Physiology Quizzes
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Physiology deals with
the functions of the human body.
Polypeptides are made by linking which monomers together in a chain?
amino acids
Which of these lists the components of a general reflex arc or homeostatic feedback loop in the order that information typically flows through them following a stimulus?
receptor, afferent pathway, integrating center, efferent pathway, effector
Positive feedback helps to maintain homeostasis in the body. (Thinking question)
False
When the body is incapable of maintaining homeostasis due to some internal or external stimuli, disease or poor health is a likely outcome.
True
In a homeostatic feedback loop, the integrating center is always the brain (or spinal cord).
False
Homeostasis means
Keeping physiological variables within some predictable, normal range
What type of bond links one amino acid to another in the formation of a polypepdtide
peptide bond
Which of the following membrane transport mechanisms requires ATP?
Active transport
Primary structure is the final 3-dimensional folding of a polypeptide chain into a protein.
False
All individual amino acids are ions.
True
What provides the driving force for simple diffusion of a substance across a cell membrane?
The concentration gradient of the substance across the cell membrane
The movement of an ion across a membrane through a voltage gated ion channel is an example of...
Facilitated diffusion
The synthesis of proteins occurs at which cell structure?
Ribosome
Parturition is an example of Feed Forward control.
False
Indirect Active Transport typically involves both an ATP dependent pump and a uniporter.
False
The sodium potassium pump is an example of an antiporter.
False
The R-groups of amino acids are always charged.
False
Approximately how many different amino acids help to make proteins?
About 20
If I touch a hot stove and my hand pulls away from it, what is the effector organ for this negative feedback mechanism?
biceps muscle
As potassium diffuses out of a cell, the inside of the cell becomes electrically more
Negative
What ion, of those specifically discussed in Module 2, typically has a higher concentration in the extracellular fluid than in the intracellular fluid?
Na+
For nearly all cells, because of specific ion concentrations across the cell membrane, the inside of the cell will be negative with respect to the outside of the cell. This results in an electrical gradient across the cell membrane.
True
The parts of the neuron that receive information are called the
dendrites and cell body
The junction between two neurons where one neuron alters the electrical activity of the other is called a synapse.
True
Select the TWO myelin-producing glial cells.
Oligodendrocytes, Schwann cells
The active transporter responsible for helping to maintain the physiologically normal concentrations of sodium and potassium in the intracellular and extracellular fluids is the
Na+/K+ Pump
The membrane becomes less negative than the resting level.
Depolarization
The membrane potential becomes more negative than the resting level.
Hyperpolarization
When a membrane potential that has been depolarized returns to the resting value.
Repolarization
Voltage-gated ion channels open in response to a change in electrical potential across the membrane (like depolarization for example)
True
Opening of voltage-gated Na+ ion channels and Na+ entry into a neuron causes
Depolarization
Ligand-gated channels open in response to a change in electrical potential across the membrane (like depolarization for example)
False
The voltage-gated Ca2+ channels at the axon terminal stimulate the neurotransmitter to be released into the synaptic cleft.
True
Voltage-gated ion channels are quite numerous at the dendrites and soma.
False
A metabotropic neurotransmitter receptor is also a channel.
False
At the axon hillock, what happens if a neuron depolarizes, but not enough to reach threshold.
It will not fire an action potential
The nAchR is a ligand-gated channel.
True
Which neurotransmitter and receptor combination is present at the effector organ of the parasympathetic nervous system.
acetylcholine and the muscarinic AchR receptor
Which neurotransmitter would cause an increase in heart rate (directly at the heart)
Epinephrine
Which neurotransmitter is released at the effector organ of the somatic motor nervous system?
Acetylcholine
Skeletal muscles are made up of bundles of muscle fibers attached to bone by connective tissue called tendons.
True
What protein is the principal component of skeletal muscle thick filaments?
Myosin
In skeletal muscle cells, calcium initiates contraction by binding to which protein?
troponin
According to the sliding filament mechanism of skeletal muscle contraction, during contraction
The sarcomeres shorten.
The phenomenon of rigor mortis demonstrates that myosin can remain bound to actin in the absence of additional ATP, but the bond cannot then be broken.
True
The removal of calcium ions from the cytosol of skeletal muscle causes
the myosin binding sites on actin to be covered by tropomyosin.
An action potential in the post synaptic membrane of the neuromuscular junction rapidly spreads to the interior regions of a muscle cell by means of the
transverse tubules
The site of Ca2+ storage in muscle cells is the transverse tubules.
False
Calcium entry into the alpha motor neuron axon terminal triggers which of the following events at a neuromuscular junction?
Fusion of synaptic vesicles with the plasma membrane of the axon terminal and release acetylcholine.
Action potential generation and propagation in a skeletal muscle fiber ceases when
acetylcholine is degraded by acetylcholinesterase.
