Ocular anatomy and histology part 1-3
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
what are the 3 gross parts of the eye
orbit
globe
adnexa
what structures are a part of the anterior segment of the eye
cornea
anterior sclera
anterior chamber
posterior chamber
iris
iridocorneal angle
ciliary body
lens
what structures make up the posterior segment of the eye
vitreous humor
retina
choroid
optic nerve
posterior sclera
what is the difference in orbit from a herbivore to a carnivore
a herbivores orbit makes a complete boney rim
why would it be easy for carnivores to get proptosis
because they have an incomplete bony rim
what other structure lies within the orbit
foramina for nerves and vessels
what muscles move the globe in the orbit
rectus muscles
oblique muscles
retractor bulbi
the eye moves, up, down, left, right what muscle is causing that movement
the rectus muscles
the globe of the eye is rotated what muscle is causing that
oblique muscles
the globe is pulled back into the orbit what muscle is causing that
the retractor bulbi
what about the eyelid skin varies with species and breed
elasticity
what structure originates just outside the meibomian gland openeings
cilia
what structure opens at the mucocutaneous junction and secretes the lipid layer of the tear film
meibomian gland
lies between the cilia and meibomian glands and provides the eyelid margin with rigidity
tarsus
you watch a dog open its eyes what muscle is responsible for the elevating the upper eyelid
Levator palperbrae suparioris(LPS)
you watch a cat slowly blink at you what muscle is responsible for the closing the eyelids
Orbicularis oculi
what cranial nerves innervate the eyelid and what are their function
cranial nerve 5- sensory
cranial nerve 3,7 - motor
autonomic - sympathetic nerve
what eyelid muscle is innervated with cranial nerve 3
levator palpebrae superioris
what eyelid muscle is innervated with cranial nerve 7
Orbicularis Oculi Muscle
what eyelid muscle is innervated with the autonomic nerve
Muller’s muscle
you scare a dog and see his eyes widen what muscle is responsible for this
Muller’s muscle
what structures anchor the eyelid into the eye socket
medial and lateral canthus ligaments
what is a mucocutaneous junction
a transition point between the mucous membrane (mucosa) and the skin
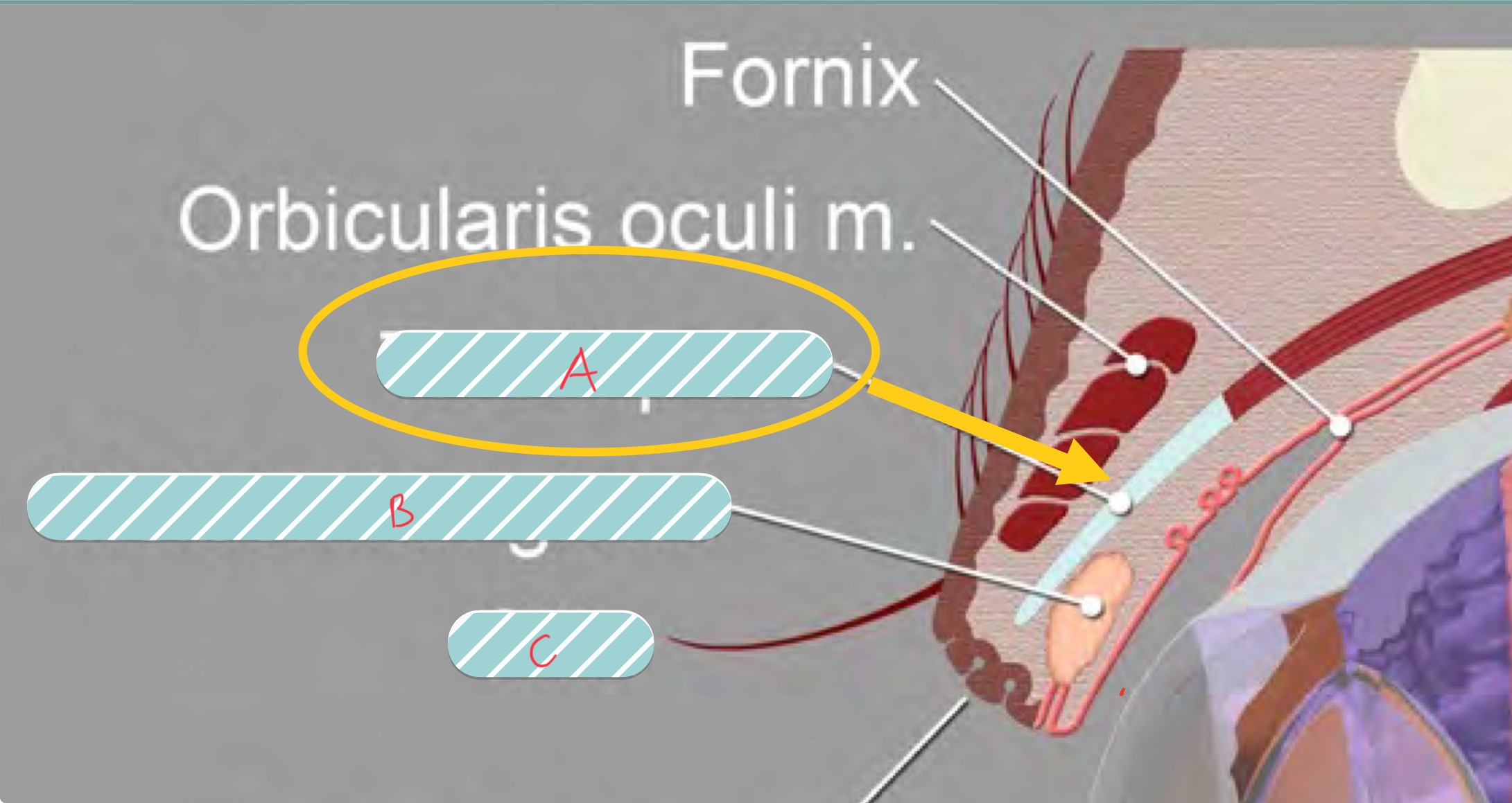
label the covered structures of the eyelid
A. Tarsus
B. meibomian gland
C. cilia
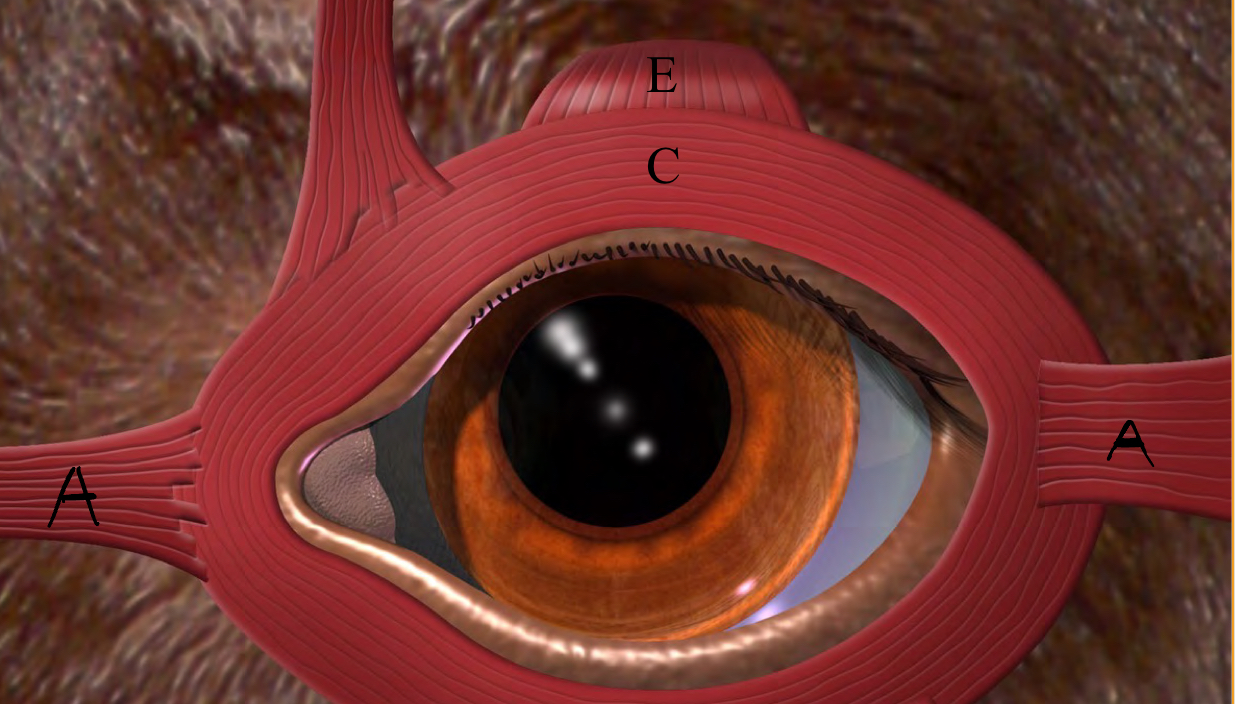
label the muscles of the eyelid
A. medial and lateral canthus ligaments
C. Orbicularis Oculi
E. levator palpebrae superioris
what is the conjunctiva
a mucous membrane of the eyelid
what are the parts of the conjunctiva
palpebral
bulbar
fornix
nictitans
if looking at a histology slide what will the conjunctiva look like
