overripe oceans
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
wave steepness max non-break ratio
1/7
wave base
½ wave height
saltiest ocean
atlantic
deepest ocean
pacific
how much phytoplankton in cubic meter of water
20,000
______ % plate boundaries in ocean
90%
convergent boundaries: ocean ocean (wh + feats)
denser (older) one subduction, makes deep trenches, volcanic island arcs, basaltic lava
convergent boundaries: continent to ocean (wh + feats)
ocean subducts, making trench and continental volcanic arc
convergent boundaries: continent to continent (wh + feats)
continent to continent, folds and deforms crust and makes uplifted mountains, intervening ocean crust is subducted
divergent boundaries
common as mid ocean ridges
oldest at trench, youngest crust at ridge
transform bondaries
occurs perpendicular to mid ocean ridges
inactive faults
called fault zones and act as scars to show past plate movement
intraplate volcanism
hotspots arising from mantle plumes and can make islands
nematath
hotspot track made as ridge moves over
paleomagnetism
bc igneous rocks usualy has magnetite that aligns with earths magnetic field when melted then stays fixed.
wilsons cycle
about how oceans form,
uplift creates valley
divergence creates narrow seas with matching coast, then ocean basin with continental margins
convergents creates island arcs + trenches, then eventually shrinks sea and creates young mountains
uplift and convergence creates young/mature mountain bels
epipelagic
0-200m mixed surface layer where oxygen decreases with depth and has a seasonal thermocline, not that much nutrients because photosynthesis consumes it
mesopelagic
200-1000m contains oxygen minimum layer w lots of nutrients (bc marine snow, etc) and permanent thermocline
bathypelagic
1000 - 4000m oxygen increases with depth
abyssaopelagic
>4000m in trenches
euphotic
zone where photosynthesis can occur ~0-100m
photic zone
zone to where light penetrates (at most 200 m)
disphotic zone
zone where light penetrates but no photosynthesis
aphotic zone
no light reaches
passive margin characteristic
well developed continental rise with deep thick sediment and no tectonic activity
convergent active boundaries caracteristic
onshore active volcanoes, narrow shelf, steep slope, offshore trench
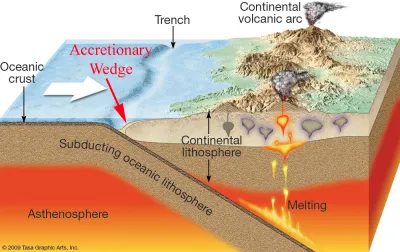
accretionary wedge
where sediment/ crust is scraped from the subducting plate
continental shelf
