13 & 14-Segmented Multifocal and Single Vision Lenses
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Single-vision lens
optics calibrated for one distance only
Multifocal lens
optics calibrated for more than one distance
Segmented multifocal
Multifocal constant near power
-"Visible" segment
Progressive addition lens (PAL)
Multifocal with variable near power
-"Invisible" segment
Lens power
the prescription in the major portion of the lens
Add power
power added to the major portion of the lens (within the segment)
Why do (most) people eventually need reading glasses?
age related loss of accommodation
What does an add do?
compensates for the loss of accommodation
How do you decide what the right add power is?
-Age based norms
-Working distance in Diopters
Refractive index
a ratio of speeds
-The amount of resistance to the speed of light
-How much light slows down in that material
Speed varies slightly with wavelength
n=c/v
-increase in index of refraction decreases lens thickness
Increase in lens curvature increases what?
the refractive power
types of segment construction
-fused
-cemented
-one piece
Fused segment
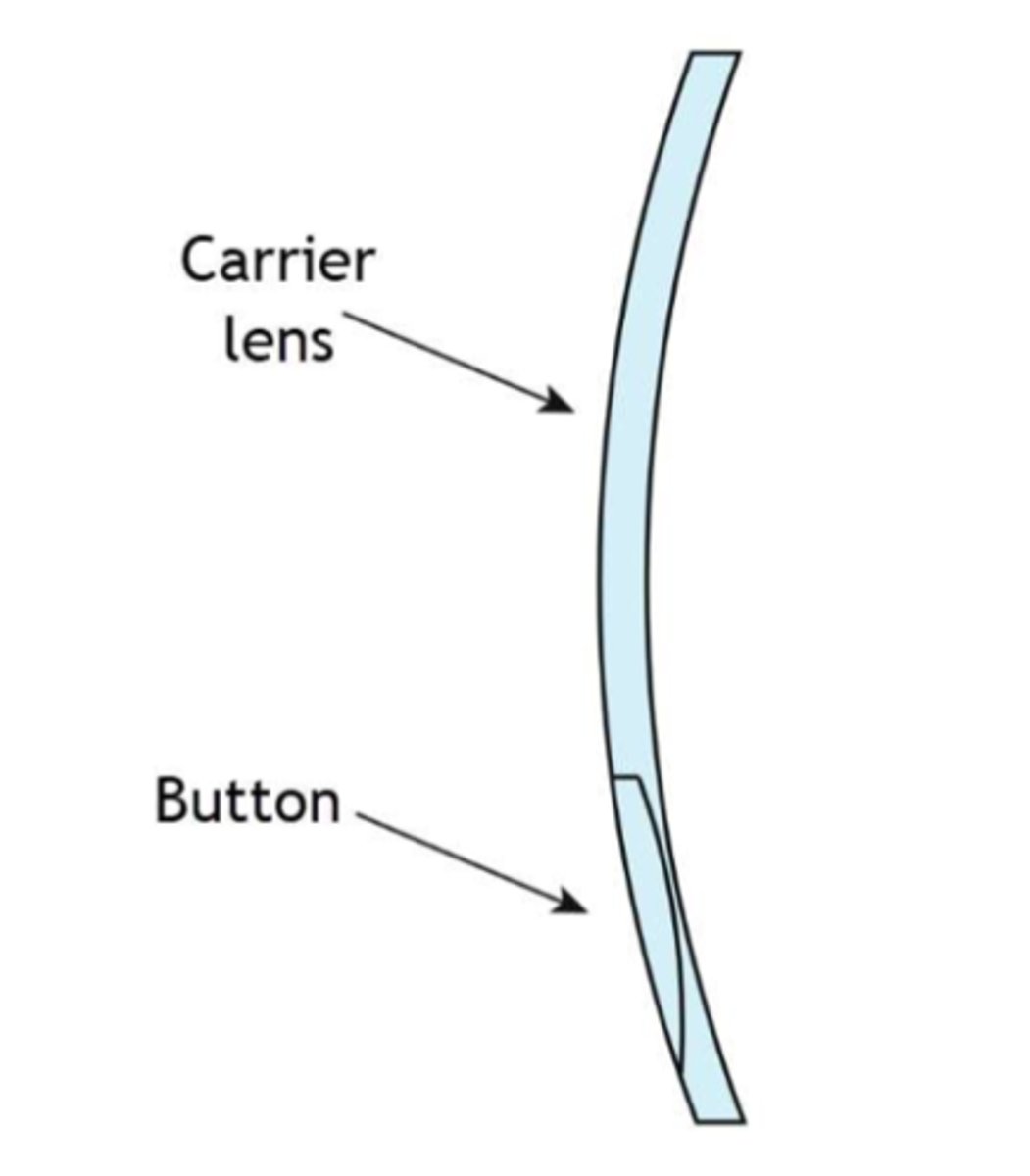
Carrier lens with countersink "button" of different refractive index but identical curvature.
-Astigmatic correction is ground onto back surface of carrier lens
-Only available with glass materials
Cemented segment
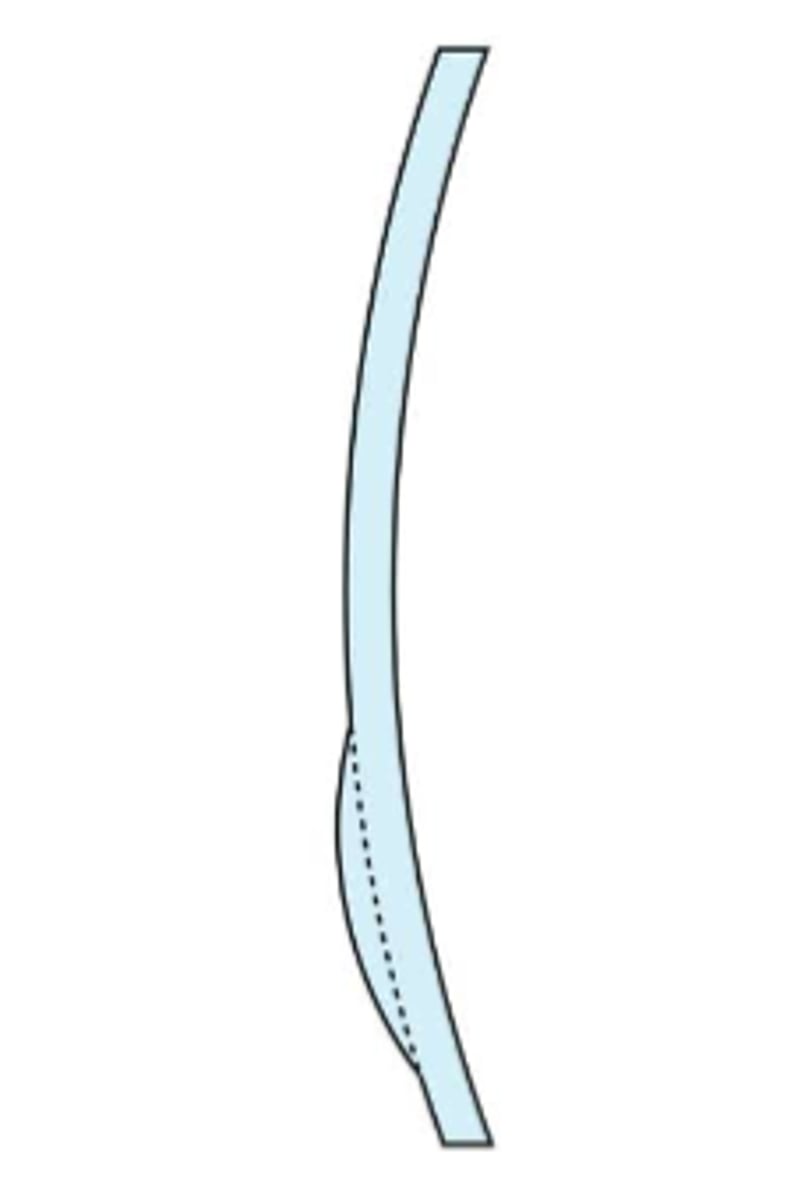
Wafer of identical refractive index different curvature is cemented onto either the front or back
-Astigmatic correction is ground onto the surface without the wafer
One piece segment
