Biology 3.2 - photosynthesis
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
What is photosynthesis?
the process in green plants by which water and carbon dioxide combine using light energy to form glucose and oxygen
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
What type of reactions does photosynthesis consist of?
light dependant reactions
light independent reactions
what are the two types of light dependant reactions?
non-cyclic photophosphorylation
cyclic photophosphorylation
Where do the light dependent reactions occur?
in the thylakoid membrane
happen in presence of light
What happens in the light dependent reactions?
light energy is harvested and used to produce atp and a reduced hydrogen carrier (NADP → reduced NADP)
water is split forming an oxygen
where do the light independent reactions occur?
in the stroma
do not require light
what happens in the light independent reactions (calvin cycle)
use the atp and reduced NADP from light dependant reactions
glucose is produced from carbon dioxide
A chloroplast is a transducer, what is a transducer?
a transducer changes energy from one form to other
chloroplasts change energy in photons of light into chemical energy
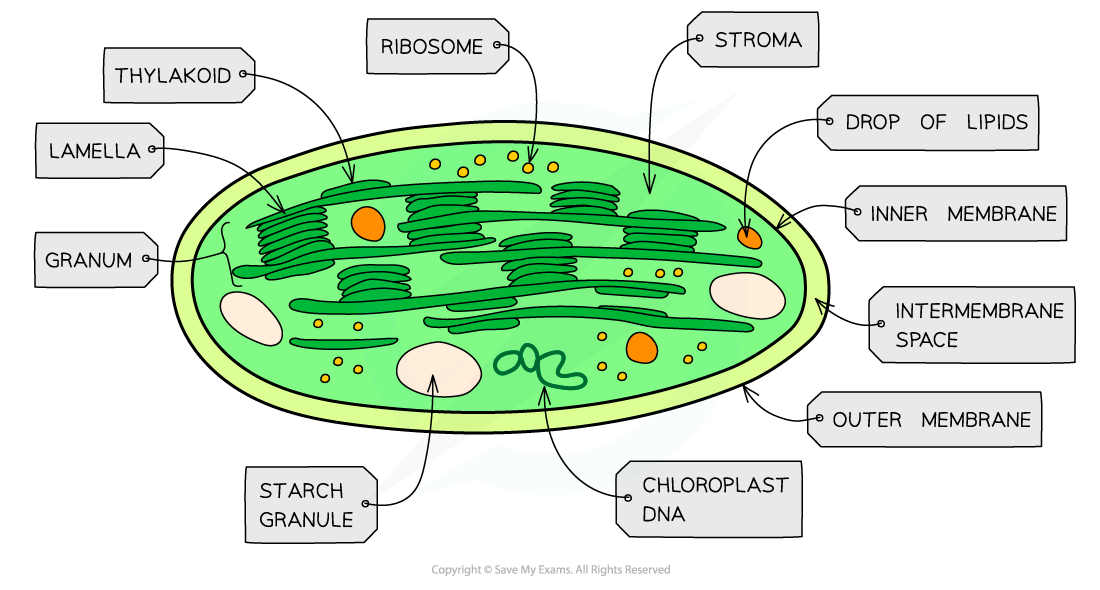
diagram of chloroplast
What was englemann’s experiment?
