FMSC Final - Labor and Delivery
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
obstetric dilemma
too little too late (delivering late/not enough care)
increased risk for other and newborn
don’t deliver early enough to save a mother and newborn
eclampsia
obstructed labor
too much too soon (excessive or early intervention)
increased risk for mother and newborn
cascade medical intervention
cesarean delivery
risks related to surgery
Modes of Delivery
vaginal birth
spontaneous
induced or augmented
assisted
forceps
vacuum extraction
cesarean birth
primary (first) or repeat (had a previous c-section)
low-risk (singleton, head-first, full term, not given birth before)
vaginal birth after cesarean
stages of labor and delivery - stage 1

stages of labor and delivery - stage 2

stages of labor and delivery - stage 3

secundagravidas (second-time mothers) vs nulliparas (first-time mothers) labor
labor is faster in women who have given birth before
women undergoing cesarean prior to progression? leads to faster cervical dilation compared to clinical standard labor
labor is non-linear
benefits of vaginal delivery
fewer medications if desired
more freedom to move
shorter hospital stay
breastfeed sooner
fewer complications in subsequent pregnancies (e.g., placenta previa, placenta accreta)
oxytocin - mother/infant bond
infant
less respiratory distress at birth
beneficial vaginal microbiome (reduces obesity, autoimmune conditions, and allergy/asthma)
risks of vaginal delivery
pain and exhaustion
perineal tears (3rd/4th degree)
hemorrhoids and bowel issues
urinary incontinence
pelvic floor trauma
negative reactions to epidural
(VBAC only) slightly higher risk of uterine rupture
the effect maternal microbioata has on the child
can influence child’s risk for disease
for example, if unhealthy microbiome (dysbiosis) can vertically transmit diseases to child
reasons for planned cesarean birth
*Can be life saving for mother/infant
Previous C-section
Expecting multiples
Placenta previa
Breech baby
Certain birth defects, Fetal macrosomia (big babies)
Uterine fibroid/obstruction/pelvic size
Maternal indication (e.g., HIV, herpes)
reasons for unplanned cesarean birth
*Can be life saving for mother/infant
Fetal distress
Failure to progress
Umbilical cord prolapse
Placental abruption
Maternal indication (pre-eclampsia
risks of cesarean birth
Infection
Loss of blood or excessive bleeding
Blood clot – embolism
Injury to bowel or bladder
Longer recovery
Longer hospital stay
Longer time to expression of breastmilk
Abdominal adhesions
Increased risk in future pregnancies (placenta accreta, uterine rupture)
risks of adverse maternal and neonatal outcomes by mode of delivery (vaginal delivery vs cesarean delivery)
maternal: vaginal delivery risk lower (8.6%) compared to cesarean delivery risk (9.2%)
neonatal - cesarean risk higher except for shoulder dystocia
global and regional rend pf ceserean delivery as years go by
percentage of cesarean section goes up as years increase
what is the variability between countrys for cesearean deliverys?