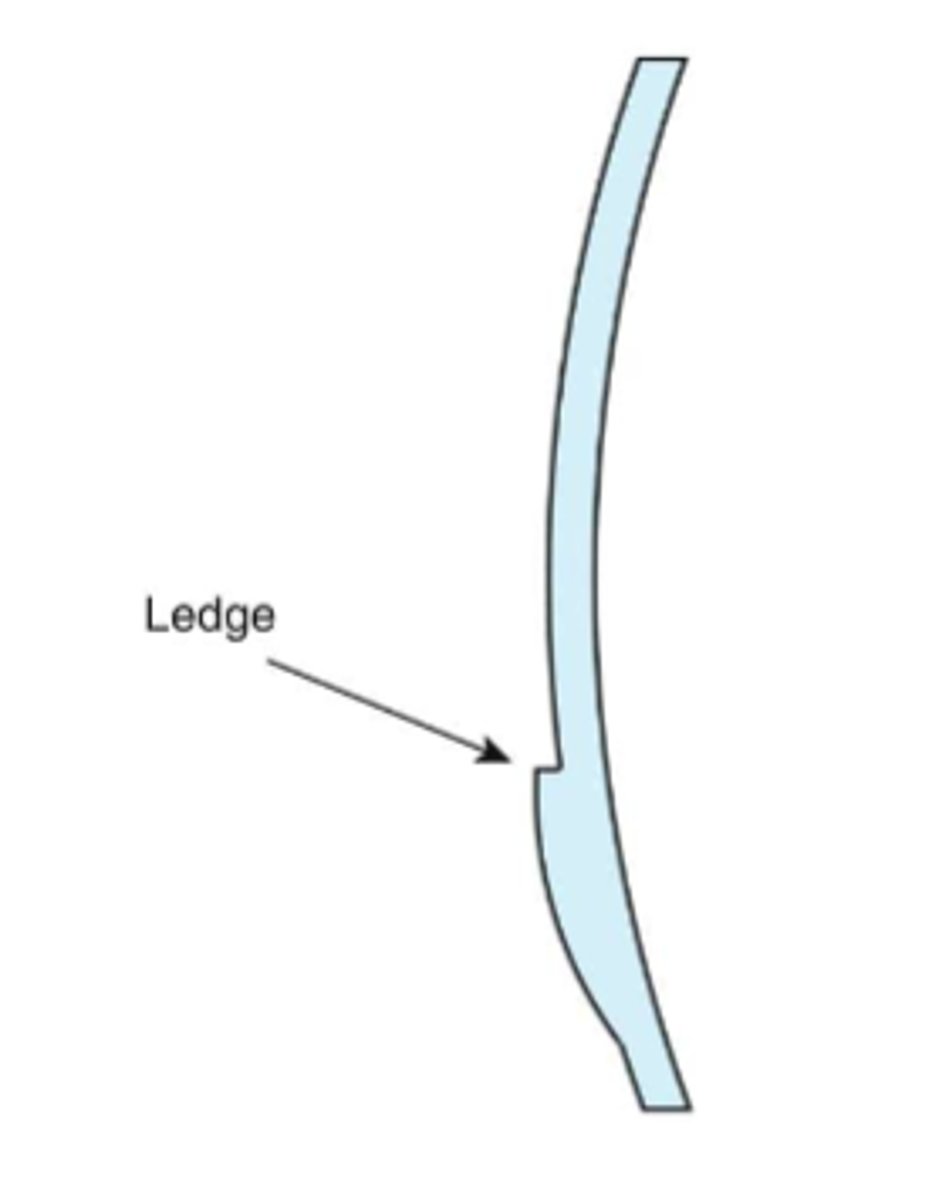
One lens material, but a change in curvature in the segment
-Astigmatic correction is ground onto the back surface of lens
-All plastic lenses are one piece
Major Reference Point (MRP)
-aka Prism reference point
-aka Distance reference point
The point on the lens where the prism is equal to that called for by the prescription
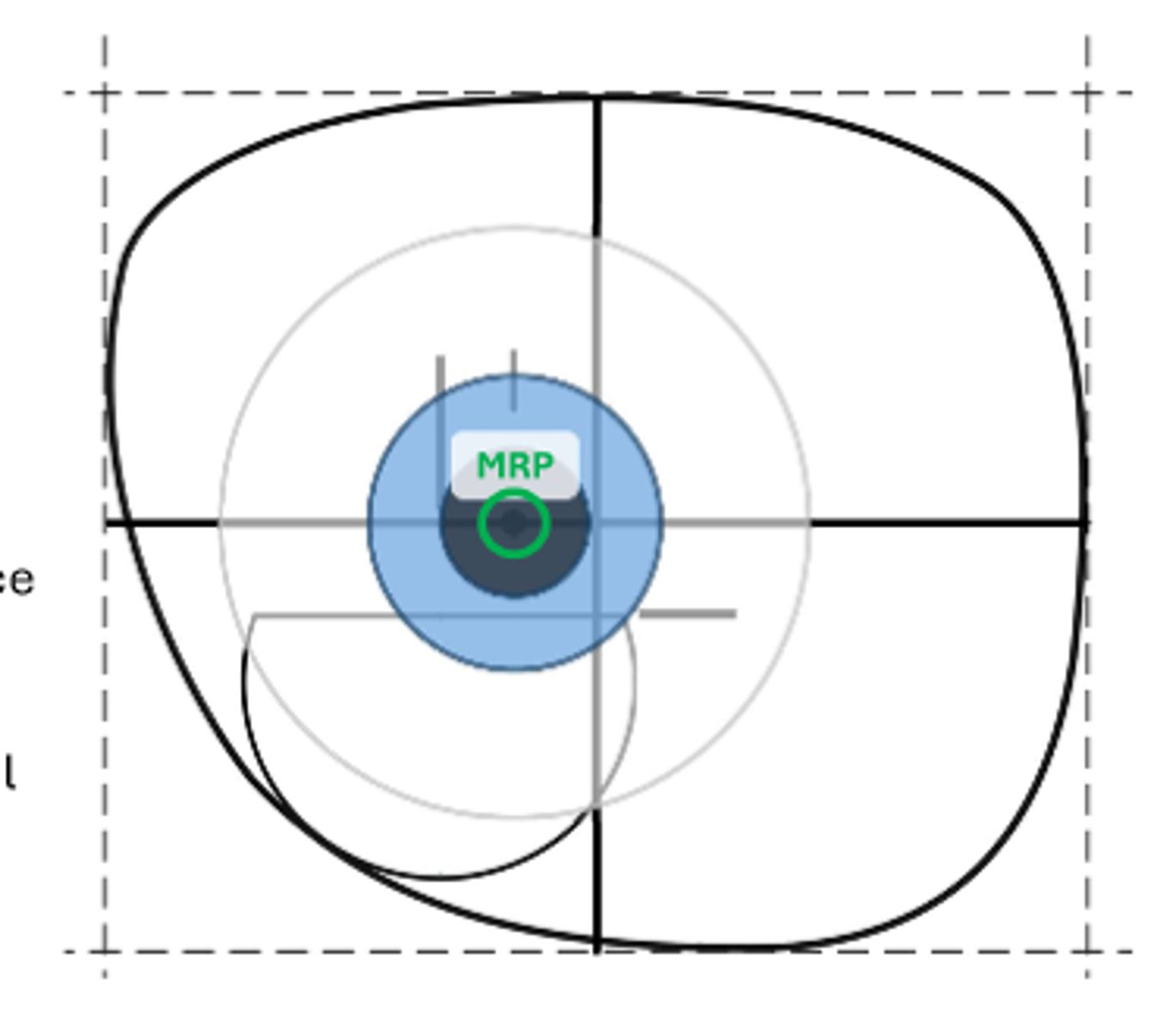
Inset (or outset)
-aka distance decentration
The amount the MRP is moved laterally away from the geometric center (GC) of the lens
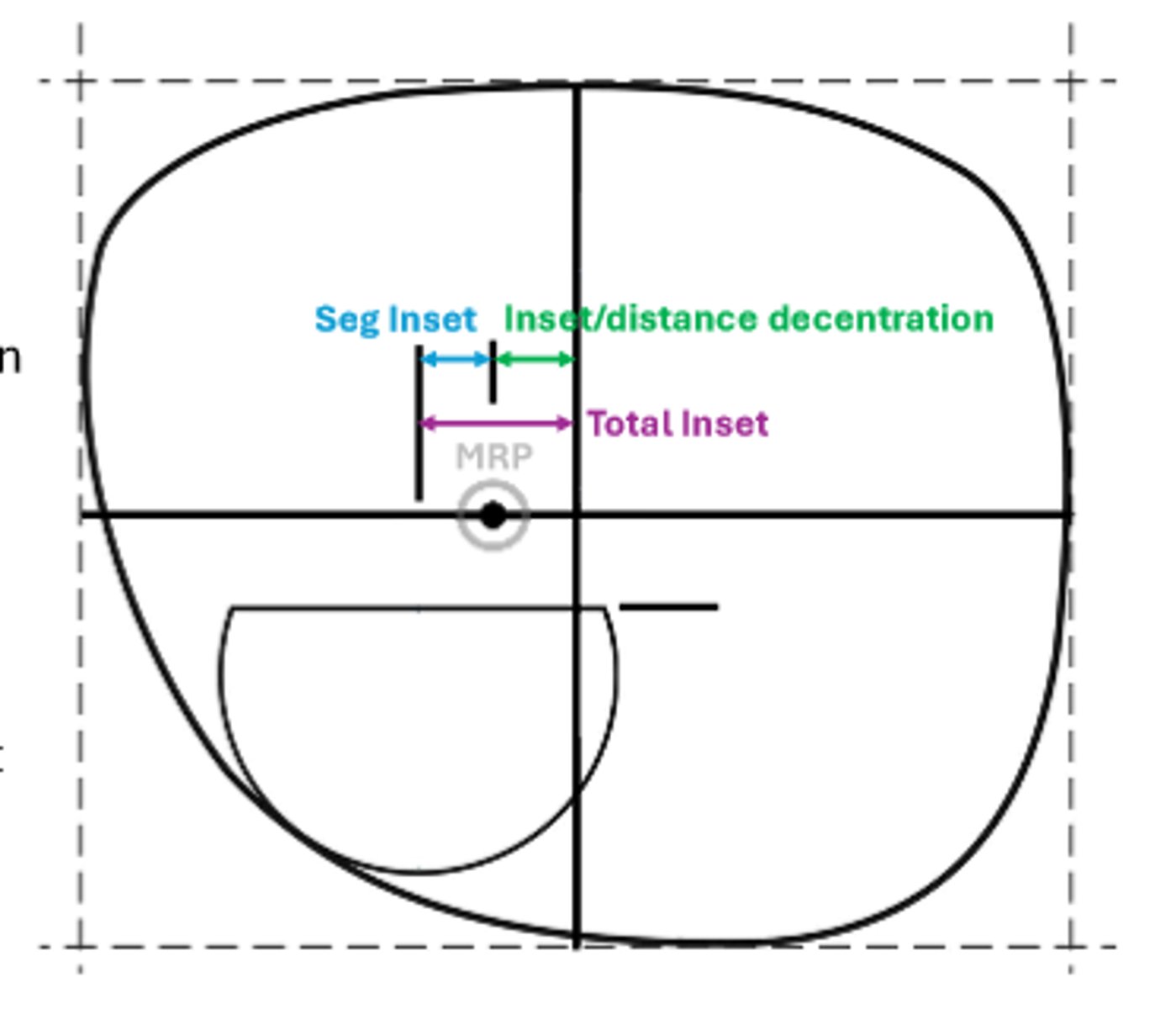
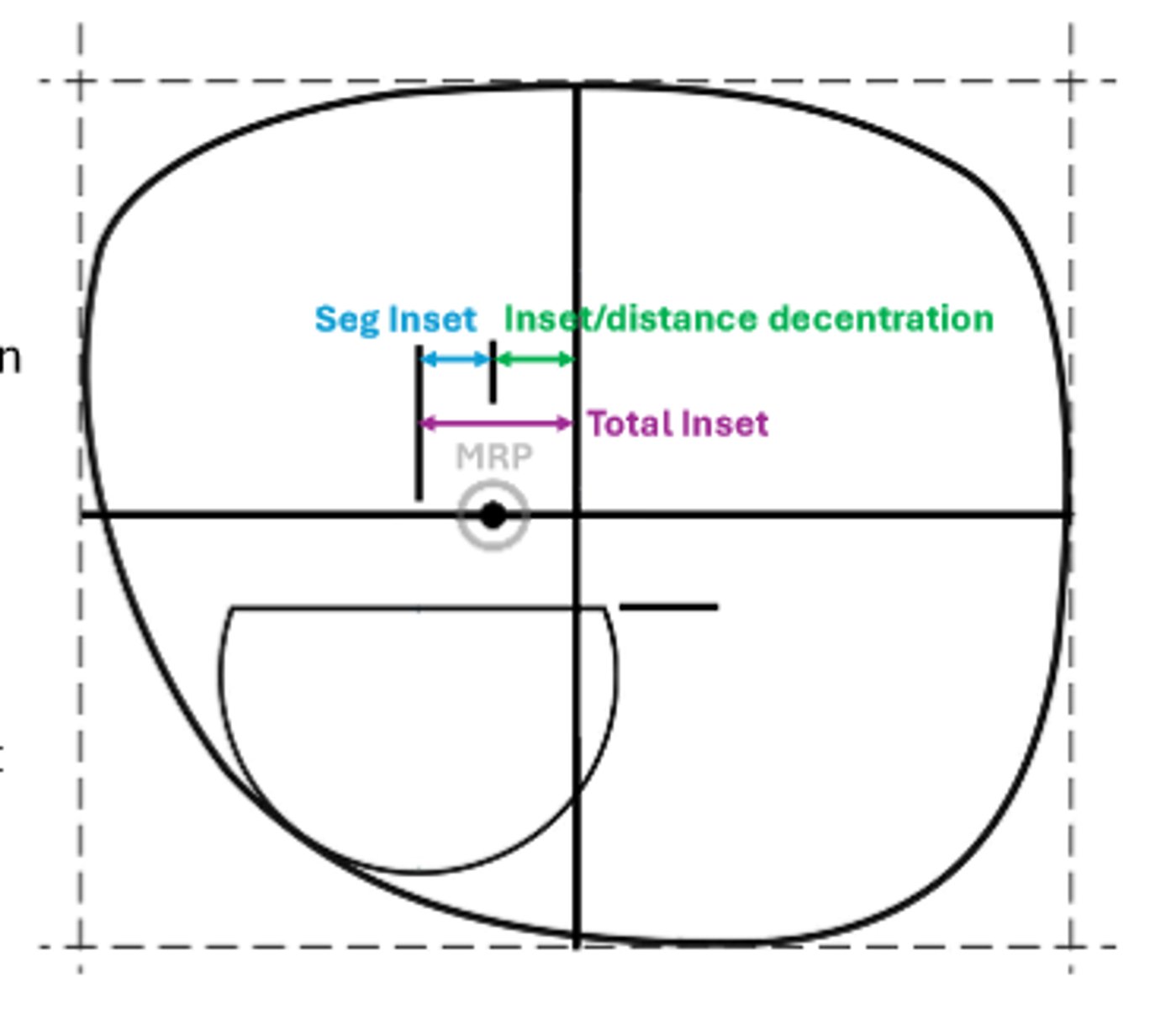
Seg inset
additional amount of the center of the near segment is moved inward from the MRP
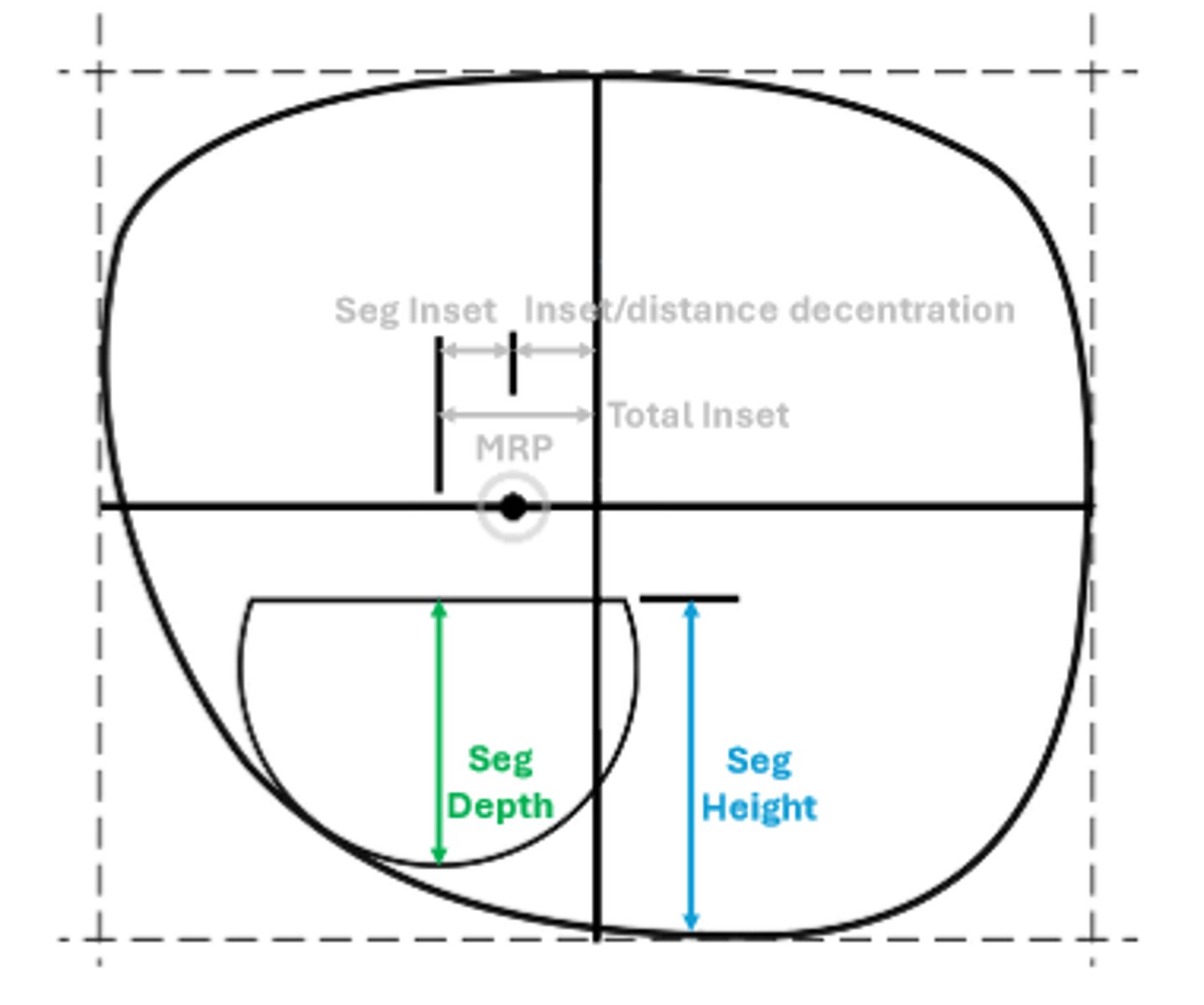
Seg depth
The longest vertical dimension of the segment
