0.5 Vocab: biology review and intro to stats
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Central Tendencies
Tendency of observations to center around a particular value/category rather than spread evenly across the range/categories; mean, median, mode
Chi-Square
Form of statistical analysis used to compare the actual results (observed) with the expected results.
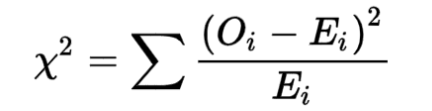
Constants
Controlled variables; factors kept consistent for all groups to ensure only the independent variable affects the outcome.
Control Group
A group not exposed to the independent variable in an experiment to act as a baseline for comparison.
Negative Control Group
A group not exposed to any treatment OR exposed to a treatment known to have NO effect.
Positive Control Group
Group not exposed to the independent variable but is exposed to a treatment known to have an expected effect.
Dependent Variable
Factor that is measured and affected by the independent variable; typically graphed on the y-axis.
Descriptive Statistics
Methods used to summarize or describe observations/samples, including measures of central tendencies and variability.
Experimental Group
Group exposed to the independent variable.
Hypothesis
Prediction that can be tested by recording more observations and experiments; often phrased as “if…then…because.”
Null Hypothesis
Hypothesis which the researcher attempts to disprove, reject, or nullify.
Alternative Hypothesis
Hypothesis that states there is a relationship between two variables.
Independent Variable
Factor that is changed between groups; what is being manipulated; variable that is graphed on the x-axis.
Inferential Statistics
Using observations to make estimates or predictions; generalizing from a sample to a wider population.
EX: SEM, hypotheses tests (t-test, chi-square, etc.)
Mean
Average of a data set.
Median
Middle number in a range of data points.
Mode
Value that appears the most often in a data set.
Range
Difference between the largest and smallest value in the data set.
Scientific Method
Step-by-step process used by scientists to investigate questions, gather evidence, and draw conclusions based on experiments and observations.
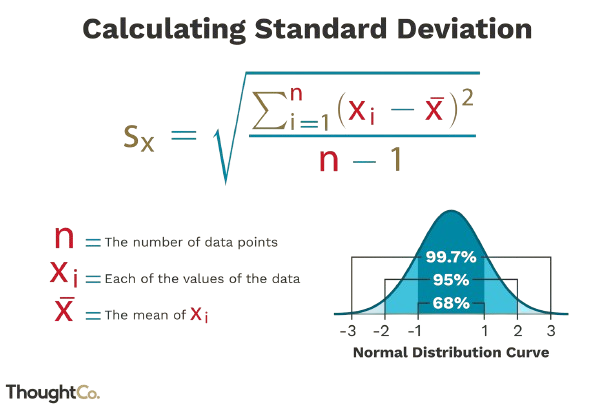
Standard Deviation
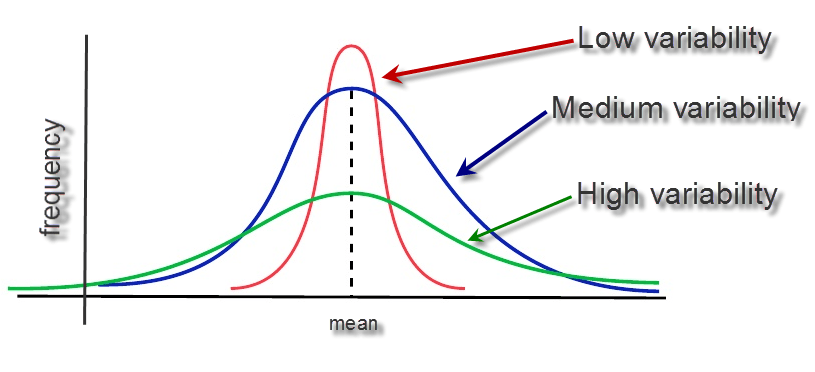
Measure of how spread out the data is from the mean.
Standard Error of the Mean
Used to determine the precision of and confidence in the mean value.

Statistics
Methods used to collect, process, or interpret quantitative data.
Variability
Measure of how spread out or dispersed the values in a data set are.