wide variability
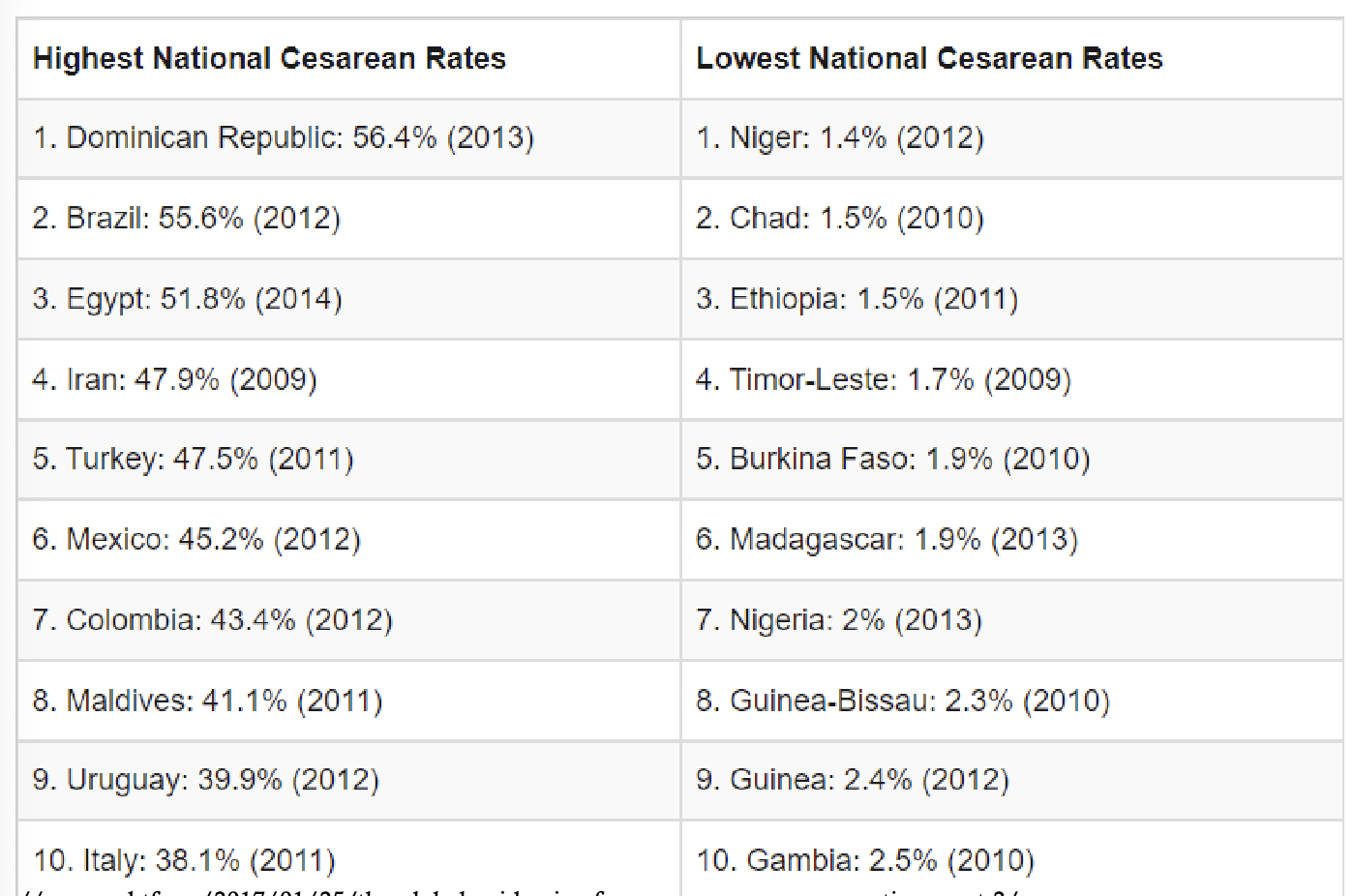
U.S. Cesarean delivery trends
steady decline in the early 1990s → increased rapidly from 1996 - 2009 → rate plateaued after