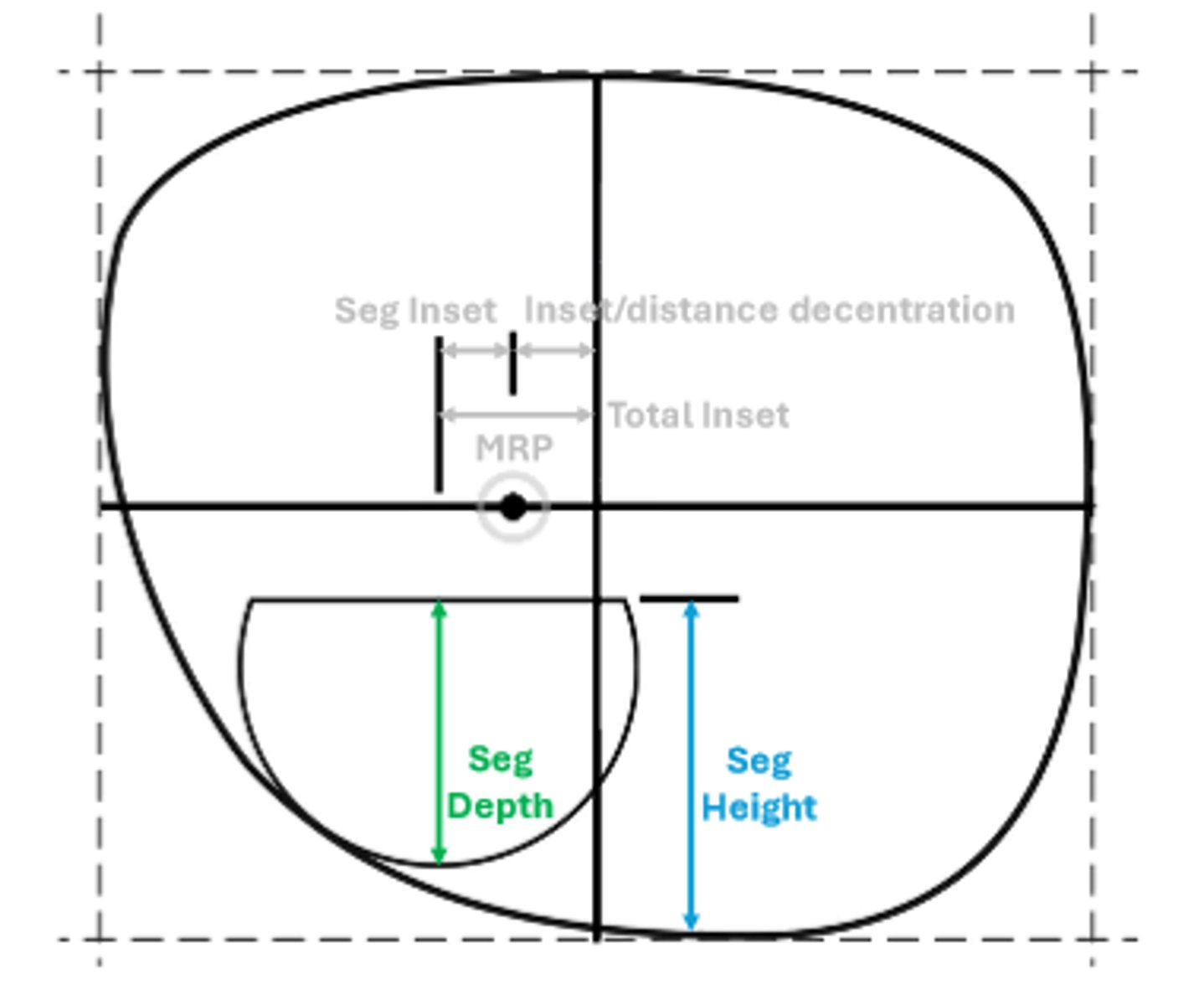
Seg height
The vertical dimension from the bottom of the lens to the top of the segment
Seg drop
The vertical distance between the MRP and the top of the segment
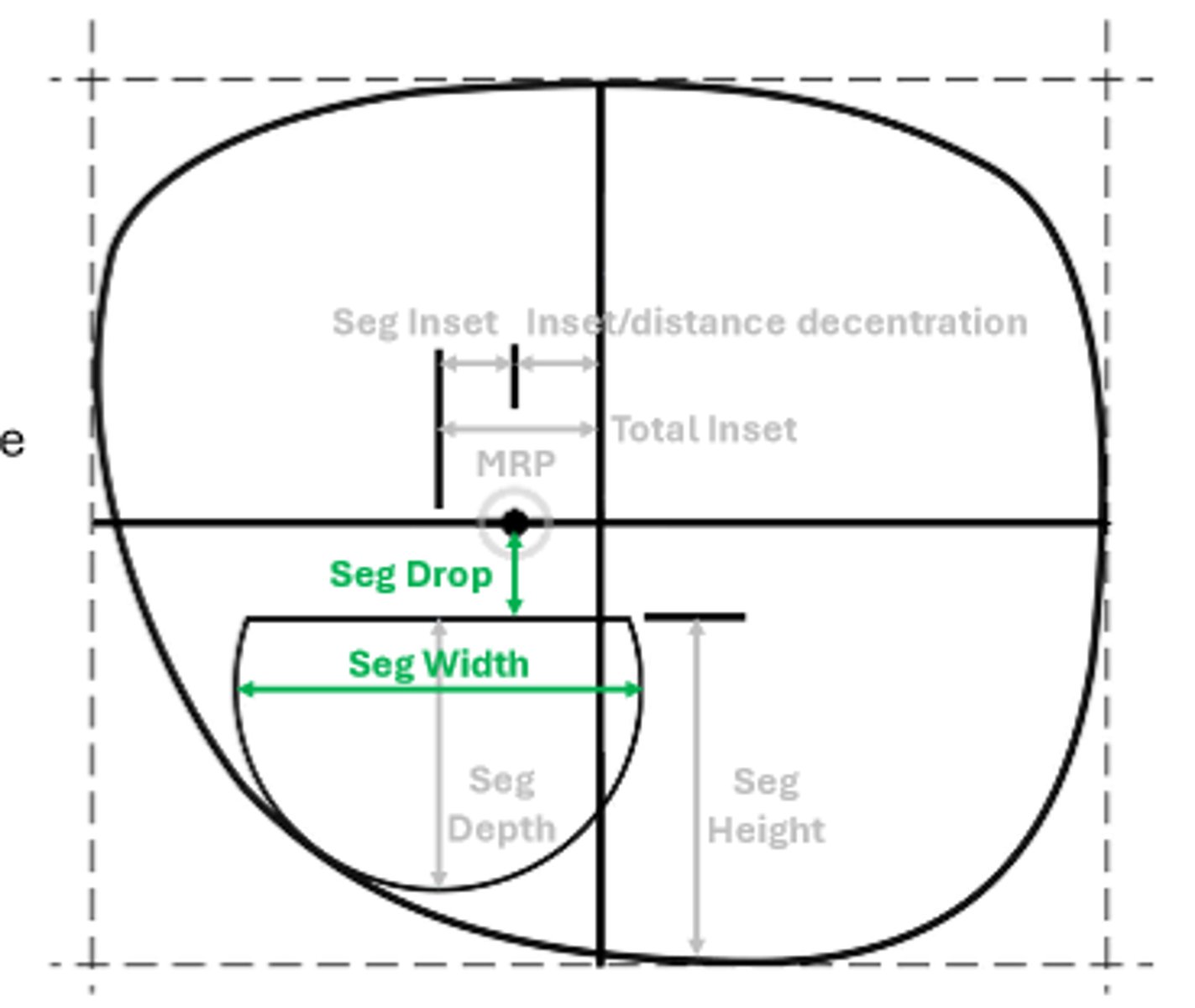
Seg width
the widest horizontal measurement of the seg
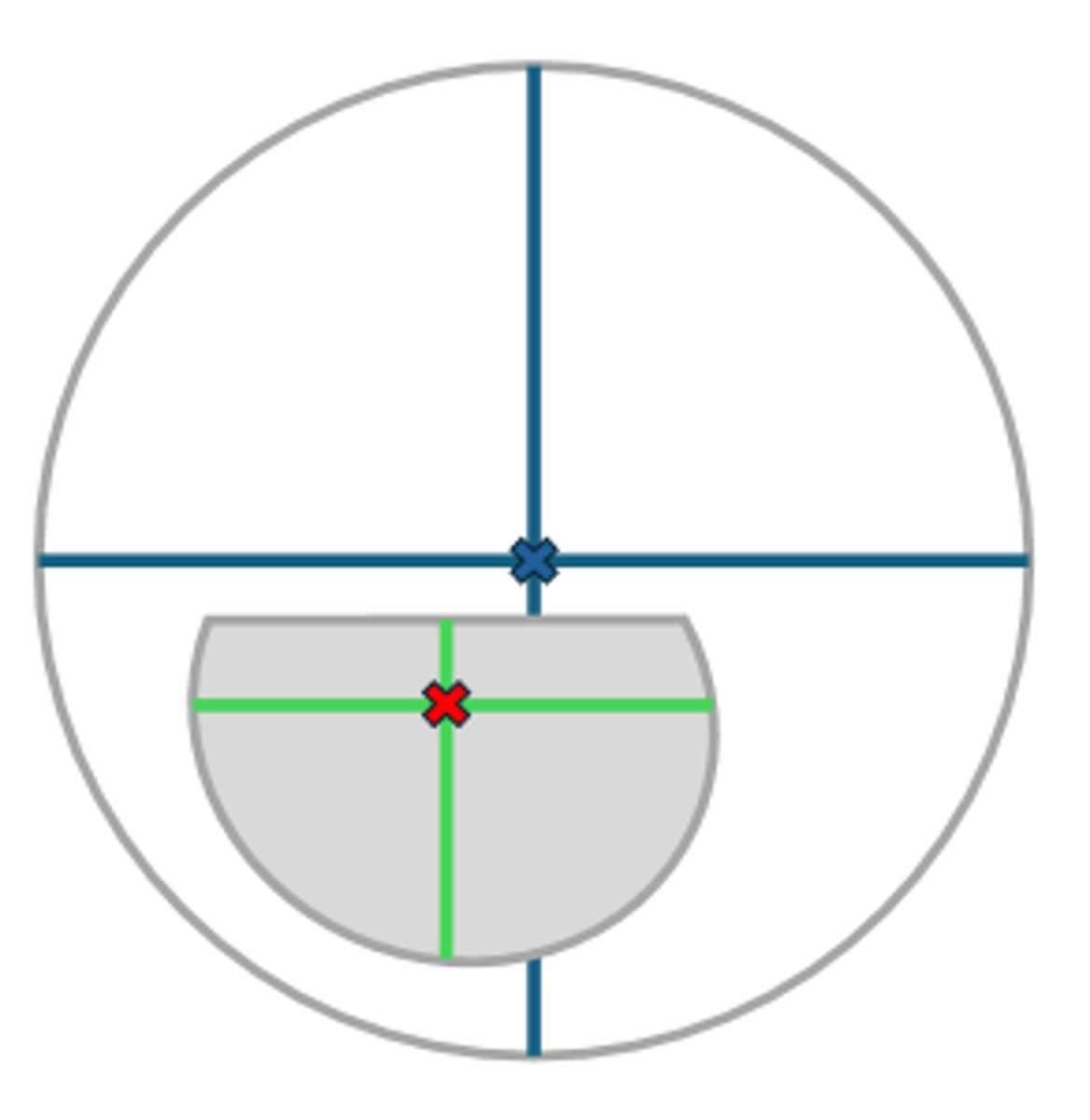
Optical center
Both the distance and near sections have their own optical centers
Multifocal styles
1. Flat-top
a)ribbon
2. Round
3. Curve-top
4. Executive
5. Blended*
Flat-top multifocal
AKA straight-top or D-seg
-Most common style
-Variety of segment widths and optical center locations
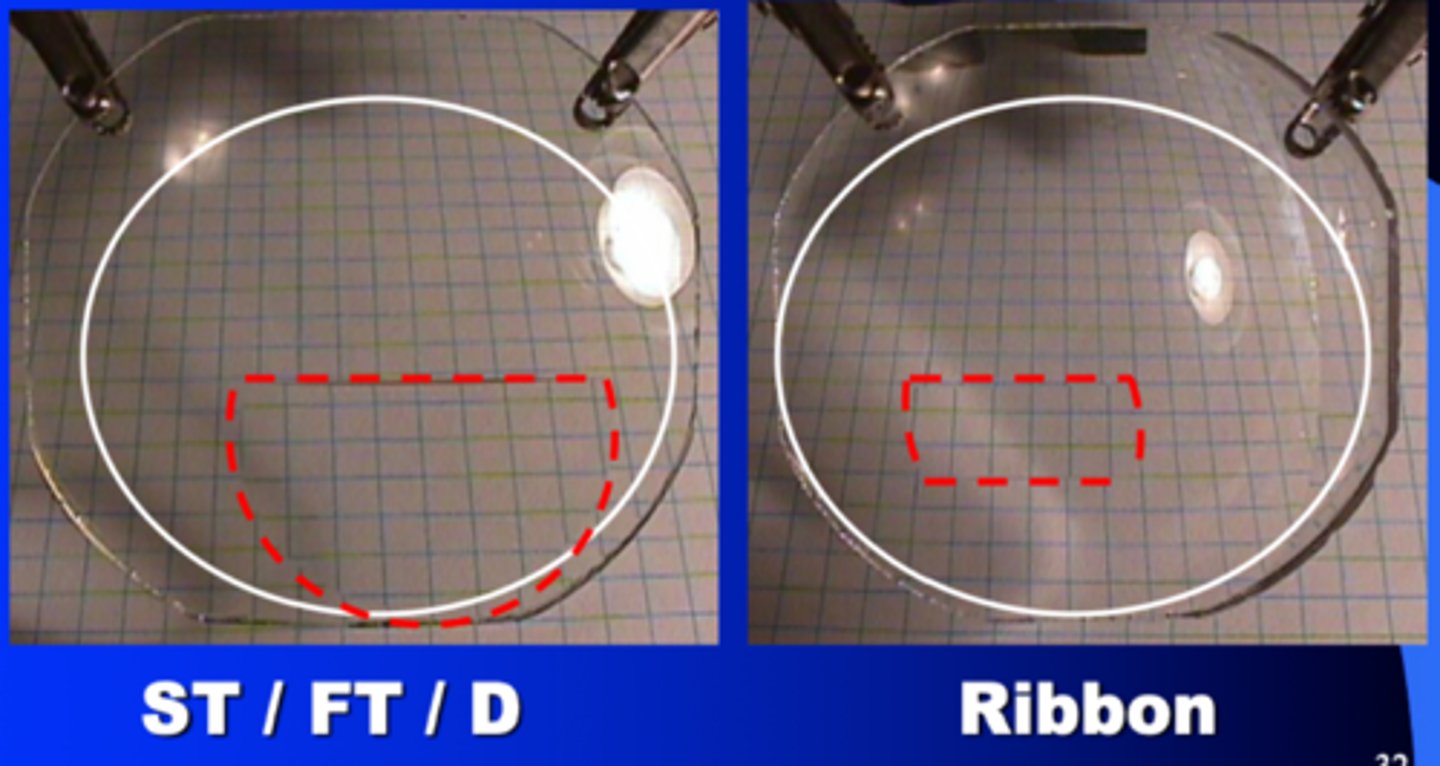
Flat-top ribbon
remove a strop from both top and bottom of a segment
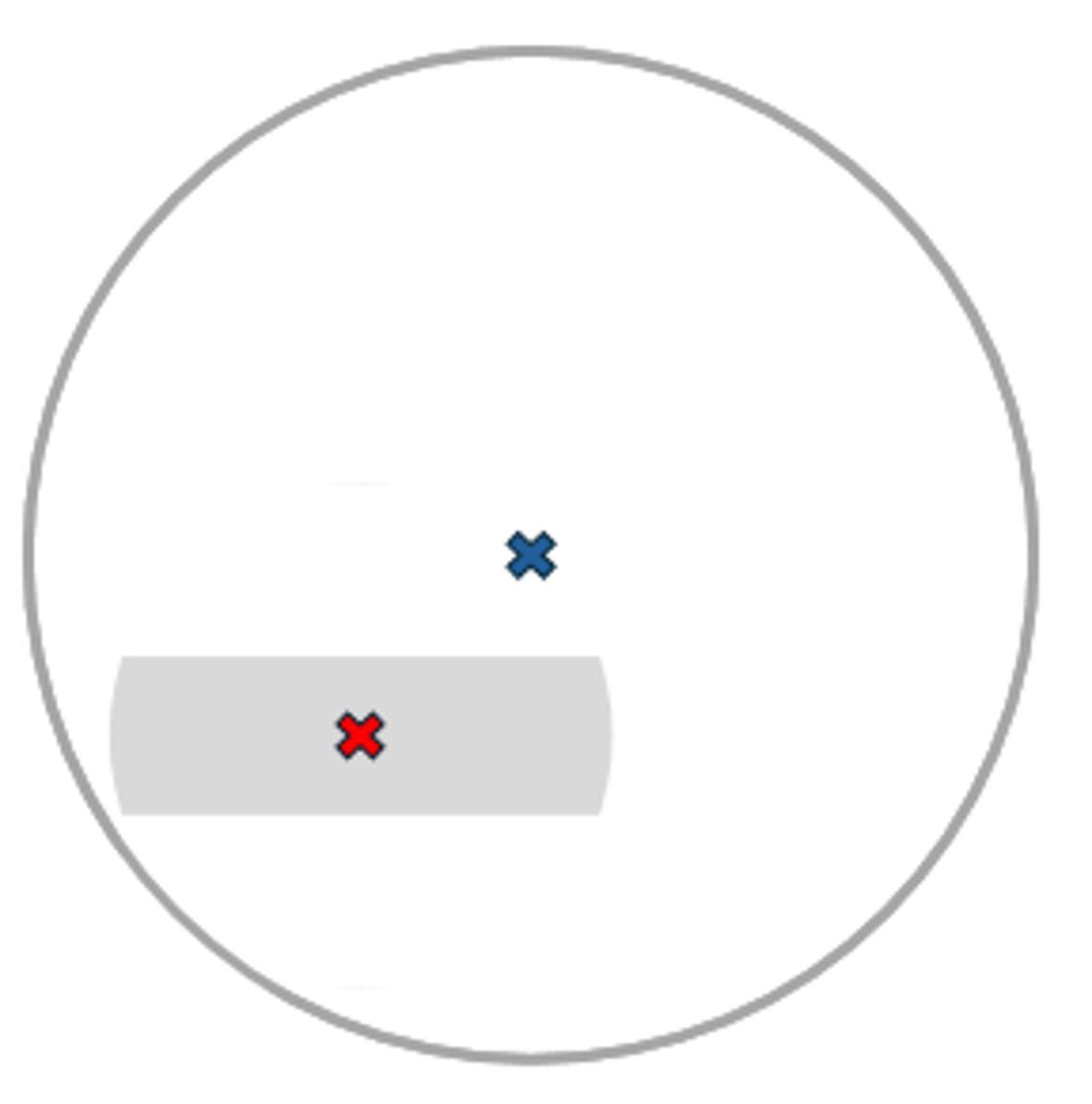
Curve-top
