Lecture 6: theoritical approaches in urban archeology (part 2)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
what’s another name for “new archeology”?
processual archeology
why do we say that procedural archeology is a critique of the old archeology? (3)
projects didn’t have a structure: no hypothesis
focused on artefacts, not people
don’t try to understand the past
what was the goal of processual archeology?
to move away from object description towards humans
what are the scientific characteristic used for processual archeology? (2)
nomothetic: scientific laws established around the world
quantitative approach: no qualitative evidence, must be as objective as possible
why did early cities have social inequalities?
it was the result of the concentration of growth
define “settlement patterns”
distribution of archeological sites over the landscape
relation between sites and environment
what was the goal of settlement patterns?
to understand the relationship between sites, landscapes and neighbourhoods (entire region)
define “archeological survey”
method used to collect information about the location of sites
what’s the difference between an archeological survey and a settlement pattern?
survey: find sites, explore it
settlement pattern: understand spatial distribution across landscape
you need to do a survey before doing this
what can settlement patterns inform us of? (5)
economic strategies
defensive concerns
religious/ritual activities
demography and population
political relationships and organization
explain the central place theory
the landscape is a system of trade between places: consumers would go to the nearest town to get goods
efficient hexagon: the hexagonal organization ensures that you have all services close by
cities are at the center, town and villages are on the outside
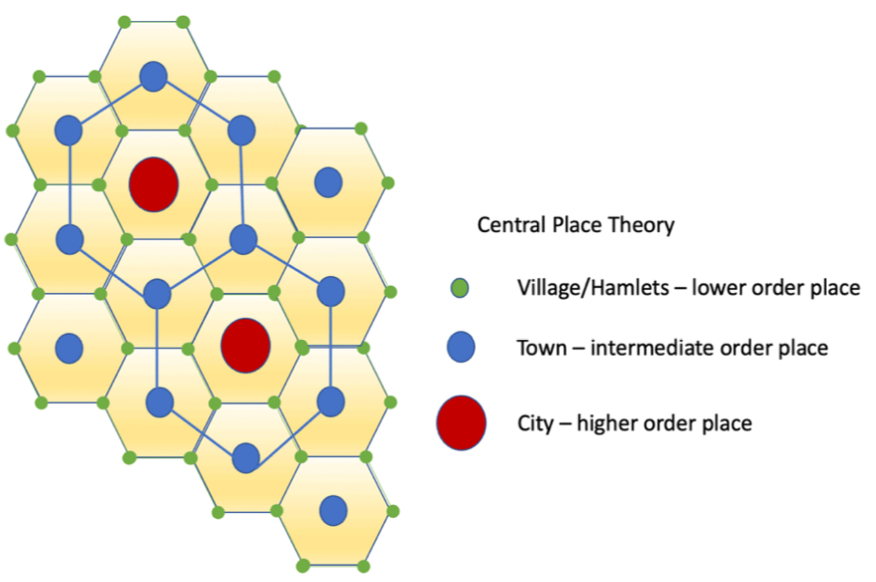
why is the central place theory only theoritical?
because in real life, the landscape isn’t flat or sometimes has obstacle
archeology isn’t only about the size of the city but also about […]
the siege of market place
what’s the difference between settlement patterns and central place theory?
pattern: how are city organized
cities: organized in an hexagonal shape
according to Richard Ford, how could use cities for the present? (3)
find the benefits of doing archeology: examine the past to have a better present
learn from past environmental management: have better agricultural system
focus more on cities than villages because they have more impact on the environment
why did we go from processual to post-processual archeology? (3)
archeology is a social science, not a pure science: you need to leave room for ideology (things that aren’t quantitative)
meaning, you can’t have laws that apply for everywhere
we want to focus on the role of material culture: what’s the meaning of this object, how did it impact people
archeology can’t be objective
[Ian Hodder/Lewis Binford] influenced [processual/post-processual] archeology
processual: Lewis Binford
post-processual: Ian Hodder
what’s the difference between structure and agency according to Anthony Giddens?
