8 peds - intellectual disability
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
A group of disorders
characterized by deficits in adaptive and intellectual function,
with an onset before maturity is reached.
What is intellectual disability?
subaverage intellectual functioning
IQ 70 or below
What does DSM-IV-TR require regarding intellectual functioning in intellectual disability?
requires deficits in at least two adaptive areas:
communication
self-care
home living
social/interpersonal skills
use of community resources
self-direction
functional academic skills
work,
leisure
health
safety
What adaptive functioning criteria does DSM-IV-TR specify for intellectual disability?
Symptoms must appear before age 18 years.
At what age must symptoms appear according to DSM-IV-TR?
disorder with onset during the developmental period
includes intellectual and adaptive functioning deficits
domains:
conceptual
social
practical
How does DSM-5 define intellectual disability?
“intellectual developmental disorders”
to indicate impaired brain functioning early in life.
What term does ICD-11 use for intellectual disability, and what does it indicate?
As a meta syndrome متلازمة واسعة
occurring in the developmental period
analogous مماثلة to dementia or neurocognitive disorder in later life.
How does ICD-11 describe intellectual developmental disorders?
Mild, moderate, severe, and profound.
What are the four subtypes of intellectual developmental disorders in ICD-11?
1%, with prevalence rates varying by age
What is the general population prevalence of intellectual disability?
6 per 1,000
What is the prevalence of severe intellectual disability?
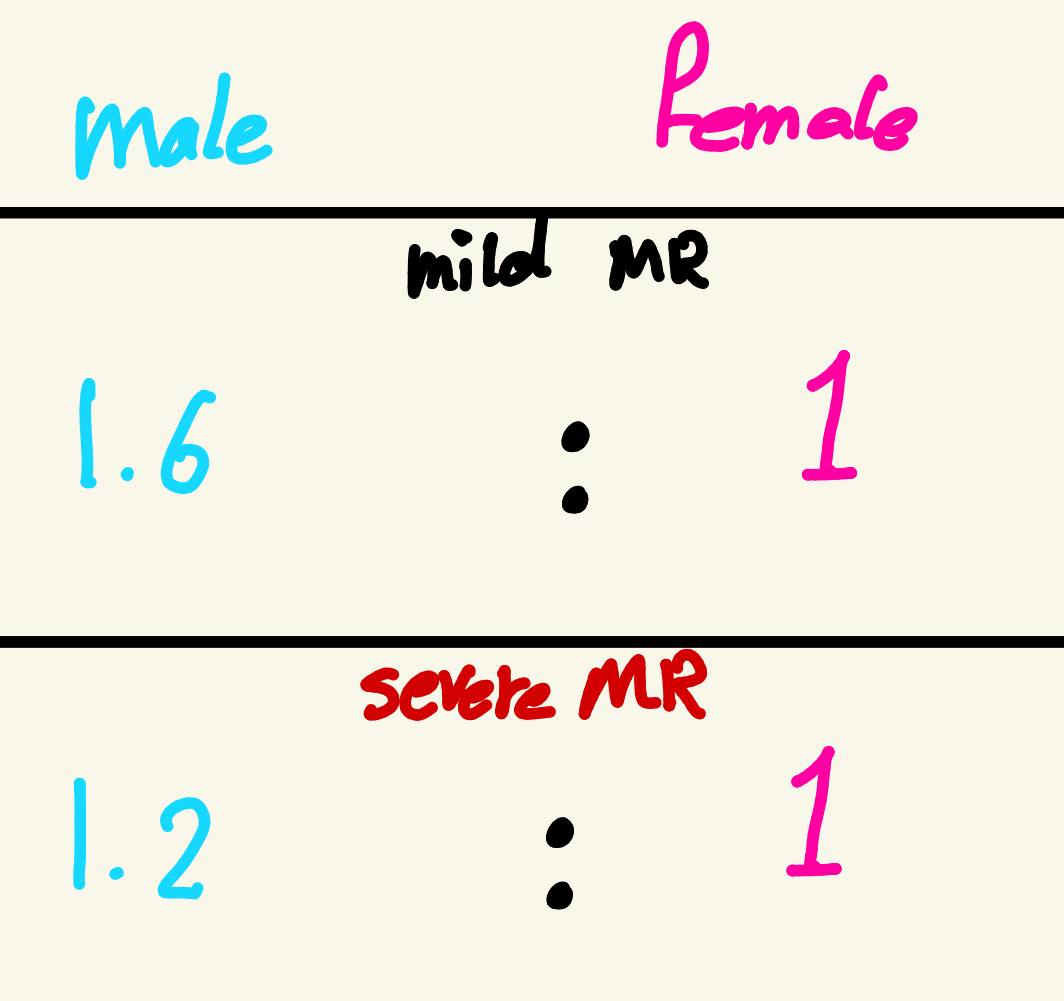
males
Are males or females more likely to be diagnosed with intellectual disability?

