FL1 AAMC bio/biochem
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
A man with a CRC mutation that results in the synthesis of HSP110ΔE9 and a woman that does not carry this mutation in any of her tissues have a child. What is the percent chance that the child will inherit the CRC mutation?
“People with MSI CRC have HSP110ΔE9 transcripts in cancerous tissue only.”
A.
0%
B.
25%
C.
50%
D.
100%
A, in the passage it states transcripts in cancerous tissue only, the mother doesn’t have this tissue meaning no chance at all
The information in the passage best supports the conclusion that Intron 8 of HSP110 most likely contains which of the following?
“Intron 8 of the gene encoding heat shock protein 110 (HSP110). HSP110 can bind structurally similar heat shock proteins and functions to facilitate proper protein folding and to reduce levels of nonfunctional protein aggregates. The larger HSP110 T17 deletions cause Exon 9 to be omitted from the final sequence during pre-mRNA processing”
A.
Stop codon
B.
Splice acceptor site
C.
HSP110 gene promoter
D.
Partial coding sequence of HSP110
B, deletion of intron 8 causes exon 9 to be omitted/sliced out
Clathrin
form vesicles to assist in transport within cells
enzymes
catalyze chemical reactions via lowering activation energy barriers, converts substrate to products
nuclear localization signal
tags protein to be transported into nucleus
signal sequence
sequence for protein that required embedding domain
Pellagra also results from a deficiency of nicotinamide, which is synthesized from tryptophan. Nicotinamide nucleotides are neither oxidized nor reduced during which step of cellular respiration?
A.
Glycolysis
B.
Chemiosmosis
C.
Citric acid cycle
D.
Electron transport chain
B, only place nothing happens to nicotinamide aka NAD
what happens to nicotinamide (NAD) in glycolysis
reduced to form NADH
what happens to nicotinamide (NAD) in citric acid cycle
reduced to form NADH
what happens to nicotinamide (NAD) in ETC
NADH is oxidized to form NAD(nicotinamide)
If a man with a mutant copy of Ace2 has a child with a woman that is heterozygous for the mutant Ace2 allele, what is the probability that the child will be a female and homozygous for the mutant Ace2 allele?
A.
0
B.
0.25
C.
0.75
D.
1
B
During the initiation of muscle contraction, myosin binds actin after troponin binds to which ion?
A.
H+
B.
K+
C.
Na+
D.
Ca2+
D, myosin and tropin just think of calcium
What is the total number of fused rings present in a steroid?
A.
1
B.
2
C.
4
D.
6
C
Epilepsy may result in motor seizures due to massive synchronous firing of neurons in a small area of the cerebral cortex (the epileptic focus). Excitation spreads from the focus, involving an increasingly larger area of the cortex. A drug for the treatment of epilepsy would be most effective if it caused which of the following changes in the epileptic focus?
A.
An increase in the neuron-firing threshold
B.
An increase in extracellular Na+ concentration
C.
A decrease in axon–membrane permeability to negative ions
D.
A decrease in the length of the depolarization stage
A
PCT
first part of glomerular filtrate absorbing 65%
When concentrated urine is being produced, in which of the following regions of the kidney will the glomerular filtrate reach its highest concentration?
A.
Proximal convoluted tubule
B.
Distal convoluted tubule
C.
Cortical portion of the collecting duct
D.
Medullary portion of the collecting duct
D
DCT
impermeable to water
cortical portion of collecting duct
semi permeable to water, low conc
aldosterone
increases Na reabsorption, inadversly water
ADH (vasopressin)
makes distal nephron and collecting duct permeable to water, increases urine concentration
medullary interstitium is what
hyperosmoic meaning high NA and urea
descending loop does what
loses water, filtrate conc
ascending loop does what
pumps out ion, filtrating dilutions
Which approach does NOT measure the activity of the Na+K+ ATPase?
A.
Measuring the rate of ATP hydrolysis
B.
Measuring the free energy of the ion transport
C.
Measuring the rate of ADP production
D.
Measuring the change in ion concentration within the liposome
B, free energy has no connection to enzyme activity (atpase)
Na+/K+ ATPase does what
pump 3 Na out 2 k in per ATP hydrolyzed
Na/K Atpase is acitivty of what
movement of ions = rate of ATP hydrolysis
What is the function of the Na+K+ ATPase during a neuronal action potential?
A.
Stimulation of the action potential
B.
Depolarization of the membrane
C.
Hyperpolarization of the membrane
D.
