Collision Theory + Maxwell Boltzmann Curves
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What are the 5 factors affecting rate of reaction?
-Concentration(solids)
-Surface Area(solutions)
-Pressure(gases)
-Temperature
-Catalysts

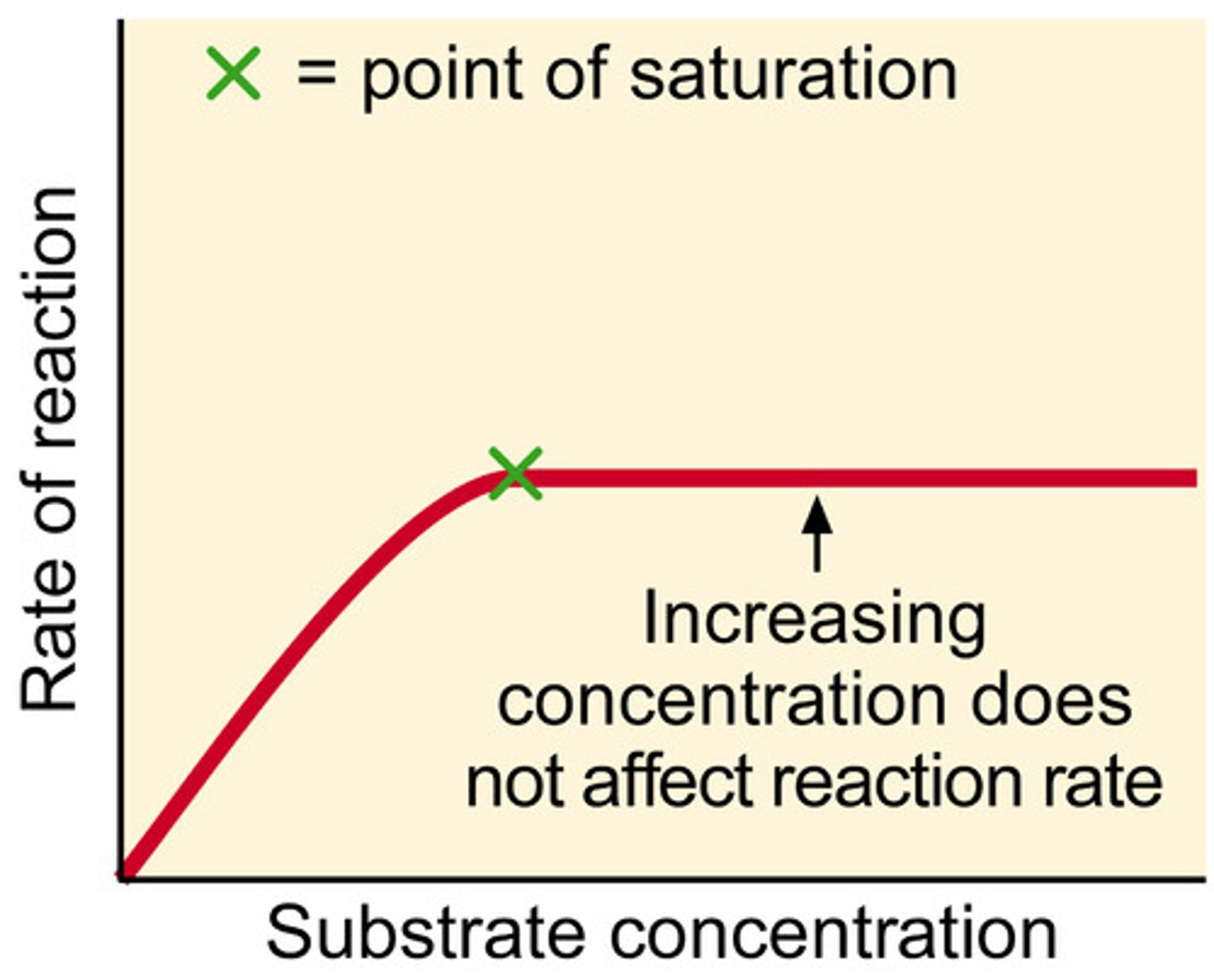
How does concentration affect the rate of reaction?
-There is a greater concentration of reactants or products, so there is a higher frequency of successful collisions, therefore increasing the rate of reaction
How does pressure affect the rate of reaction?