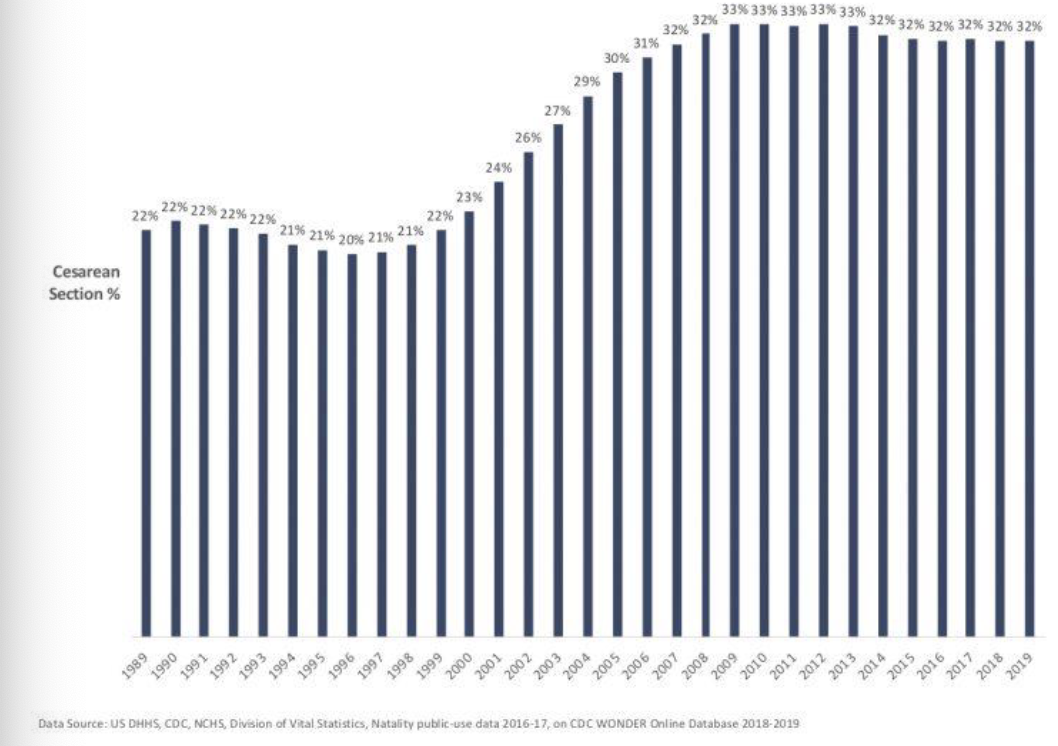
Cesarean rates by states
Increase in MD, and Florida regions
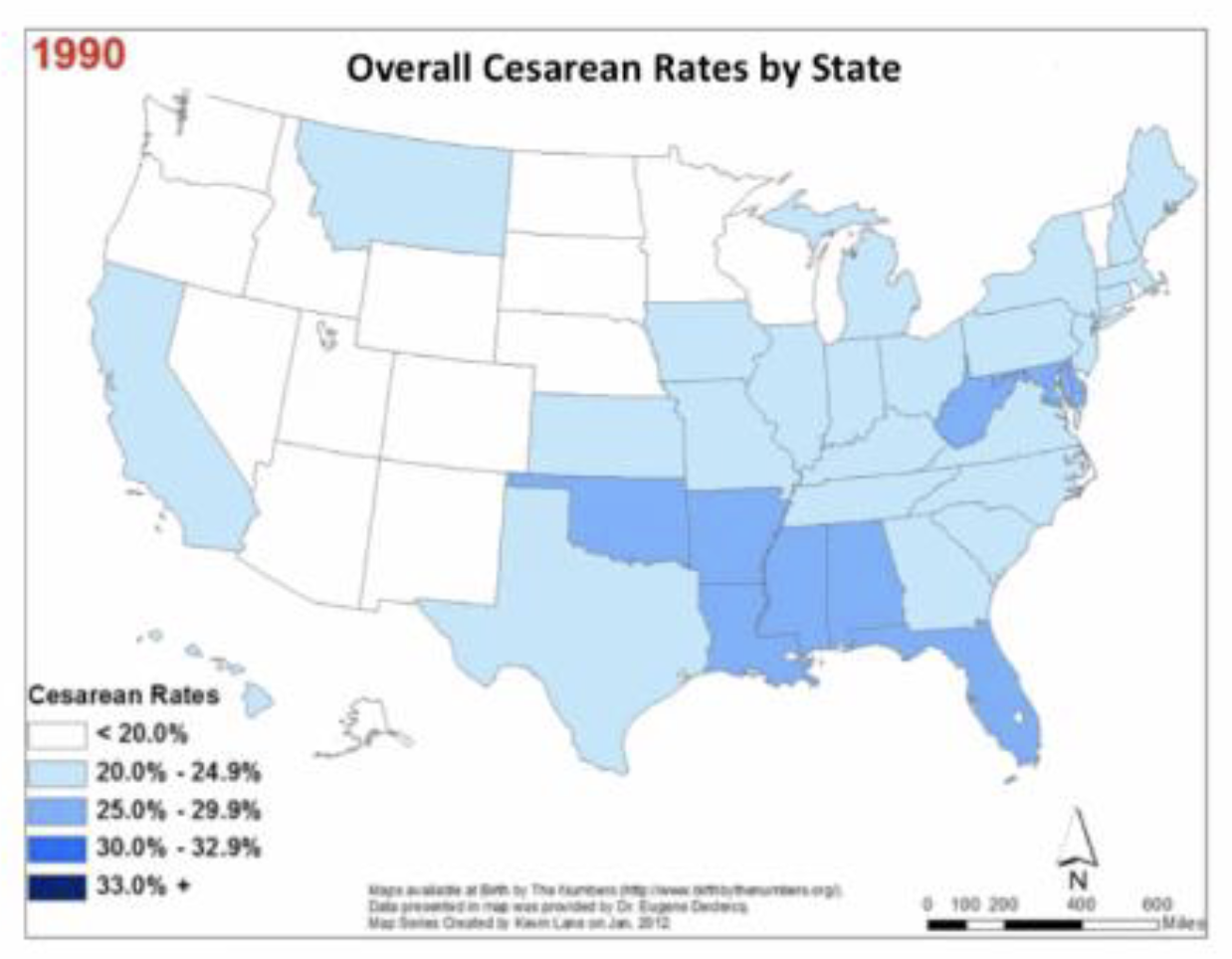
cesarean rates in U.S. vs M.D.
