Apologia Advanced Biology Module 11 The Cardiovascular System
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Heart
A hollow muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body.
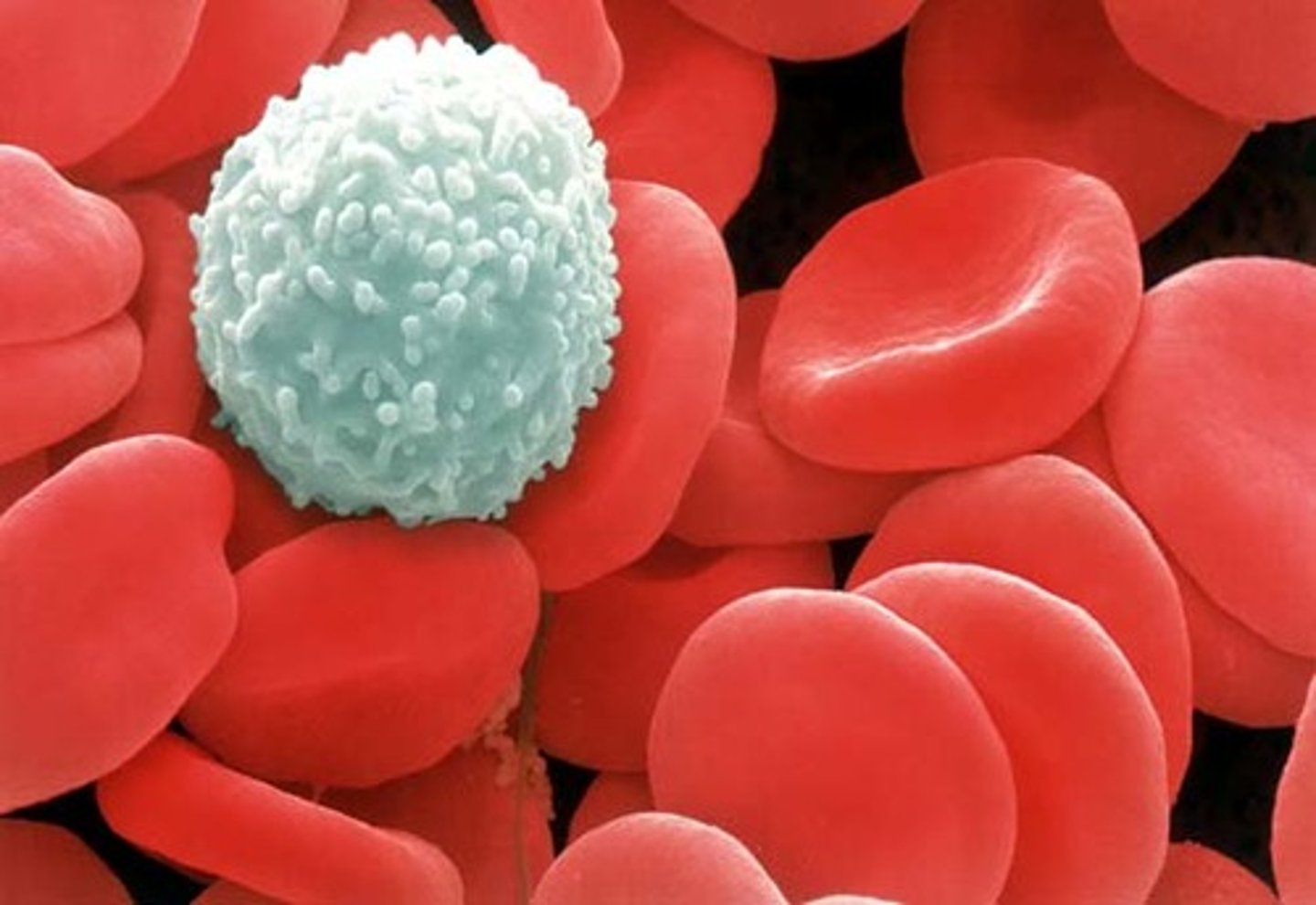
Blood
A circulating connective tissue made of plasma, cells, and platelets. (Watery Substance) ----- means life.
Transport Medium
Blood is a --------- ------. It picks up oxygen (O2) from the lungs and drops it off in the tissues. It also picks up picks up carbon dioxide (CO2) and drops it off at the lungs. It even transports nutrients from the small intestines to the liver and then to all the body cells. It also transports wastes from the tissues to the kidneys, and hormones from the endocrine glands to the cells throughout the body.
Regulatory Tissue
It regulates fluid volume. It also equalizes temperature difference in the body by constricting and dilating blood vessels.
Protective Tissue
It (Blood) protects against fluid loss.
Viscosity
The resistance to flow and alteration of shape due to cohesion. (Thickness of Blood) Blood is thicker than water.
Plasma
The fluid portion of the blood, which is mostly water, about 55% by volume.
Formed Elements of Blood
The red blood cells, white blood cells, and cell fragments called platelets, about 45% by volume.
Albumin
Is a small protein, synthesized by the liver that regulates the movement of water between tissues and the blood by the process of osmosis.
Globulins
Consist just over one-third of the proteins in the plasma. Some --------- act as carrier proteins, while others, called gamma --------- area antibodies for fighting off infections.
Fibrinogen
Is an inactive protein, but it plays a critical role when injury occurs. It can be activated to form a blood clot if bleeding occurs.
Erythrocytes
Red Blood (RBC) cells that carry O2 in blood. Make up approx. 95% of the blood. Contain Hemoglobins. Mature ------------ do not have a nucleus. (Since they don't have a nucleus, they can only live four months.)They run off of ATP through glycosis which does not require oxygen. They have only a limited metabolism.
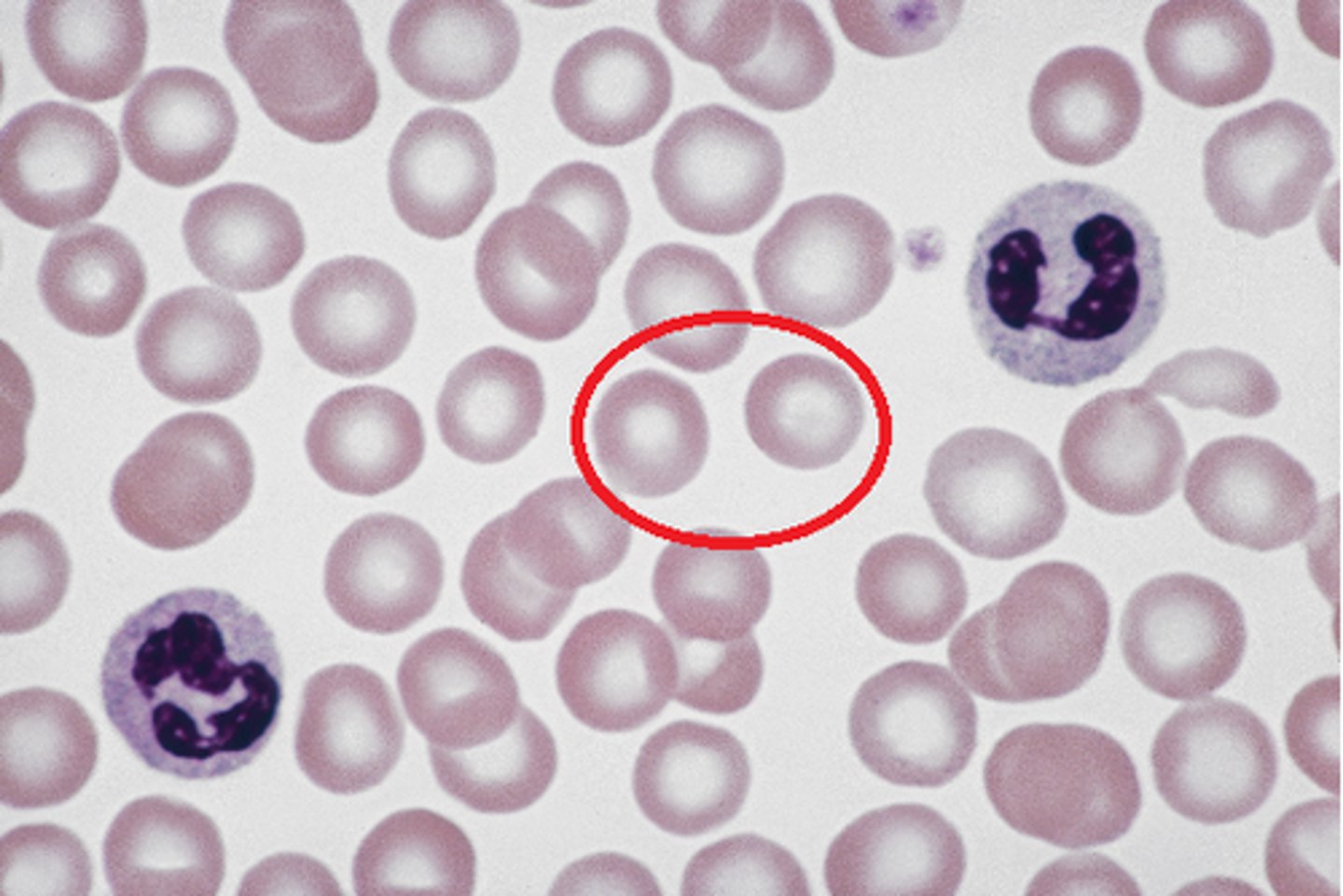
Leukocytes
White Blood cells that perform defensive functions in blood. Ratio of whit blood cells are 700:1.
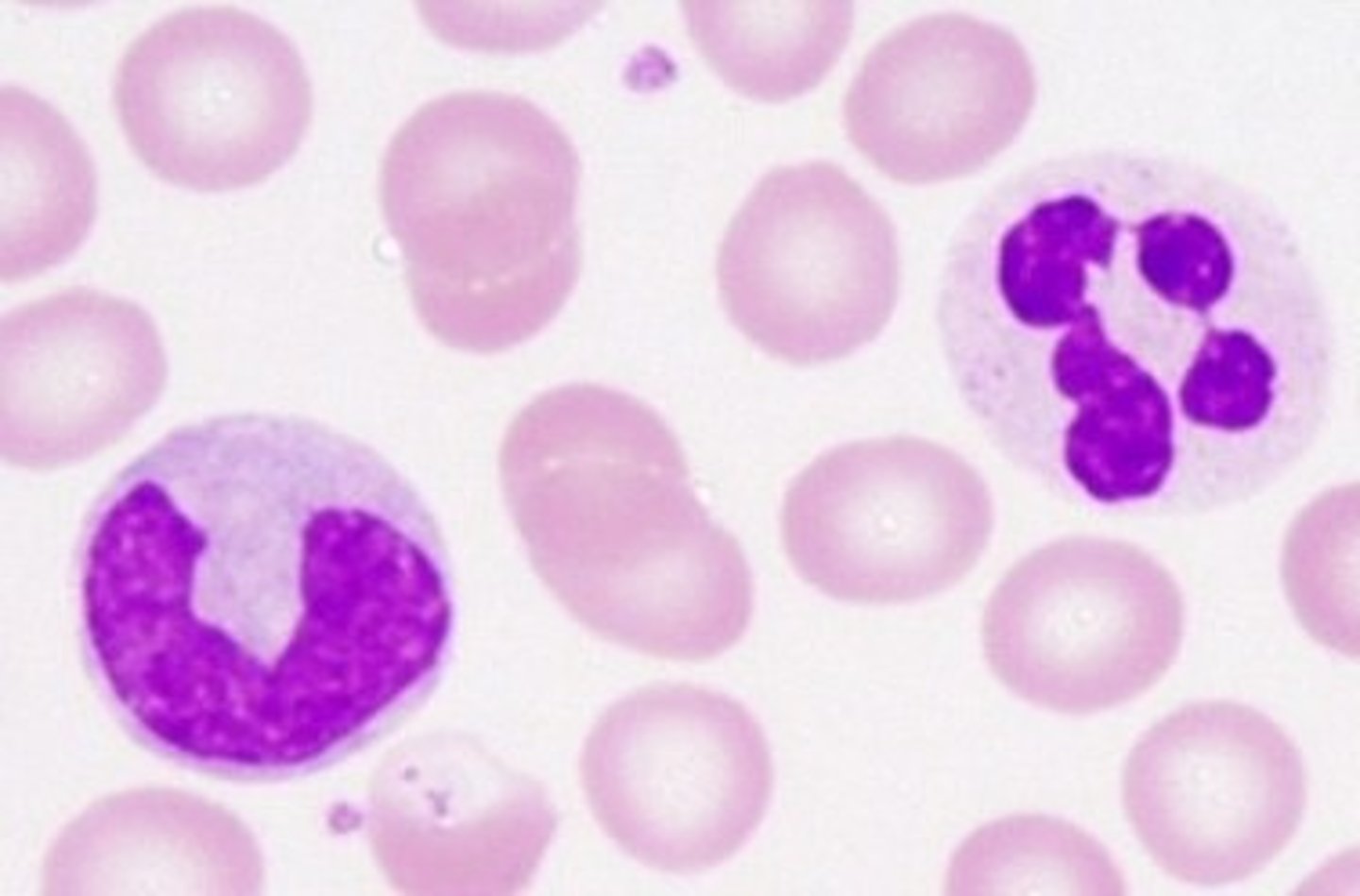
Thrombocytes
Cell fragments in blood that help prevent blood loss.
Hemoglobin
Gives blood its color. Is composed of four protein chains (called globins), each of which is neatly folded into a particular shape. When it drops off O2, its color darkens.
Anemia
Also known as iron-poor blood.
Sickle Cell Anemia
A human genetic disease of red blood cells caused by the substitution of a single amino acid in the hemoglobin protein; it is the most common inherited disease among African Americans.

Hematocrit Blood Test
Tests the percentages of RBCs in the blood. Normal adult male = 44% - 48% of the blood. Normal adult female 38% - 45% of the blood.
Hemaglobon Test
Can determine how much hemoglobin is in those RBCs.
Diapedesis
Passage of white blood cells through pores in blood vessel to get into the tissue space.
Chemotaxis
Attraction of cells to chemical stimuli.
Granulocyte
Have vesicles that are filled with a substance that stains easily. This makes the vesicles visible in a microscope and gives the cell a grainy, or granular, look.
Agranulocyte
Also have vesicles, but they are small and not easily stained.
Neutrophil
Most common white blood cell. They're distinguished by a multi-lobed nucleus.
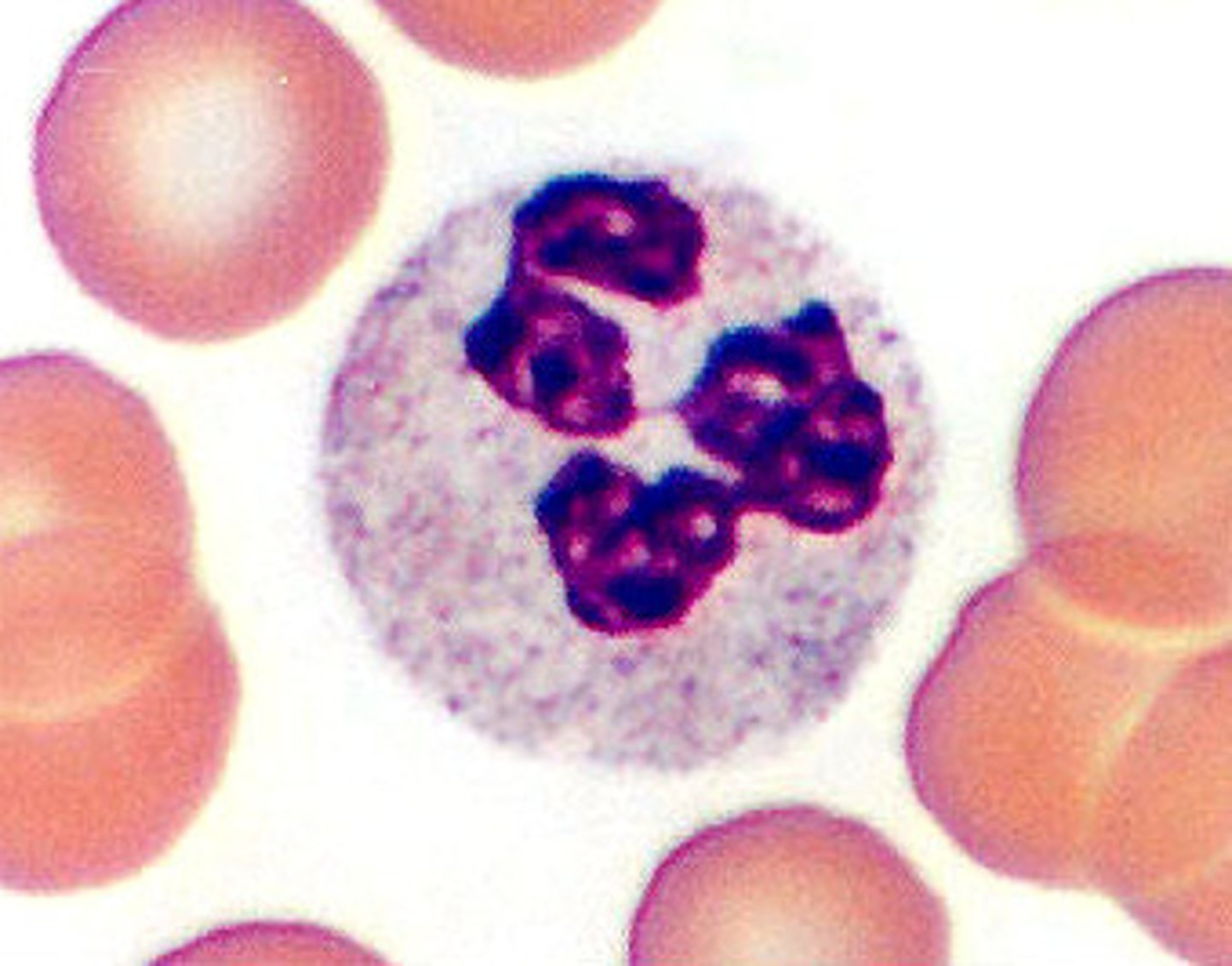
Basophil
Are the rarest of the granulocytes. Are attracted to a basic blue dye. Has a two lobed nucleus. They release histamine which promotes inflammation.
