CHEM1100 Final
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Assumptions for an ideal gas
Molecules have negligible volume
No intermolecular interactions
Molecules move in random motion
When does ideal gas behaviour break down?
High pressure and/or low temperature
HP LT!!!
Open system
Can exchange matter and energy w surroundings
Closed system
Can only exchange energy w surroundings
Isolated system
Cannot exchange matter or energy w surroundings
Adiabatic system
Can only exchange work with surroundings
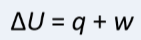
Positive w means
work done by surroundings on the system
Is internal energy (U) a state function
Yes
Is enthalpy a state function?
Yes
Standard enthalpy of formation for an element
0J
Is entropy a state function?
Yes (delta S = final S - initial S)
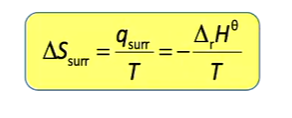
Relationship between entropy of surroundings and change in reaction enthalpy
Third law of thermodynamics
At absolute zero, the entropy of a perfectly ordered pure crystalline substance is zero.
System at equilibrium has delta G of…
0J
At a phase change, delta G is
0J
Which quantity cannot be measured directly?
Standard Gibbs Energy Change
Is G a state function
Yes
When is G a minimum?
When a system is in equilibrium
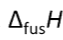
Molar enthalpy of fusion
Heat needed to melt 1 mol of substance at normal melting point
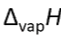
Heat needed to vaporise 1 mol of substance at its normal boiling point

Molar enthalpy of sublimination
Heat needed to vaporise 1 mol of substance from solid phase
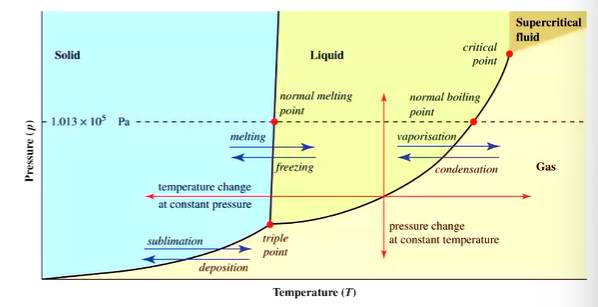
Axis on phase diagram
Steps to dissolving a gas
Form pockets in solvent to hold gas (endothermic bc imf are overcome between solvent molecules)
Mixing - gas goes into pockets, create IMF between solute and solvent (exothermic)
Colligative properties - freezing point ___ (and why is this the case)
Depression
Solute will be in liquid phase. Solute disrupts process of forming interactions btwn solute to reform solid
So melting point is lower
Boiling point ___
Elevation
Ions in liquid prevent solvent molecules from entering gas phase
More energy needed to enter gas phase
how to calculate b for colligative properties
b = molality
For nondissociating solutes (ions)
b = moles of solute / mass of solVENT
moles/kilogram
Do colligative properties depend on the identity of particles?
NO
Only depends on quantity of particles (b)
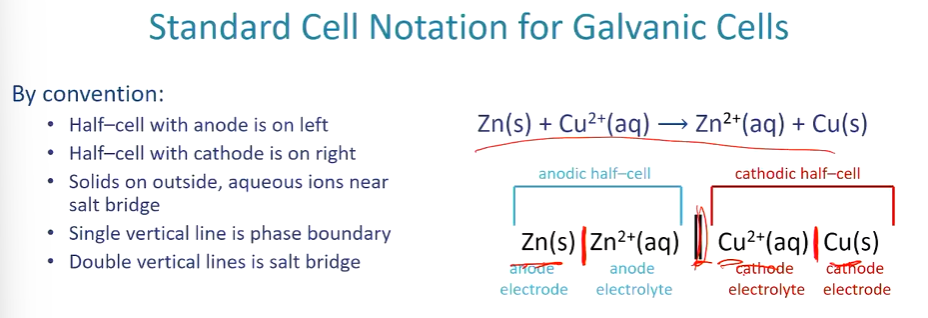
Cell notation rules
Carbon oxidation state rules
C-C bonds don’t change oxidation state
Each bond with H or metal = -1
Each bond with electronegative element (NOF or halogens) = +1
Is work a state function
No
Is heat a state function
No
The formula that Lucas wanted me to add in
delta H = delta U + RT delta n
delta n = change in number of moles
Intensive property
A characteristic that does NOT depend on the amount present
YIPPAROONI THAT IS ALL!!! Flip over this card for a reward

What does “free” mean for gibb’s free energy
Energy that can be transferred in forms other than heat and PV work