he was trying to discover which wavelengths of light are absorbed most by plants and used in photosynthesis
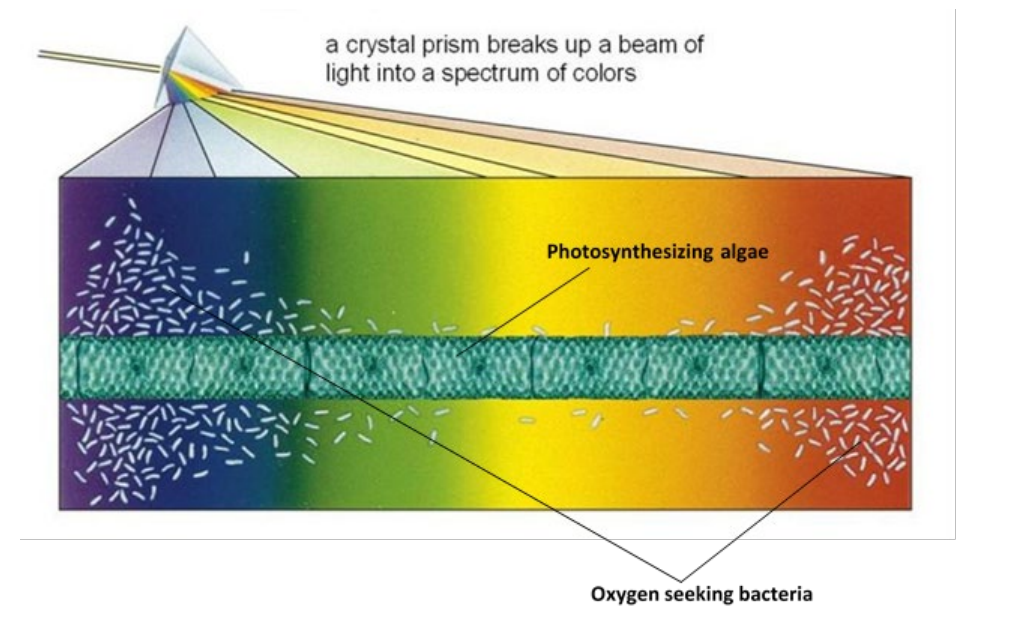
Describe and explain the results of englemanns experiment?
bacteria clustered in red and blue region of the spectrum because they are the wavelengths of light that are absorbed the most
There will be a higher rate of light dependant stage in those wavelengths and more photolysis of water to release the oxygen
So the bacteria clustered there because they need the oxygen for aerobic respiration
very few bacteria in green region because very little green light is absorbed/it is reflected
Describe a suitable control for englemanns experiment and explain why
use white light only
bacteria would distribute themselves evenly along the tube
shows that it is the different wavelengths of light causing the distribution of bacteria seen in the investigation
What is a pigment?
a coloured substance that absorbs specific wavelengths of light
Where does the colour of the substance in a pigment come from?
comes from the light/wavelengths reflected, not absorbed
what are the two main classes of photosynthetic pigments that act as transducers in flowering plants?
chlorophylls
chlorophyll a = blue/green colour and is primary pigment
chlorophyll b = yellow/green (absorb red and blue/violet light and reflect green)
chlorophyll c + b are accessory pigments
carotenoids
what are carotenoids?
carotenes + xanthophylls
accessory pigments
help absorb a range of wavelengths of light not absorbed by chlorophyll a and pass the energy to chlorophyll a
are orange or yellow in colour
absorb blue/violet light
how would a lack of magnesium result in poor growth in a plant?