Restoration of the resting potential
D, maintaining ion conc of potential at equilibrium, high sodium out high potassium in
what’s the purpose of pumping 3 Na out and 2 K in during atp hydrolyzes in Na/K ATPase?
maintain the resting ion gradient, keeping a high sodium conc out and high potassium in
what triggers stimulation of action potential
opening of sodium channels
what causes depolarization of membrane
sodium influx via voltage gated channel
what causes hyperpolarization of membrane
potassium going out via voltage gated channel
Anything about depolarization or hyperpolarization is ____________ not ATPase activity.
voltage gated channel activity
In which direction does the Na+K+ ATPase transport ions across the cell membrane upon ATP hydrolysis?
A.
Na+ is transported out of the cell; K+ is transported into the cell.
B.
Na+ is transported into the cell; K+ is transported out of the cell.
C.
Both Na+ and K+ are transported into the cell.
D.
Both Na+ and K+ are transported out of the cell.
A
Upon activation, p65 and cRel control the level of IL-6 mRNA by:
“Their activation leads to increased cell proliferation and suppression of apoptosis. Activation occurs when the inhibitory IκBα protein is degraded. This frees the nuclear localization sequence (NLS) on p65. The NLS is composed of four amino acids (KRKR) and interacts with an importin on the nuclear envelope.”
A.
binding RNA.
B.
binding DNA.
C.
replicating RNA.
D.
replicating DNA.
B, “frees nuclear localization sequence on p65, interacts with importin on nuclear envelope indicates binding of DNA
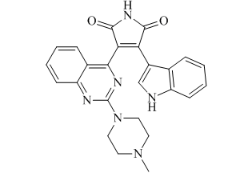
what can you tell about this molecule
alot of aromatic rings meaning its hydrophobic
only what kind of structure can diffuse directly through membrane
hydrophobic
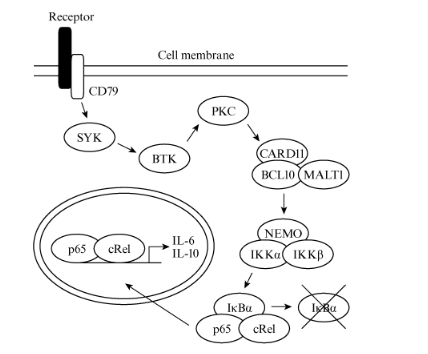
Assuming no mutations to the signaling pathway described in the passage, what event directly activates CARD11?
A.
Proteolytic cleavage
B.
GTP binding
C.
Membrane association
D.
Phosphorylation
D, always comb through figures in this section, in the figure it shows PKC affecting CARD11, PKC is phosphorylation
Which mechanism best describes how P-gp facilitates drug resistance?
“P-gp is responsible for multidrug resistance (MDR) in tumor cells by preventing drugs from accumulating to cytotoxic levels. Studies show that P-gp overproduction in the membrane of tumor cells produces an MDR phenotype.
It has been shown that P-gp exhibits ATPase activity and is localized in cholesterol-rich domains within the membrane.”
A.
P-gp binds to antitumor drugs in the presence of ATP and degrades the drugs.
B.
P-gp serves as a pump and uses active transport to move antitumor drugs outside the cell.
C.
P-gp prevents the entry of anti-tumor drugs into the cell.
D.
P-gp causes increased membrane permeability, which causes antitumor drugs to exit the cell.
B, From passage we are given that P-gp uses ATPase and produces phenotype MDR answer B fulfills ATPase criteria and since it produces a resistance phenotype it can’t be A or D cant be C doesn’t match ATPase description
What is the most likely location of P-gp within the plasma membrane?
“P-gp exhibits ATPase activity and is localized in cholesterol-rich domains within the membrane.”
A.
Associated with lipids on the cytoplasmic side only
B.
Associated with lipids on the extracellular side only
C.
Peripheral to the plasma membrane
D.
Within a lipid raft
D, lipid raft are cholesterol rich domains
glomerular capillary pressure
force filtrate into bowman capsule
capsular hydrostatic and blood colloid osmotic pressure
promote movement of filtrate in opposite direction
The initial filtration step in the glomerulus of the mammalian kidney occurs primarily by:
A.
passive flow due to a pressure difference.
B.
passive flow resulting from a countercurrent exchange system.
C.
active transport of water, followed by movement of electrolytes along a resulting concentration gradient.
D.
active transport of electrolytes, followed by passive flow of water along the resulting osmolarity gradient.
A
glomerulus and bowman capsule filter via
pressure gradient
how is glomerulus filtration drive
passively via pressure
what does loop of henle establish
medullary osmotic gradient
loop of Henle act as what
countercurrent system to concentrate urine
The half-life of urea is the time it takes for its concentration to fall by one-half. The graph illustrates the clearance of urea from an initial plasma concentration of 200 ng/mL. If it takes five half-lives for urea to be considered eliminated from the body, how long did it take to eliminate the urea?
A.
1.5 h
B.
2.5 h
C.
3.5 h
D.