What are the conceptual domain characteristics of mild intellectual disability?

What are the social domain characteristics of mild intellectual disability?

What are the practical domain characteristics of mild intellectual disability?
التواصل (communication)
المهارات الأكاديمية العملية (functional academics)
توجيه الذات (self-direction)
مفاهيم المال (money concepts)
What are the conceptual skills in intellectual disability?
المهارات الشخصية بين الأفراد (interpersonal skills)
تقدير الذات (self-esteem)
السذاجة أو القابلية للخداع (naiveté/gullibility)
الحكم على النفس واتباع القواعد (self-governance / obeys rules)
What are the social skills in intellectual disability?
العناية بالذات (self-care)
المهارات المنزلية (domestic skills)
العمل (work)
الصحة والسلامة (health & safety)
What are the practical skills in intellectual disability?
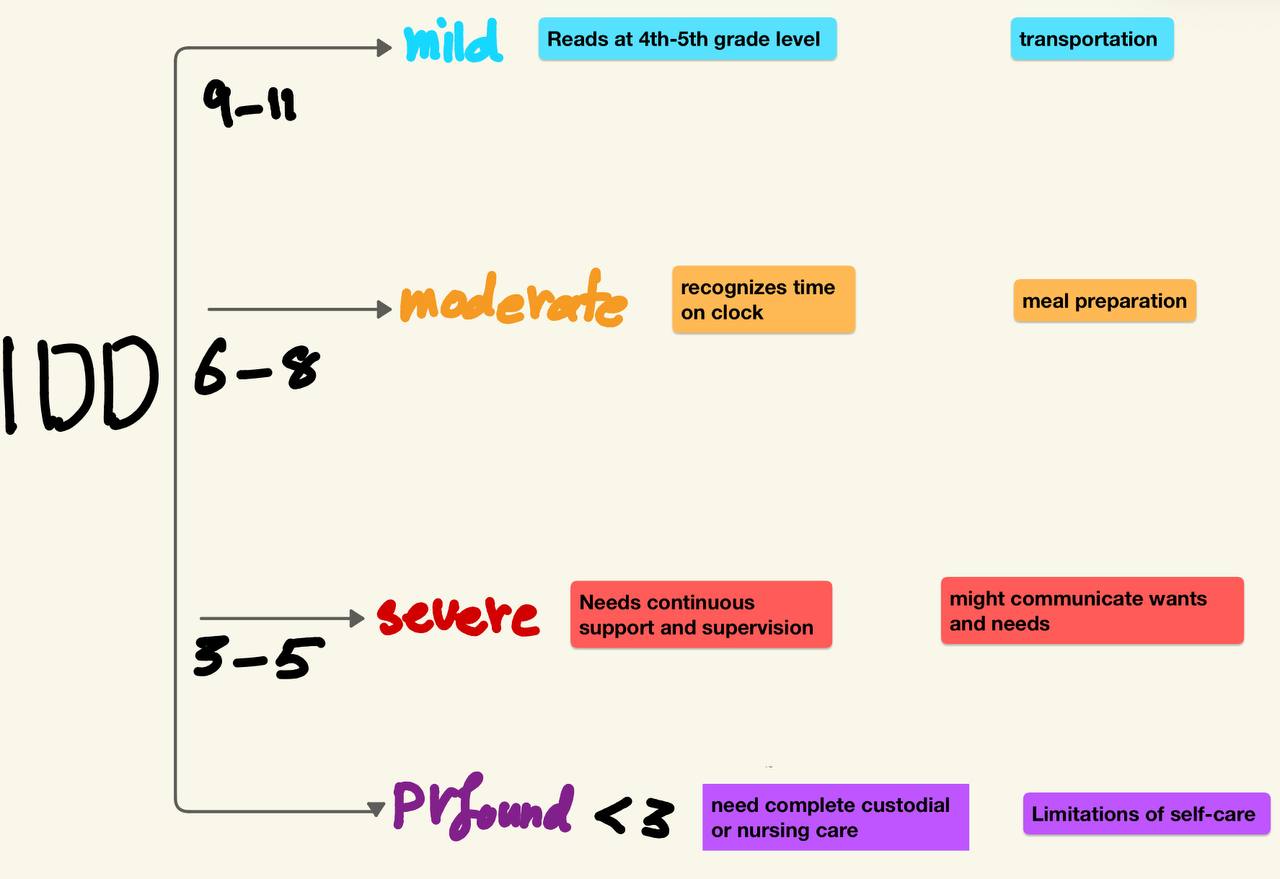
mention severity of ID & adult age function?
They are frequent
rates of some conditions (e.g., mental disorders, cerebral palsy, and epilepsy) three to four times higher than in the general population
How common are co-occurring mental, neurodevelopmental, medical, and physical conditions in intellectual disability?
ADHD
ASD
depression & anxiety
bipolar disorder
stereotypic movement disorder (with or without self-injurious behavior) SMD
impulse-control disorders ICD
major neurocognitive disorder MND
What are the most common co-occurring mental and neurodevelopmental disorders in intellectual disability?
ADHD 10%
ASD 25%
What are the rates of co-occurring autism and ADHD in children with intellectual disability?