VERY gentle slope from shore to shelf break, basically the part of continental crust transitioning to oceanic crust
continental slope
often boundary between ocean and continent crust, which is a steep slope down to the level of ocean basin
continental rise
graded bedding slope which is the final transition between continent and ocean, it is beyond the continental slope
turbidity currents
underwater avalanche of sediment down the continental slope, causes a lot of erosion
submarine canyons
BIG canyons in the continental shelf
mid ocean ridge description
continuous + fractured mountain range in all ocean basins, which is lifted up because its made of less dense newly formed crust that is pushed up by mantle. lots of volcanic activity
mid ocean ridge features
seamounts, pillow lavas,
fault zones
extensions of transform faults that show past movements
ocean basin
30% of earths surface, aka abyssal plain, which is very smooth bc covered in a deep layer of fine sediments
seamount
a underwater volcanic mountain that is more than 1km high
guyot/tablemount
a seamount with a flat top
abyssal hill/sea knoll
lots of these, which usually have rounded tops; less than 1 km tall
shield volcano
broad large volcanoes that form most seamounts

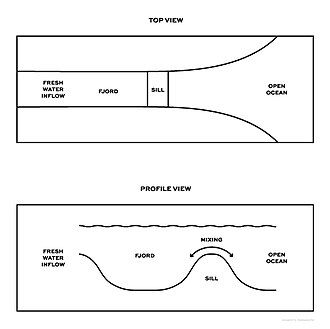
sill
a “speed bump” of the ocean floor, not very high raised ridge that restricts flow a little
forearc basin
flat basin in front of the trench caused by the accretionary arch
shore
low tide to highest point affected by storm waves
foreshore
low to high tide
coast
shore to as far as ocean related features are seen
beach
deposit of waveworked shore sediments
wavecut bench
flat, wave eroded surface that sediment moves over
longshore bar
sand bar parallel to cost that can trip waves
longshore trough
trough of the longshore bar
berm
high tide to coastline
sand movement w/ light waves
swash soaks in sand, dominates ,so deposition
heavy waves
not as much swash soaks in so more backwash, so erosion
summer beach
lighter waves = wide berms, steep beach face, little to no longshore bar
wintertime beach
heavy wave activity, narrow berm, gently sloping beach face with longshore bar
3 beach compartment
1) rivers/coastal erosion that supply sand 2) longshore transport 3) offshore canyon where sand is drained away from beach
erosional shores
places w/ tectonic uplift, so have rocks and cliffs
erosional shore features
wave cut cliffs > sea caves > sea arches > sea stacks
waves concentrate at headlands