U.S: 32.3%
MD: 35%
what is a troubling epidemic for c-sections?
troubling epidemic of unnecessary c-sections around the world
what are commonly used explanations for the high cesarean rate?
mothers are getting older
more multiples being born
babies are getting bigger
maternal health is worse: obesity, diabetes, and hypertension
mothers are asking for elective cesareans
hospital practice patterns have changed - hospitals are doing C-sections for the same medical reasons as before, but they are deciding to do them earlier or with less strict criteria [same indications but lower threshold]
primary cesarean and VBAC rates as guidelines changed over time
Primary cesarean rate went up and VBAC rate went down
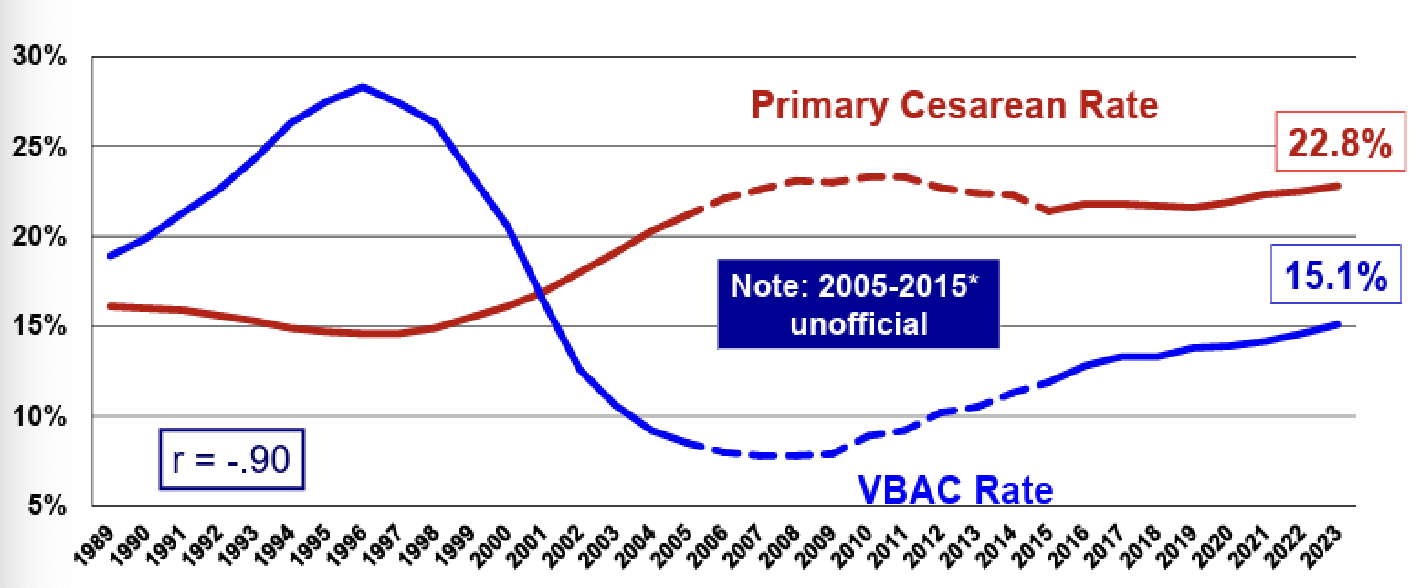
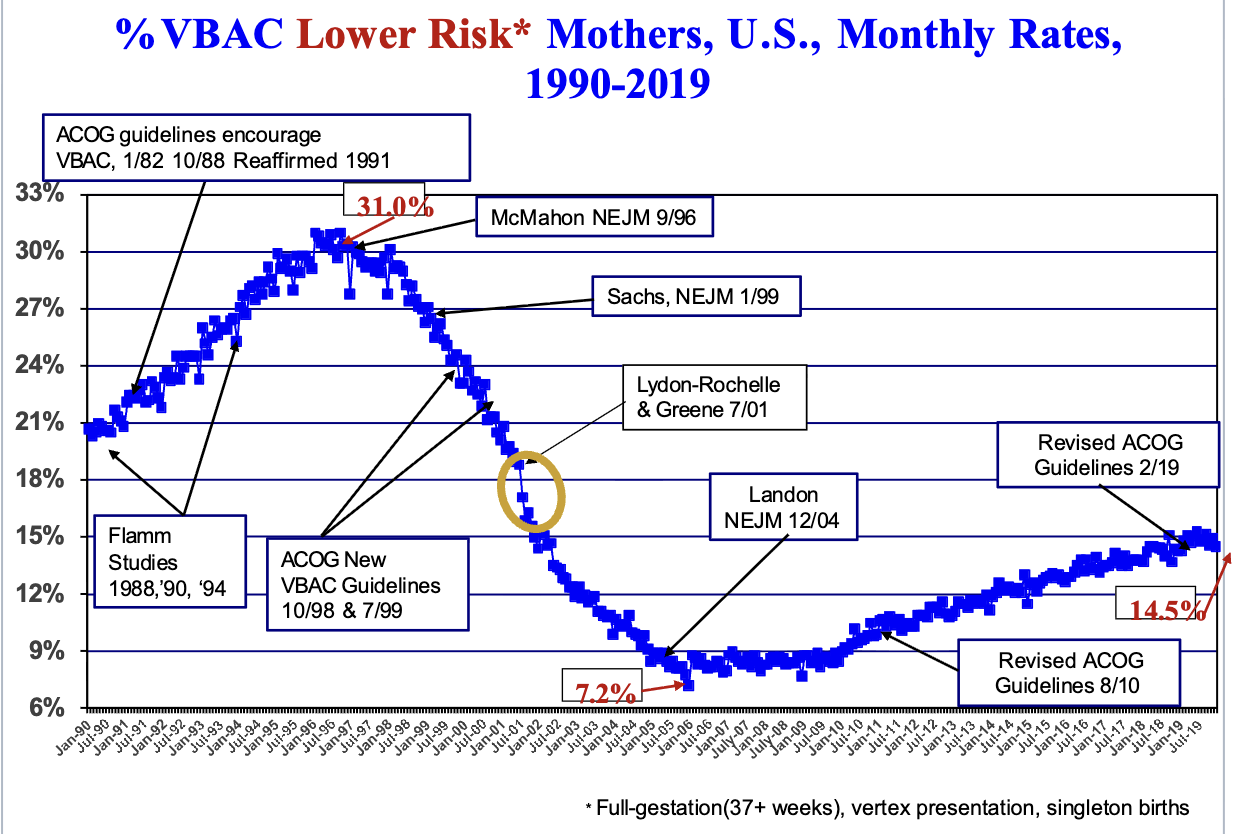
How do guidelines affect VBAC availability?
