APHUG Unit 1 Key Terms
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
from barrons review guide
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Absolute distance
A distance that can be measured with a standard unit of length, such as a mile or kilometer.
Absolute location
The exact position of an object or place, measured within the spatial coordinates of a grid system.
Accessibility
The relative ease with which a destination may be reached from some other place.
Aggregation
To come together into a mass, sum, or whole.
Anthropogenic
Human-induced changes on the natural environment.
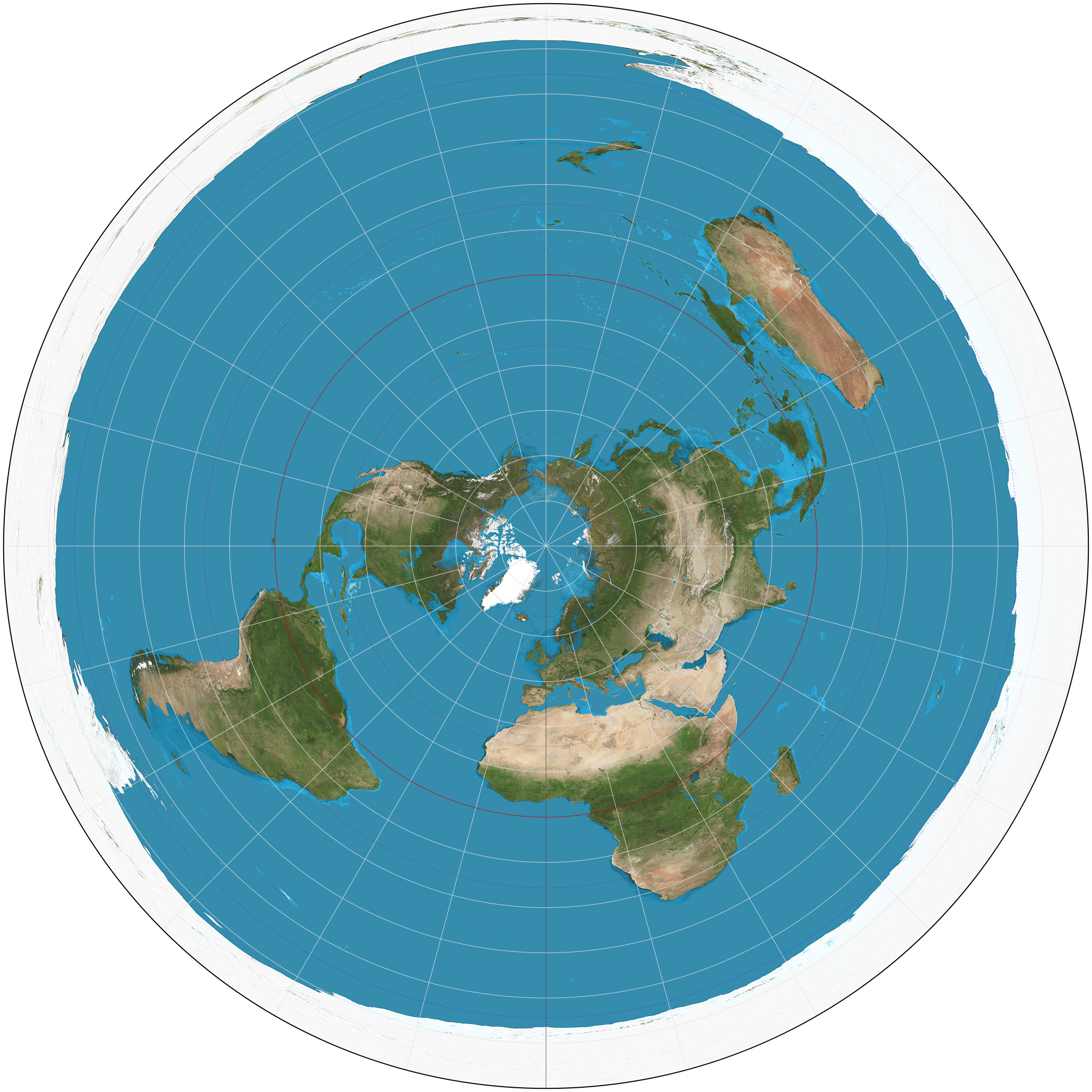
Azimuthal projection
A map projection that shows the Earth's surface as if it were viewed from a point above it, typically from a pole or the equator.
Breaking point
The point where people stop going to one city for shopping or services and start going to a different, closer one.