depositional shores
lots of sasnd deposits
spit
linear ridge of sediment extending from longshore drift direction into a bay
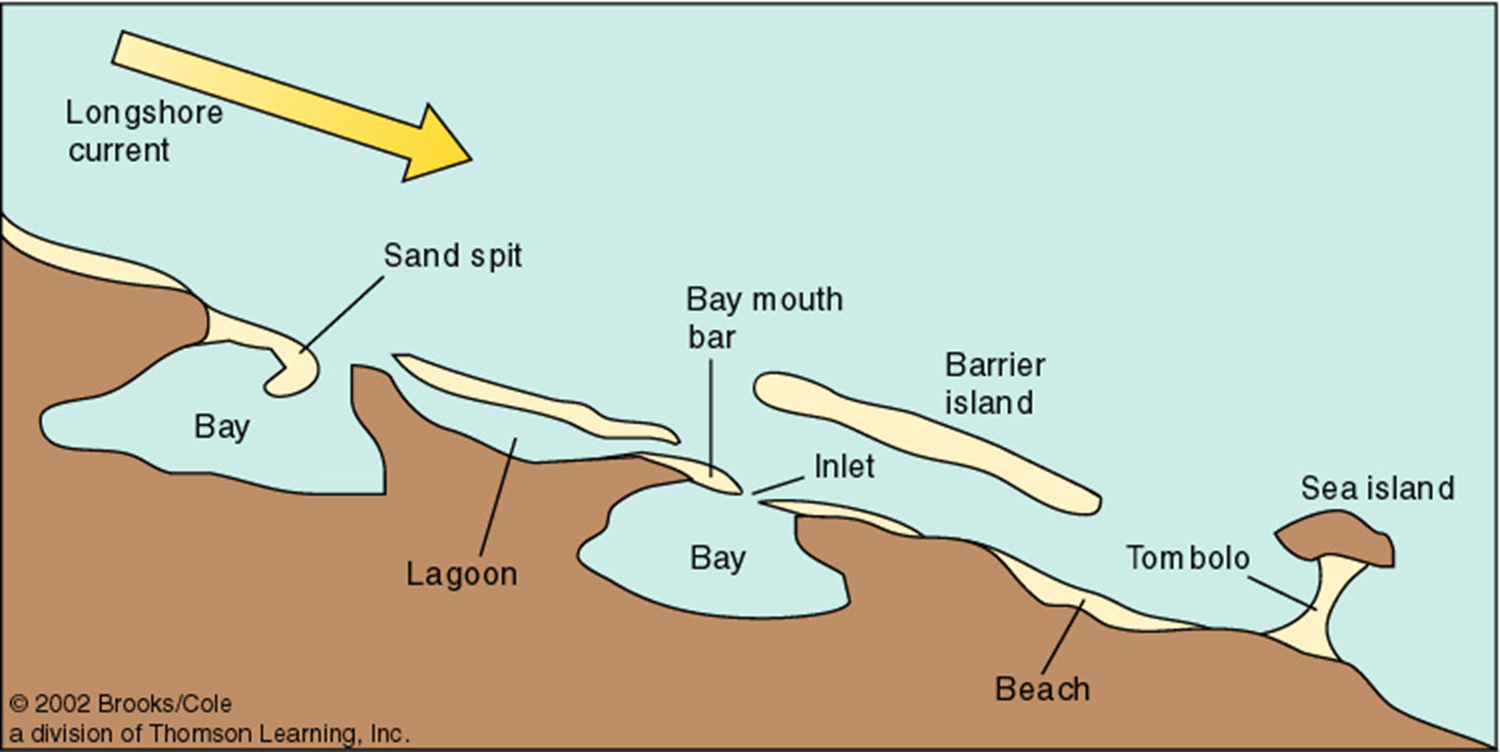
baymouth bar
when bay opening not cleared by currents, a spit extension forms
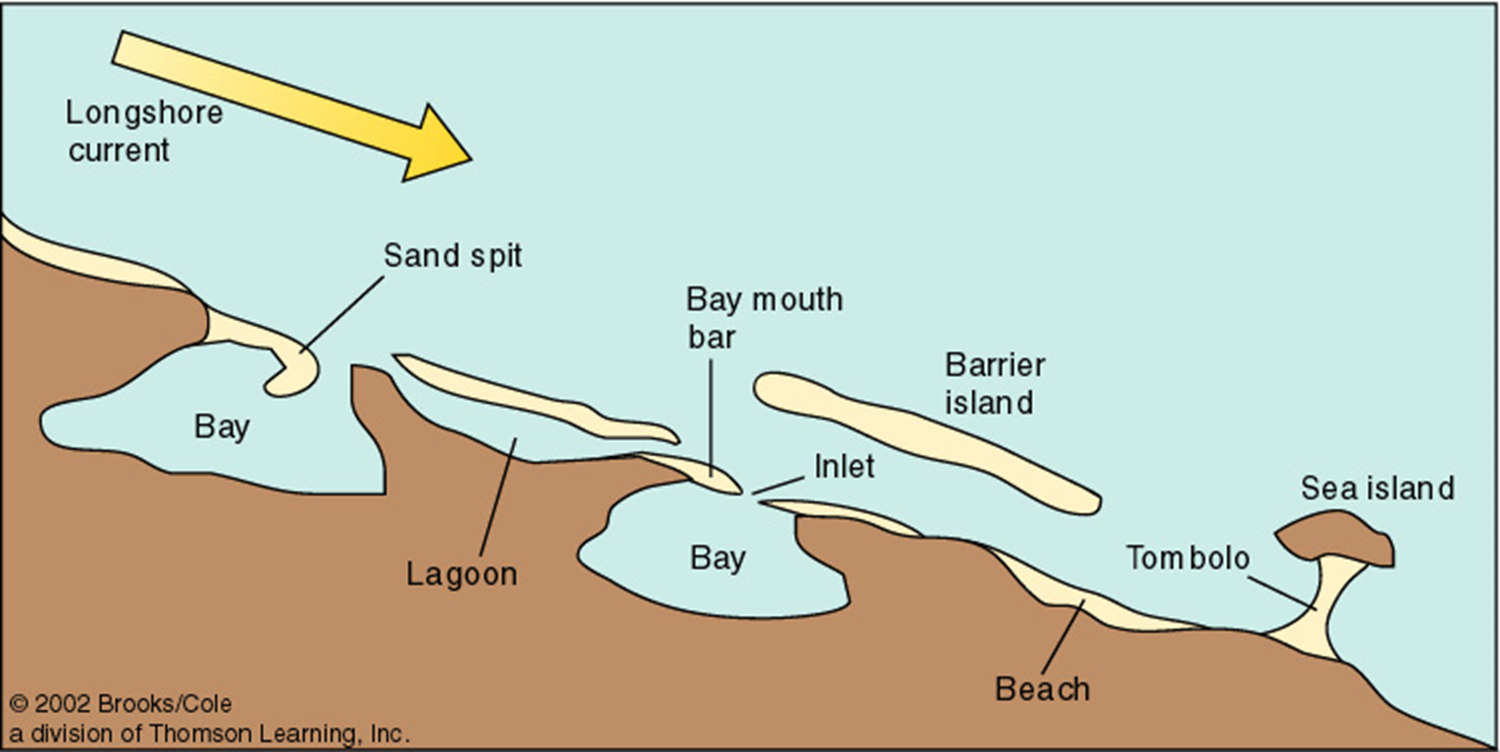
tombolo
a sand ridge connecting island to mainland, forming in island wave shadow
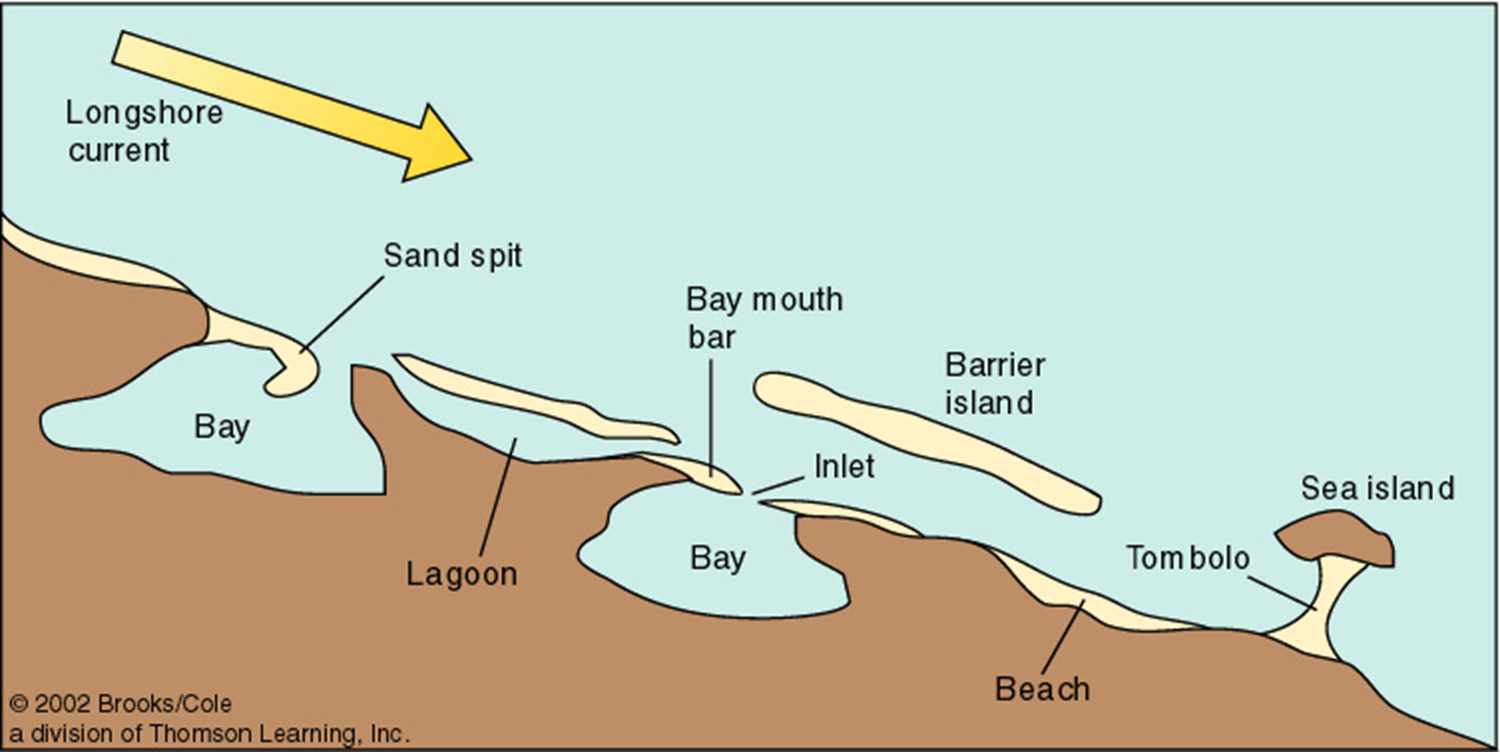
barrier island
long ofshore deposit of sand parallel to coast
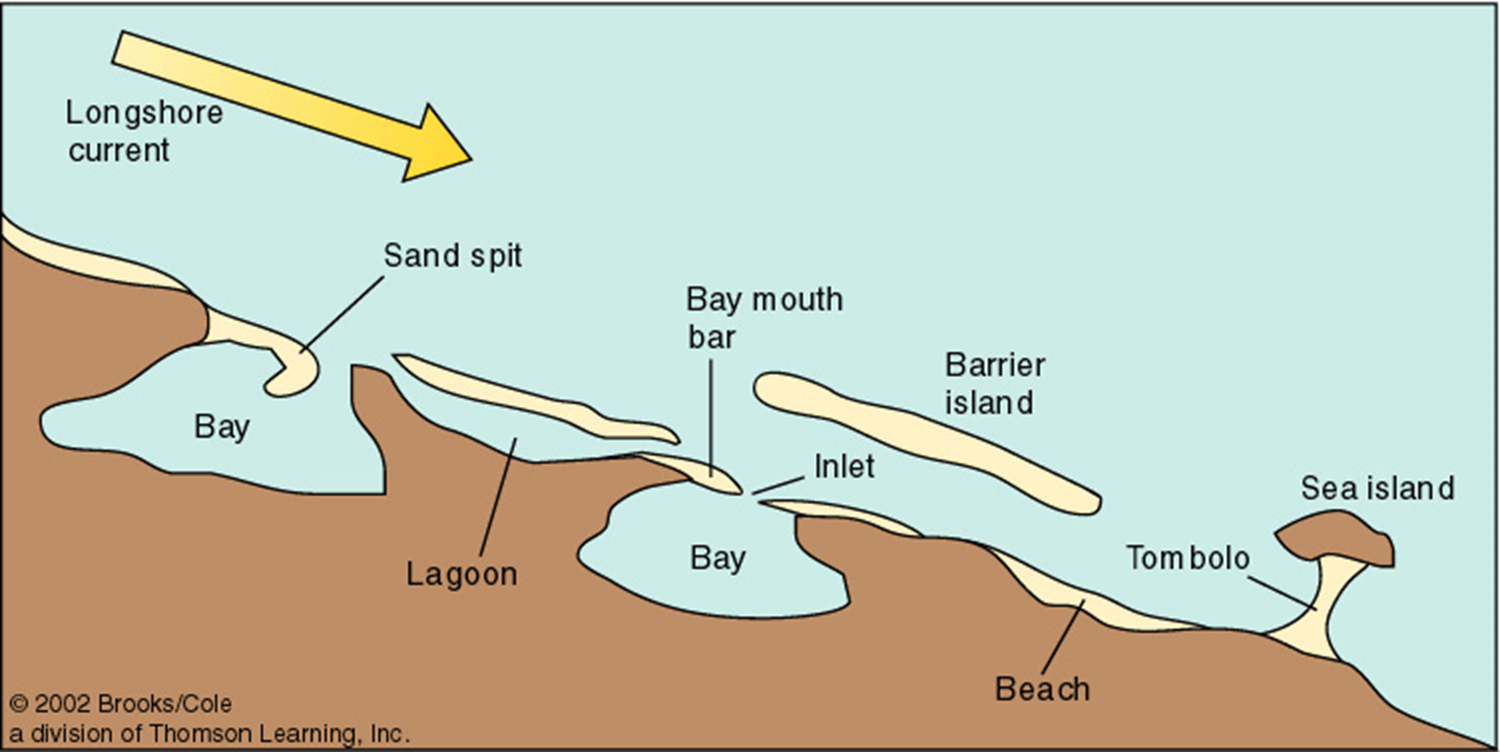
lagoon
between barrier island and shore
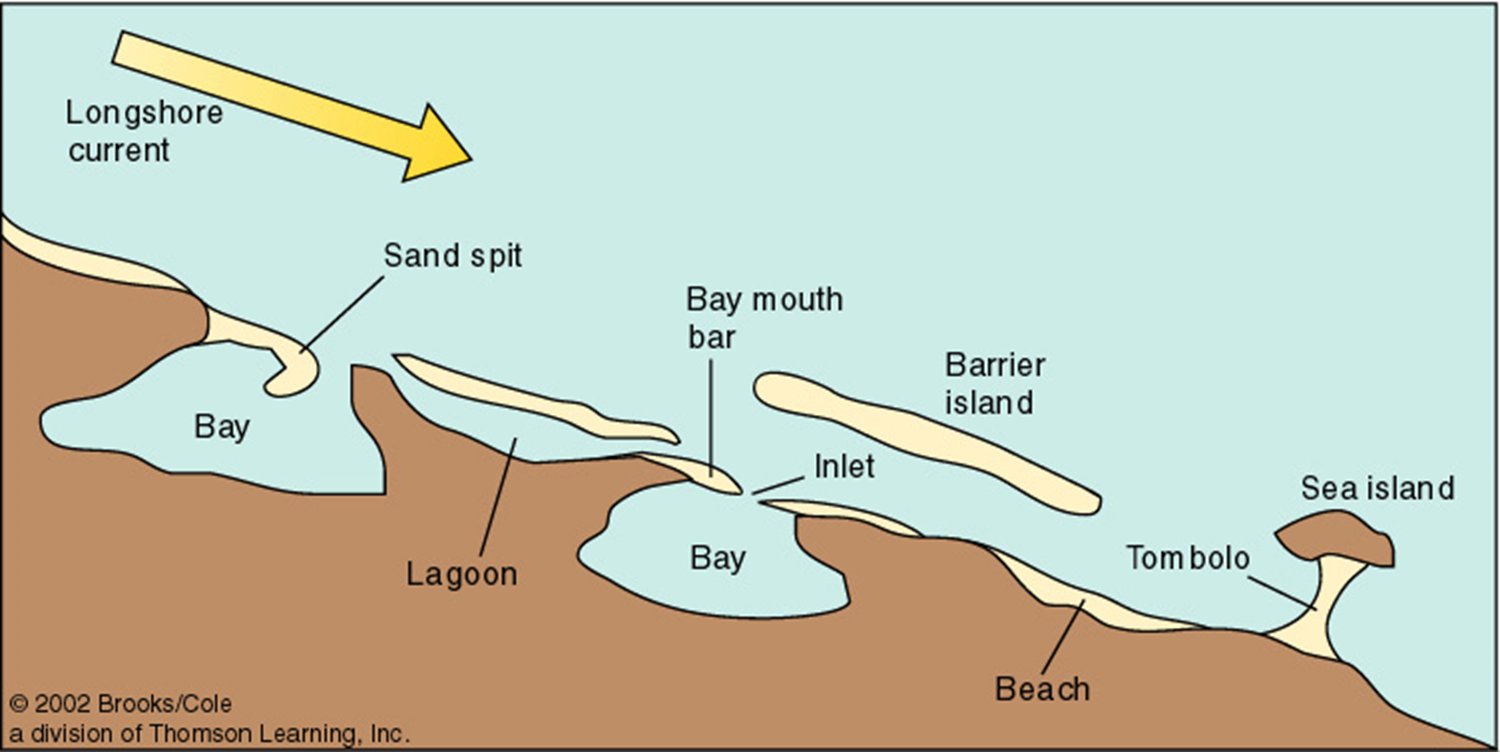
barrier island migration
it rolls over on itself and they are currently moving towards land bc rising sea level
deltas
triangular sediment deposits at river mouth that deposit more than longshore drift can take away, they are very fertile
emerging coastlin
has marineterraces and stranded beach deposits, also cliffs etc
submerging coastline
drowned beaches, river valleys
relative sea level changes
local sea level change due to tectonic, isostatic adjustment
isostatic adjustment
land rising/sinking bc weight of ice from before/now
eustatic sea level changes
worldwide changes bc of seawater volume or ocean basin capacity changes, ex formation/destruction of large lakes, seafloor spreading, ice ages