-It brings gas particles closer together, so it increases the frequency of successful collisions, hence increasing the rate of reaction

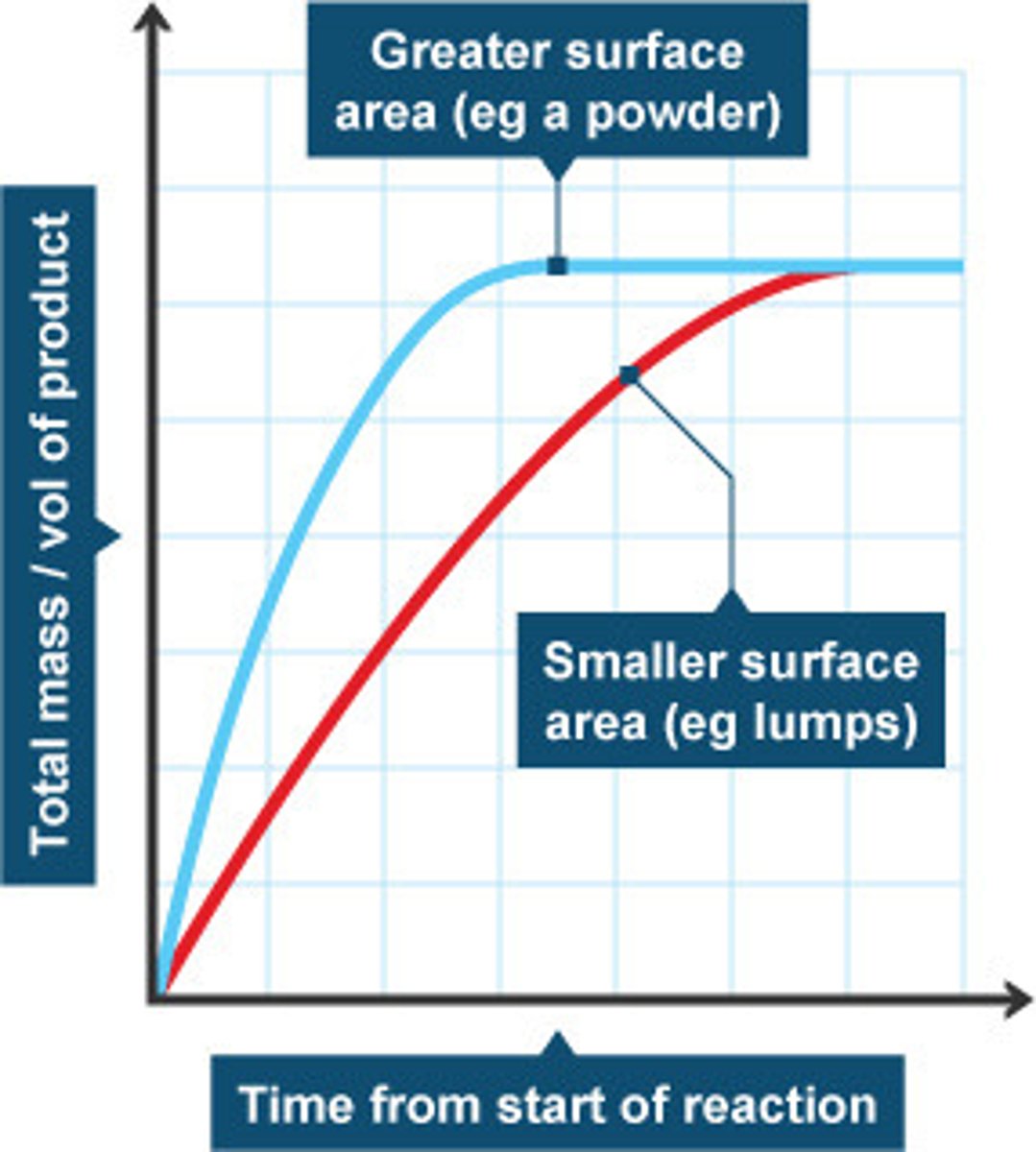
How does surface area increase the rate of reaction?
-Increasing surface area means that there is a greater surface exposed for collisions, increasing the collision frequency, increasing the rate of reaction
How does temperature increase the rate of reaction?
-Increasing the temperature means that more particles have a higher kinetic energy, so it increases the frequency of successful collisions as well as the fact that there's more energy to overcome activation energy, increasing rate of reaction

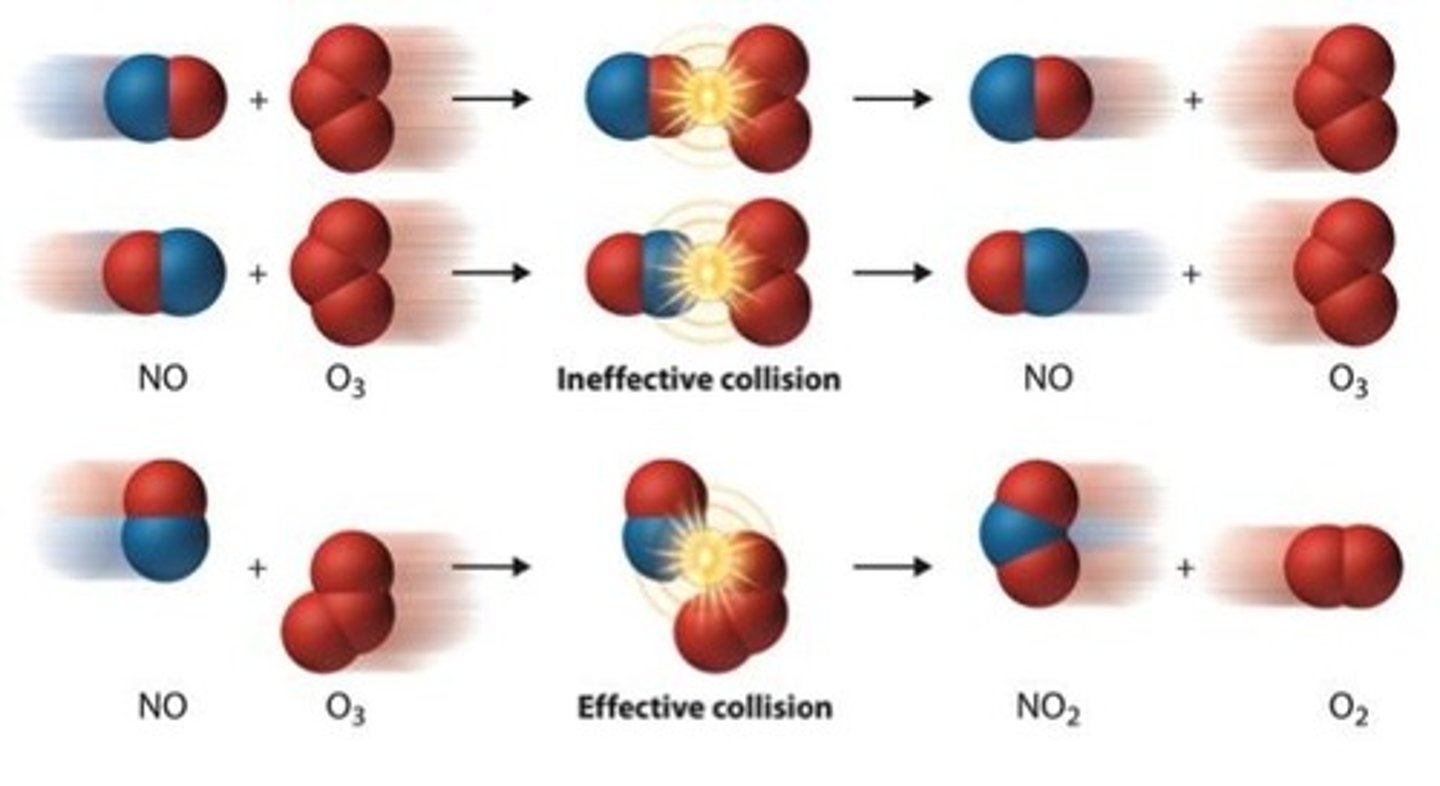
What are the rules of collision theory?