leads to a lack of chlorophyll so it cannot absorb as much light energy
so less light dependent stage would occur and it wouldn’t produce as much ATP and NADPH for the light independent stage
the rate of photosynthesis will decrease so there will be less glucose produced
there is less glucose for respiration meaning less ATP for protein synthesis or cell division
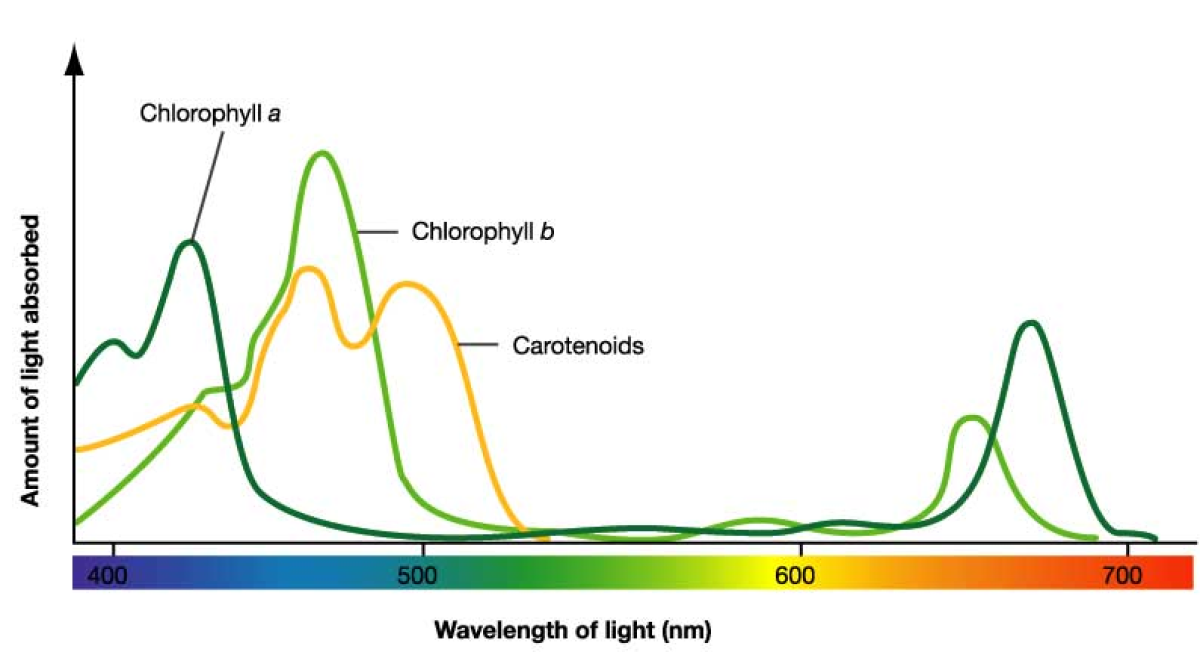
What graph is this?
absorption spectrum of photosynthetic pigments
what does the absorption spectrum show?
how much light energy a particular pigment absorbs at each wavelength
why is there less absorption in green light on the absorption spectrum?
it is reflected
what is the advantage of having multiple photosynthetic pigments?
can absorb a wider range of wavelengths of light
more light dependent stage
more ATP + reduced NADP formed for light independent stage
rate of photosynthesis higher
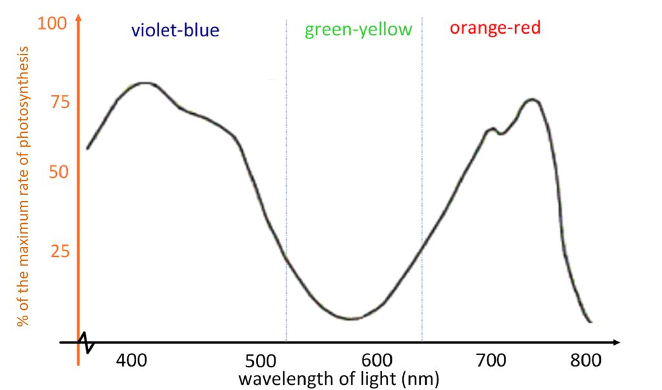
what graph is this?
action spectrum of photosynthetic pigments
what does the action spectrum show?
the rate of photosynthesis at different wavelengths of light
(the amount of carbohydrate synthesised by plants exposed to different wavelengths of light)
what is the correlation between the absorption spectrum and the action spectrum?