4.0 h
B, takes 5 half lives to clear, an half live is ½
to find hour, 1/2h x 5 =0, solve for h which is 2.5
Enzymes alter the rate of chemical reactions by all of the following methods EXCEPT:
A.
co-localizing substrates.
B.
altering local pH.
C.
altering substrate shape.
D.
altering substrate primary structure.
D
how do enzymes alter rate of chemical reactions
-co localizes substrate
-alters local pH
-alters substrate shape
Which of the following statements gives the most fundamental reason why ornithine is unlikely to be found in proteins synthesized in vivo?
“Ornithine (R = –CH2CH2CH2NH2) is an amino acid that is found in cells, but not incorporated into proteins.”
A.
There is no codon for it in the standard genetic code.
B.
It cannot form a peptide bond.
C.
It is not available in the diet.
D.
It has a net positive charge in aqueous solution.
A, it cant be incorporated into protein but still an amino acid it being an amino acid crosses out B and C, Cant be D because all amino acids can be found in protein synthesizing even ones with polar charge
is all decarboxylase function as catalyst
Yes, instance nitro decarboxylase, nitro is enzyme and decarboxylase is the catalyst removing the COOH group releasing CO2
Which of the following terms best describes the role of ornithine decarboxylase in the reaction shown in Equation 1?
A.
Catalyst
B.
Cofactor
C.
Substrate
D.
Activator
a
substrate
molecule being acted on like changed by an catalyst
The statement that the ornithine decarboxylase assay is highly specific means that it:
A.
requires radioactive ornithine of high specific activity.
B.
generates diaminobutane of high specific activity.
C.
can distinguish ornithine decarboxylase activity from the many other enzymatic reactions in a cell.
D.
can measure the small amount of ornithine present in a cell.
C, “highly specific” means being able to distinguish its specifically that
Ethanol may be metabolized to acetic acid, then condensed with a coenzyme to form acetyl coenzyme A. Acetyl coenzyme A may then participate in:
A.
the Krebs (citric acid) cycle.
B.
glycolysis.
C.
electron transport.
D.
oxidative phosphorylation.
A, in question key terms, acetyl coenzyme A only kreb cycle incorporates it
The lung cells of heavy smokers would be expected to have greatly increased concentrations of cP-450 and:
A.
DNA sequences that code for cP-450.
B.
mRNA sequences that code for cP-450.
C.
rRNA that process cP-450.
D.
tRNA that are specific for cysteine.
B, recall central dogma DNA produces mRNA WHICH PRODUCES FUCKING PROTEIN YOU DUMB FUCK CENTRAL DOGMA PROTEIN IS FUCKING PRODUCED BY mRNA
The pericytes used in these experiments were probably in which phase of the cell cycle?
“Pericytes, smooth-muscle cells, and fibroblasts were growth-arrested—that is, treated so that they would not divide but other metabolic processes would function normally.”
A.
Telophase
B.
Metaphase
C.
Anaphase
D.
Interphase
D, the cells were growth arrest meaning they cannot divide the only phase given that can’t divide is interphase
The process of culturing bacteria often involves inoculation of cells on a noncellular, agar-based medium. Such a methodology would NOT result in growth of animal viruses because animal viruses:
A.
are obligate parasites.
B.
lack DNA.
C.
assimilate carbon.
D.
require essential vitamin supplements for growth.
A
what genomes do some viruses have
DNA or RNA, meaning they can’t lack DNA
what can animal virus only affect
only other animal cells, meaning they cannot grow on agar plates with bacteria
Which of the following best describes the bond that would form between the following two nucleotides if they were located adjacent to each other as shown in a single strand of DNA?
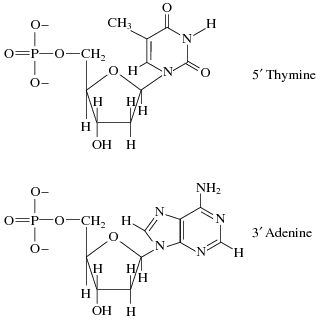
A.
A bond between the phosphate of the thymine and the phosphate of the adenine
B.
A bond between an oxygen in the thymine base and a nitrogen in the adenine base
C.
A bond between the phosphate of the thymine and the sugar of the adenine
D.
A bond between the phosphate of the adenine and the sugar of the thymine
D, nucleotide formed from 5 to 3
During an action potential, the movement of sodium ions into a neuron causes the neuronal membrane to do which of the following?
A.
Inactivate
B.
Hyperpolarize
C.
Repolarize
D.
Depolarize
D
The aldosterone deficiency associated with Addison's disease will cause a decrease in the serum levels of all of the following ions EXCEPT:
“A diagnosis of primary adrenal gland insufficiency, or Addison’s disease, is made.