-Particles must collide with sufficient energy
-Particles must collide at the correct orientation
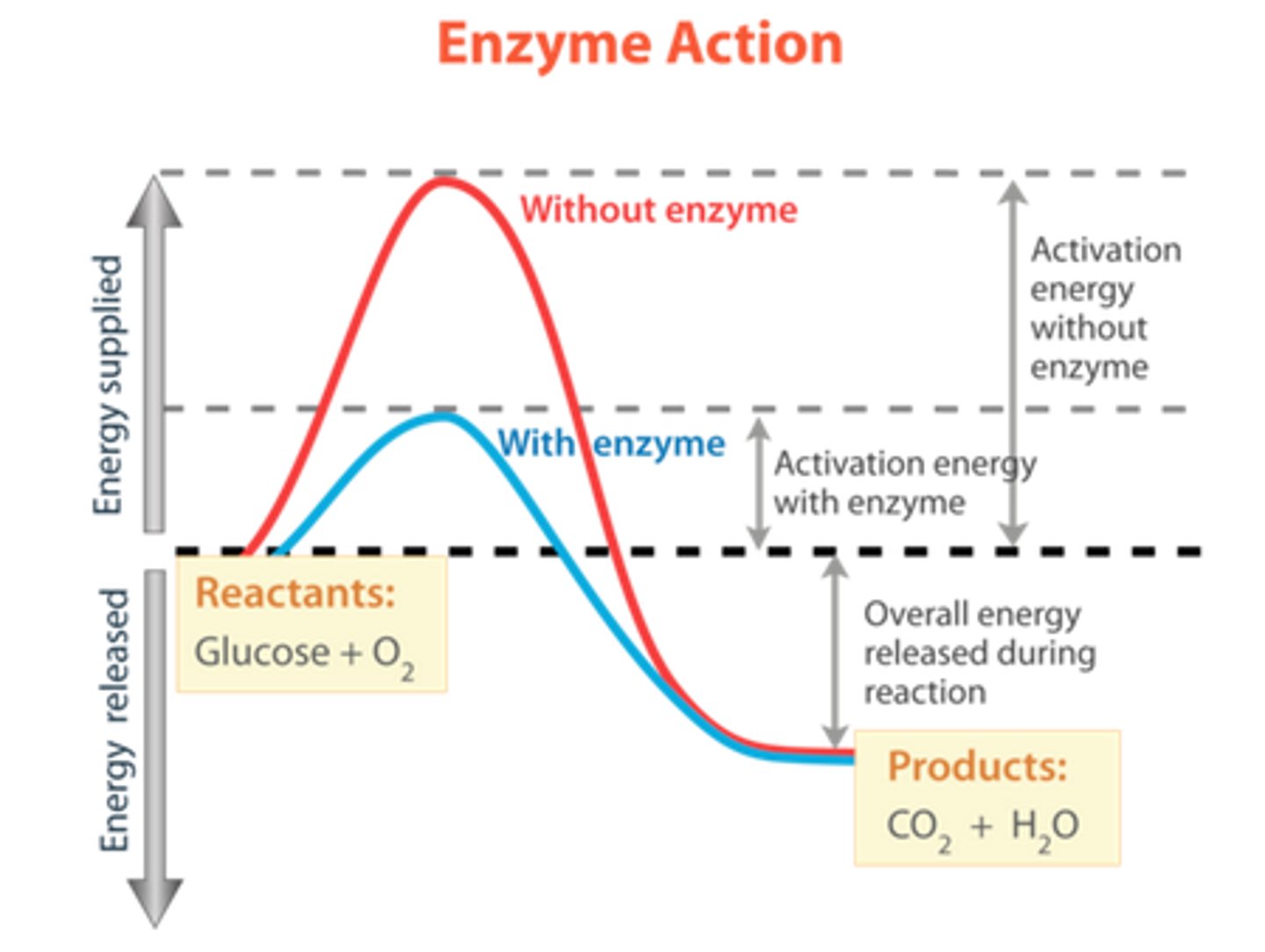
What is activation energy?
the minimum amount of energy needed to start a reaction
What is reaction rate?