coastal water properties
low salinity w/ halo cline
prevailing dry offshore winds
only isohalinen if shallow w/ significant tidal mixing
coastal waters properties at dif latitudes
low: warm (up to 45 C), isothermal with no mixing con open ocean
mid: summer = shallow warm, winter = cool + sinking, small thermocline
high: uniform cold of about -2c (isothermal)
estuary
partially enclosed coastal waters that are diluted by freshwater from rivers
coastal plain estuary
flooded river valley
fjord
flooded glaciated valley, and u shaped walls (may have sill as well)
coastal wetland
where watertable is at the surface so saturated hydric soils, ex coastal swamps, tidal flats, etc
freshwater lens/ghyben herzberg lens
convex layer of fresh groundwater that floats about denser saltwater usually in small coral/limestone islands/atolls
reef development
fringing > barrier > atoll
fringing reef
develop on margin of landmass when suitble conditions (esp active volcanos), development will stop if land does not subside or sea level not rise
barrier reef
reefs separated from landmass by well-developed lagoon
atoll
a circular reef that encloses a lagoon, no landmass inside
where does general surface circulation occur
in and above pynocline (=< 1000 m), about 10% of ocean.
wind transfers ___ energy in speed
2%
subropical gyres
5 gyres, in N/S pacific and atlantic, also indian ocean
3 yrs to circle small gyre, 6 yrs for large
4 currents of gyre
equatorial (westward current)
western boundary (warm water)
N/S boundary (flows east bc westerlies wind)
eastern boundary current (cold and deflected to equator by coriolis and land barriers)
equatorial countercurrent
east flowing current caused by gravity (bc equatorial current piles of a hill of water thatn wnats to go down)
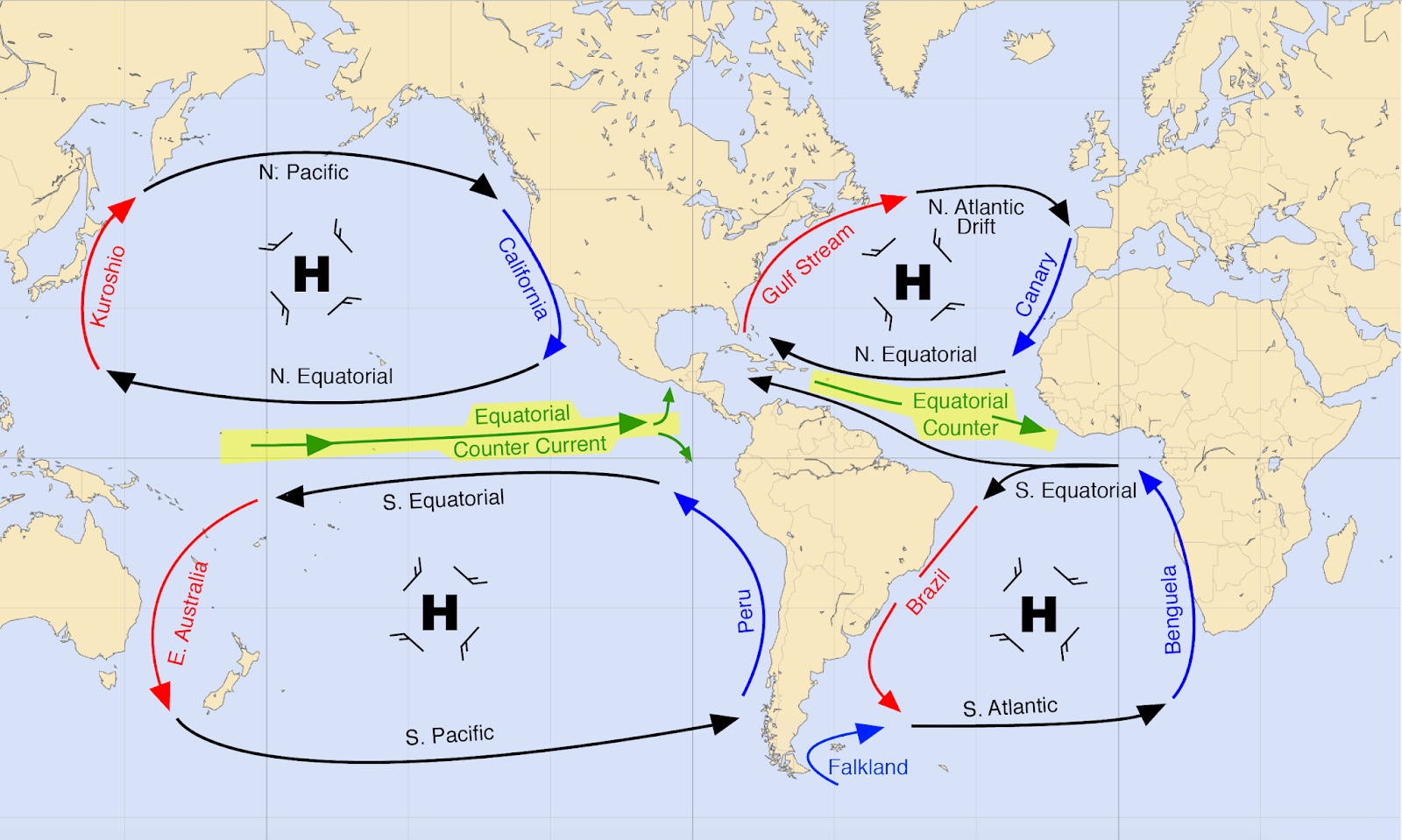
subpolar gyres
flows opposite of st gyres, above 60 degrees, when boundary currents flow into high latitueds and are then pushed by polar easterlies
ekman transport
net transport 90 to the right of wind but only in ideal conditions so usually 70
el nino period
trade winds get weaker or even reverse
east pacific warms up + thermocline becomes deeper + lower pressure (more rising air)
warmer and negative.
el nino 3.4 region becomes 0,5 C hotter.
bjerknes feedback
positive feedback system of enso
El nino reduced ocean temp contrast reduces trade winds which increases El nino & so on
la nina
trade winds extra strong
more cold water upwelling in east pacific, higher pressure
colder and positive
El nino 3.4 0.5 colder
sea water avg ph
8.1
how does ph change w/ depth?
surface is about 8.1, drops from 100-1000m from CO2 of animal respiration (since photosynthesis not happening so no counterbalence), then gradual increase after 1000m from carbonate buffering
carbonate buffering
CaCO3 (from organisms) neutralizes acids, H2CO3 is also a buffer
thermocline
layer where water temp changes rapidly w/ depth, usually between 300 - 1000m
greatest in low latitude and basically non-existent in high latitudes
highest impact on density
halocline
layer where water salinity changes rapidly w/ depth
low impact except at poles (bc poles isothermal)
pressure effect on ocean
density increases up to 5% bc of water
only significant in deep ocean
pynocline
layer where density changes rapidly with depth
decreases with increasing latitude
AABW (antarctic bottom water)
densest cold and salty water forming bc ice formation makes seawater very salty, which makes it sink
important in powering deep water circulation
north Atlantic deep water
second densest water from Greenland and sea sinking in the chimmenies,