Solid Oral MR Dosage Forms - Hydrophilic & Insoluble Polymer Matrix Systems
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Immediate release dosage form (IR)
release the active drug promptly upon contact with GI fluids, allowing rapid dissolution and absorption
Key characteristics of IR dosage form
rapid drug release
no modification of release or site
typically produce a quick rise in plasma drug concentration
Common types of IR dosage forms
conventional tablets/capsules
oral solutions/syrups/suspensions
powders for reconstitution
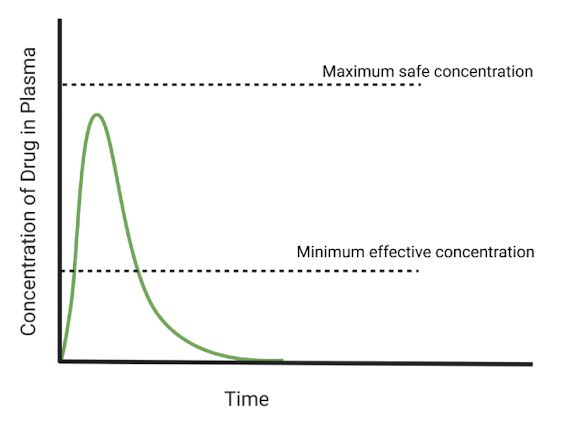
What type of dosage form does the chart show?
immediate release
Modified release dosage form
manipulation of drug release from a dosage form with the specific aim of delivering APIs at:
desired rate
predetermined time point
specific sites in the GI tract
Classifications of modified release dosage forms
extended release (ER)
delayed release (DR)
Extended-release (ER) dosage forms
maintain therapeutic plasma concentrations over an extended duration
How might an ER formulation dosing differ from IR formulation dosage?
reduced dosing frequency
once or twice daily
more stable plasma concentration
Advantages of ER dosage forms
less fluctuation in drug blood levels
frequency reduction in dosing
enhanced convenience and compliance
reduction in adverse side effects
reduction in overall health care costs
Hydrophilic matrix system
also known as swellable soluble matrices
drug is blended with water-swellable hydrophilic polymer
blend is compressed into tablets by compression or dry granulation, resulting in a tablet with drug particles are interspersed among polymer particles
Hydrophilic polymers used for hydrophilic matrix system
HPMC or other polyethylene oxide
20% of HPMC results in satisfactory rates of release
Hydrophilic matrix system mechanism of drug release
upon contact with GI fluid, the polymer hydrates and swells to form a viscous gel layer around the tablet
water continues to penetrate, gradually thickening gel
drug is released by diffusion through gel or erosion/dissolution of the gel
Role of gel structure and tortuosity in hydrophilic matrix system
hydrated hydrophilic polymers form a network of entangled chains
spaces between chains create continuous aqeous phase, allowing water and dissolved drug to move
pathways are tortuous, not straight
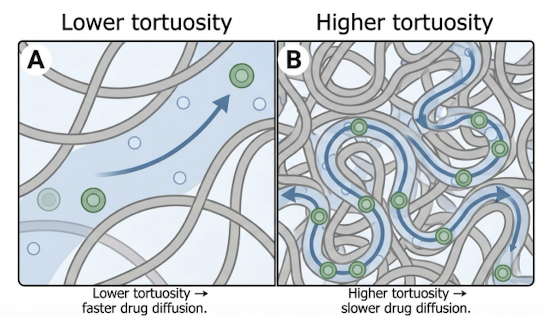
What factors increase the number of pathways in a hydrophilic matrix system, slowing release?
high polymer concentration
higher molecular weight polymer
How can a slow-release profile be achieved in a hydrophilic matrix system?
high-viscosity or high molecular weight polymers
increased percentage of polymers
polymers with greater degree of cross-linking
adding excipients that strengthen/stabilize gel
How can a faster-release profile be achieved in a hydrophilic matrix system?
lower-viscosity polymers or lower molecular weight
lower polymer content
incorporation of more soluble excipients that loosen gel structure
Insoluble (inert) polymer matrix system
drug is embedded in an inert, water-insoluble polymer often described as a “sponge-like” structure
tab enters GI tract, water penetrates channels and pores, dissolves drug
dissolved drug diffuses out water-filled pores
What types of drugs are insoluble polymer matrix systems suitable for?
drugs that are less water soluble
Insoluble polymers used for insoluble polymer matrix systems
polyethylene
polyvinyl acetate
polymethyl methacrylate
What effect does porosity have on controlled release of insoluble polymer matrix systems?
↑porosity, faster drug release
↑compaction, ↓porosity, slower drug release
pore-forming agents can be added to facilitate drug release
What effect does tortuosity have on insoluble polymer matrix system release rate?
increased tortuosity, decreased drug release
Describe the intact nature of insoluble polymer matrix systems
polymeric matrix does not dissolve/degrade in GI tract
once drug is released, remaining matrix retains structural integrity
excreted unchanged in feces; “ghost tablet”
What is an important counseling point when dispensing a drug with an insoluble polymer matrix system?
patients may notice empty shell in stool