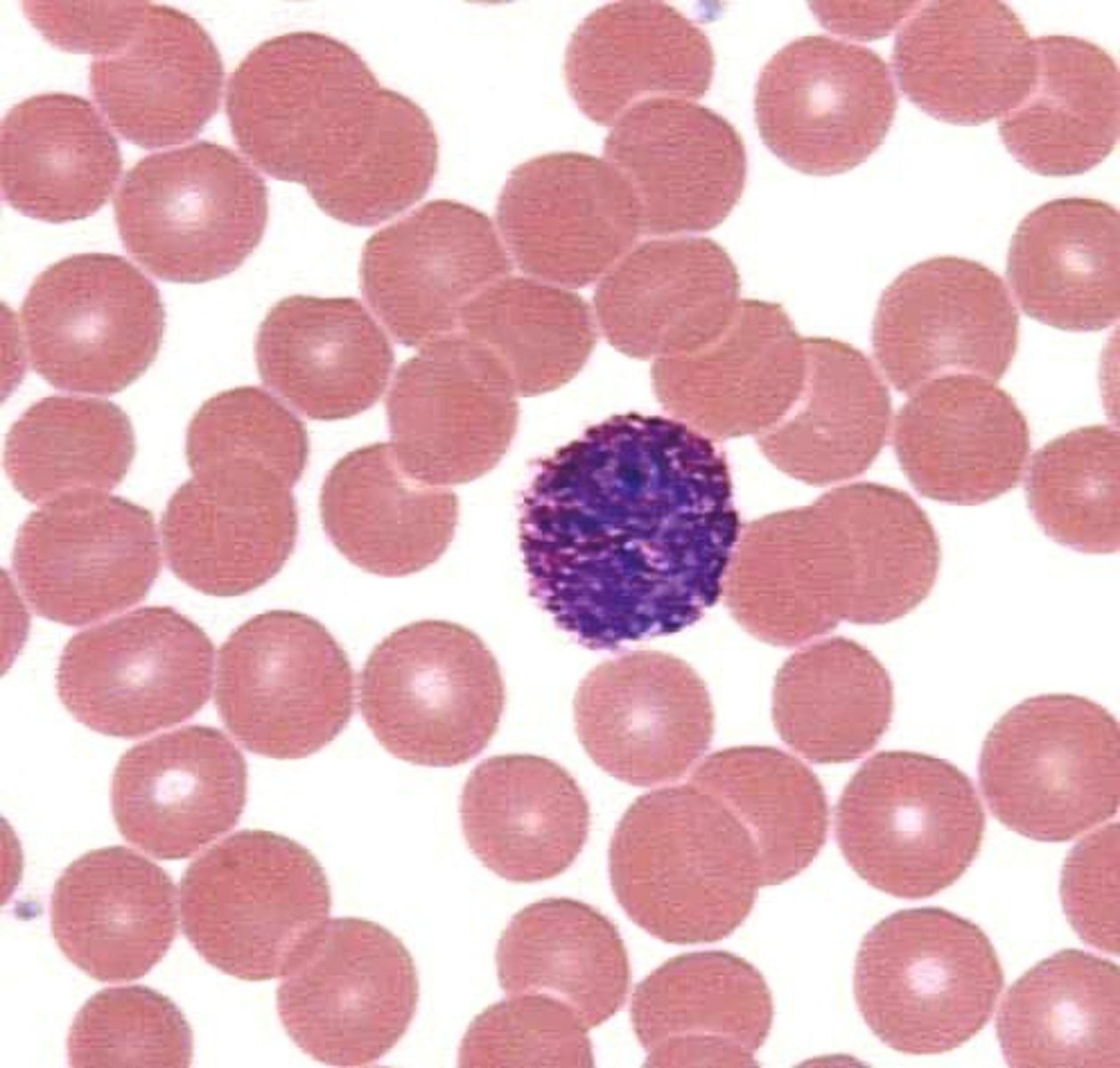
Eosinophil
Are uncommon, but are more plentiful than Basophils. They have a two-lobed nuclei, and their granules stain red. Increase in number during allergic reactions and parasitic infections. Tend to balance out basophils because they reduce inflammation.
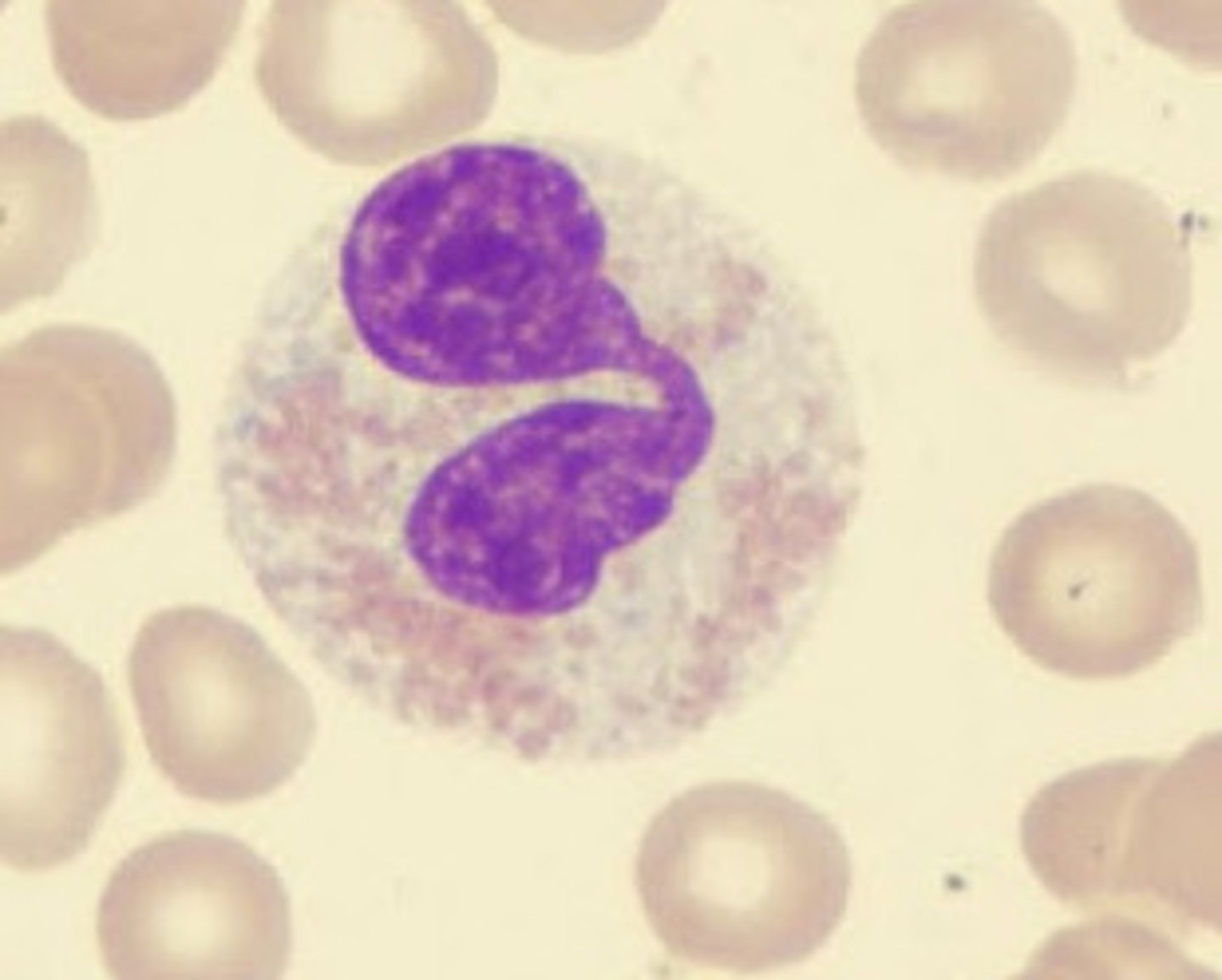
Lymphocyte
Are the smallest white blood cell. Produce antibodies, which are proteins that are specifically protect against foreign invaders.
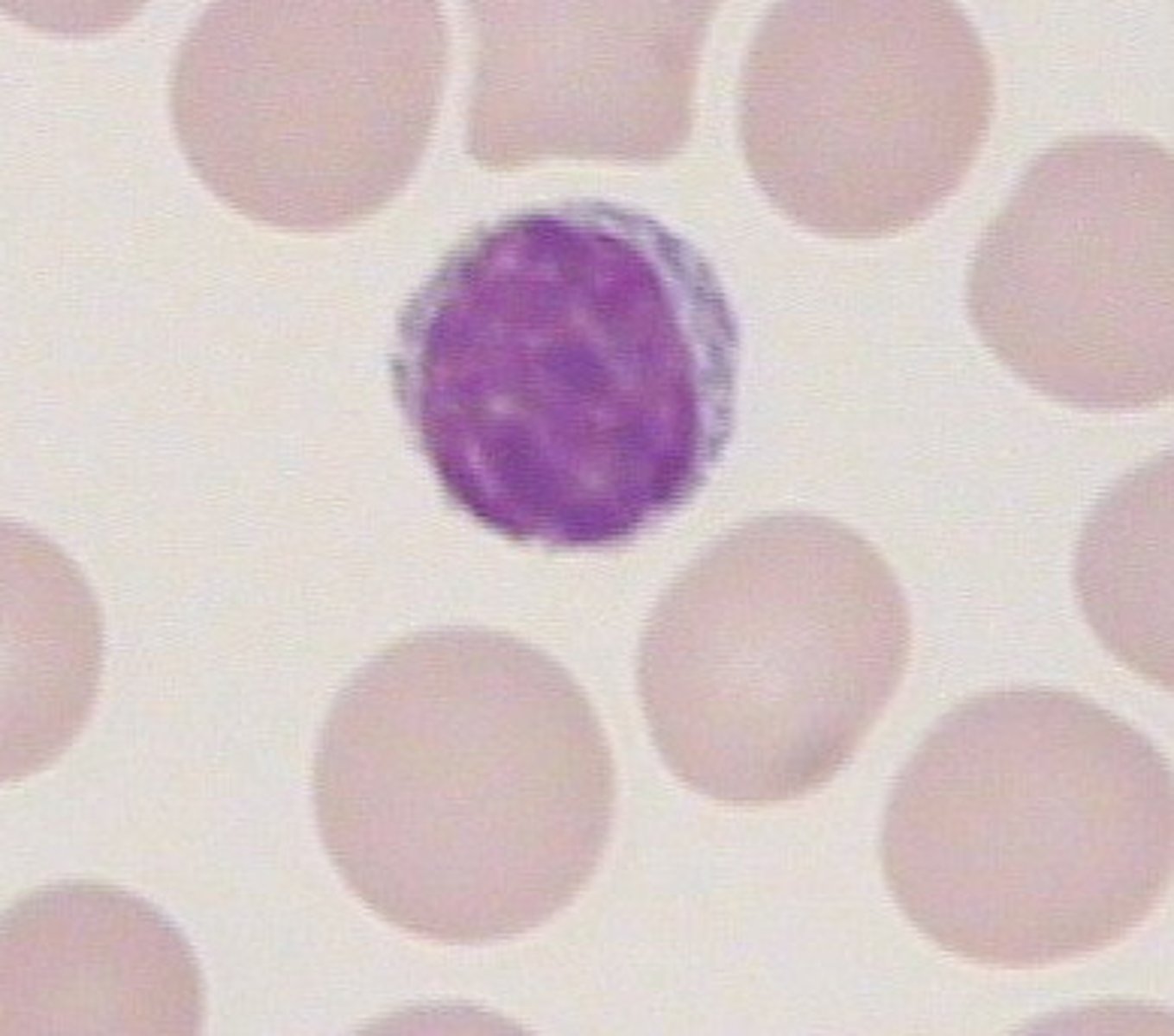
Monocyte
Are the biggest white blood cells, but they are uncommon in terms of numbers. They have a kidney-shaped nucleus. These cells destroy invading organisms and foreign material by phagocytosis. Are much more phagocytic that neutrophils.
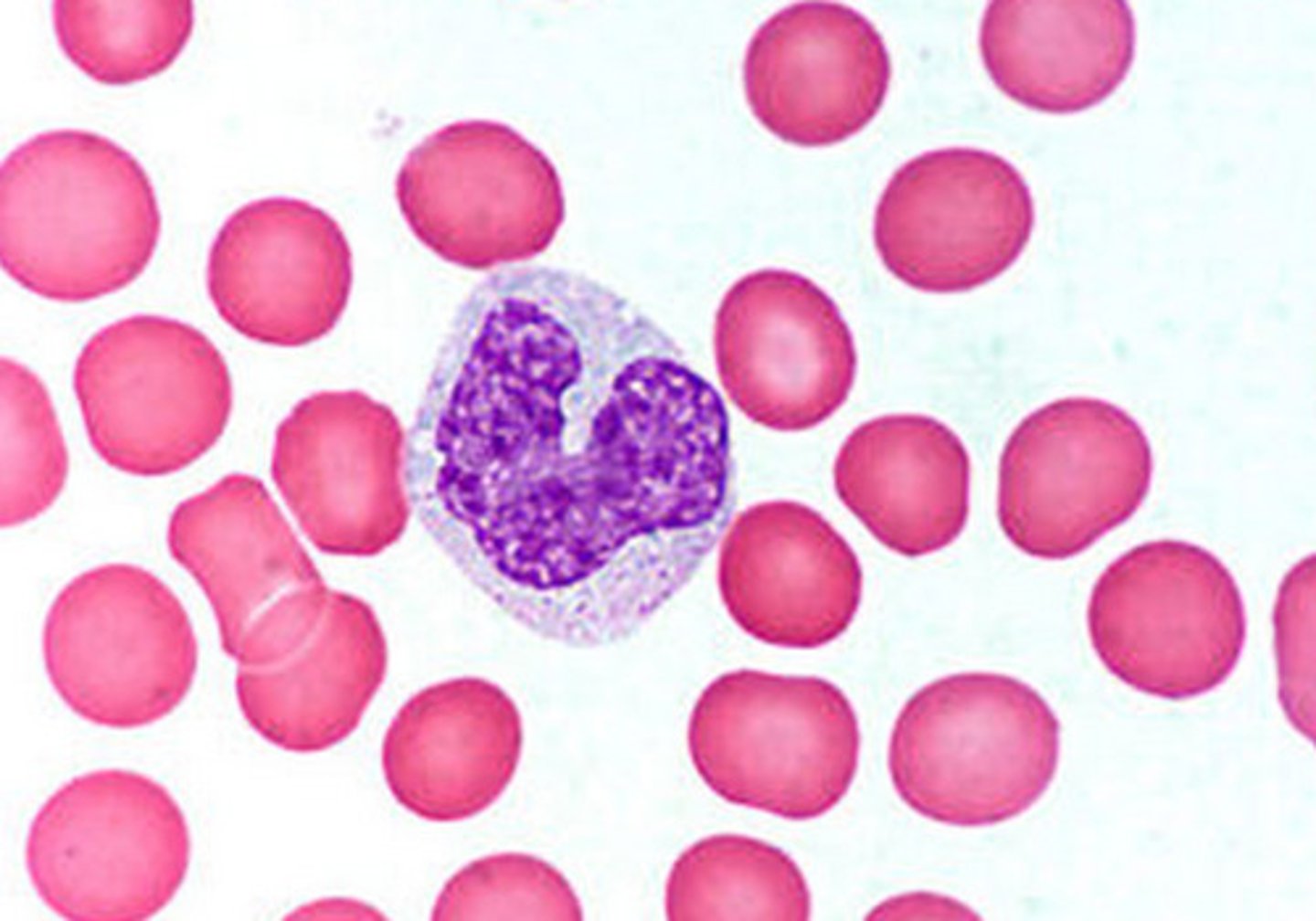
Phagocytosis
Literally, cell-eating. The process by which a cell engulfs and ingests a foreign or dead cell or cell part.
Pus
A mixture of dead or dying white blood cells, foreign cells such as bacteria, and fluid.
Hemopoiesis
The process by which the formed elements are made in the body.
Stem Cells
A class of undifferentiated cells that are able to differentiate into specialized cell types.
Hemostasis
The process by which the body stops blood loss.
Vasoconstriction
1st step of Hemostasis. Narrowing or constriction of a blood vessel. Helps reduce blood loss in case of a cut.
Platelet Plug Stage
2nd step of Hemostasis. Platelets form a plug to stop blood from leaking out of the tear.
Thromboxane
The release of this chemical stimulates several chemical processes that cause other platelets to stick.
Coronary Thrombosis
Is commonly called a heart attack.
