StemUp: AQA A level Biology 3.4.1 DNA, genes and chromosomes
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
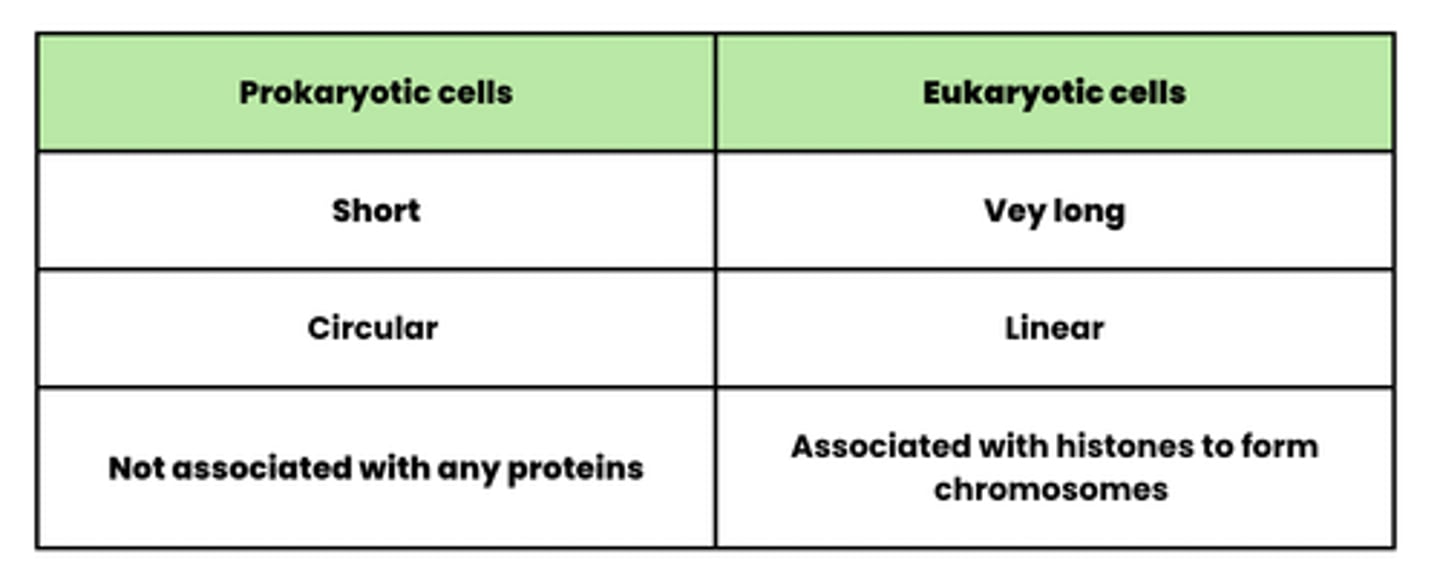
Describe the properties of the DNA molecules present in prokaryotic cells (3)
- Short
- Circular
- Not associated with proteins
Describe the properties of the DNA molecules present in eukaryotic cells (3)
- Very long
- Linear
- Associated with histones (a protein)
How are chromosomes formed? (2)
DNA + histones join together
Compare the DNA present in prokaryotic cells with the DNA present in eukaryotic cells (6)
Please use comparative terminology when comparing!!
NOTE: The DNA in mitochondria and chloroplasts possess similar properties to the DNA in prokaryotic cells
What is a gene? (3)
- A sequence of DNA bases
- Which code for the specific amino acid sequence of a polypeptide
- And code for functional RNA e.g. ribosomal RNA and tRNAs
What is meant by a 'locus'? (2)
- Fixed position that a gene occupies
- On a particular DNA molecule or chromosome
What is a base triplet in DNA? (2)
- A sequence of three nucleotide bases
- That code for a specific amino acid
What are codons? (1)
Base triplets in mRNA
What is the genetic code? (1)
The instructions contained in a gene that tell a cell how to make a specific protein
NOTE: this is not a definition that you need to memorise, you just have to understand it for application based questions
What are the three features of the genetic code? (3)
- Degenerate
- Non-overlapping
- Universal
Describe the 'degenerate' feature of the genetic code (1)
More than one triplet could code for the same amino acid
Describe the 'non-overlapping' feature of the genetic code (1)
Each base is only read once as part of a specific triplet
Describe the 'universal' feature of the genetic code (1)
The same triplet codes for the same amino acids in all organisms
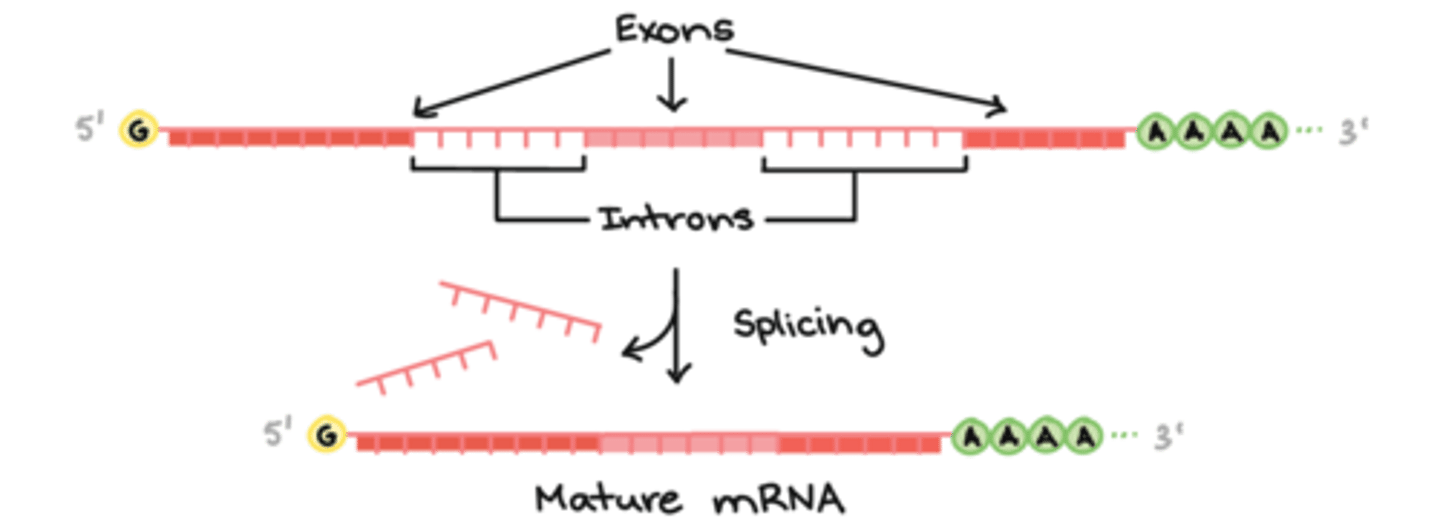
What are introns? (2)
- Non-coding part of a gene
- Base sequences present within genes but do not code for amino acids
What are multiple repeats? (3)
- Non-coding part of a gene
- Some of the base sequences present between genes
- That consists of the same base sequence occurring again and again
What are exons? (2)
- Coding part of a gene
- Base sequences in genes that code for amino acids
Describe how exons and introns are related to each other in a DNA sequence (2)
In the DNA sequence (top sequence), exons are separated by introns