Simple Harmonic Motion
1/53
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is the definition of Oscillating Motion ?
Oscillating motion is when an object moves either side of an equilibrium position in the same plane.
What are the features of an equilibrium position?
Mid point of motion.
Object resides under no force.
Position in the motion where the object would like to reside.
The object is at its lowest potential state.
There is no restoring force.
Why don’t oscillating object stay at equilibirum?
Due to Inertia
What is the difference between Oscillating motion and simple harmonic motion?
SHM is an oscillation where the acceleration of the object is directly proportional to its displacement from its equilibrium position and is directed towards the equilibrium.
What is special about SHM?
What is Restoring Force?
A force that causes the oscillating object to return back to its equilibrium position.
The restoring force is directly proportional to the displacement from equilibrium.
In Circular motion, Restoring force acts to the centre of motion and similarly in SHM the restoring force acts to the centre of oscillation.
SHM can be represented by this expression :
This shows that the acceleration is directly proportional to the negative of displacement.
Therefore, Greater the displacement - Greater the acceleration.
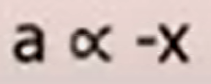
What are the different positions on which the pendulum would be when it is oscillating?
Phase 1 - Position where the pendulum would hang if there is no force placed upon it - Equilibrium position.
Phase 2 -
How can you represent the restoring force and displacement?
The negative sign implies that the restoring force and acceleration acts to the opposite direction of displacement.

What are the two conditions for SHM to be satisfied:
The acceleration is directly proportional to displacement.
The acceleration is in the opposite direction to the displacement. (towards the equilibrium point.)
Therefore this acceleration is known as restoring acceleration as this brings the object back to the equilibrium.
What is the phase difference of one cycle
2Π radians or 360
What are the different stages of an oscillating cycle?
Point 1 - Object is displaced in the negative direction.
It is released and sings through point 2 at its maximum speed.
Until it reaches point 3 where it comes to a complete stop because it has reached its maximum displacement.
It then swings to the negative direction reaches maximum speed at point 5.
It the completes a full cycle.