Embolus
Occurs when a clot forms, usually in the legs, and then breaks loose and travels through the veins toward the heart.
Prothrombinase
Tissue or blood vessel damage produces --------------, an enzyme.
Thrombin
Prothrombinase converts prothrombin into --------.
Fibrin
Thrombin converts fibrogen into ------.
Coagulation Factors
Proteins in blood plasma that help the blood coagulation process.
Anticoagulants
Chemicals that which prevent certain blood factors from being activated.
Blood Types
Humans have four different types of blood - A, B, AB, and O.
Antigen
A protein or other molecule that, when introduced into the body, triggers the production of an antibody.
Universal Donor Type
Type O blood is called the universal type. Can be used in an emergency.
Rh antigen
Rh stands for "Rhesus monkey" because that's where the antigen was first identified.
Rh-positive
If the antigen exists on the surface of the erythrocytes in blood, the blood is called -----------. About 85% of people are --+.
Rh-negative
If there is no Rh antigen on the erythrocytes in the blood, the blood is -----------.
Closed Circulatory System
In the human body, the blood travels through tubes called blood vessels. This is a ------ ----------- ------.
Open Circulatory System
Many creatures (like arthropods) have an ---- ----------- ------. In this type of system, the blood travels away from the heart in blood vessels, but the blood is then dumped directly onto the tissues. It is then collected and forced back in to other blood vessels so that it can travel back to the heart.
Arteries
Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart.
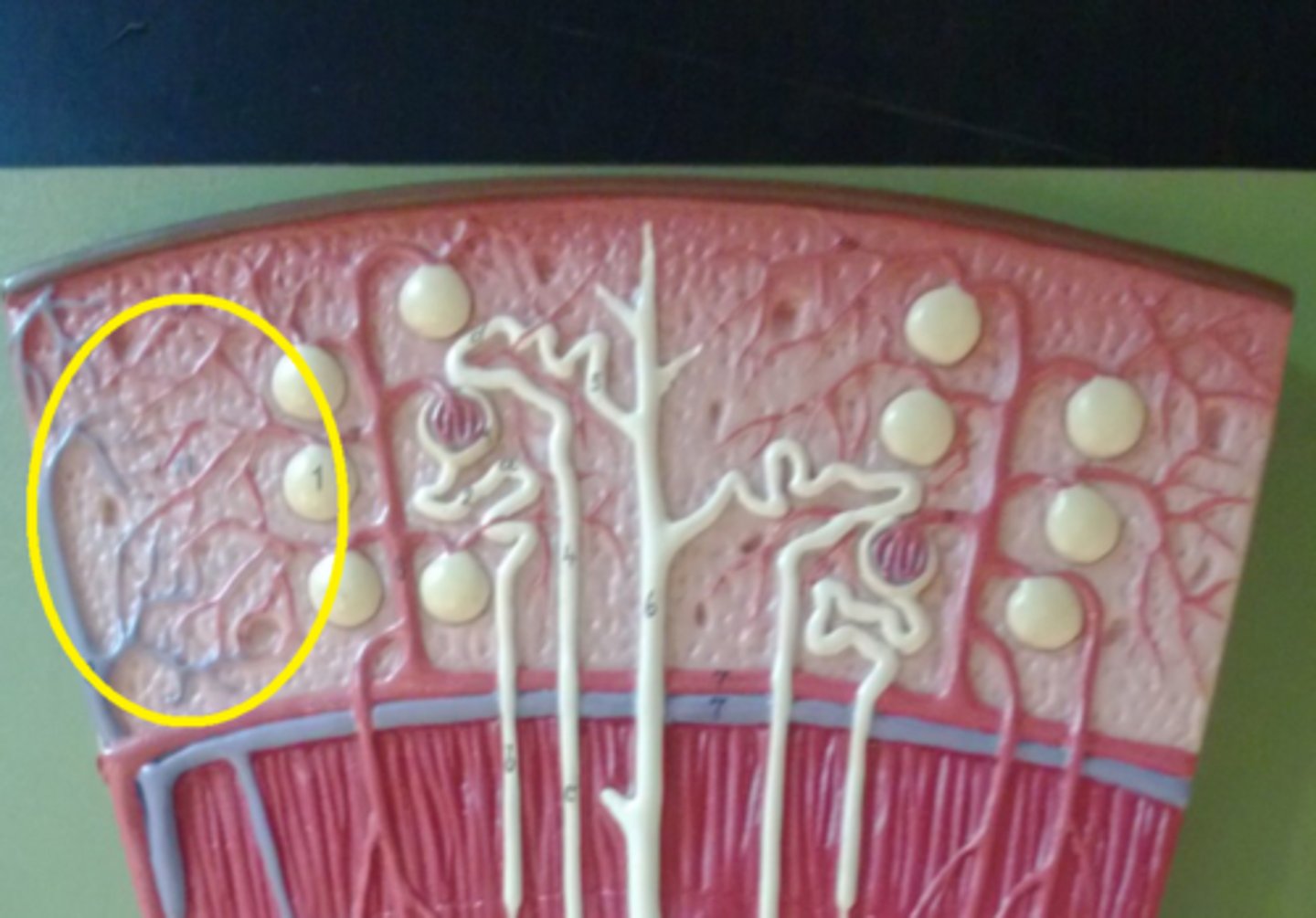
Capillaries
Microscopic, thin-walled blood vessels that allow the exchange of gases and nutrients between the blood and body cells.
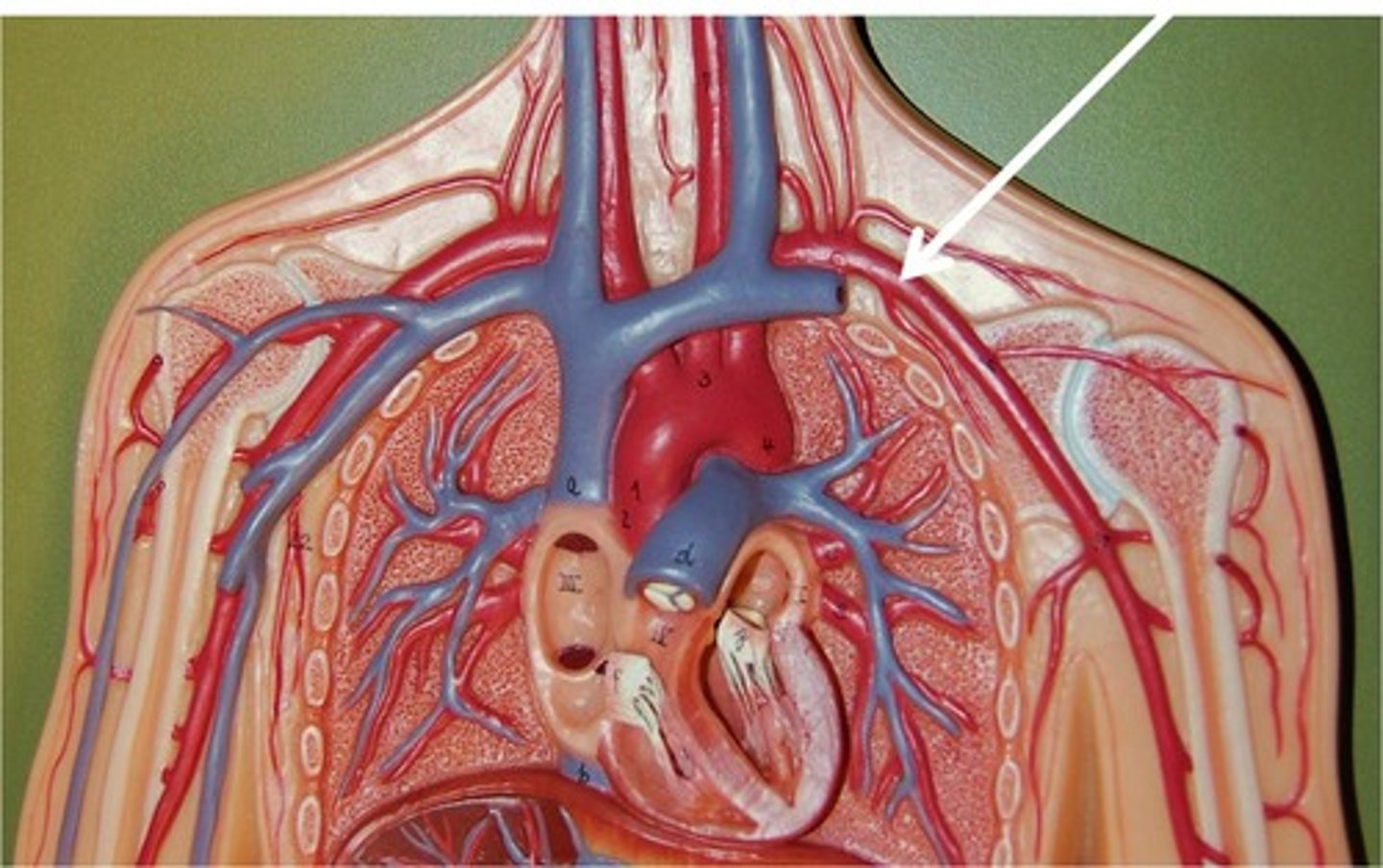
Veins
Blood vessels that carry blood back to the heart.
Pulmonary Circulation
Circulation of the blood around the alveoli (air sacs) of the lungs.
Systemic Circulation
Circulation of the blood through the other tissues of the body.
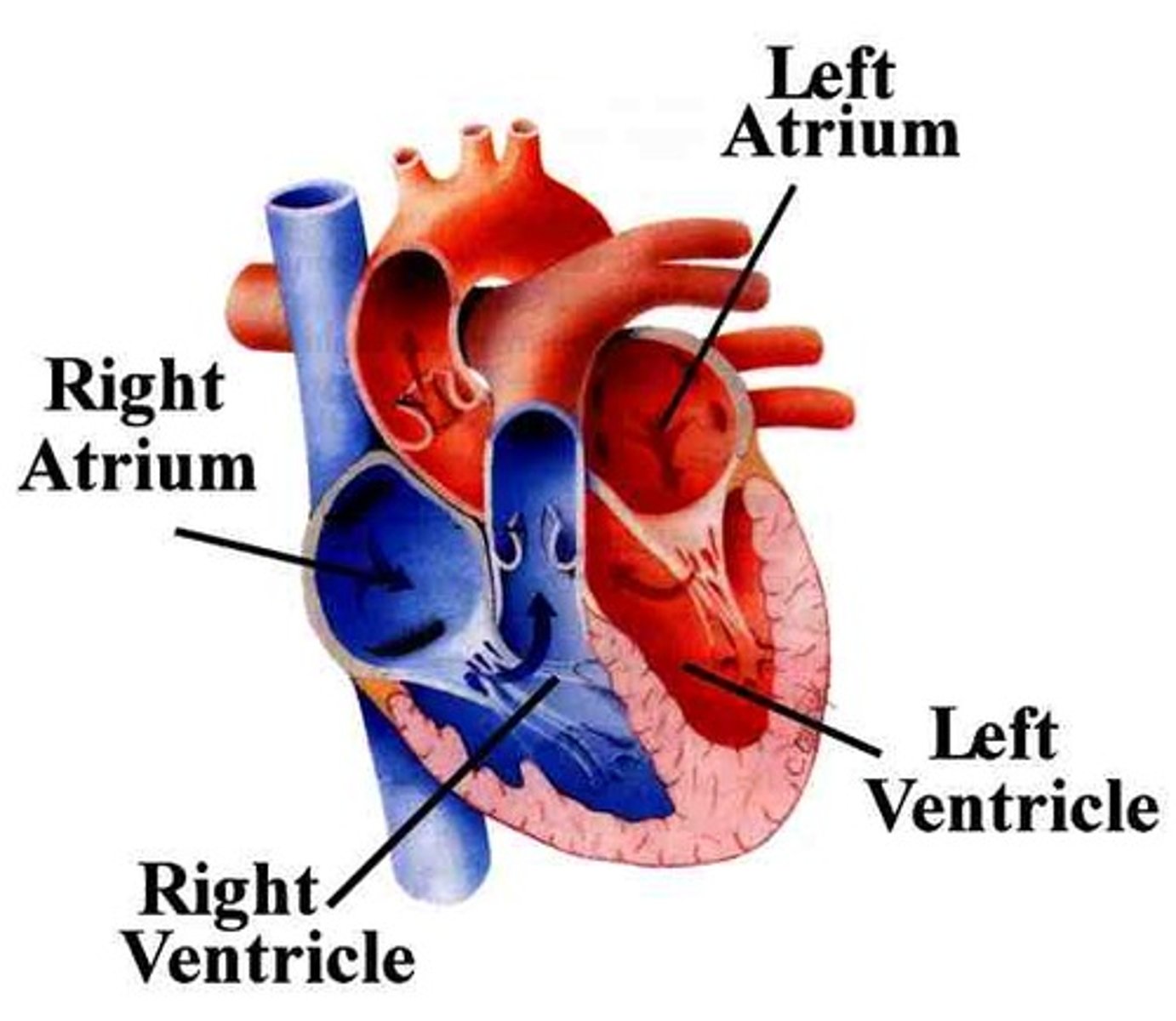
Atria
The 2 UPPER chambers of the heart.
Ventricles
The 2 LOWER chambers of the heart.
Auricles
Flap-like extensions of the atria, seen anteriorly between each atrium and ventricle. Increase the volume of the heart.