variety of segment widths
OC 4.5 mm below bifocal line
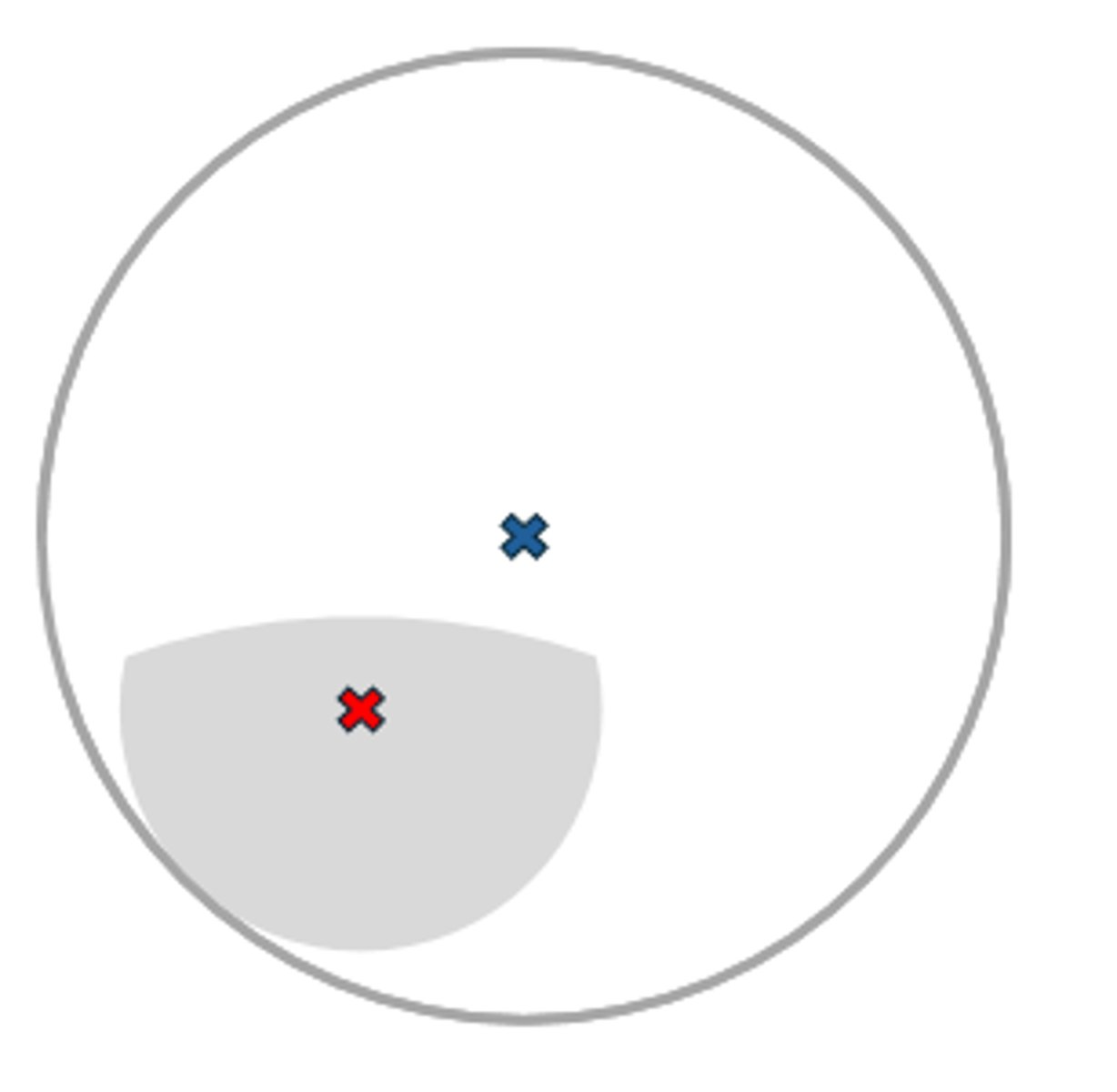
Franklin-style
AKA Executive, E-line, or full-seg
-Full width of the lens
-OC is on the bifocal line
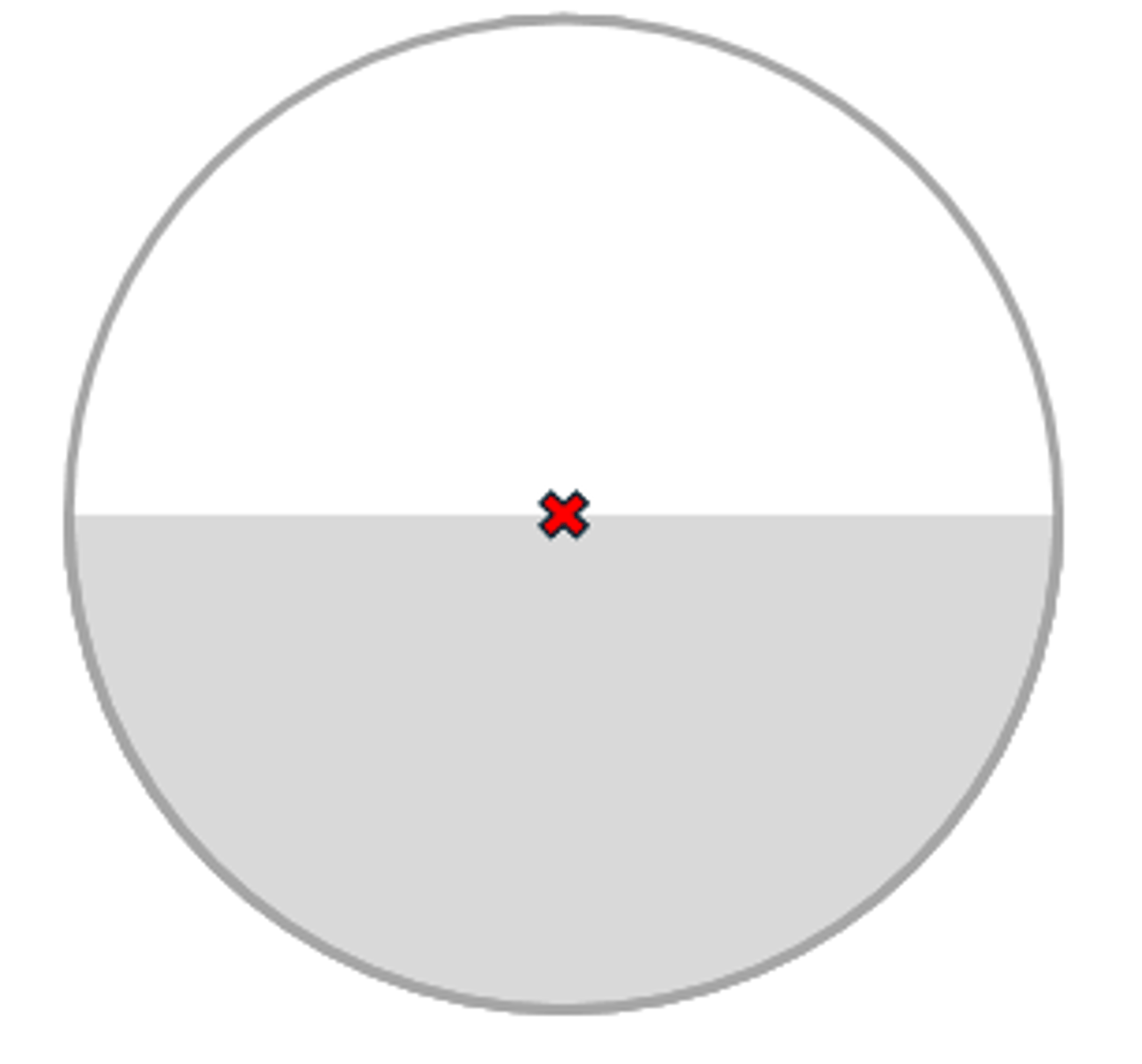
Round
Available in fused and one-piece construction designs
-Variety of segment widths
-OC is at the center of the segment
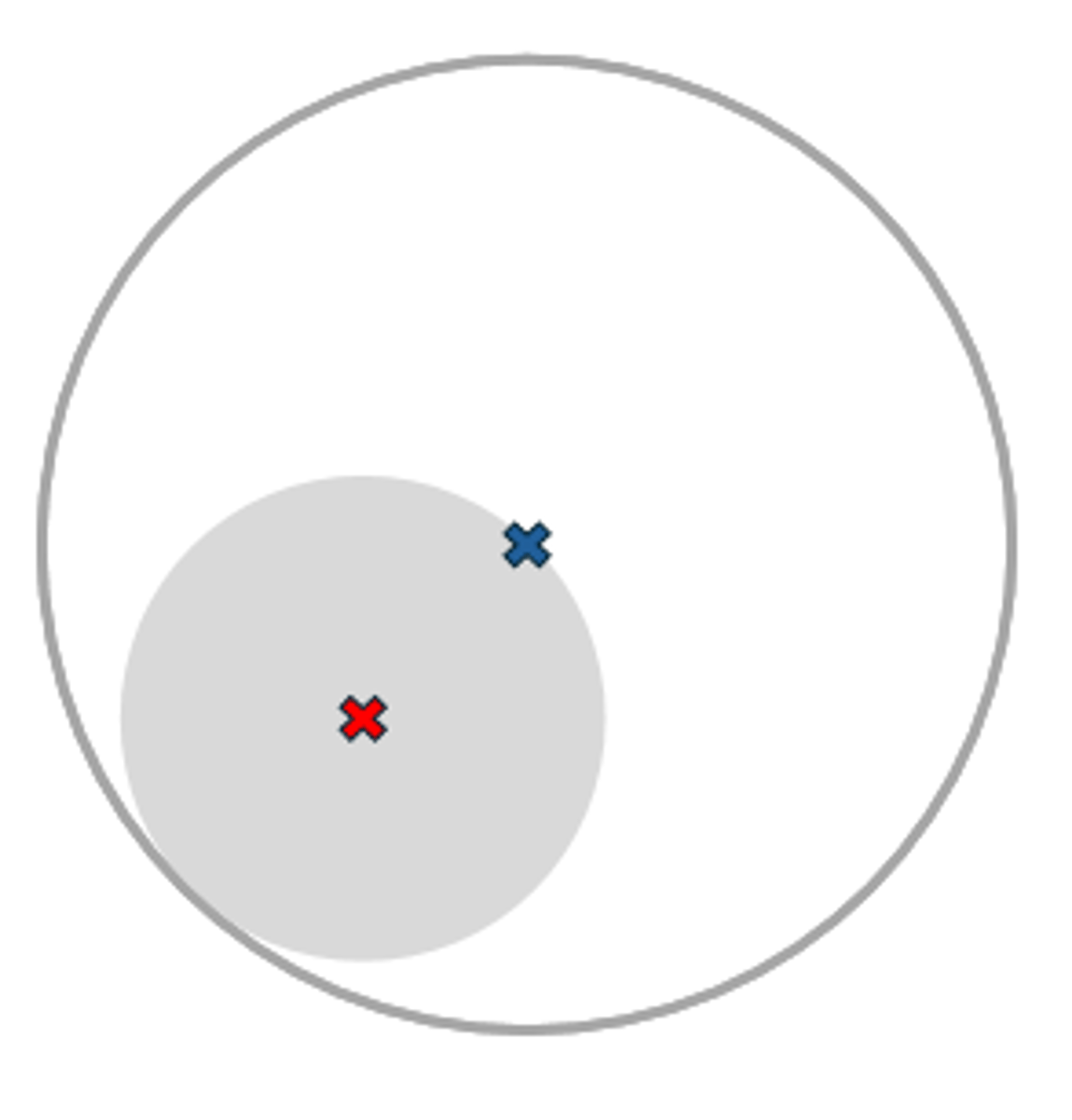
Blended
One-piece round segment with border smoothed out
-Better cosmesis
-Blended zone optically unusable
-Not the same as a PAL
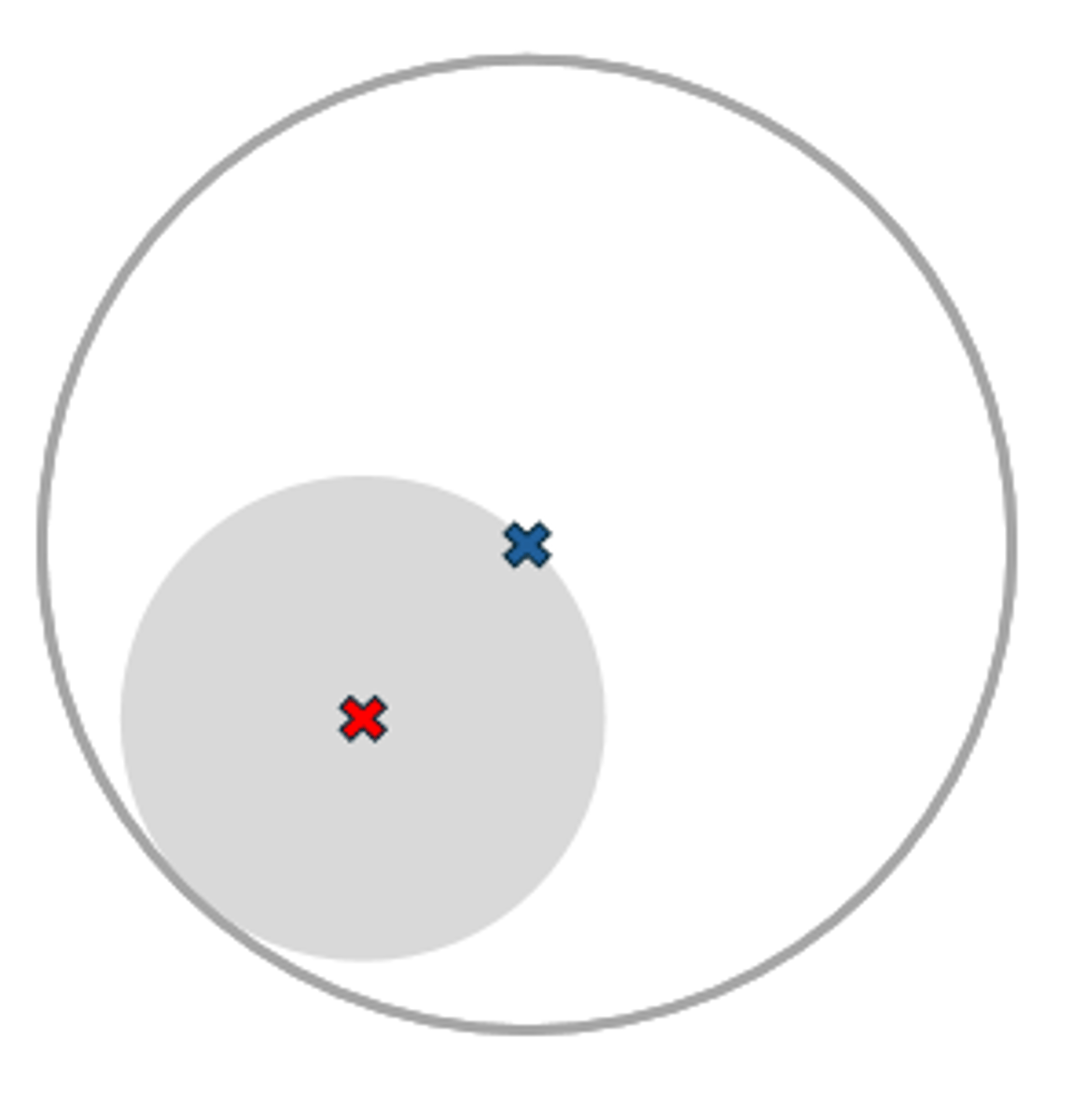
Trifocal
May be done in flat-top, round segment, straight-across (executive), and combination styles
-Flat-top is most common, but trifocals have largely been replace by PALs

how can you calculate a MF rx?