The change in concentration of a reactant/product per unit time
FORMULA: Amount of reactant used/product made ÷ Time
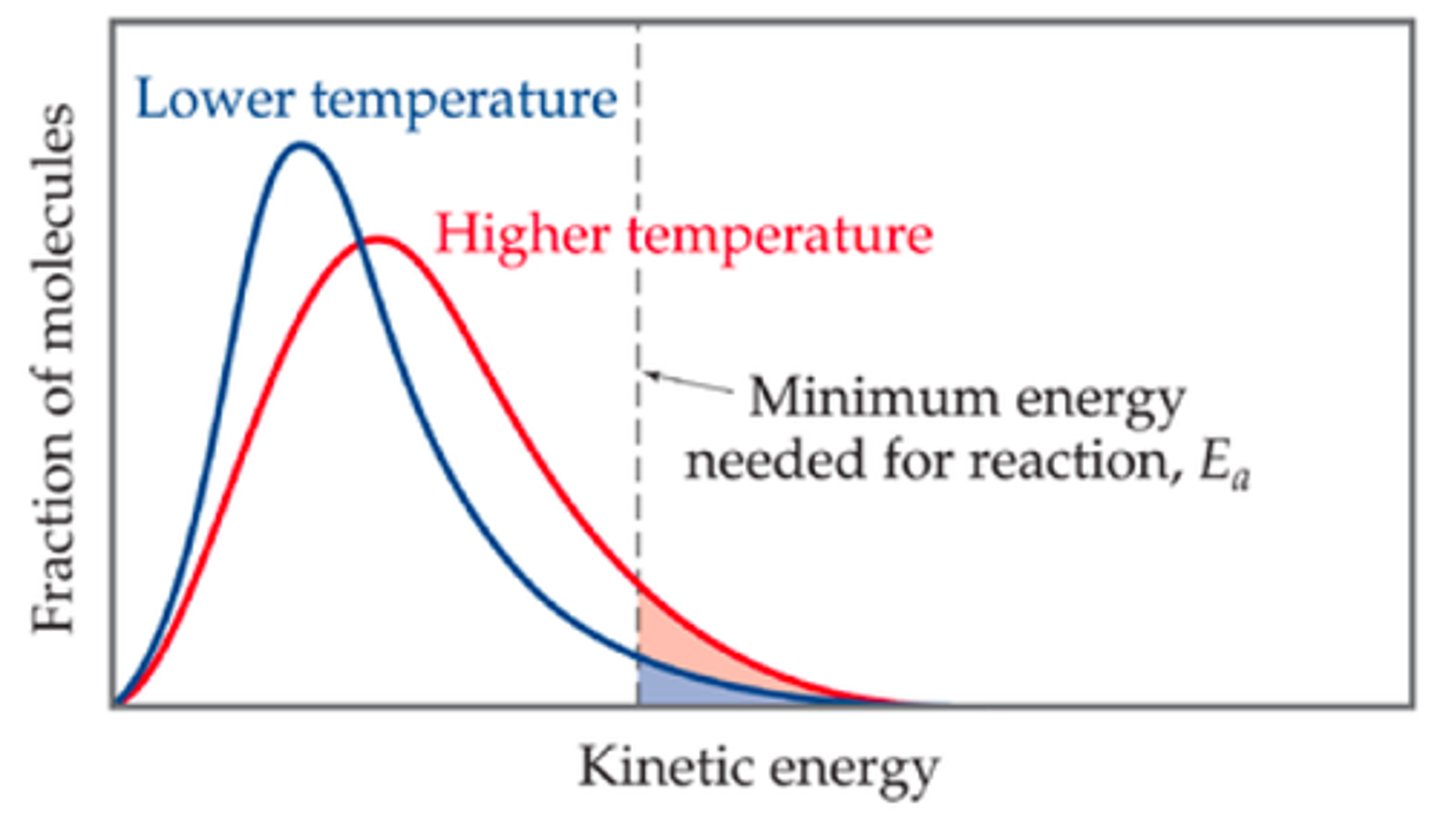
What is a Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution curve?
A graph that shows the distribution of energies at a certain temperature