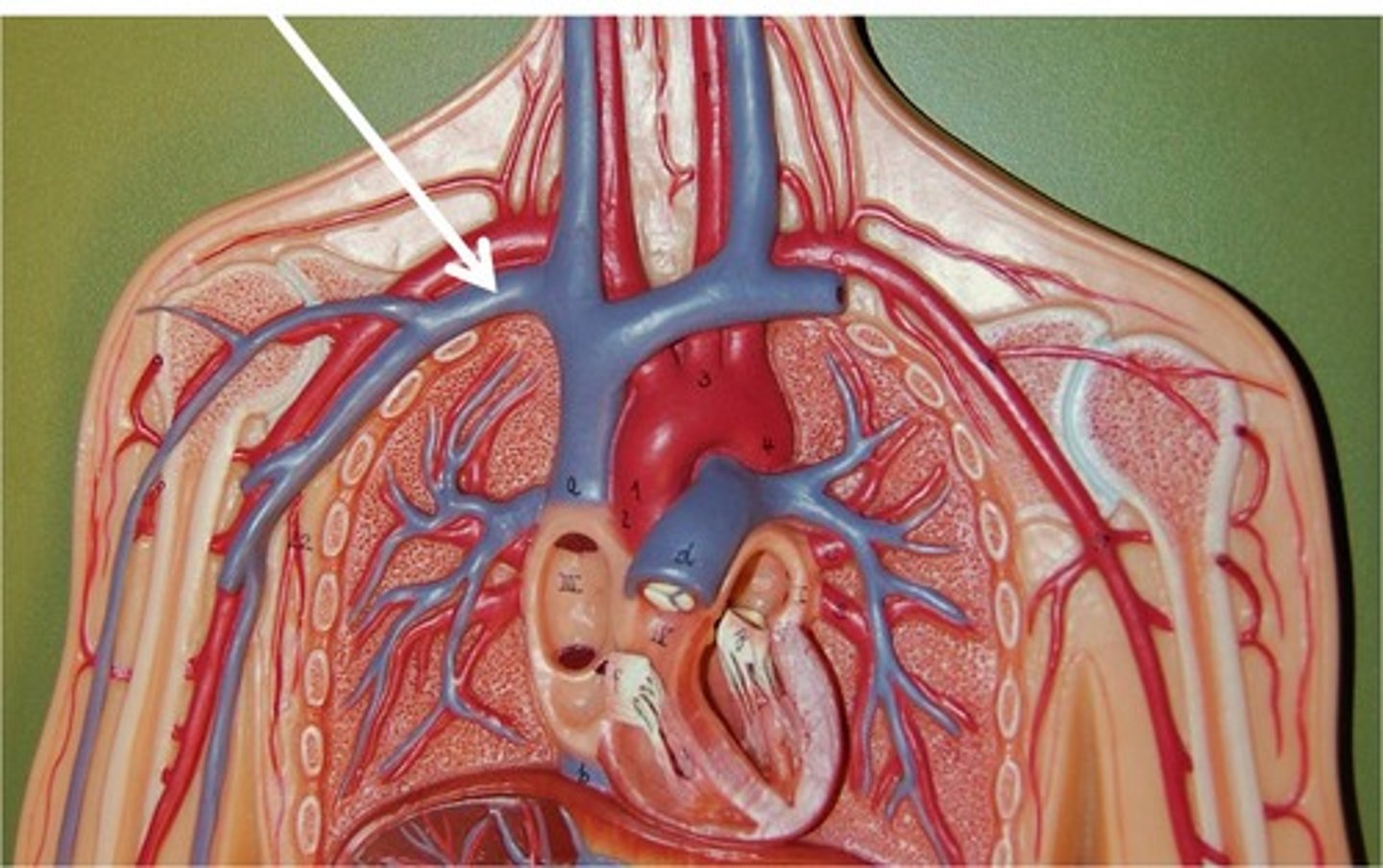
Superior Vena Cava
Inferior Vena Cava
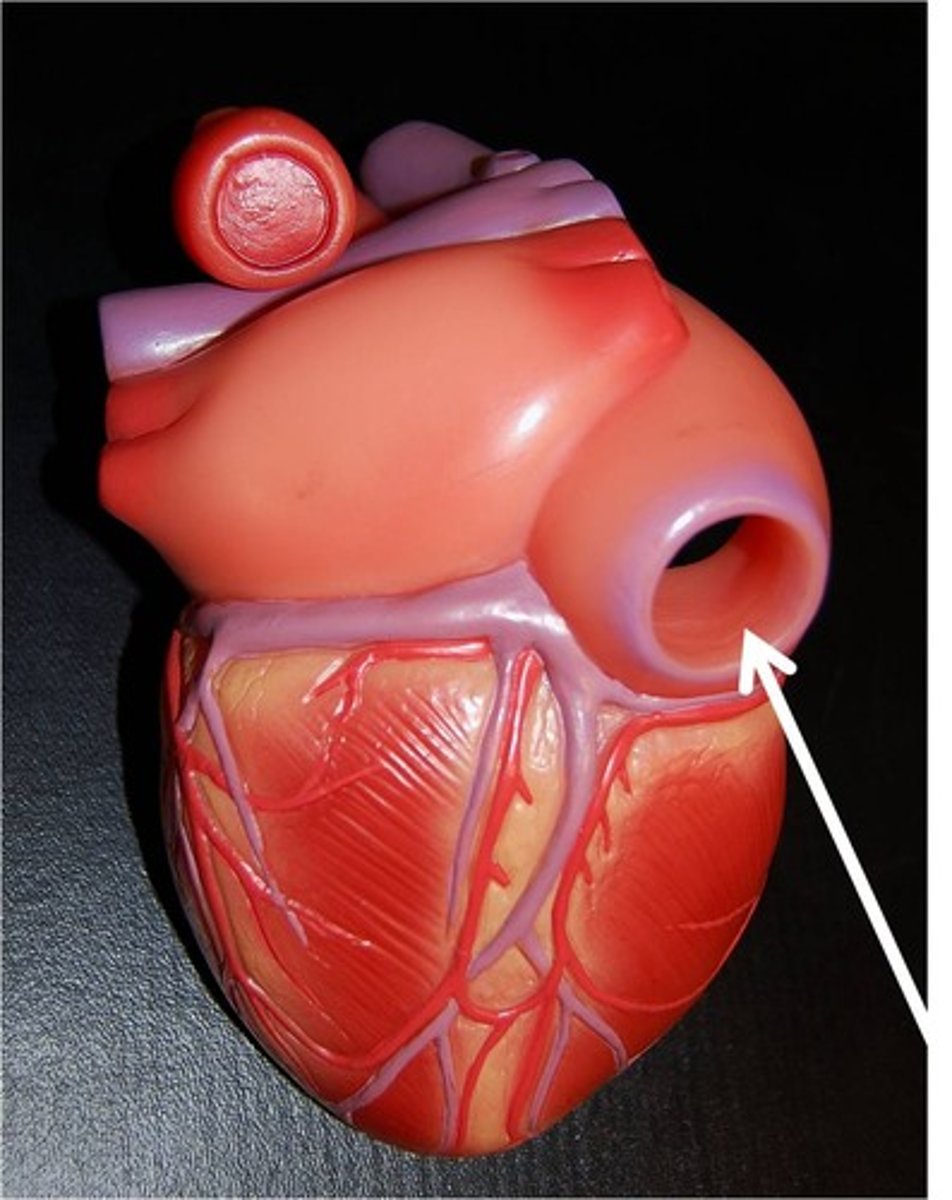
Pulmonary Veins
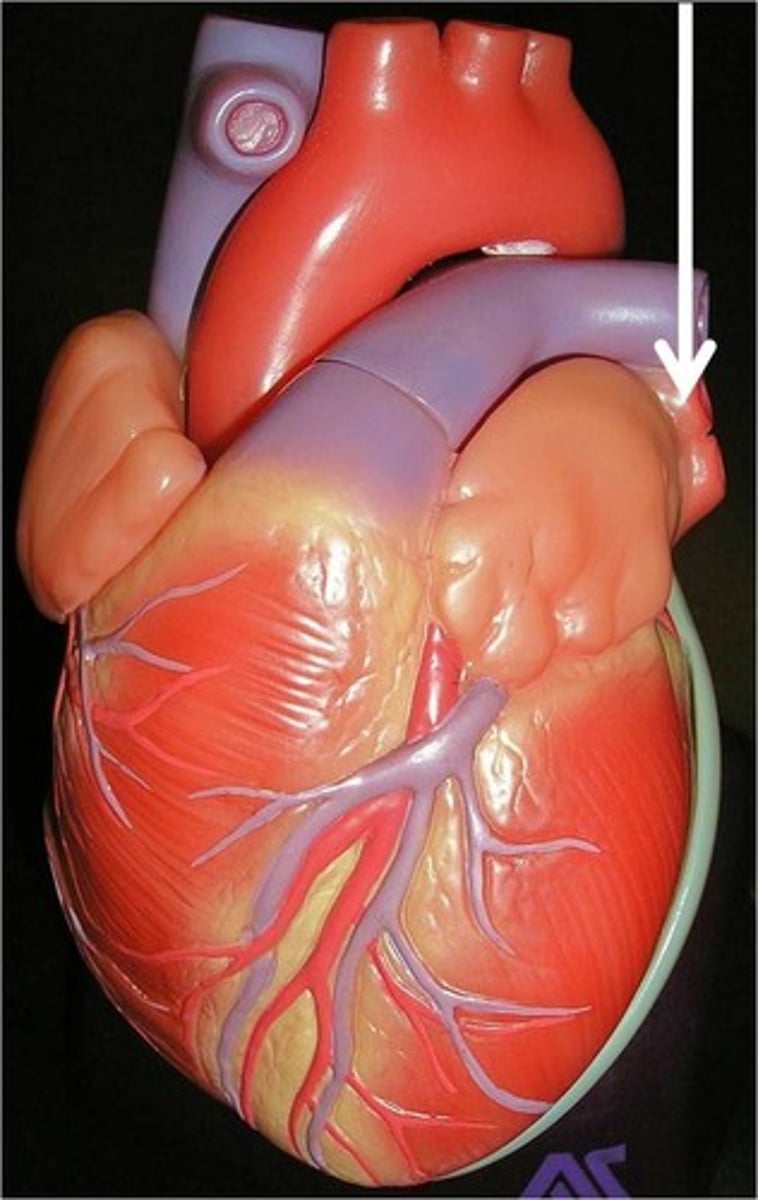
Pulmonary Trunk
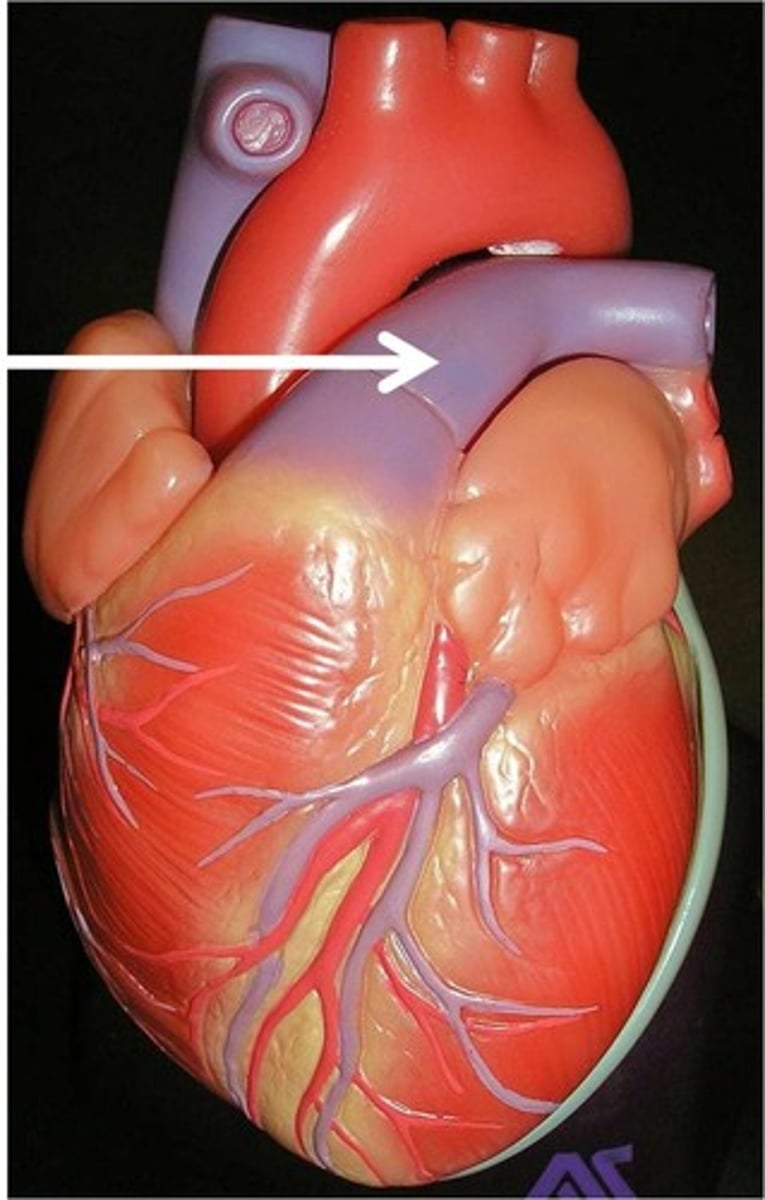
Aorta Artery
Largest artery in the human body.
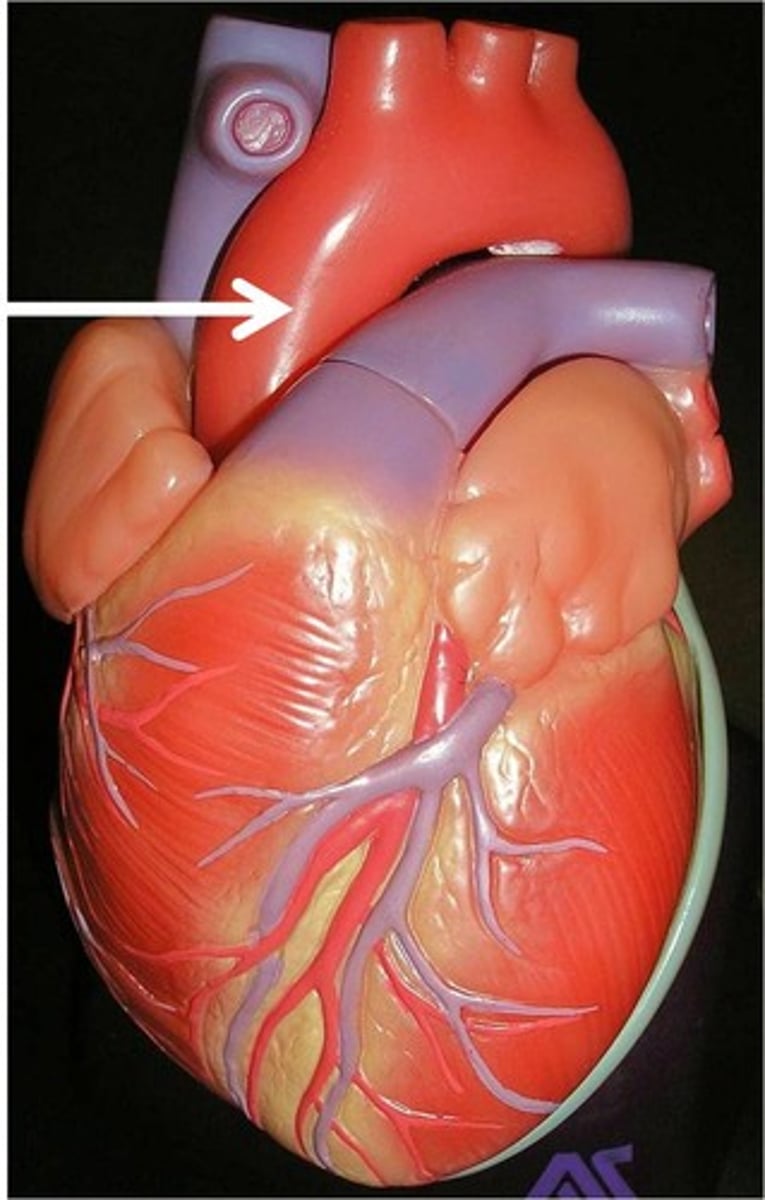
Coronary Circulation
Circulation of blood through the coronary blood vessels to deliver oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle tissue.
