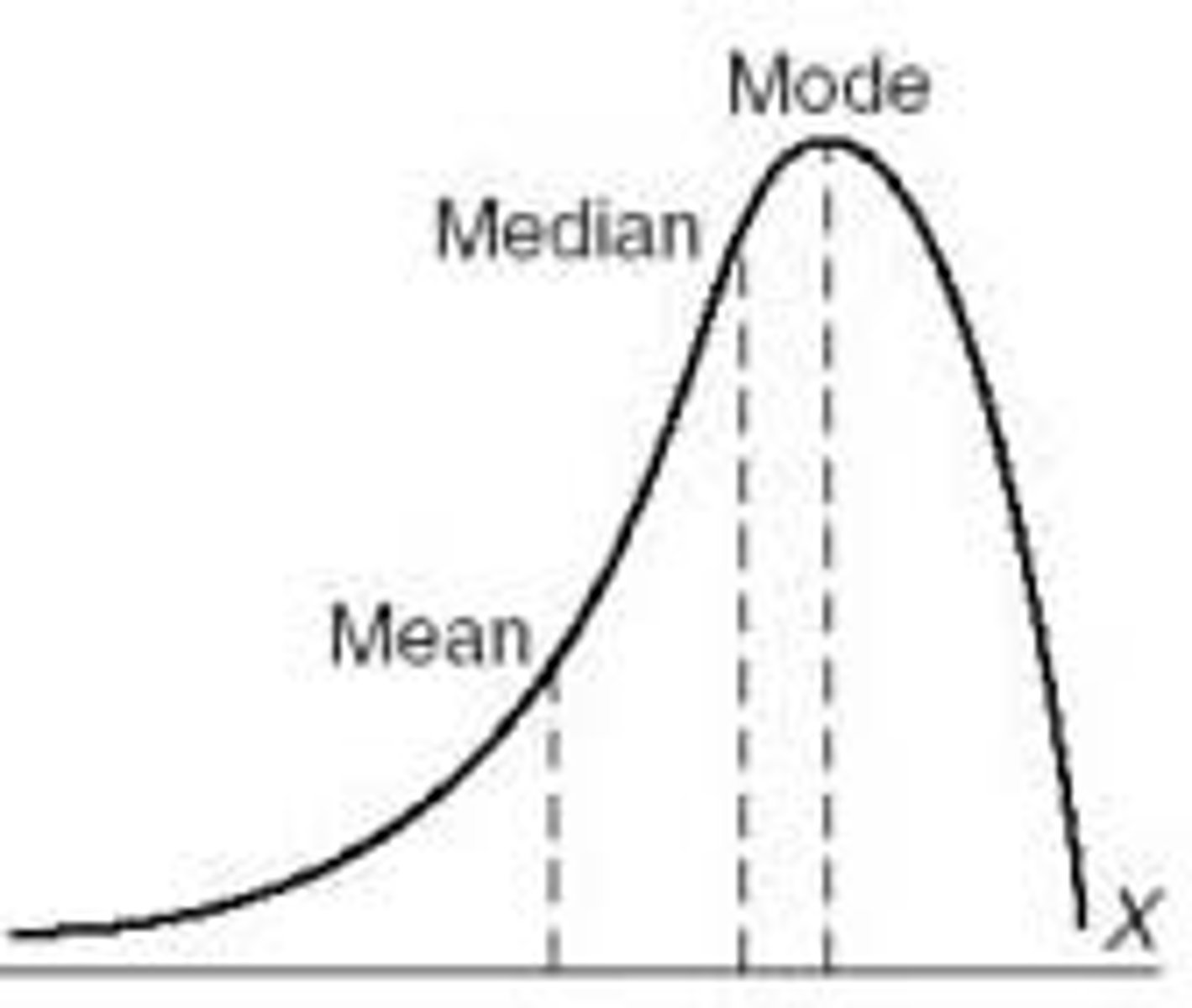
Negative Skew
This is when more numbers in a list are on the higher side, but a few really low numbers pull the average down
Statistical Significance
this tells us if the result of an experiment is probably true or just happens by chance. It checks if what we found in our experiment would happen often, or is rare when we think nothing special is going on
P-value < 0.05 = statistically significant difference
P-value > 0.05 = no statistically significant difference
Effect Sizes
This measures how big the impact of something is in an experiment. For example, it tells us how much a medicine really helps compared to not using the medicine at all
Meta Analysis
a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies
Institutional Review Boards (IRB)
A committee that reviews and approves research involving human subjects, ensuring that ethical standards are met
*Informed Consent
permission granted with the knowledge of the possible consequences, typically that which is given by a patient to a doctor for treatment with full knowledge of the possible risks and benefits
*Informed Assent
agreement by a minor or other parties not able to give legal consent to participate in the activity
Confidentiality
the requirement that private or sensitive information is not disclosed without the consent of the person who provided it
Deception
the act of misleading or wrongly informing someone about the true nature of a situation
Confederates
individuals who appear to be participants in a study but are actually part of the research team
Debriefing
providing participants in a study with a full explanation of the study after its completion, including the purpose and any deceptions used
Research Design (broader framework)
The overall plan (blueprint) for how you will answer a research question. It includes deciding what you want to study, what you want to find out, and how you will gather and analyze your information
Methodology (specific techniques)
The tools and methods you use to collect your data/specific ways to gather information
Evolutionary Perspective
looks at how human behaviors helped our ancestors survive and reproduce
*Natural Selection
process where traits that enhance survival and reproduction are passed on more frequently
*Nature
the influence of genetic factors on traits and behaviors
*Nurture
the influence of environmental factors on traits and behaviors
Twin Studies
research comparing the similarities between identical and fraternal twins to understand the influence of genetics versus environment
Adoption studies
studies that compare biologically related people, including those raised apart, to understand genetic influences
Family studies
research looking at behavioral traits in families to determine how much is genetic versus environmental
*Heredity
the passing of traits from parents to offspring through genes
*Genetic predisposition
the likelihood of developing certain traits or disorders based on genetics
*Eugenics
a controversial and unethical movement aimed at improving the genetic composition of humans through selective breeding
Cerebral Cortex
the outer layer of the brain, involved in complex mental processes such as thinking
Frontal lobes
involved in decision-making, problem-solving, and controlling behavior
Prefrontal cortex
part of the frontal lobes involved in planning complex behaviors and expressing personality
Executive functioning
higher order processes including planning, organizing, and regulating behavior
Motor Cortex
controls voluntary movements
Parietal lobes
processes sensory information like touch and spatial awareness
Somatosensory Cortex
area of the brain that processes sensory input from various body parts
Occipital lobes
responsible for vision
Temporal Lobes
involved in hearing, memory, and understanding language
Contralateral Hemispheric Organization
each hemisphere of the brain controls the opposite side of the body
Corpus Callosum
thick band of nerve fibers that connects the two brain hemispheres; severed in split brain research
Brainstem
supports basic life functions, including heart rate, breathing, and sleeping
Medulla
part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions like heartbeat and breathing
Reticular Activating System
regulates wakefulness and sleep-wake cycles
Cerebellum
coordinates voluntary movements like posture, balance, and coordination
Limbic System
involved in emotion, motivation, and memory
Reward Center
brain areas that regulate the experience of pleasure.
Thalamus
relay motor and sensory signals to the cerebral cortex
Hypothalamus
regulates body temperature, hunger, thirst, and other homeostatic systems
Pituitary Gland
the master gland of the endocrine system that regulates other glands