What are the common presentations of intellectual disability?
Difficulties with social judgment, risk assessment, self-management of behavior, emotions, relationships, or motivation in school/work.
Poor communication skills may lead to disruptive or aggressive behaviors.
Gullibility and lack of risk awareness → exploitation, victimization, fraud, unintentional criminal involvement, false confessions, risk of physical/sexual abuse.
Co-occurring mental disorders increase suicide risk → screening for suicidal thoughts is essential.
Increased risk of accidental injuries due to poor risk awareness.
What are the associated features supporting the diagnosis of intellectual disability?
Basic pre- and perinatal medical history
Three-generational family pedigree
Physical examination
Genetic evaluation (e.g., karyotype, chromosomal microarray, testing for specific genetic syndromes)
Metabolic screening
Neuroimaging assessment
What are the components of the evaluation for intellectual disability?
Assessment of intellectual capacity and adaptive functioning.
Identification of genetic and non-genetic causes.
Evaluation of associated medical conditions (e.g., cerebral palsy, seizure disorder).
Evaluation of co-occurring mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders.
What does a comprehensive evaluation for intellectual disability include?
WISC series (WISC-IV, WAIS-II, WPPSI, etc.)
Stanford-Binet V
What tools are used to assess cognitive ability in individuals suspected of intellectual disability?
Vineland II Adaptive Behavior Scales (Sparrow, Cicchetti, & Balla, 2005)
What tool is commonly used to assess adaptive behavior in individuals with intellectual disability?

What are the primary prevention strategies for intellectual disability?
Early intervention programs
Special education services (individualized educational programs)
Family support services (counseling, training, home visitation, social services)
Pharmacotherapy
Health services (including hearing and vision)
Nutrition counseling
Assistive technology (e.g., tape-recorded texts, reading scanners, voice-activated programs)
Medical diagnostic services
Transportation and other assistive technology
What are the main components of management for children with intellectual disability?
Provision of the same primary care received by peers of similar age
Anticipatory guidance relevant to the child’s functional level: feeding, toileting, school, accident prevention, sexuality education
Assessment of disorder-specific issues:
Dental examination for children with bruxism
Thyroid function in children with Down syndrome
Cardiac function in children with Williams syndrome
What are the key components of primary care for children with intellectual disability?