Right Atrioventricular Canal
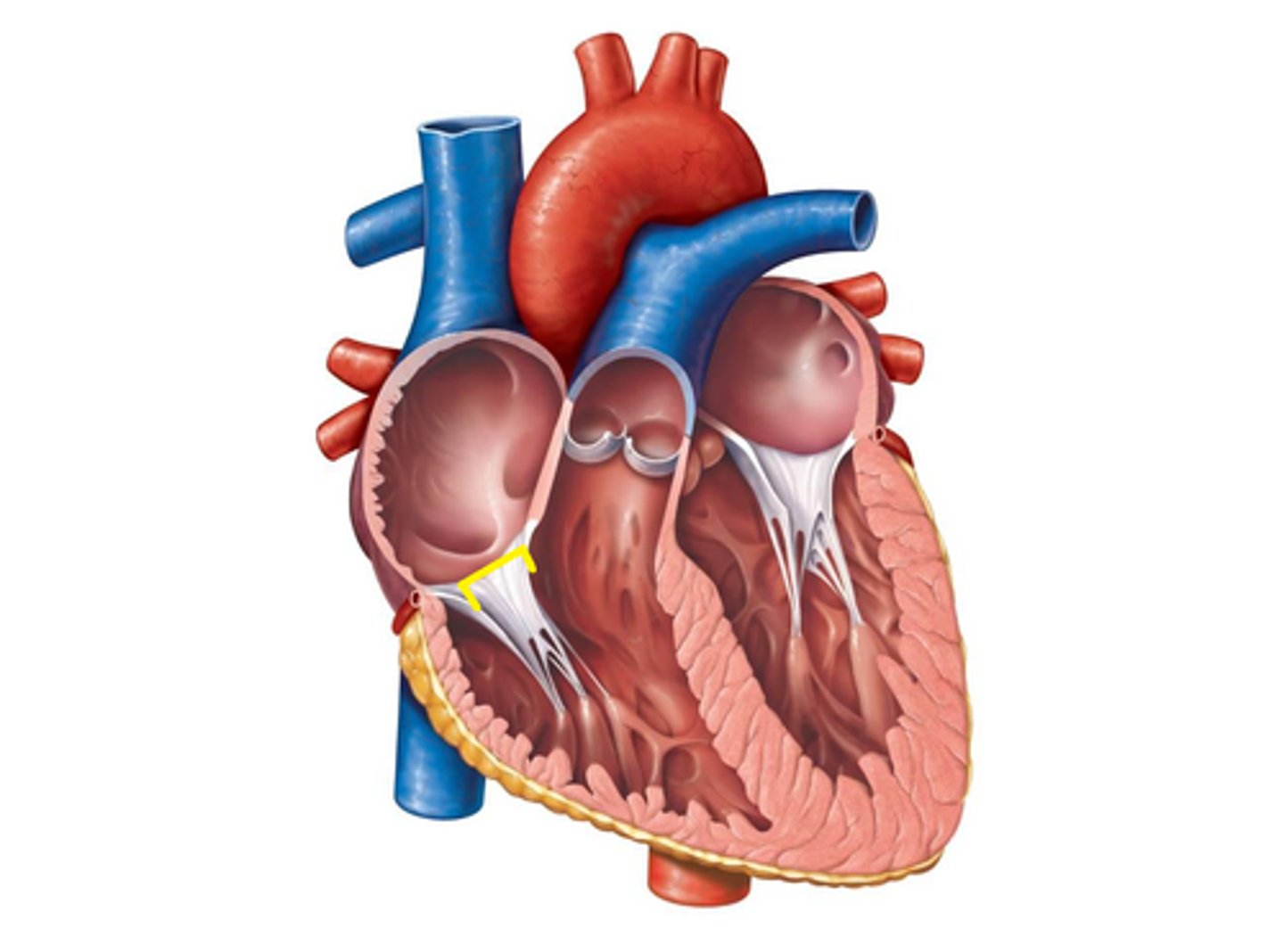
Right Atrioventricular Valve (Tricuspid Valve)
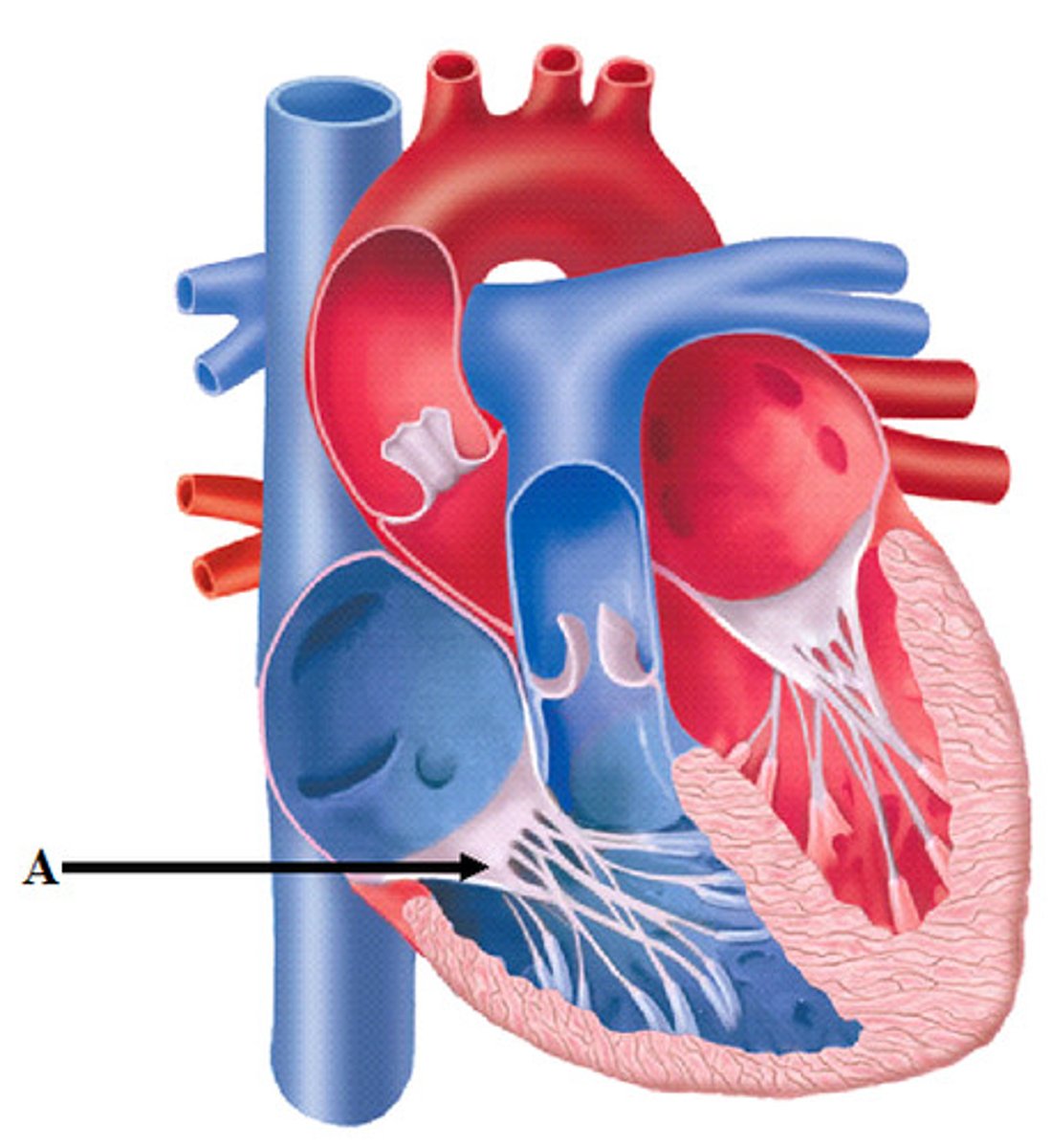
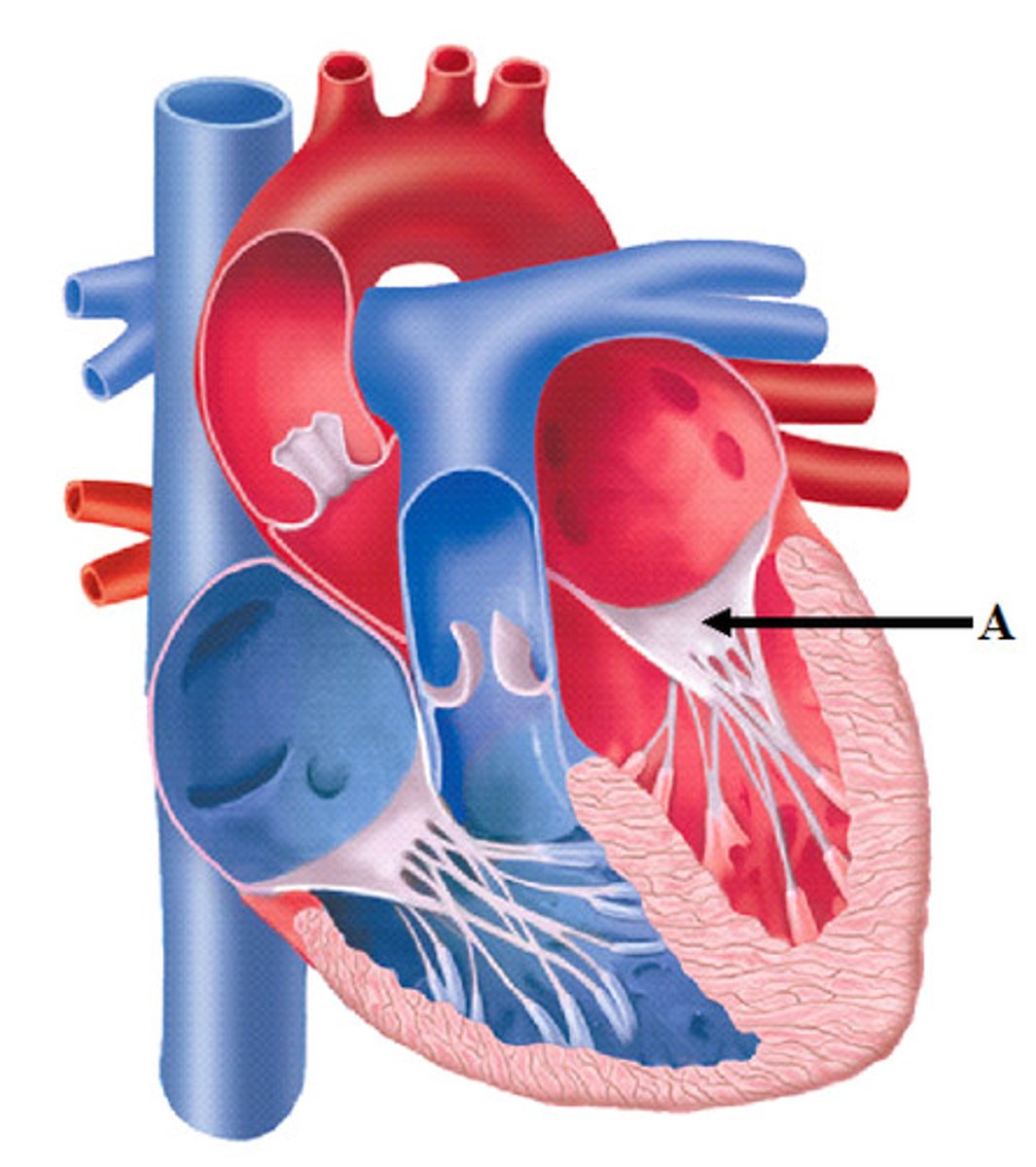
Left Atrioventricular Canal
Left Atrioventricular Valve (Bicuspid Valve or Mitral Valve)
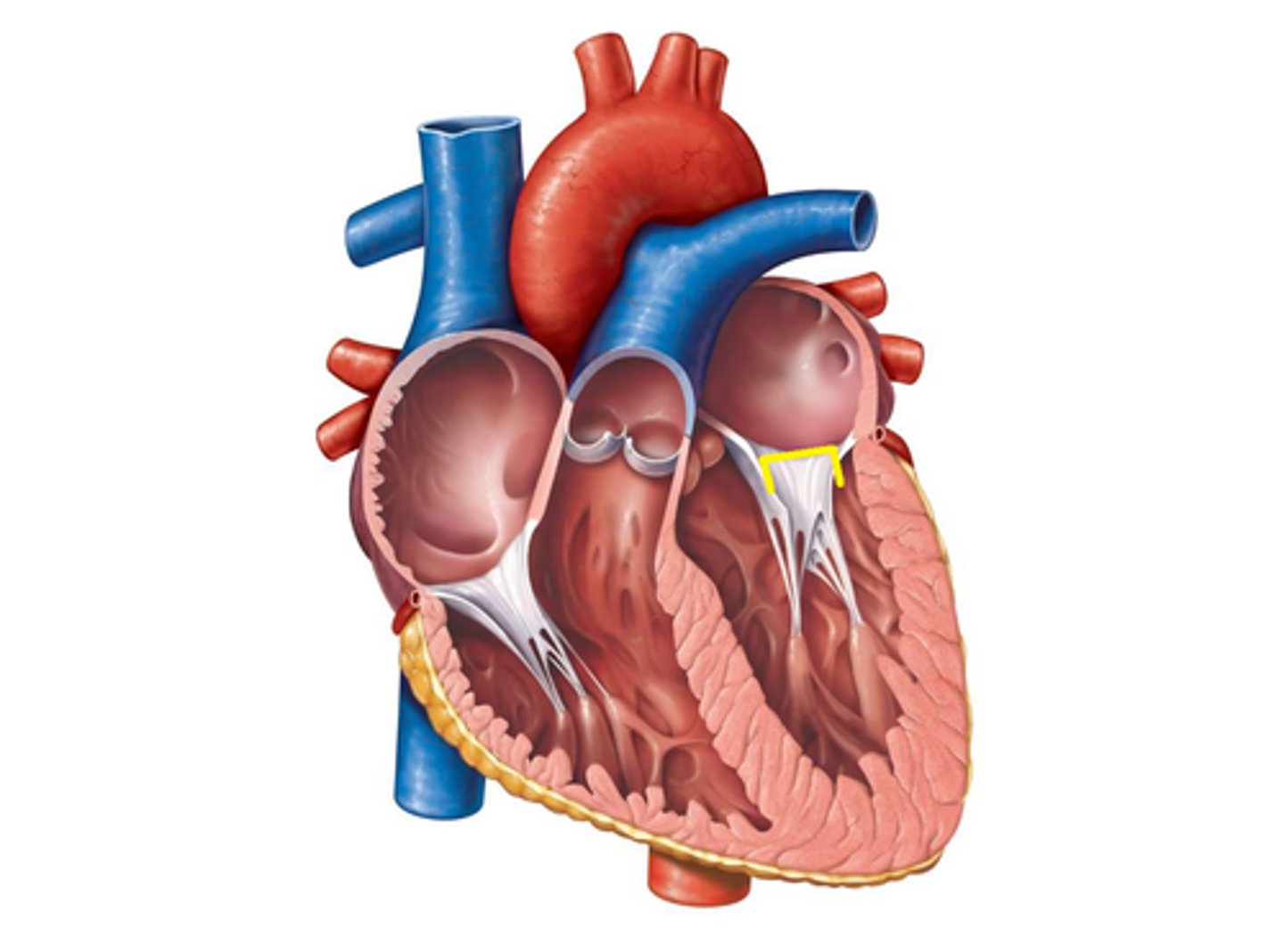
Interventricular Septum
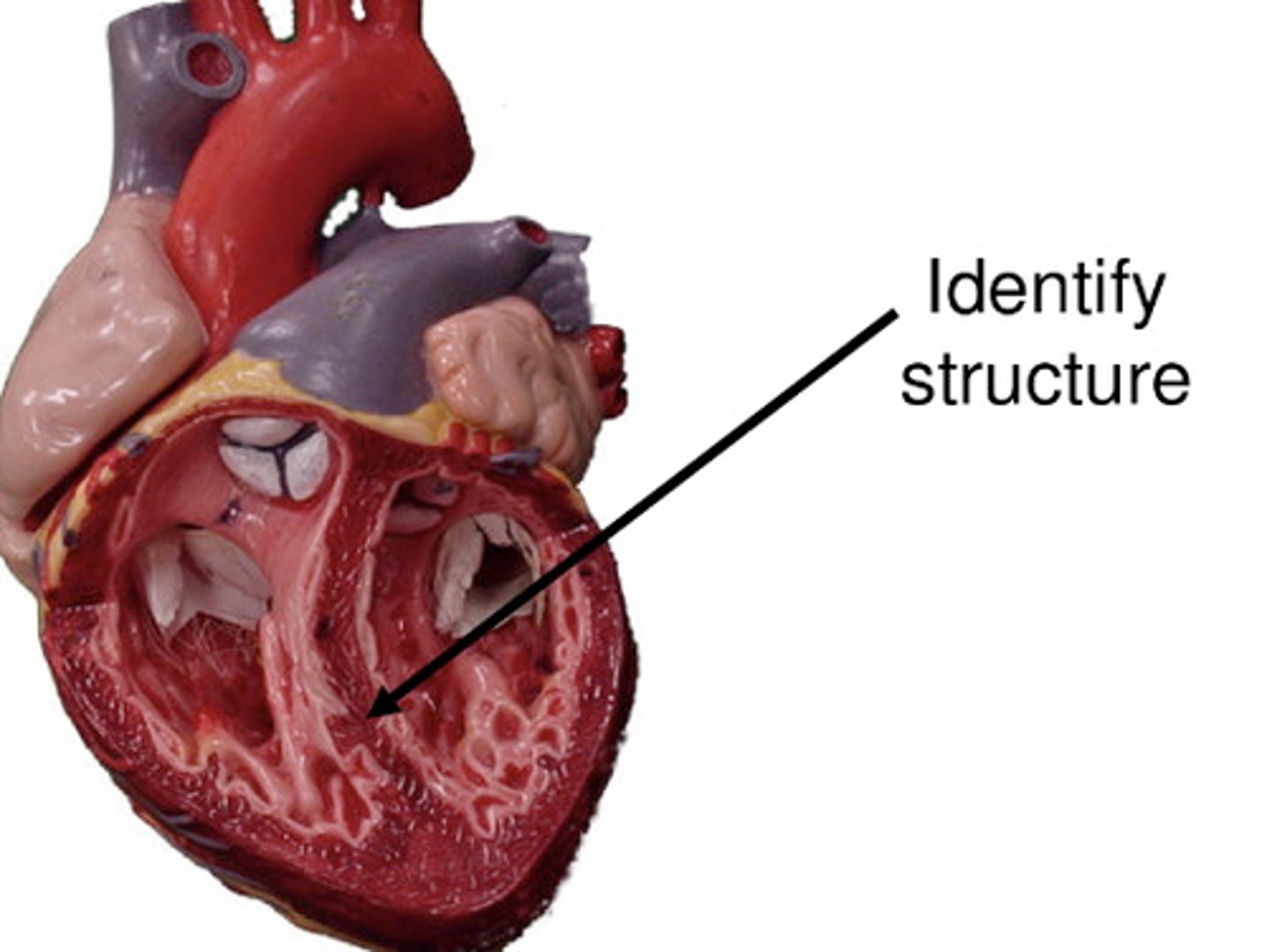
Interatrial Septum
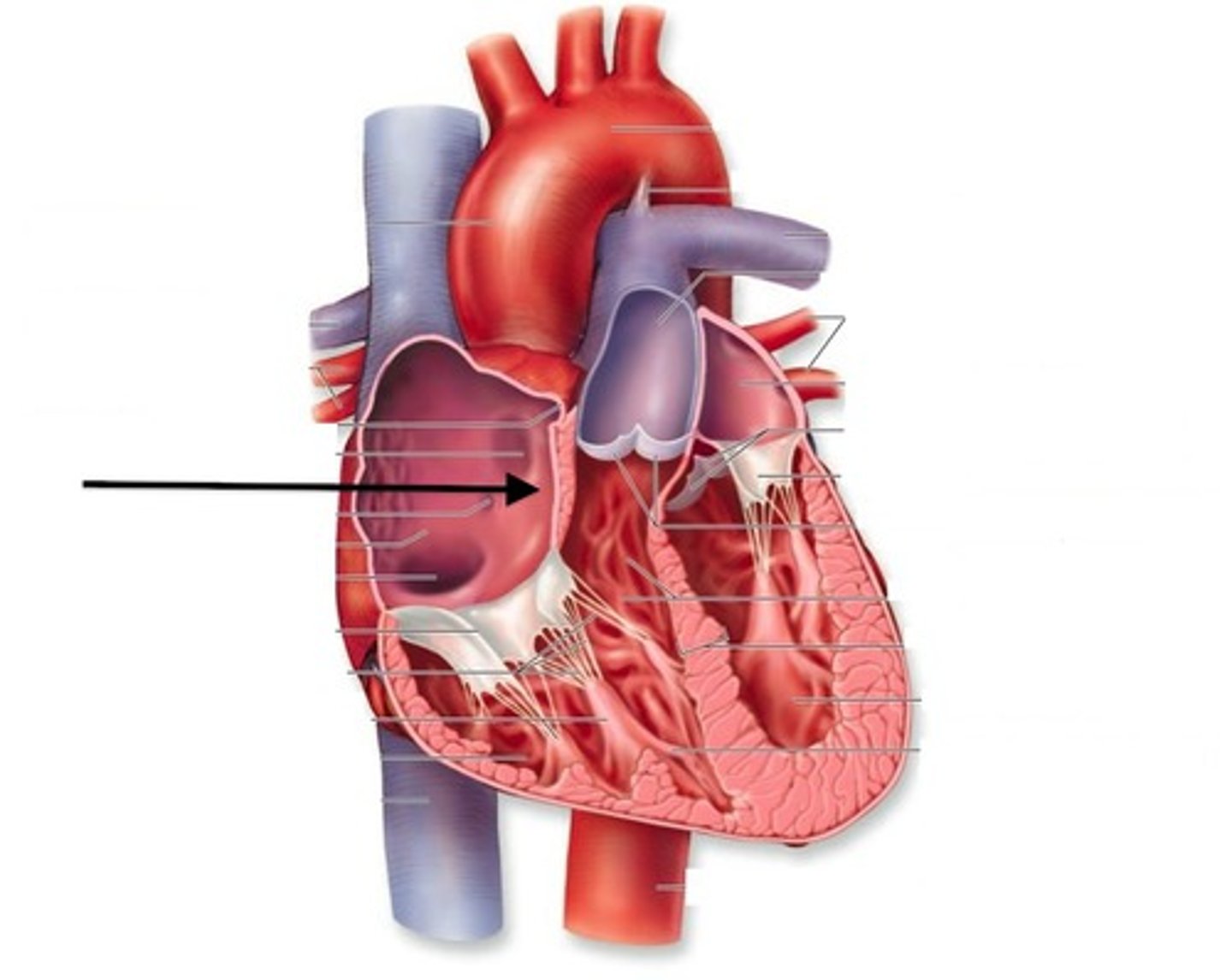
