Mechanical Waves
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
mechanical waves
waves that require a medium through which to travel
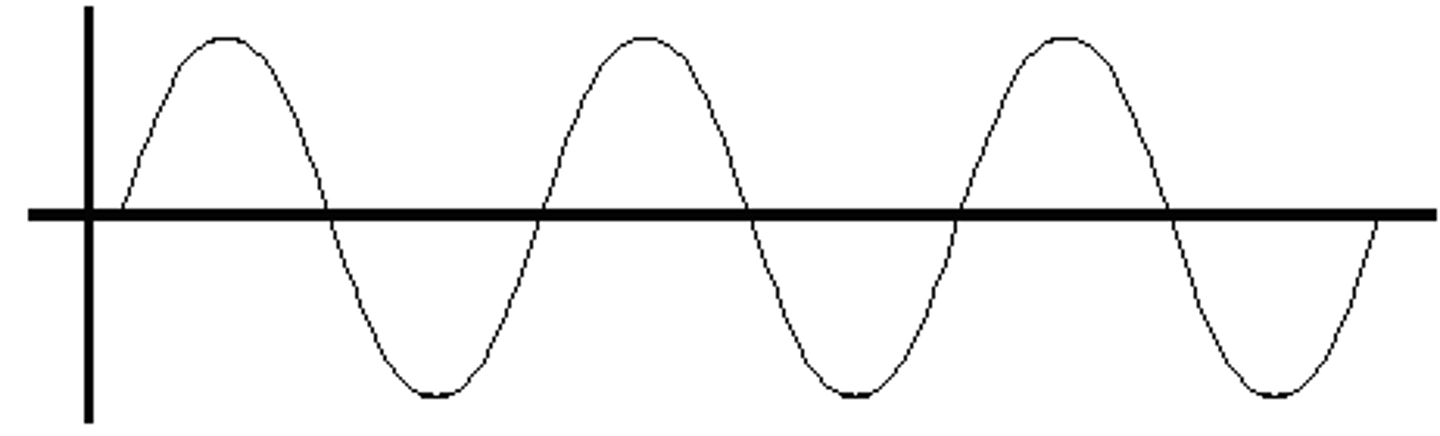
transverse waves
A wave that causes a medium to vibrate at right angles to the direction in which the wave travels.
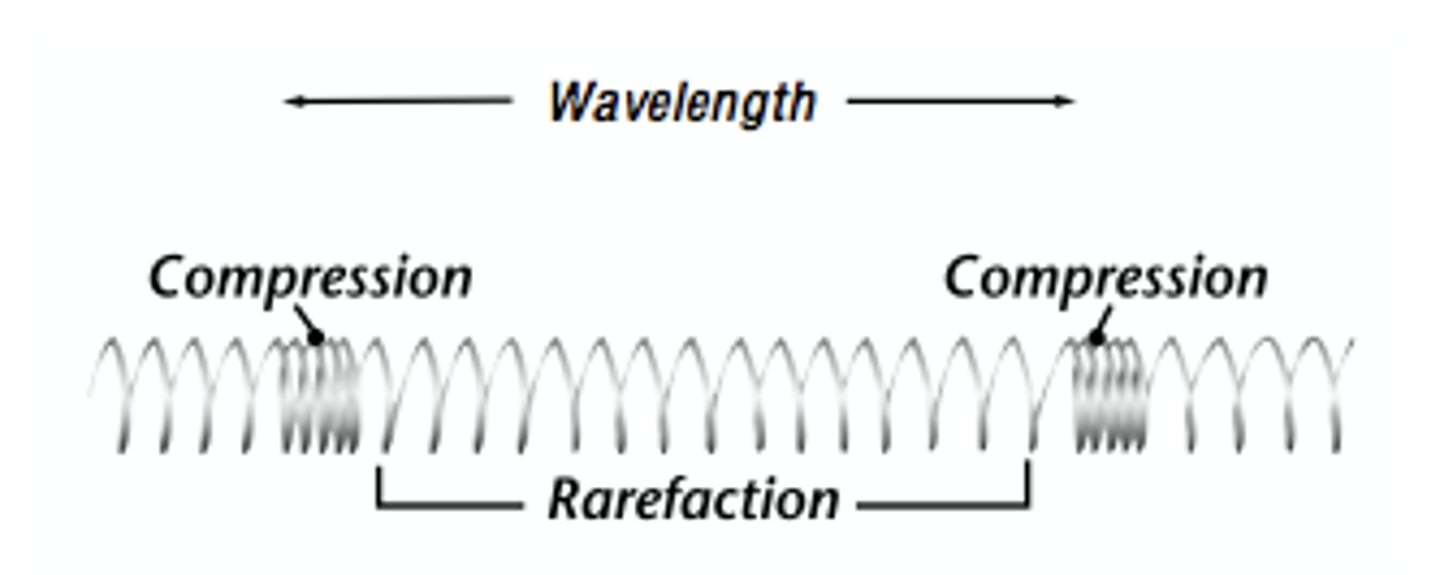
longitudinal waves
A wave in which the vibration of the medium is parallel to the direction the wave travels.
transverse wave picture
longitudinal wave picture
amplitude
Height of a wave from the rest point
frequency
the number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time
wave speed
frequency x wavelength
wavelength
The distance between two corresponding parts of a wave
medium
Material through which a wave travels
reflection
The bouncing back of a wave when it hits a surface through which it cannot pass.
refraction
The bending of a wave as its speed changes when passing from one medium to another
crest
Highest point of a wave
trough
Lowest point of a wave
compression
The part of a longitudinal wave where the particles of the medium are close together.
rarefaction
a part in a longitudinal wave where the particles are spread apart
Hertz
Unit of frequency
diffraction
The bending of a wave as it moves around an obstacle or passes through a narrow opening
Interference
The interaction of two or more waves that combine in a region of overlap.
constructive interference
The interference that occurs when two waves combine to make a wave with a larger amplitude
destructive interference
The interference that occurs when two waves combine to make a wave with a smaller amplitude
Standing Wave
a wave that appears to stand in one place, and does not seem to move through a medium.
node
A point on a standing wave that has no displacement from the rest position
antinode
a point of maximum displacement midway between two nodes in a standing wave
decibel
a unit that compares the intensities of different sounds
loudness
A physical response to the intensity of sound, modified by physical factors
pitch
the frequency of a sound as a listener perceives it
Sonar
used to determine the distance between objects underwater
Doppler Effect
A change in sound frequency caused by motion of the sound source, motion of the listener, or both.
resonance
the response of a standing wave to another wave of the same frequency, causing an increase in amplitude
surface wave
A wave that travels along a surface separating two media
periodic motion
any motion that repeats at regular time intervals
period
The time required for one complete cycle of a periodic motion
sound waves
a longitudinal wave that we can hear consisting of compressions and rarefactions, which travels through a medium
intensity
the rate at which a wave's energy flows through a given unit of area