structure: rules and resources are used by institutions to control social systems
agency: humans can make their own choices and are aware of the consequences
sometimes said as free-will
define “structures”
rules and resources are used by instructions to control social systems
define “agency”
humans are aware of their conditions and of the consequences of their actions, but can still make their decision
also called free-will, but debatable
true or false: sometimes, agency can produce unintended consequences
true
what can the balance between structure and agency help us understand?
how people were thinking: culture, belief
how can you apply agency today?
you can understand why people live this way by understand their ancestor: agency was a way of perpetuating tradition
why do we say that cities are built by agencies?
because cities are built by multiple people who have different interests
reminder: agency = we can act independently and do what we want (within limits)
explain “top-down rule”
strategies, processes and decisions are decided by rulers and imposed on society (top to bottom)
explain the “bottom-up rule”
strategies, processes and decisions are started by agents (commoners) and slowly impact the society as a whole (bottom to up)
explain the difference between top-down and bottom-up
top-down: ruler to people
bottom-up: people to entire society
what happens if you combine understanding top-down and bottom-up rule?
you see that everyone transformed society at the same time
why do some say that objects/buildings have agency?
because we depend on them and they impact our lives
why did Wheatley believe that cities started because of religion and no evolution (hunting to agriculture to irrigation, etc)? (3)
early cities were actually small religious centers
people were attracted there before the religion
then, people settles down permanently
true or false: according to Paul Wheatley, people created cities for political reasons
false: they created cities because of religion and rituals
true or false: all traditional centers around the world shared certain features, characteristics or organizations
true
define “exemplary ceremonial center”
symbolic replication of the natural and supernatural world
you have miniatures representation of places, people, gods, etc
why did Wheatley that cities were cosmograms? (big sacred maps)
because cities are organized in meaningful ways (cardinal direction, constellation) and it can be seen with streets, location or buildings
define “axis mundi”
place where ceremonial sites are because it’s a place of communication between the human and supernatural world
why do we say that traditional cities have a rigid layout?
because the centre was controlled by the elite (key member). the less important you are, the further away you are from the centre
why was it important to have ritual performances?
to reinforce the link with religion and to help leaders justify their goals
what can performances help us understand?
how events transformed and shaped identities and societies
what are the characteristics of a performance? (4)
place: built with special material
elites = ritual specialists: strengthen their power
cyclical performance: to maintain the gods in your favorited
restricted access: not everyone could see the performacne
true or false: the formation of a city can be considered as a performance
true
what are our current understanding of cities? (3)
ancient cities are more heterogeneous than we thought: it varies from culture and region
we still can’t find an agreed definition for a city
we want to find the link between early states and cities
explain the traditional explanation for city development
cities are the consequences of new rulers (top-down):
elite is created
they create a city
they create a religion to keep the power
the power is kept within a family, so it’s difficult to gain position on top
why is the idea that cities are based on a top-down model challenged? (2)
there was a difference in status, but sometimes the power was shared
mechanisms were put so that people could exercise their agency
how can we define a city? (2)
demography/sociology: permanent settlements, population size, social heterogeneity
functional: role of city for people and institutions that affect the larger realm
→ we should combine both to define a city
define “overburden”
a city is built on top of another, meaning you can’t always find the foundations of it
what are the aspects you should focus on to understand a city? (5)
ceremonies, procession ways, sacred areas: religion, rituals
technologies: writing, calendar
change in urban landscape: change on the environment
economy and influence: import/export
social inequality and hierarchy
what are the stages of a city? (4)
settlement/founding
transformation
abandonment
reoccupation
true or false: if you examine a city closely, you can see all the changes
false: you can see the major transformations, but not the small ones
what are the characteristics that makes us choose where to build a city? (3)
economy: potential for market place and attract others
security: after war or natural disasters
religion: you should build here
what are the components of a ritual centre according to Wheatley? (5)
exemplary replication of the natural and supernatural world
cosmogram
axis mundi
template for social, political and moral order
place of ritual performance