With any combination of distance-intermediate-near if you know the distance RX and intermediate/near needs
How is add power achieved?
either by a change in curvature or an increase in index of refraction
Off-axis viewing & decentration
an image experiences displacement when viewed through an off-center point of a lens
-Prentice's Rule
Image Displacement
-An image experiences additional displacement when viewed through the add of the lens.
-Displacement due to major lens and add must be calculated separately and then put together to determine the total prismatic effect.
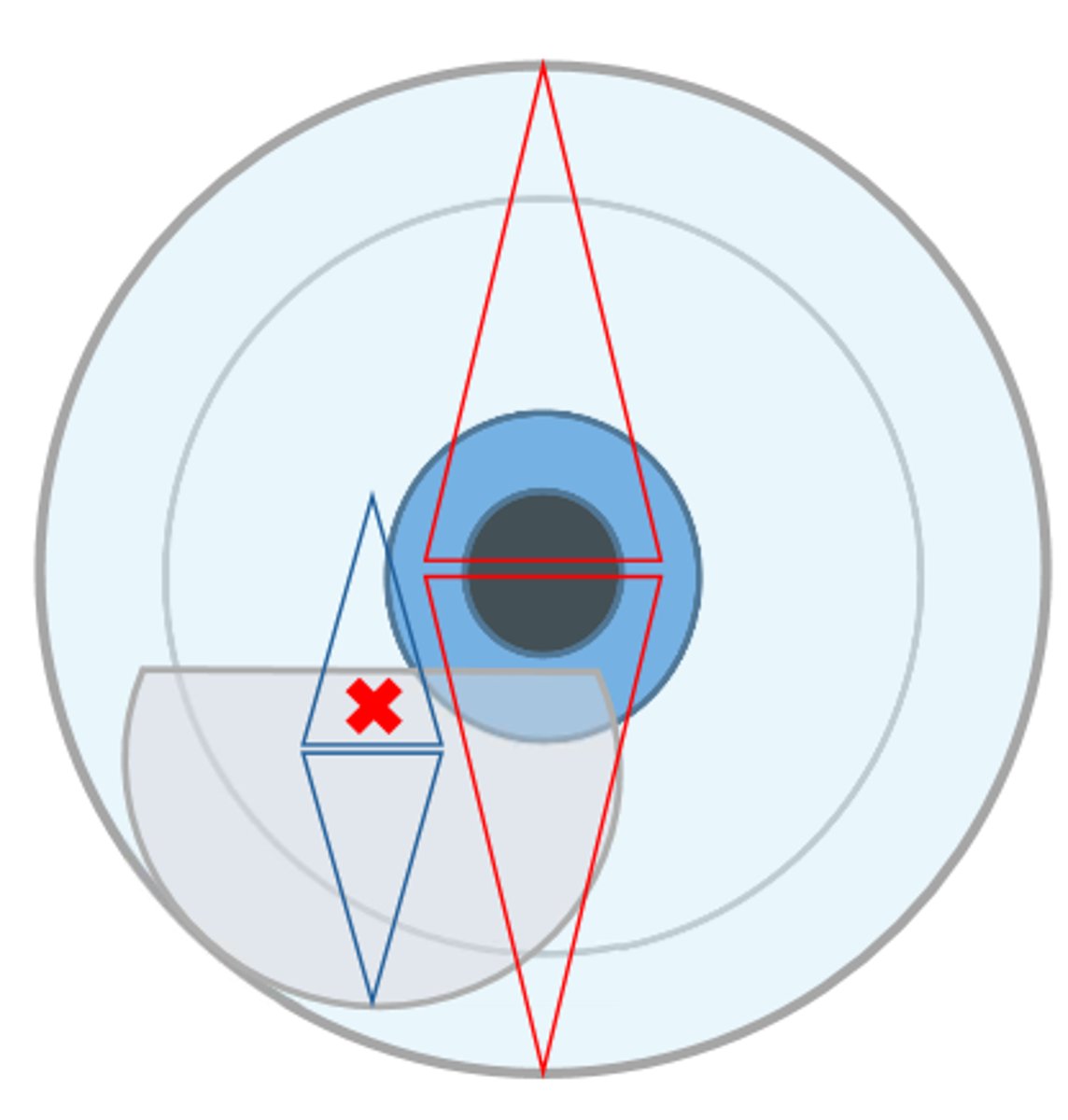
Image Jump
Most segments will induce an image jump UPwards when the viewer drops their gaze from the major lens to the bifocal
-The amount of the jump depends ONLY on the add power and the location of the segment OC.