A sustained contraction in a muscle fiber occurs when
the sarcolemma and t-tubule undergo repeated action potentials and result in sustained high Ca2+ levels in the myoplasm
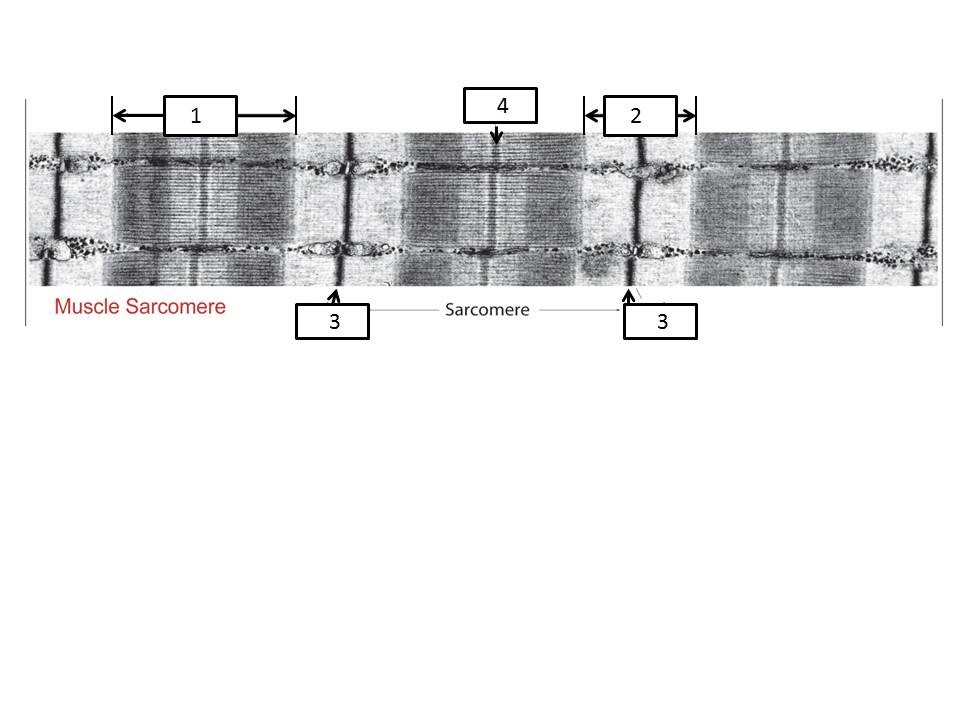
Based on this image identify #1
A-Band
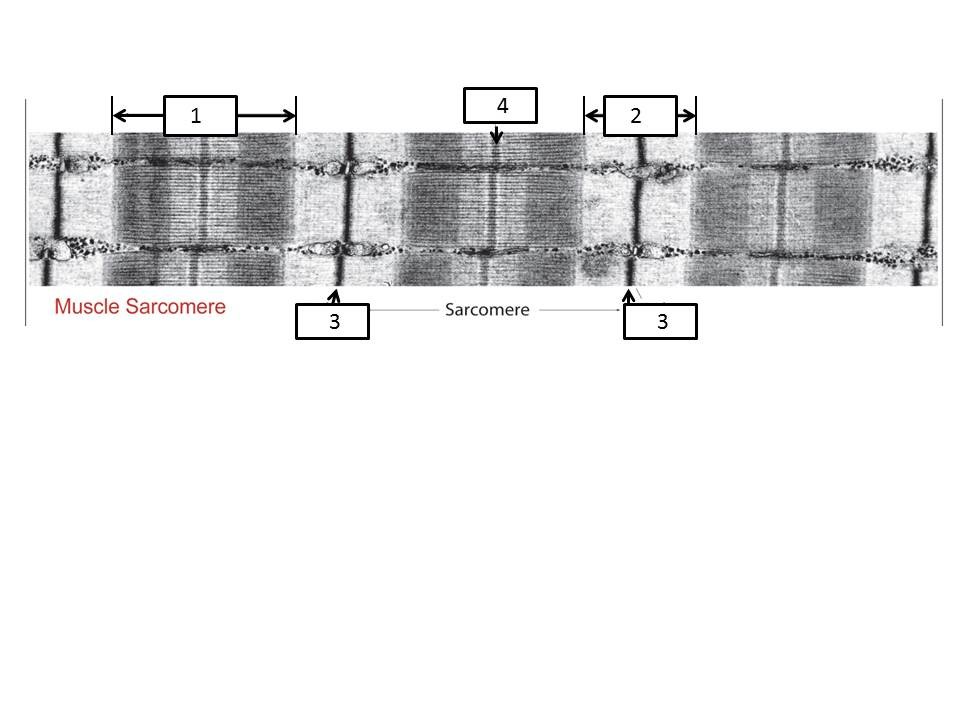
Based on this image identify #3 (at bottom of image)
Z-line
The Dihydropyridine Receptor (DHPR) is the Calcium release channel in the sarcoplasmic reticulum
False
The voltage sensor protein is the DHPR in the T-tubule membrane at the triad
True
During the cross bridge cycle, ATP binding to the myosin head causes the power stroke
False
Increasing the frequency of muscle stimulation (and action potential generation) results in summation of Ca2+ release events from the SR allowing for an increase in muscle force development.
True
Recruitment is the process by which
increasing the number of activated motor units increases whole muscle force output
Maximal muscle fiber concentric (shortening contraction) contractile velocity occurs at maximal load.
False
The force produced during an isometric contraction occurs at a shortening velocity of zero.
True