non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium with goblet cells
when looking at conjunctiva histology you see loose CT with leaky capillaries adjacent to the stratified squamous epithelium what is this area called
substantia propria
in inflamed conjunctiva you see fluid filling areas where there would be space, this would mean there was a loss of what?
subconjunctival space
what do the goblet cells of the conjunctiva produce
the mucus layer of the tear film
what is the most important function of the nictitating membrane
spreads tear film
what is the main function of the lacrimal apparatus
produce, distribute, and drain the precorneal tear film to maintain health of the ocular surface
what are the layers of the tear film
lipid layer
aqueous layer
mucin layer
what structure produces the lipid layer of the tear film
meibomian gland
what structure produces the aqueous layer of the tear film
lacrimal and nictitating gland
what structure produces the mucin layer of the tear film
goblet cells
what is the flow of the lacrimal outflow apparatus
ocular puncta
canaliculi
lacrimal sac
nasolacrimal duct
nasal puncta
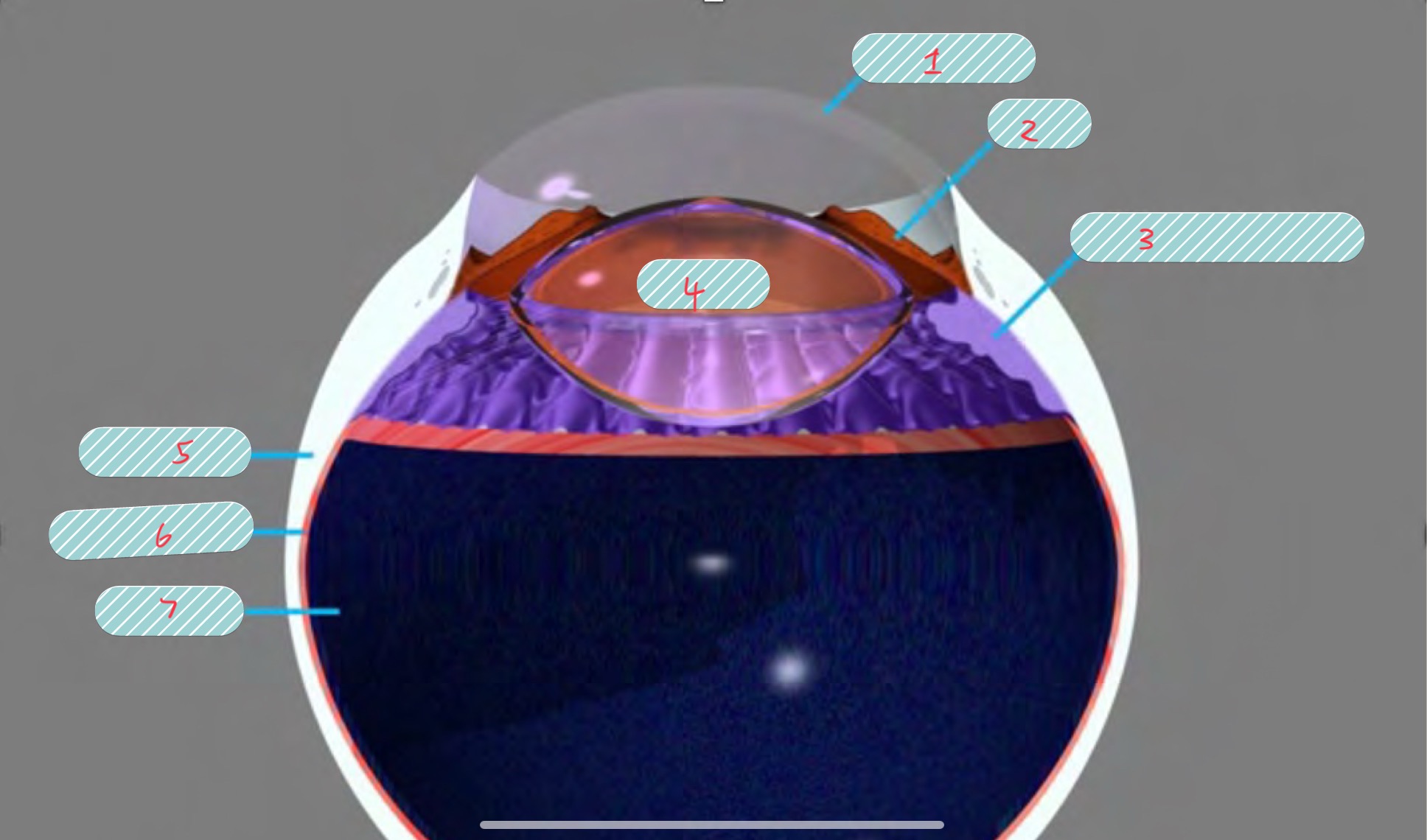
label the covered parts of the globe
cornea
iris
ciliary body
lens
sclera
choroid
retina
what are the 3 concentric tunics of the eye
fibrous
vascular
nervous
what are the parts of the fibrous tunic
cornea
sclera
what are the parts of the vascular tunic
iris
ciliary body
choroid
what are the parts of the nervous tunic
retina
optic nerve
what are the functions of the cornea
transmit light
refract light
protect internal contents
the anterior portion of the cornea is innervated by what cranial nerve
5
what are the 4 layers of the cornea
epithelium
stroma
descemet’s membrane
endothelium
what type and how thick is corneal epithelium
non keratinized squamous epithelium
8-15 layers thick
how do microvilli aid the corneal epithelium
they stabilize the tear film
what is the turnover rate of the cornea epithelium
7 days
what are some important aspects of the stroma
collagen is regularly arranged
no blood vessels
78% water
hydrophilic
in order to remain clear the corneal stoma must be
dehydrated
focal corneal edema is caused by
ulceration of corneal epithelium
diffuse corneal edema is caused by
damage to corneal endothelium
what is the function of the corneal endothelium
they actively pump fluid out of the corea
do corneal endothelial cells undergo mitosis
no
as corneal endothelial cells die and slough off how does the tissue heal itself
through enlargement and migration
what is the limbus of the eye
it is the junction between the corneal and scleral tissues
what is the difference between corneal and scleral collagen
scleral collagen is is nor regularly arranged