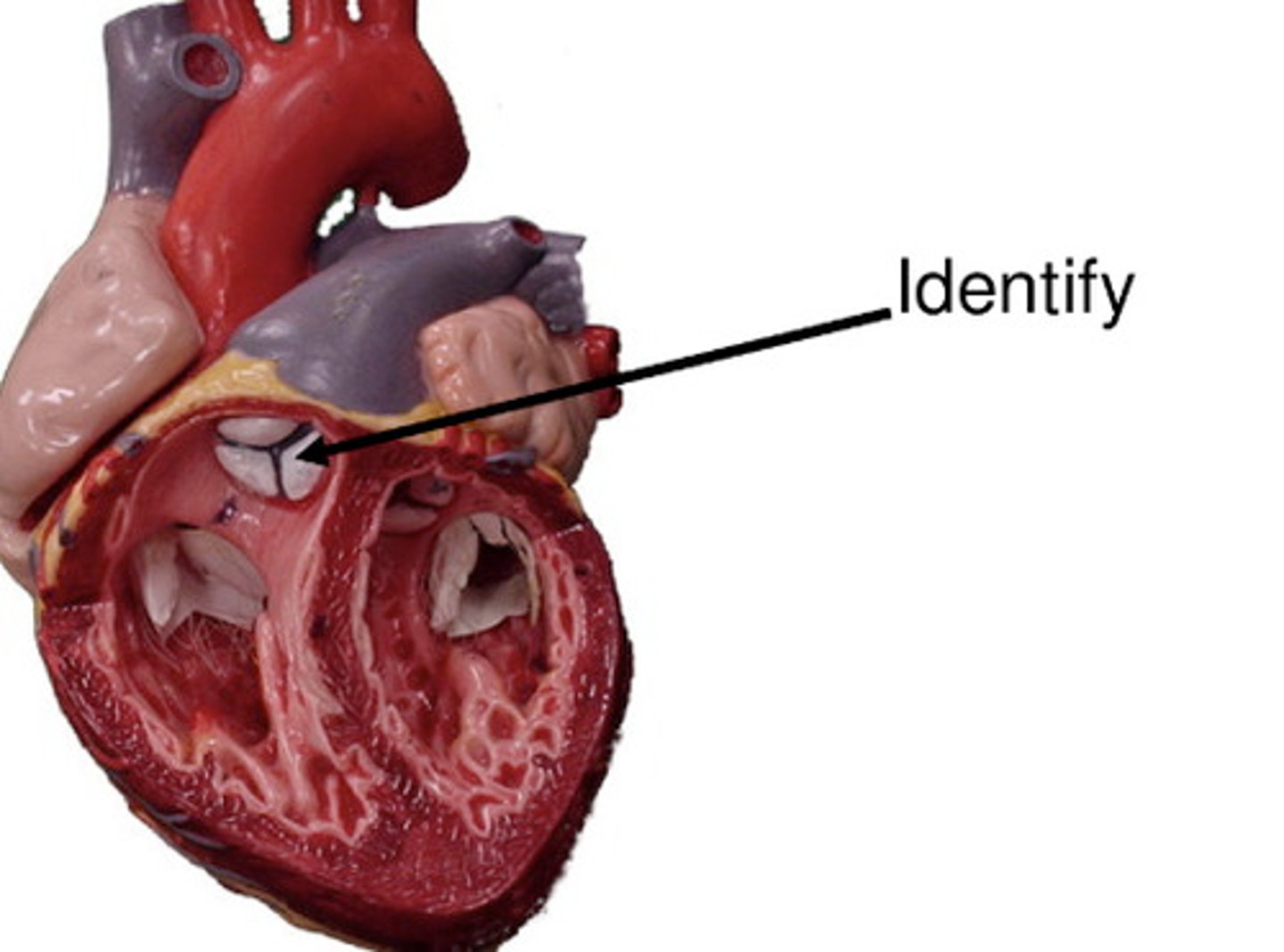
Pulmonary Semilunar Valve
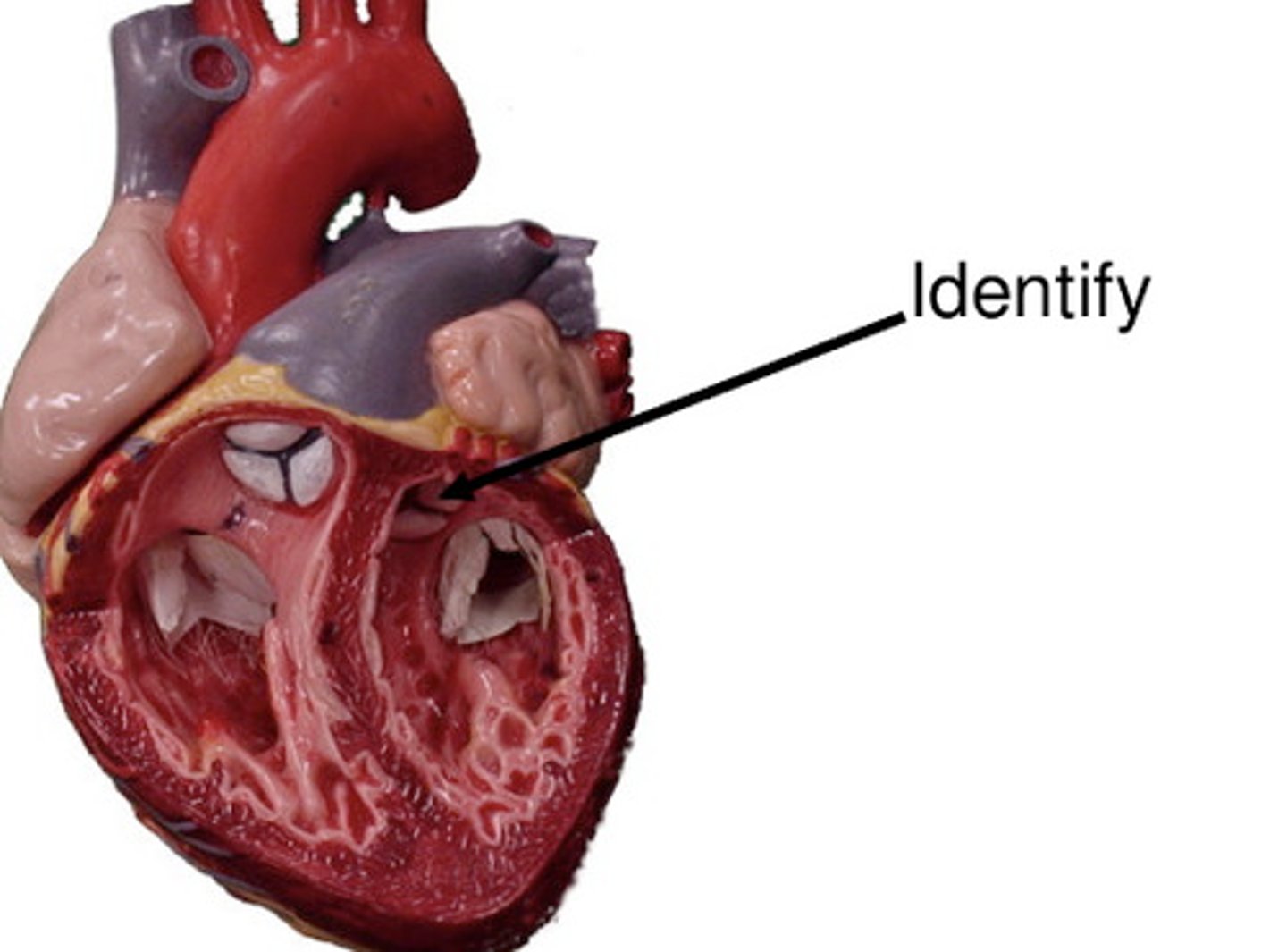
Aortic Semilunar Valve
Right Atrium
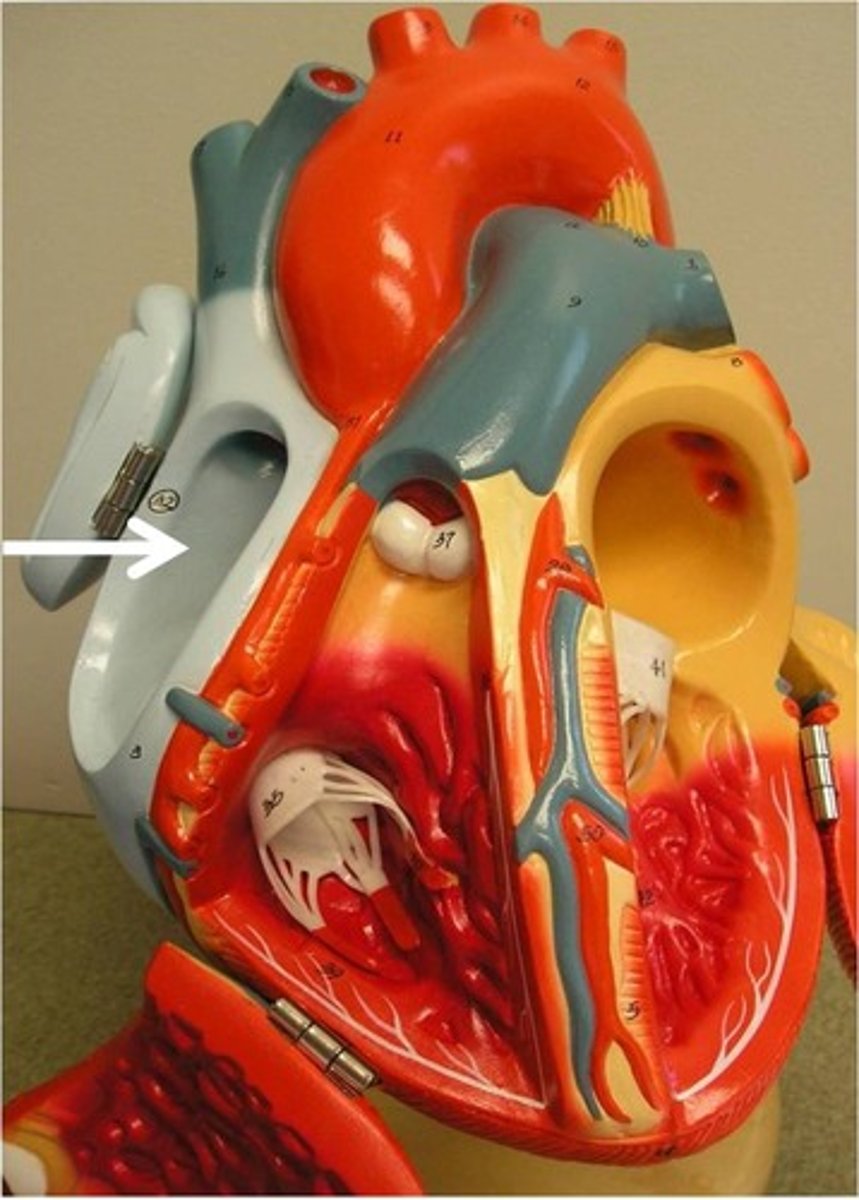
Right Ventricle
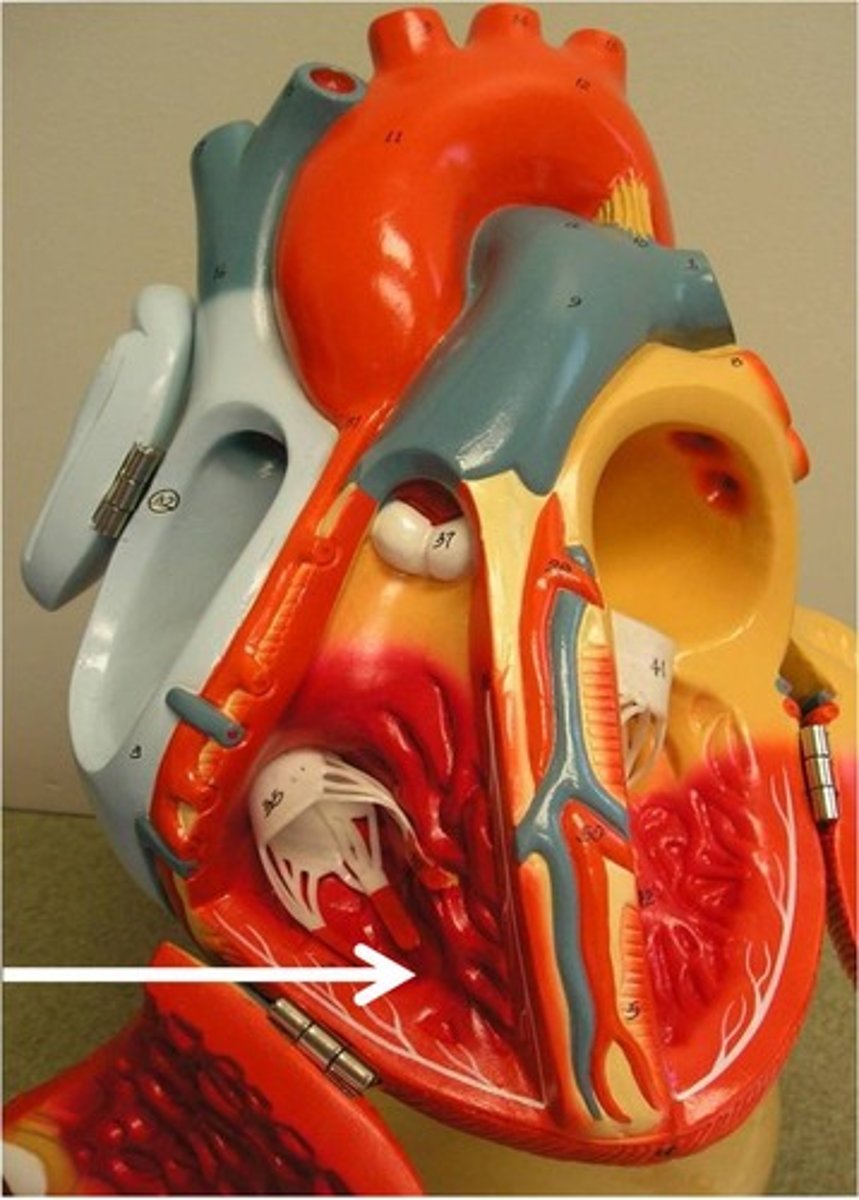
Left Atrium
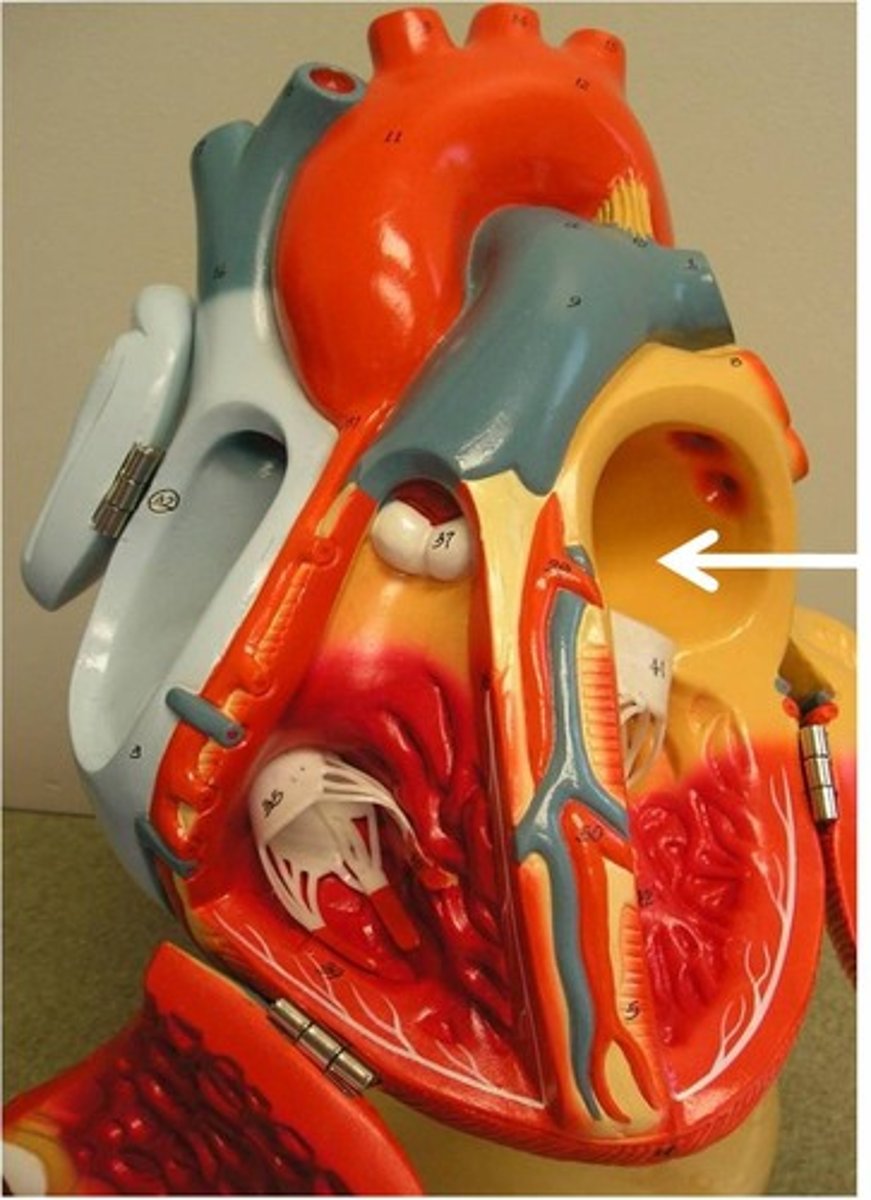
Left Ventricle
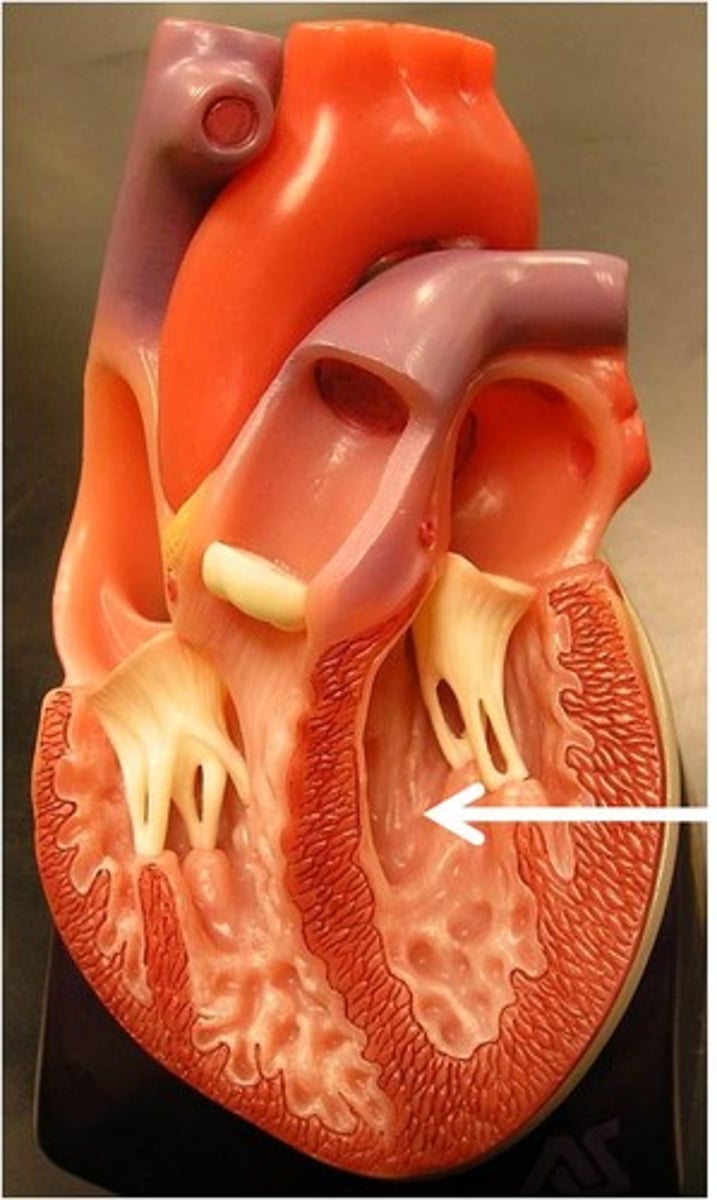
Intercalated Disks
These disks conduct action potentials from one cell to another. (Found ONLY in the heart.)