Addison’s disease occurs when cells of the adrenal cortex are destroyed, leaving the gland unable to secrete either glucocorticoids or mineralocorticoids. A major function of cortisol, the body’s primary glucocorticoid, is to stimulate gluconeogenesis (formation of glucose from noncarbohydrate sources) in the liver by activating DNA transcription to produce liver enzymes and by mobilizing amino acids from muscle tissue. Aldosterone, the primary mineralocorticoid, maintains ionic balance by causing conservation of Na+ and excretion of K+.”
A.
Na+ ions.
B.
Cl– ions.
C.
K+ ions.
D.
HCO3– ions.
C, from understanding the passage we know that aldosterone gets rid of potassium but in the question its asking the effect of Addison disease which impairs adrenal cortex in mineral cords production which is what keeps sodium in an potassium out so when this is not working everything besides potassium will be excreted
what feedback does hypothalamus (CRH) and anterior pituitary (ACTH) have?
negative
what is negative feedback
It’s a control mechanism where the output of a system inhibits the system itself to maintain balance.
Normally, a hypothalamic factor stimulates the release of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from the pituitary gland. In a patient with Addison's disease, the secretion of the hypothalamic factor will:
A.
be lower than normal.
B.
be higher than normal.
C.
be unchanged.
D.
increase before disease onset and decrease thereafter.
B, Addison diseased cased cortisol to lower which allows negative feedback so without negative feedback it cant regulate to maintain low so it increases
glucocorticoids
set of steroid hormone that are synthesized adrenal cortex that regulates glucose metabolism
whats the body primary glucocorticoid
cortisol
what does glucocorticoids at high level do
cause Cushing syndrome
Cushing syndrome
-decreases muscle mass by increasing protein degradation
The most rapid rate of gluconeogenesis will most likely occur in the body when:
A.
blood glucose levels are high.
B.
cortisol release is inhibited.
C.
the body’s stores of carbohydrates are low.
D.
the body’s stores of proteins are low.
C
what is gluconeogenesis
pathway for carbohydrate synthesis from other metabolic compounds like lipids, amino acids.
If a patient with Addison’s disease is given too high a replacement dose of glucocorticoids, the effect over time will be an increase in:
A.
muscle mass.
B.
muscle weakness.
C.
white blood cell count.
D.
heart rate.
B
whats glycolysis
metabolic pathway that occurs in cytosol of cells that breaks down glucose into two three carbon compounds and generates energy
insulins role in glycolysis
stimulates glycolysis in hepatocytes which leads to decreases cellular concentration of glucose
Glucose transporter proteins in the liver do not require the presence of insulin to facilitate the uptake of glucose. However, insulin does stimulate the first step in the glycolytic pathway within the liver. Therefore, in liver cells, insulin most likely:
A.
hinders glucose uptake by increasing the cellular concentration of glucose.
B.
aids glucose uptake by decreasing the cellular concentration of glucose.
C.
hinders glucose uptake by using the ATP needed by the glucose transporter proteins.
D.
aids glucose uptake by providing the ATP needed by the glucose transporter proteins.
B
Exercise promotes the insulin-independent uptake of glucose in working skeletal muscles. Given this, regular exercise would most likely reduce blood glucose levels in patients with which type(s) of diabetes?
A.
Type 1 only
B.
Type 2 only
C.
Both Type 1 and Type 2
D.
Neither Type 1 nor Type 2
C
where do polypeptide modification take place
ER or Golgi
nucleus
contains genetic material that determines the entire structure and function of that cell
ribosomes
macromolecules made up of rRNA and proteins that act as sites of protein synthesis
endomembrane system
set of membrane bound organelles that modifies and transport proteins (polypeptides)
Despite the effects of diabetes, the brains of diabetic patients still receive adequate nourishment. This is most likely because the brain uses:
A.
less glucose than do other body tissues.
B.
insulin-independent transporters for the uptake of glucose.
C.
fatty acids for energy instead of glucose.
D.
insulin-dependent transporters for the uptake of glucose.
B, brain cells got transporters that dont need insulin to work
can the brain use fatty acid as a energy source
no
Based on the passage, which of the following is LEAST likely to be a symptom of diabetes mellitus?
A.
Loss of appetite
B.
Sweet-tasting urine
C.
Unexplained weight loss
D.
Feelings of fatigue
D
DNA replication
semi conservative, each strand in DNA double helix is a template for the new complementary strand so a section of each parent goes into making kiddos gene
A certain bacterium was cultured for several generations in medium containing 15N, transferred to medium containing 14N, and allowed to complete two rounds of cell division. Given that the bacterium’s genome mass is 5.4 fg when grown in 14N media and 5.5 fg when grown in 15N medium, individual bacteria with which of the following genome masses would most likely be isolated from this culture?
A.
5.4 fg only
B.
5.4 fg and 5.45 fg
C.
5.4 fg and 5.5 fg
D.
5.45 fg only
B