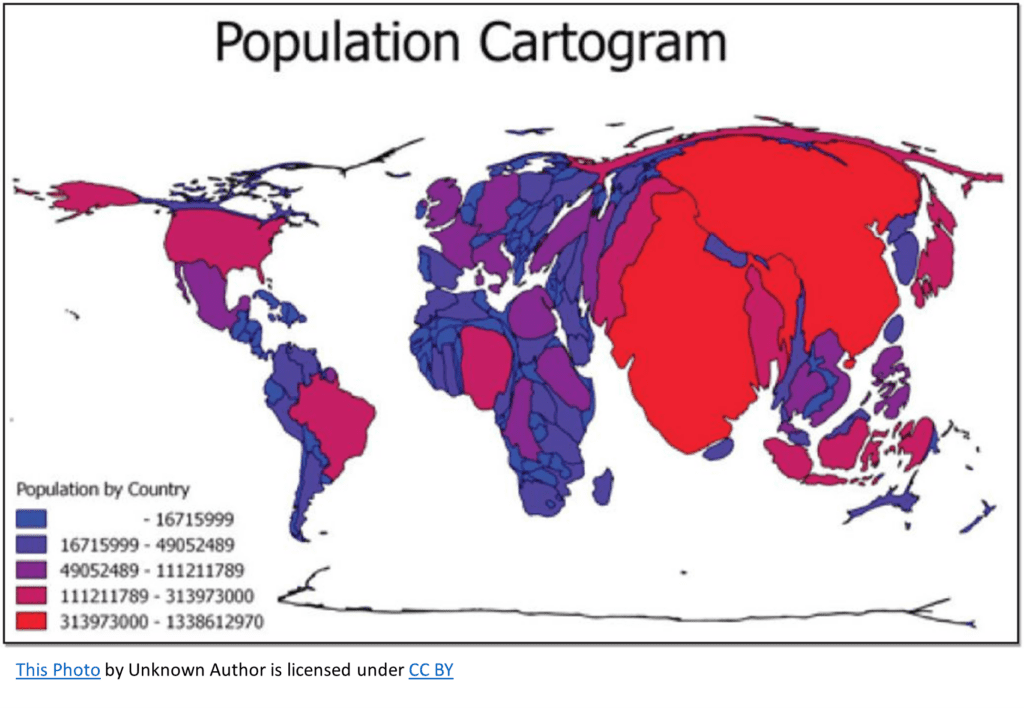
Cartograms
A map that changes the size of places to show data, like population or income, instead of actual land area. Done according to a specific statistic, often distorting the actual shapes and distances of regions.
Cartography
The theory and practice of making visual representations of Earth’s surface in the form of maps.
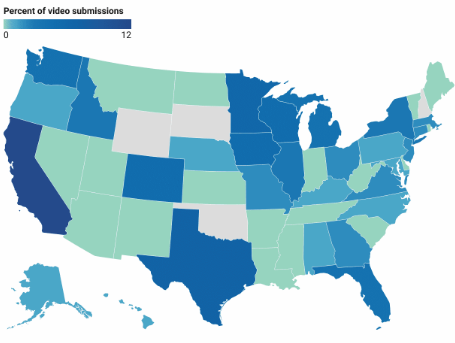
Chloropleth map
A thematic map that uses tones or colors to represent spatial data as average values per unit area.
Cognitive map
An image of a portion of Earth’s surface that an individual creates in his or her mind. Can include knowledge of actual locations and relationships among locations as well as personal perceptions and preferences of particular places.
Complementarity
The actual or potential relationship between two places, usually referring to economic interactions.
Connectivity
The degree of economic, social, cultural, or political connection between two places.
Contagious diffusion
The spread of a disease, an innovation, or cultural traits through direct contact with another person or another place.
Coordinate system
A standard grid, composed of lines of latitude and longitude, used to determine the absolute location of any object, place, or feature on Earth’s surface.
Cultural ecology
Also called Nature-Society Geography, the study of the interactions between societies and the natural environments in which they live.
Cultural landscape
The human-modified natural landscape specifically containing the imprint of a particular culture or society.
Distance Decay Effect
The decrease in interaction between two places or people as the distance between them increases.
Dot maps
Thematic maps that use points to show the precise locations of specific observations or occurrences, such as crimes, car accidents, or births.
Earth system science
A systematic approach to physical geography that looks at the interaction between Earth’s physical systems and processes on a global scale.
Environmental geography
The intersection between human and physical geography, which explores the spatial impacts humans have on the physical environment and vice versa.
Expansion diffusion
The spread of ideas, innovations, fashion, or other phenomena to surrounding areas through contact and exchange.
Formal region
A region defined by one or more measurable, shared traits that distinguish it from surrounding area such as political boundaries, climate, or language.
Friction of distance
A measure of how much absolute distance affects the interaction between two places.
Fuller projection
A type of map projection that maintains the accurate size and shape of landmasses but completely rearranges direction such that the four cardinal directions— north, south, east, and west—no longer have any meaning.
Functional region
A region organized around a central node or focal point, with surrounding areas linked to it by transportation, communication, or economic activities.