Self-Stimulatory
The heart is ---- - ---------. This means it creates its own action potentials.
Nodes
Bundles of cardiac muscle tissue that generate action potentials.
Sinoatrial Node (SA node)
Located in the upper portion of the right atrium. Is often called the Pace Maker since it initiates the action potentials that cause the heart to beat.
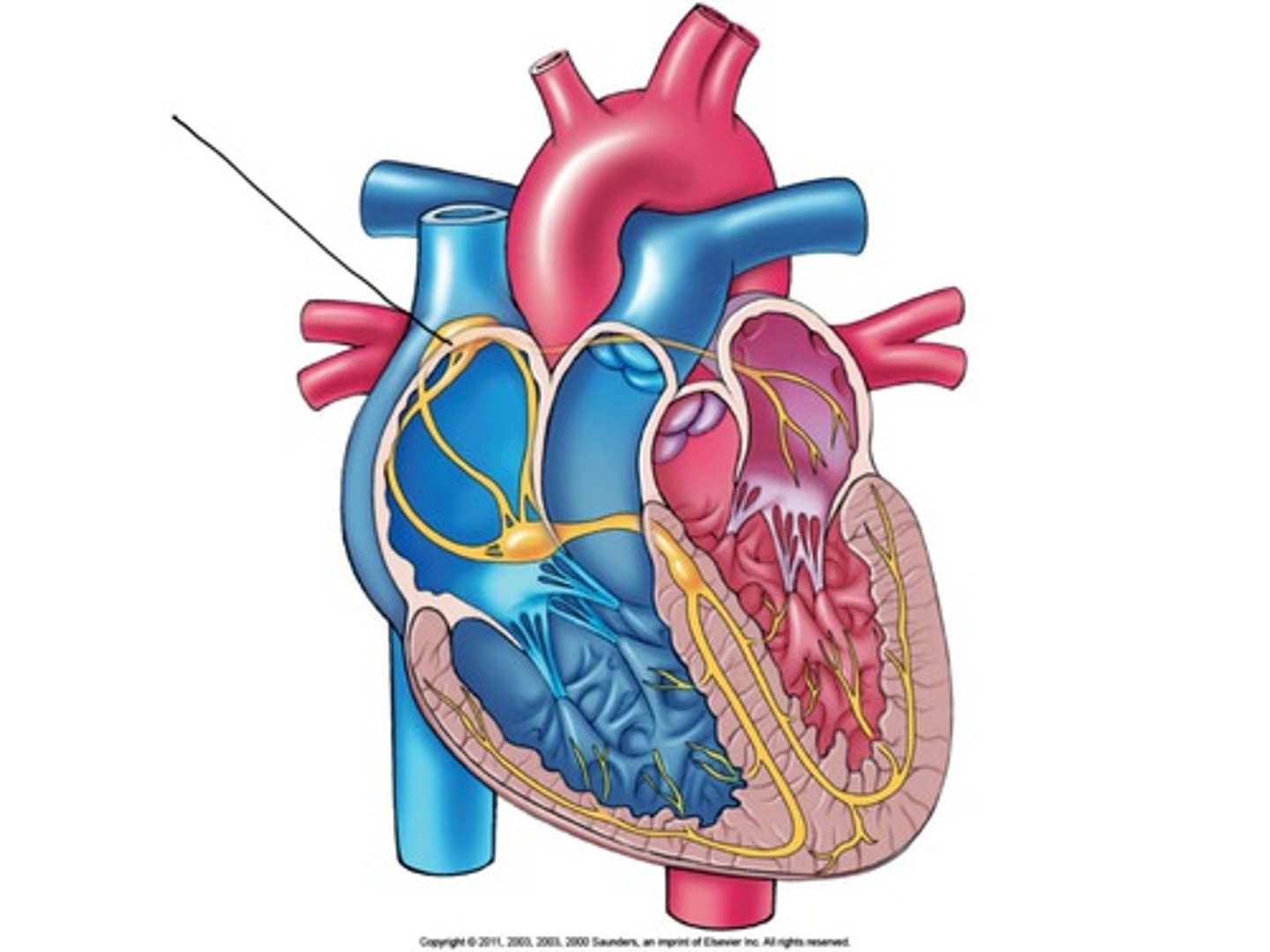
Atrioventricular Node (AV node)
Located near the tricuspid valve in the right atrium. Initiates the action potentials that cause the heart to beat.
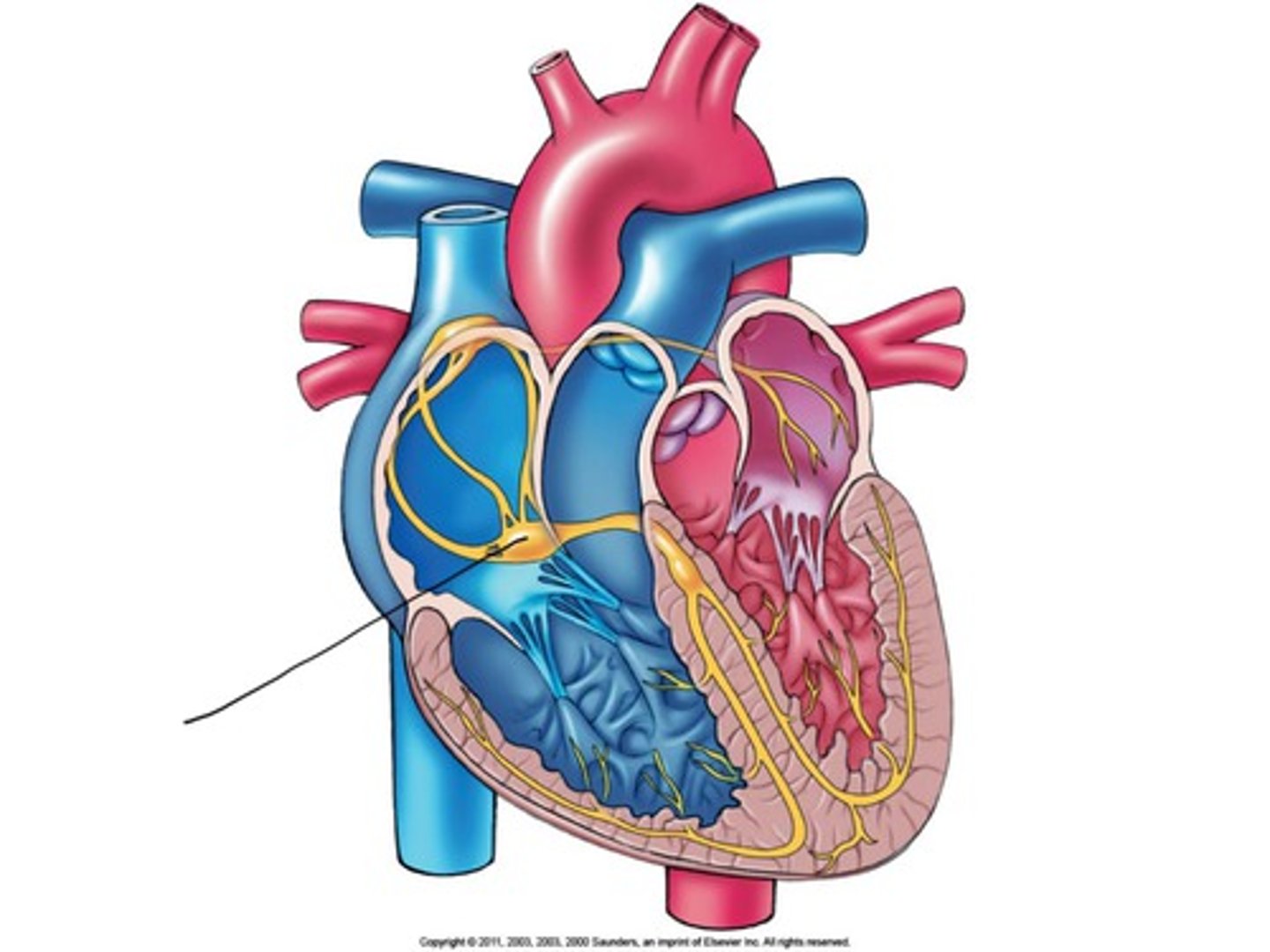
Atrioventricular Bundles
Special bundles of nodal tissue that travel through the interventricular septum and then branch and travel into each ventricle.
Punkinje Fibers
Send the action potential to the cells in the ventricles.
Passive Ventricular Filling
Blood flows into the relaxed ventricles, accounting for most of the ventricular filling (70%).
Cardiac Cycle
One complete round of diastole and systole.
Diastole Phase
The phase of the cardiac cycle ion which the ventricles relax.
Systole Phase
The phase of the cardiac cycle in which the ventricles contract.
Diastolic Pressure
Reflects the minimum pressure on the Aorta.
Systolic Pressure
Reflects the maximum pressure in the Aorta.
Tunica Adventitia
The outer layer of the blood vessel.
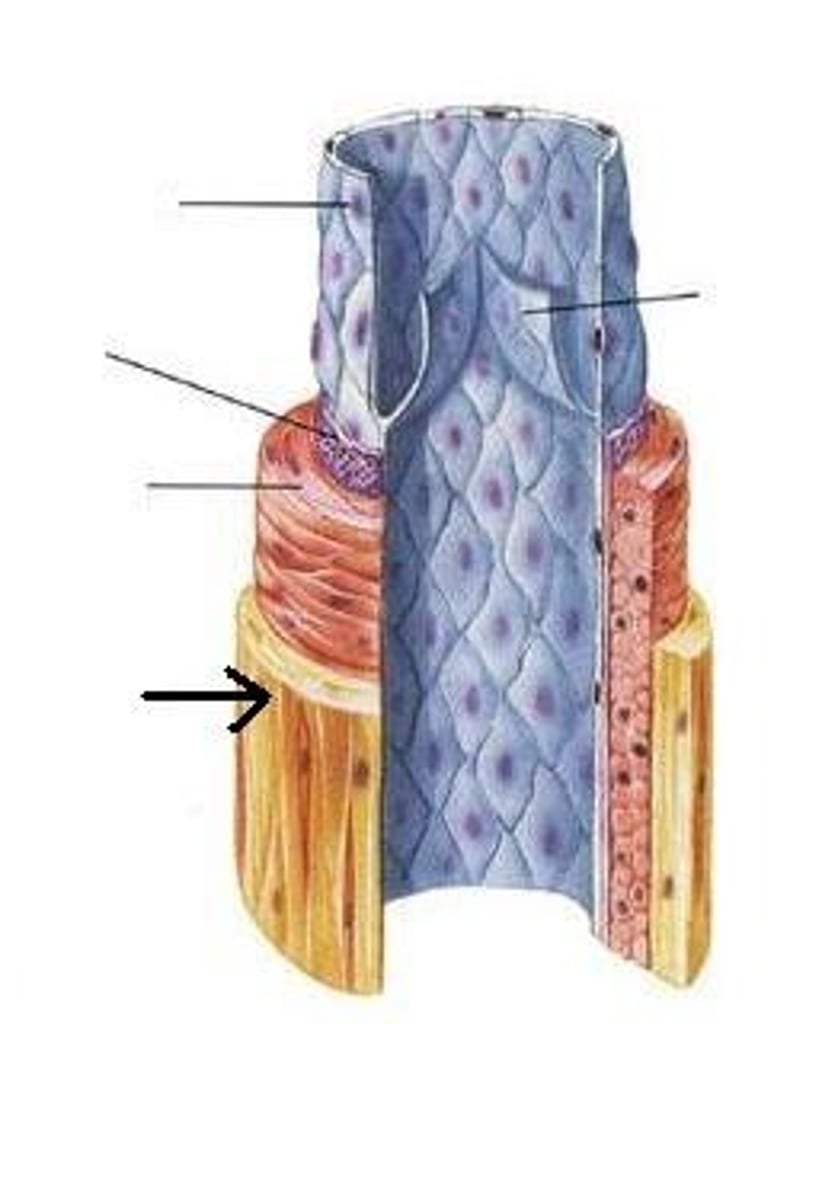
Tunica Media
Is the middle layer of the blood vessel.