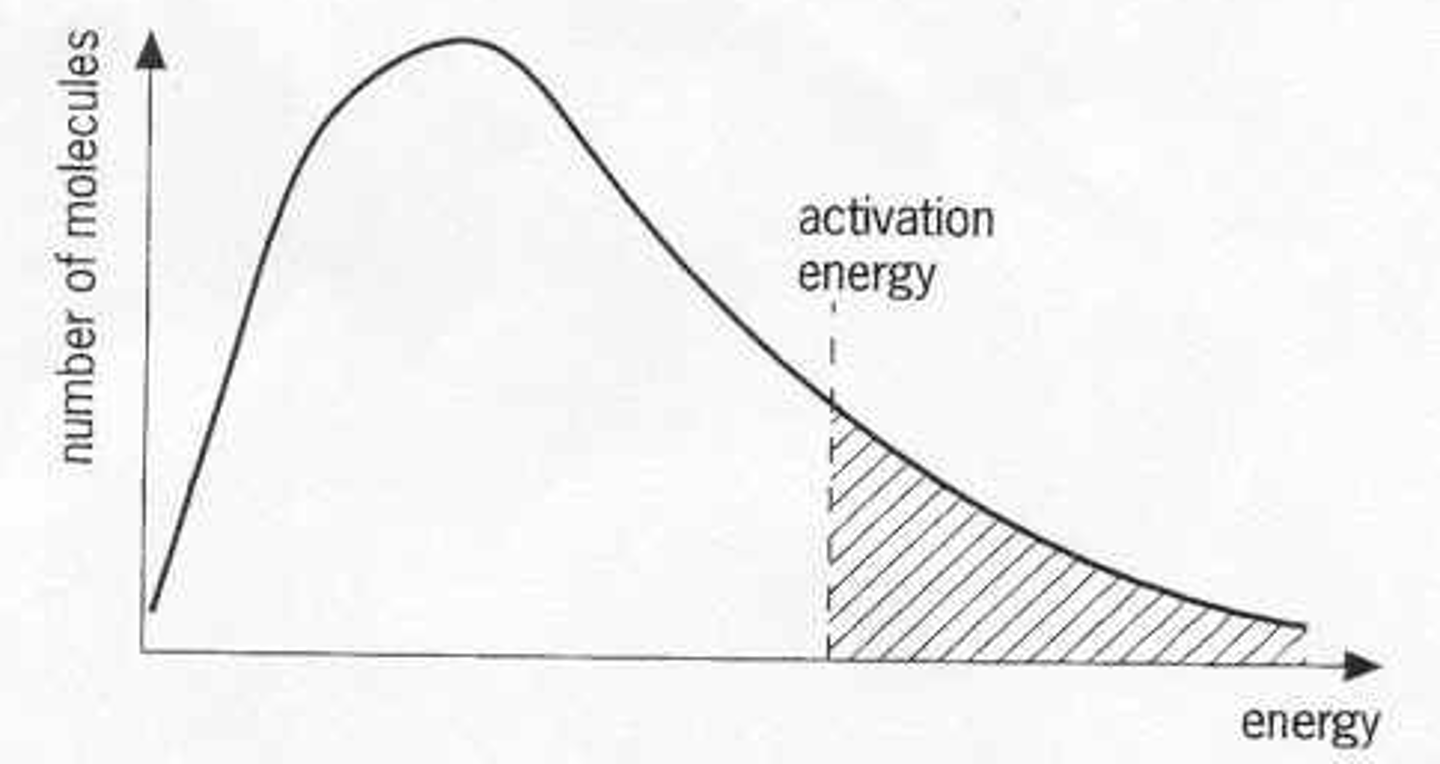
Why does a Maxwell-Boltzmann curve start at the Origin?
-Since there are no molecules with no energy in a sample
What does the peak in a Maxwell-Boltzmann curve represent?
-The most probable energy among molecules
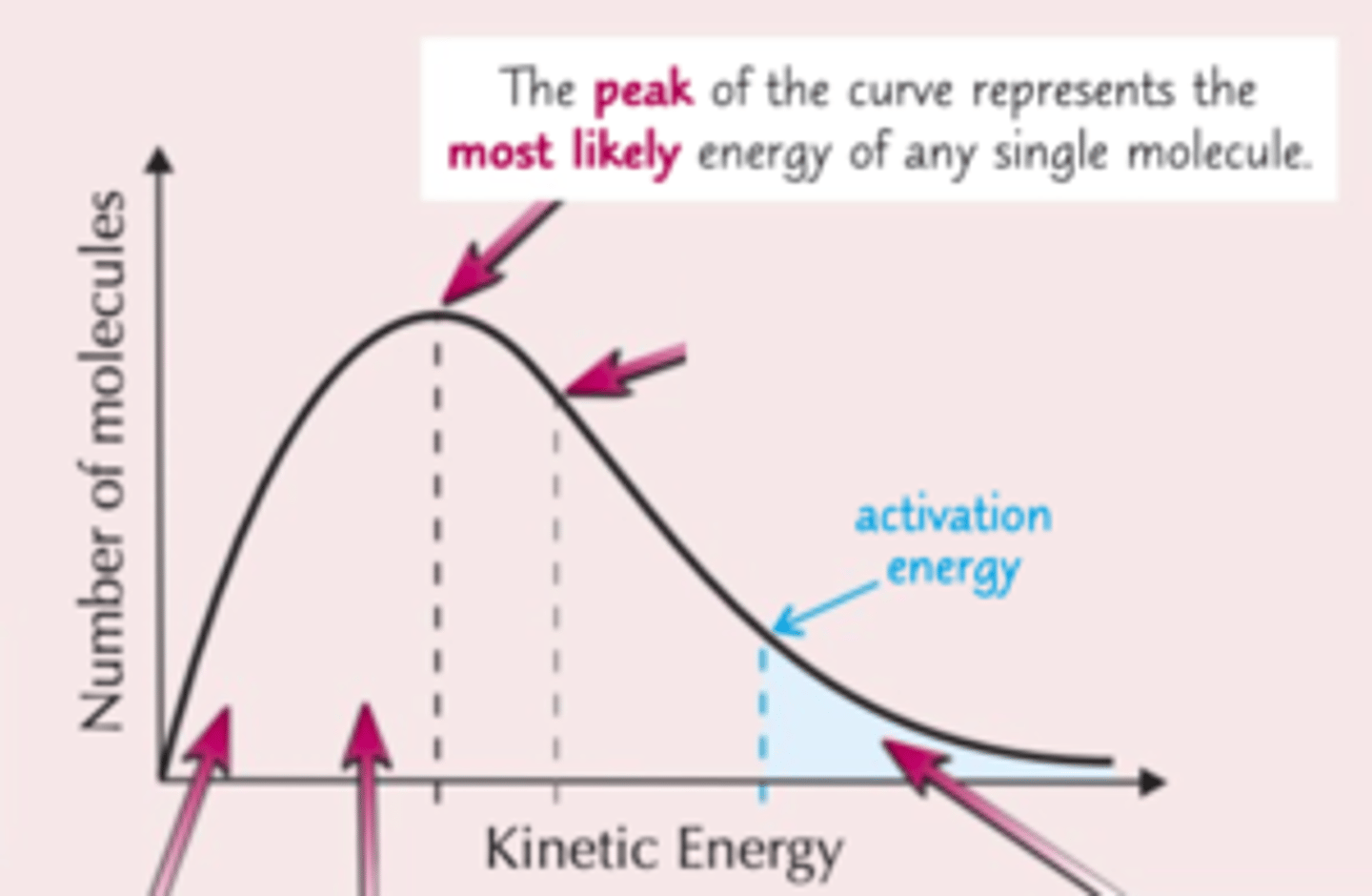
Where is the mean in a Maxwell-Boltzmann curve?