close correlation
suggests that the photosynthetic pigments are responsible for absorbing the light energy in photosynthesis
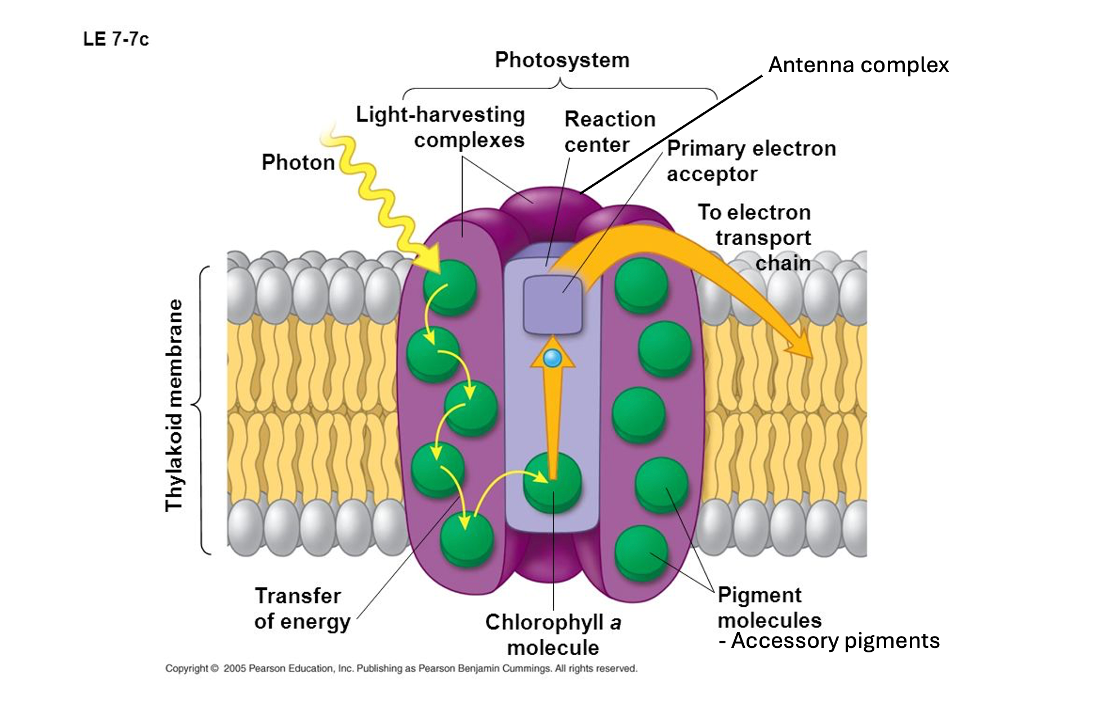
where are the photosystems located?
in the plane of the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplasts
what is each photosystem made up of?
antenna complex
reaction centre
what does an antenna complex contain?
clusters of up to 400 photosynthetic pigment molecules
chlorophylls and carotenoids are anchored into the phospholipids of the thylakoid membrane and held together by protein molecules
allows a range of wavelengths of light to be absorbed
what does a reaction centre contain?
two molecules of the primary pigment, chlorophyll a
when chlorophyll a molecules absorb light, their excitation allows each one to emit an electron
diagram of photosystem
what are the two types of reaction centre?
photosystem I (PSI)
photosystem II (PSII)
describe photosystem I
arranged around a molecule of chlorophyll a
absorption peak of 700nm
reaction centre is called P700
richer in chlorophyll than b
describe photosystem II
arranged around a molecule of chlorophyll a
absorption peak of 680 nm
reaction centre is called P680
richer in chlorophyll b than a
How can you separate the different pigments in chlorophyll?
using paper chromatography
how can you identify the separate pigments after using paper chromatography?
qualitatively - by colour
quantitatively - by calculating the retention factor (Rf) using a particular solvent
How do you calculate the Rf value?
distance moved by pigment from original position/distance moved by solvent front
what do the light dependent stages of photosynthesis produce?
atp from adp + Pi by photophosphorylation - provides the chemical from light energy to synthesise energy - rich glucose
reduced NADP/NADPH by addition of 2H’s to NADP - provides the reducing power to synthesise glucose from carbon dioxide
oxygen - produced from the splitting of water molecules by photolysis - oxygen diffuses out of the chloroplast and photosynthetic cells and out of the leaf through the stomata