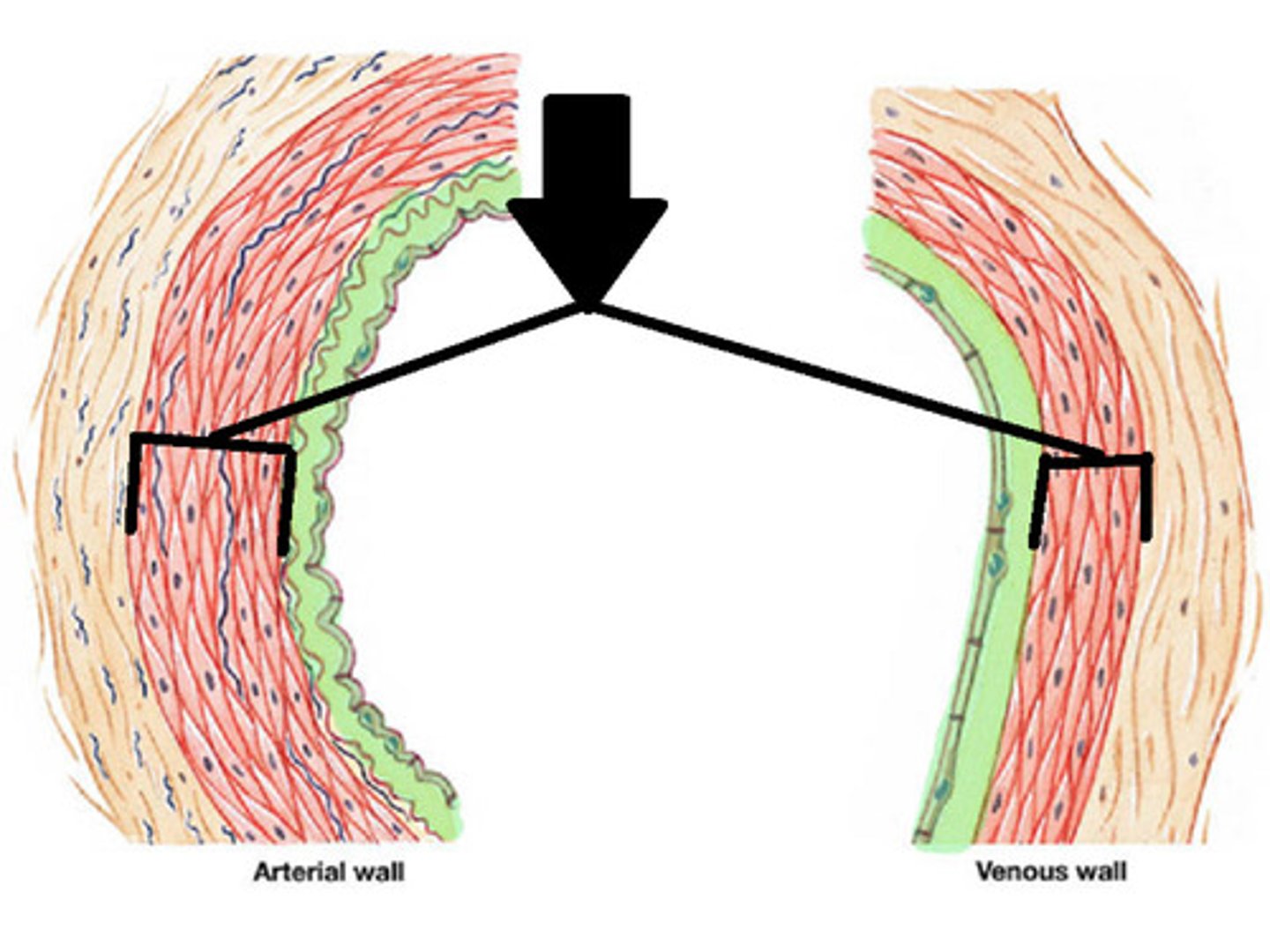
Tunica Intima
Is is the layer closest to the blood.
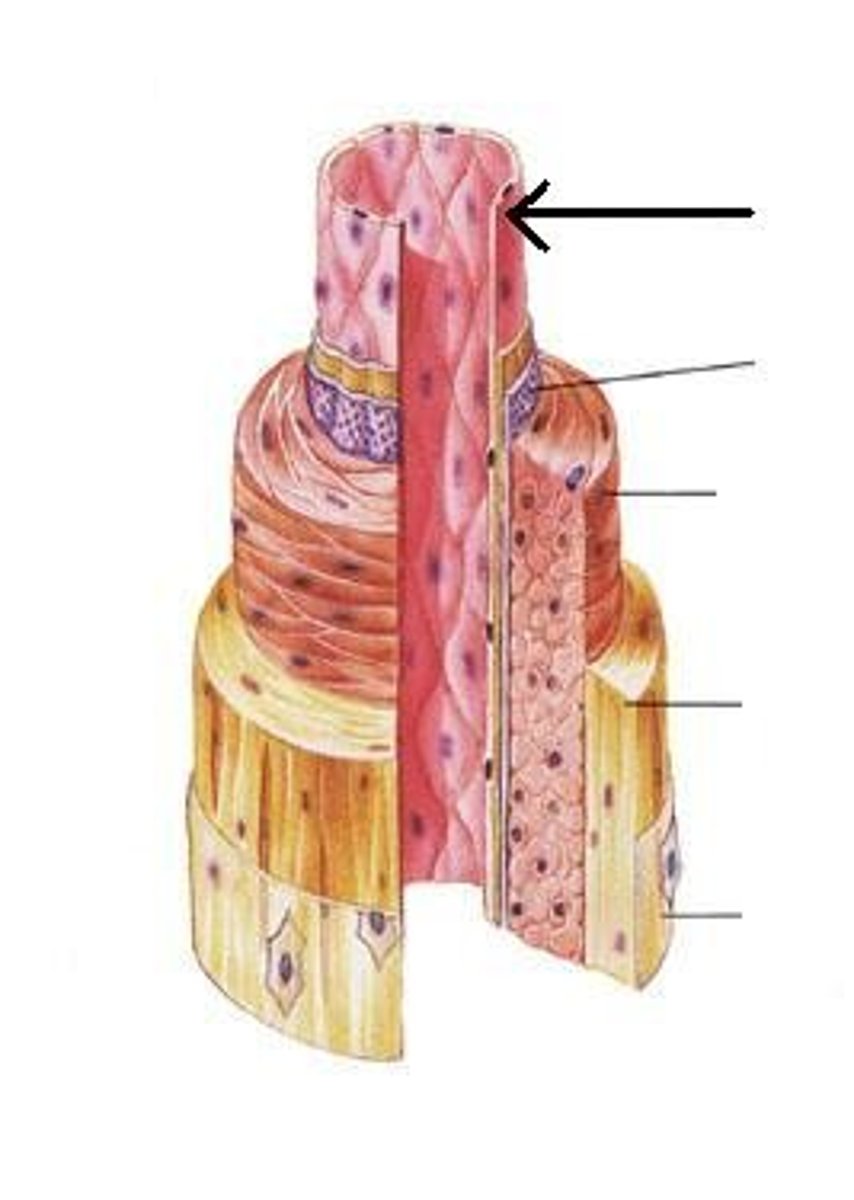
Endothelium
Simple squamous epithelial tissue that rests on a base of connective tissue in the blood vessel.
External Elastic Membrane
The outer layer of connective tissue on the blood vessel.
Vasa Vasorum
Is the set of blood vessels that supply the blood vessel walls with O2 and nutrients.
Arterioles
The smallest arteries that still have three tunics.
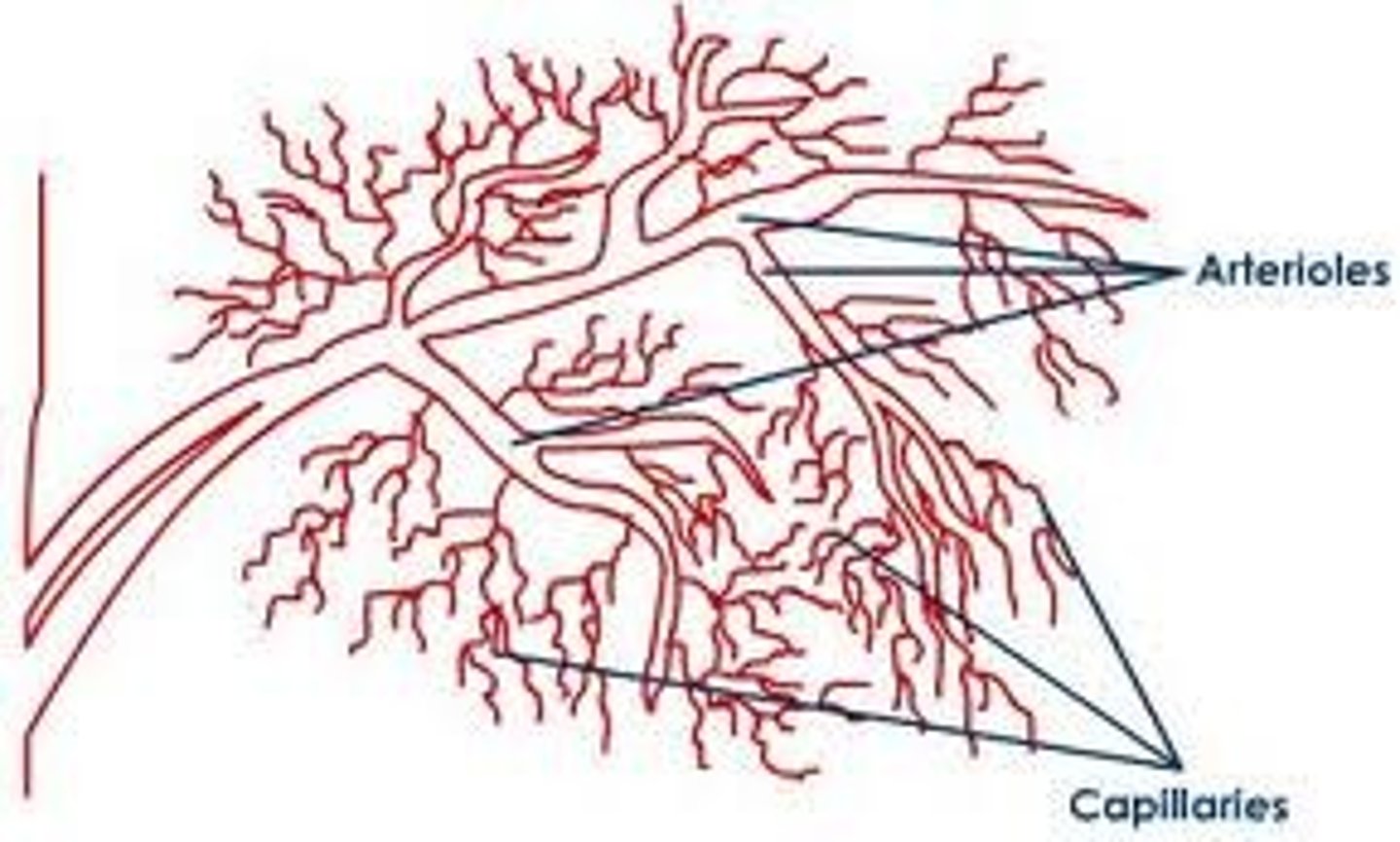
Venules
Small veins that do not have a tunic, but instead have only an endothelium, a basement membrane, and a few smooth muscle cells.
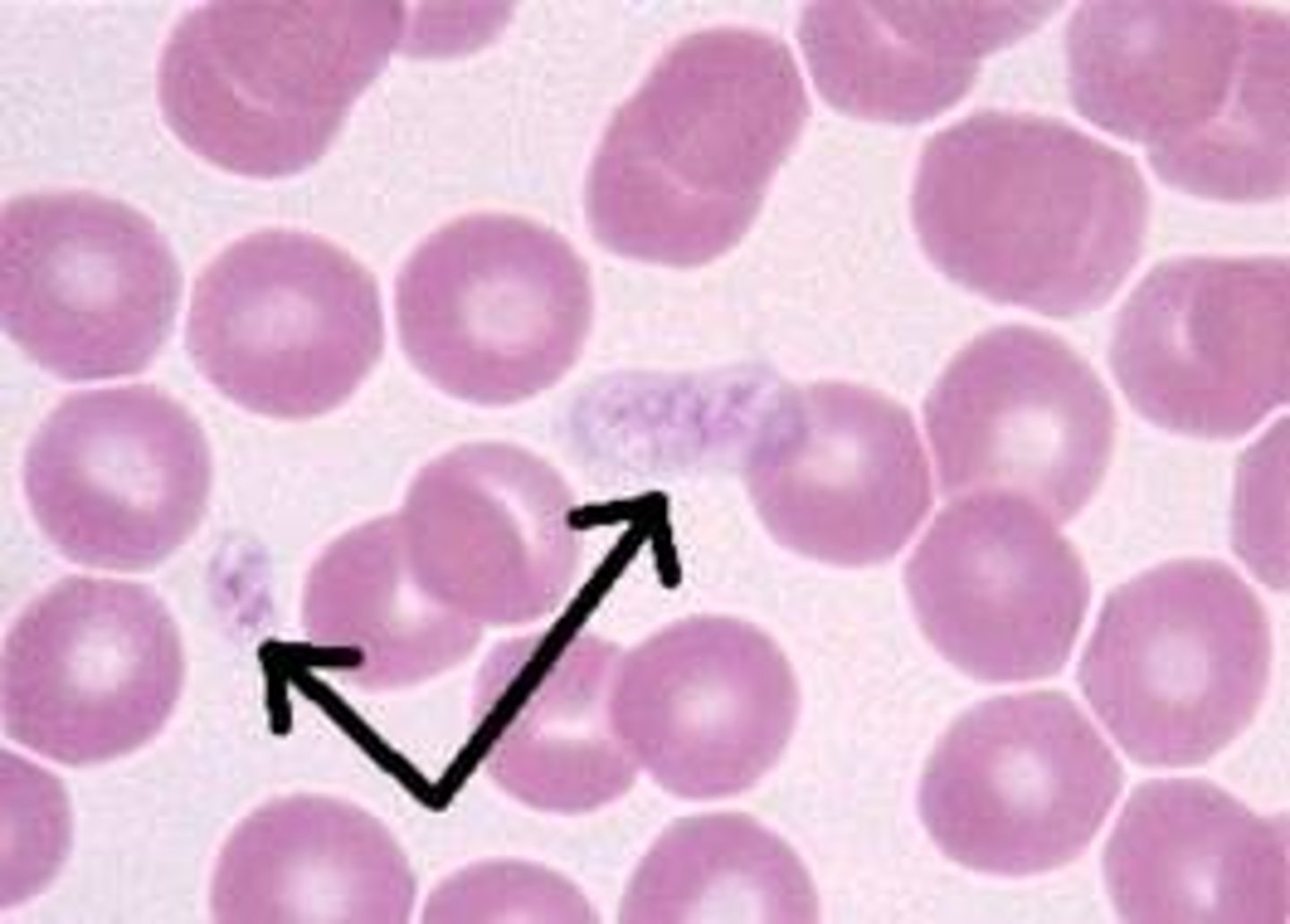
Platelets
A very small blood cell derived from the fragmented cytoplasm of megakaryocytes in the bone marrow. --------- participate in coagulation, wound healing, and inflammation
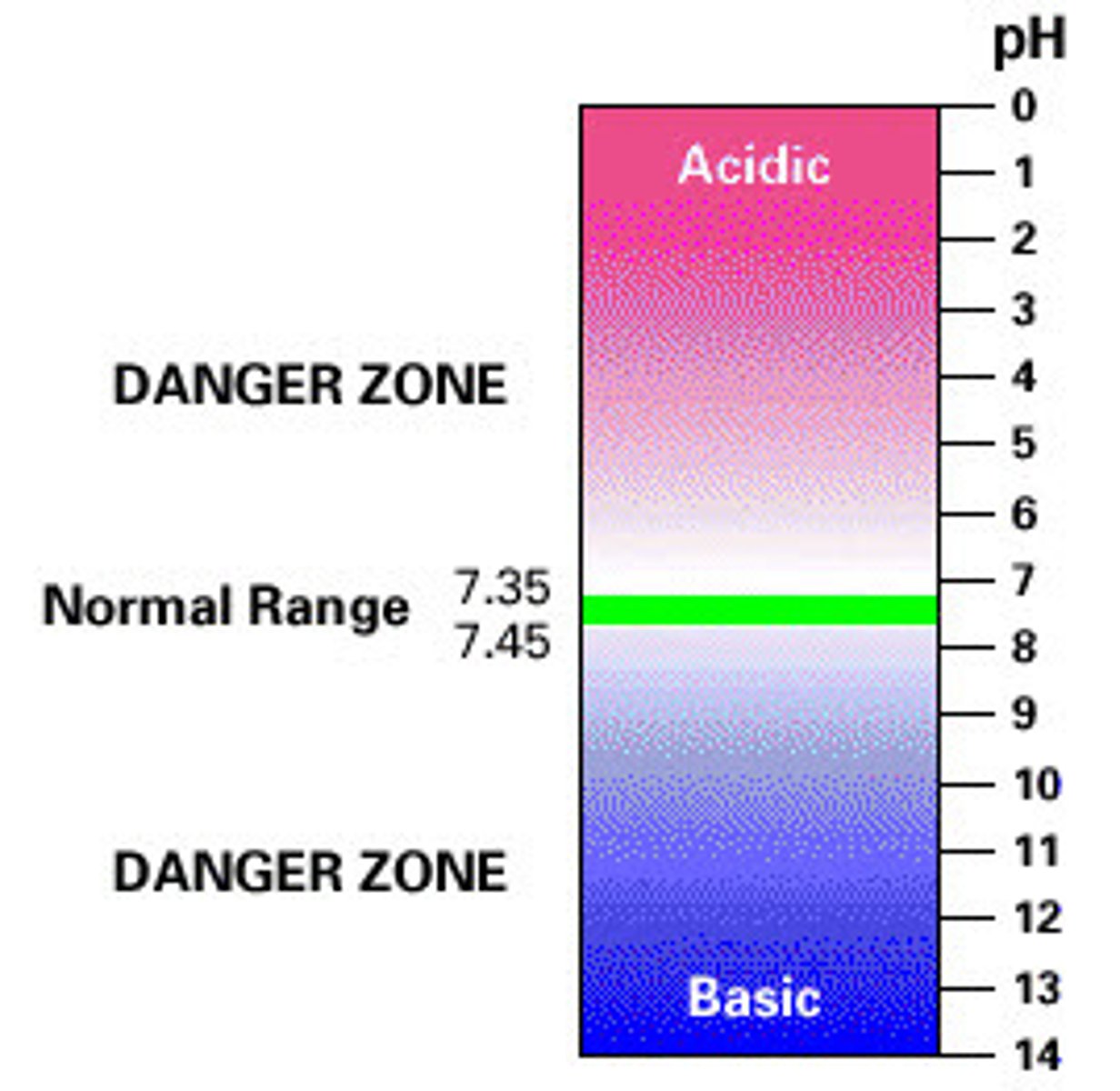
Blood Ph
7.35-7.45