- A little towards the middle of the graph

When temperature increases, what happens to the Maxwell-Boltzmann curve?
-The graph shifts to the right
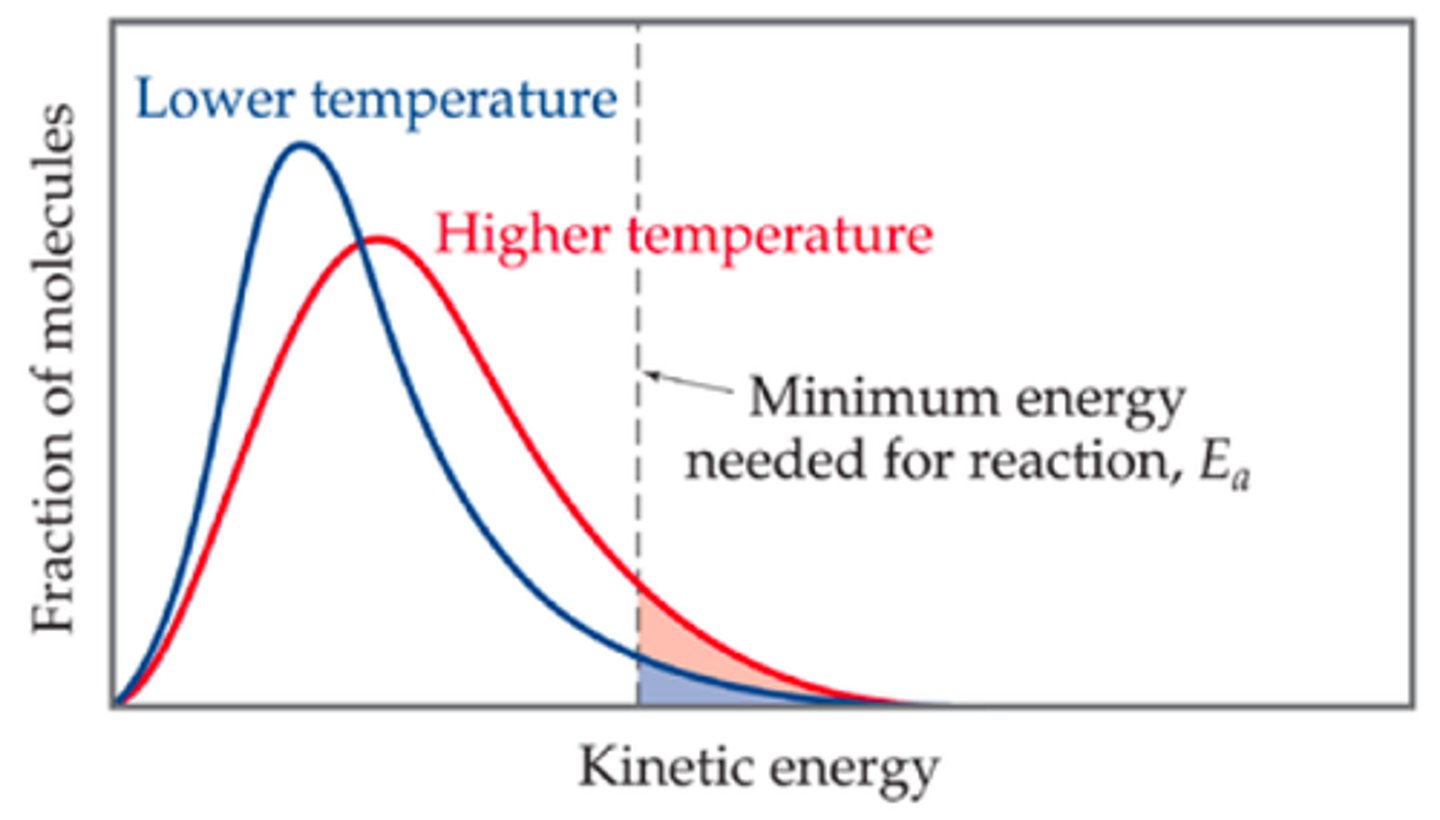
Why does the peak height of the increased temperature influenced Maxwell-Boltzmann curve decreases?