VBAC availability is extremely sensitive to guidelines
key factors in decision to perform C-sections
fear of litigation and legal consequences
perceptions of low risk and safety related to Cesarean delivery
Personal convenience by doctors, midwives viewed this as a reason for unnecessary Cesarean delivery, and disagreements in decision making and cooperation
influence of private health care systems
lack of hospital guidelines or lack of awareness of the guidelines
clinicians reported maternal request as one of the factors, influenced by preferences, demands, and fears/anxiety of the woman
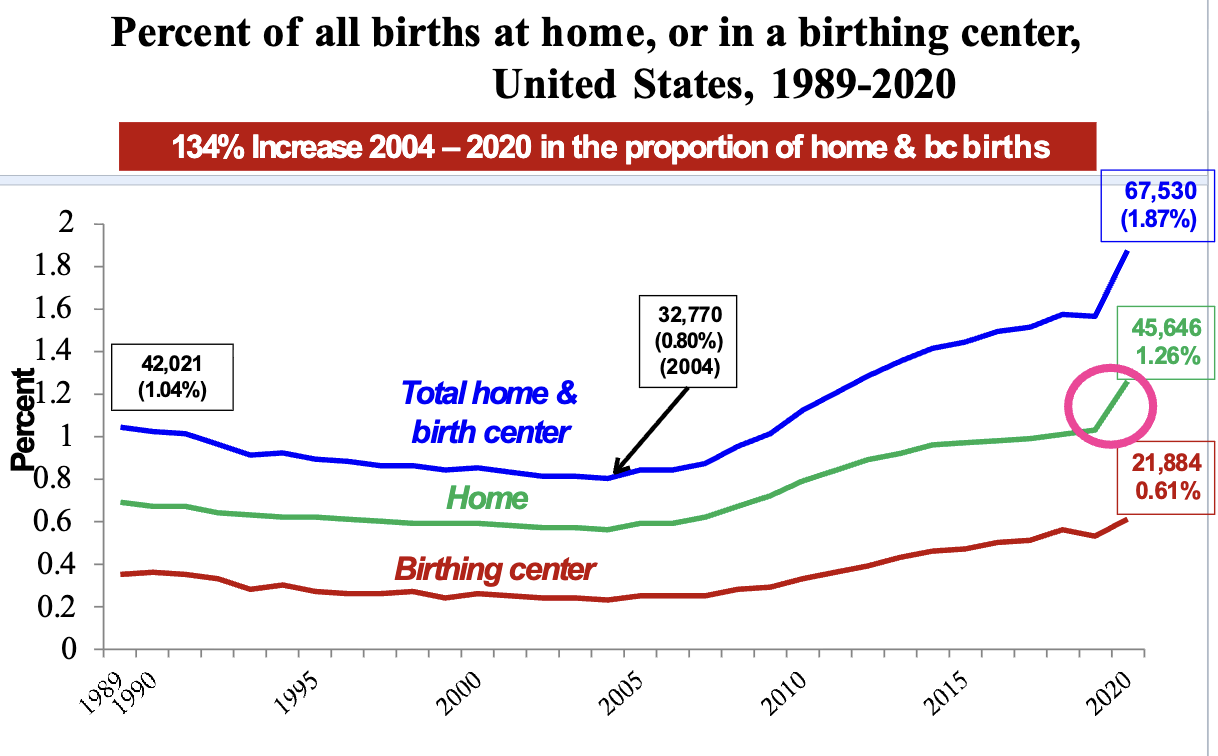
how has the proportion of home and birthing center births changed from 2004-2020?
134% increase 2004-2020 in the proportion of home and bc births
what can the healthcare system to reduce unnecessary c-sections?
remove incentives
evidence, review, feedback
publish c-section reimbursement rates (how much they make)
midwifery - led units
what can birthing people to reduce unnecessary c-sections?
ask questions
delay going to the hospital, if possible
midwives, doulas
research your hospital’s c-section rate
go to birth facility (connected to hospital)
summary
Obstetrics is balancing risks/benefits for both mother and infant
One of the few providers that is caring for 2 patients at once!
Vaginal delivery has benefits that extend beyond delivery
However, it is not without risks
The U.S. (and many other countries) Cesarean rates far exceed what may be medically necessary
Can be life-saving, but risks associated with Cesarean delivery
Reasons for these trends may have more to do with practice changes than changes in who is giving birth
Ways to advocate for changes