-More distribution of kinetic energy at higher temperatures, and as well as the fact that the area stays the same, the graph accounts for this by broadening
-However the activation energy on the graph is presented higher, but remains the same
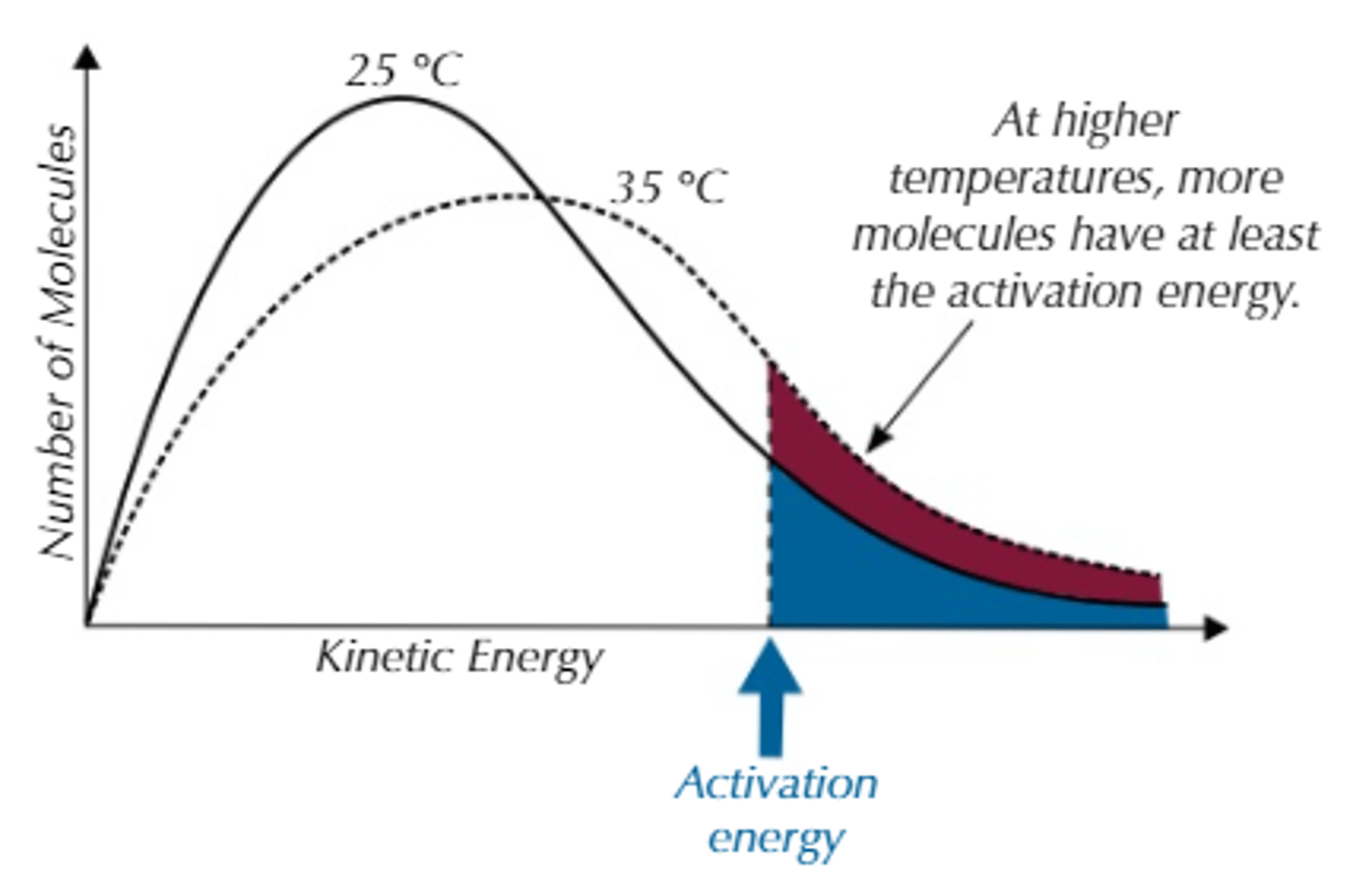
What does the total area under the curve represent?
-Total amount of particles in a system
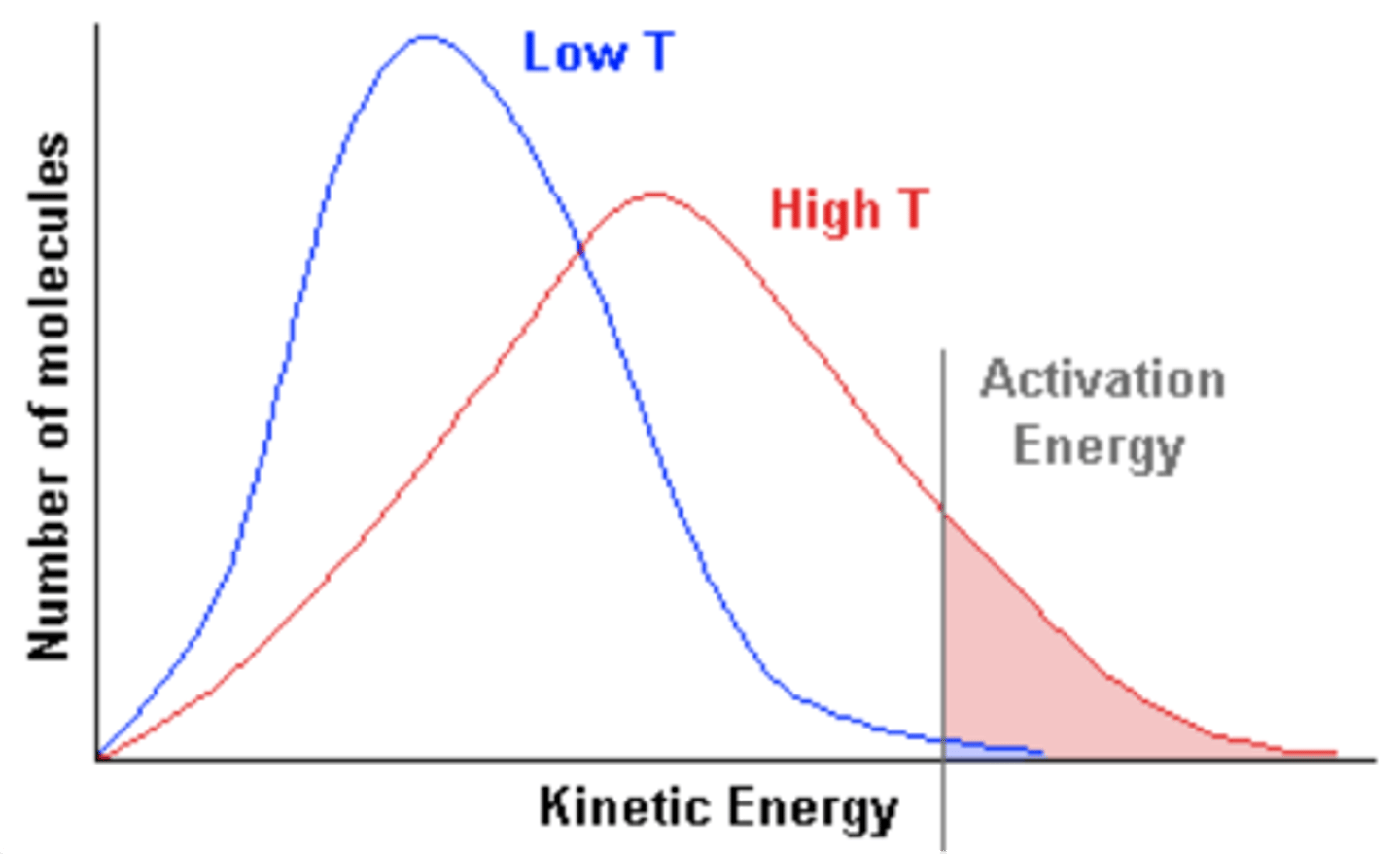
When temperature decreases, what happens to the Maxwell-Boltzmann Curve?
-Shifts to the left
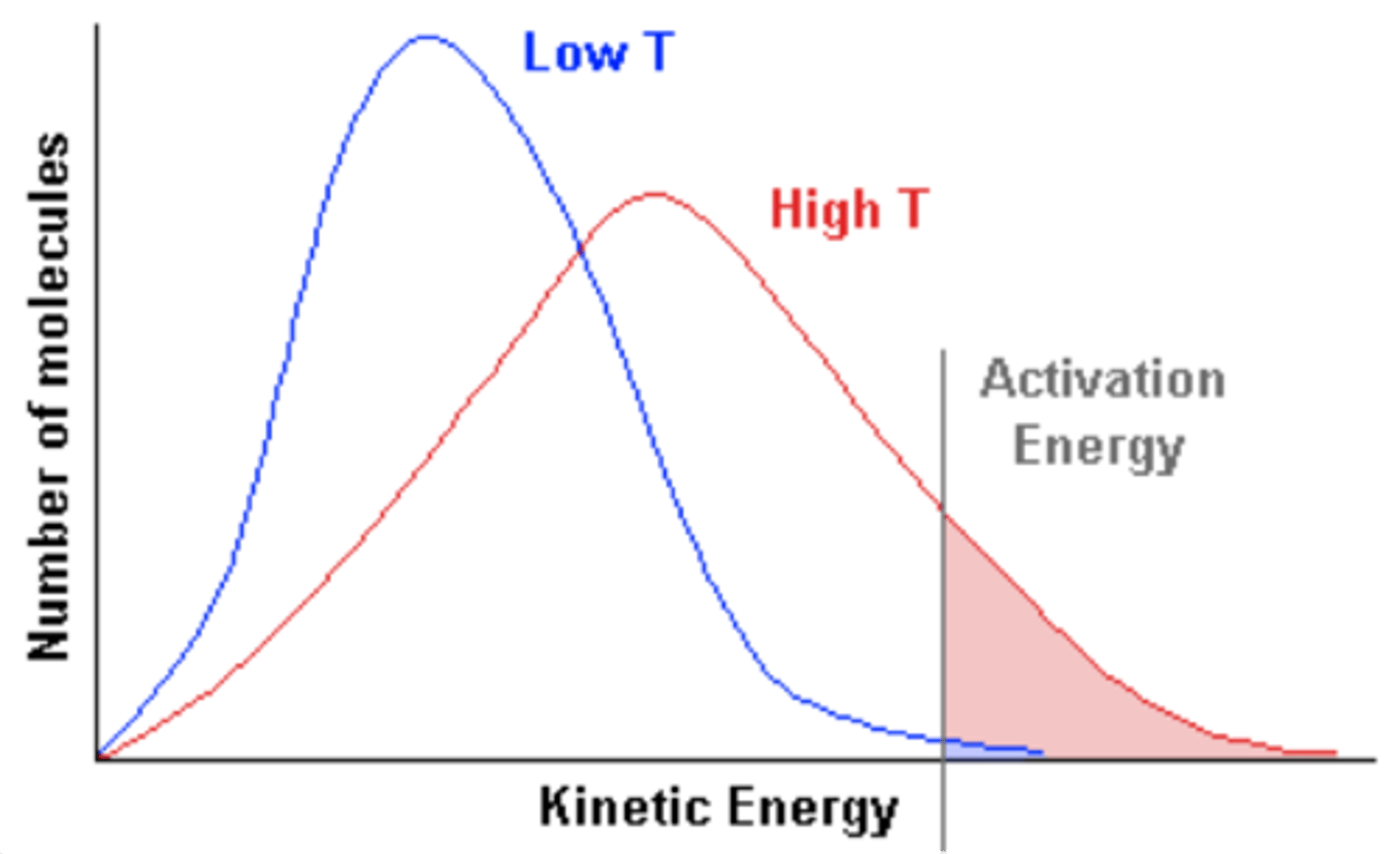
What happens to the peak height in a temperature-decreased Maxwell-Boltzmann curve represent?
-There's particles with a lower distribution of energies at these lower temperatures, so they peak more
-But activation energy remains the same