Where is the image jump calculated?
at the top edge of the segment
Anisometropia
Difference in refractive error between the two eyes
-Because the refractive error is uneven, the prismatic effect (vertical or horizontal) when looking off-center is also uneven
-This means that the total image displacement experienced by each eye is uneven
Vertical imbalance rule of thumb
Consider possible vertical imbalance issues starting at 1.50 D anisometropia
ex: OD plano DS, OS +- 1.50 DS
Possible solutions to vertical imabalance
-Contact lenses
-Separate glasses
-Drop MRP height
-Raise seg height
-Fresnel prism
-Slab off
-Dissimilar segments
contact lenses
optical center of the contact moves with the eye
separate glasses
wearer can raise or lower the head to always look through the optical center of the glasses
Drop the MRP
If no prism RX, MRP = OC
-Drop the MRP to reduce distance from major lens OC to point of near vision
-Reduced near vertical imbalance by transferring some of the imbalance to distance
Raise the seg height
Similar in concept to dropping the MRP
-If seg height is raised without also raising the OC if the major lens, the distance between major lens OC and near vision is reduced
-Limit to how much seg can be raised
Fresnel (press-on) prism
Can be placed on the lower part of one lens to counteract imbalance
-A good way to trial symptom relief, but not a permanent solution
Slab-off
AKA bicentric grinding
-Removes BD prism from back of the more minus lens (in the 90 degrees meridian)
-Effective increase in BU in that area
Dissimilar segments
Use one seg type in one lens and a different one in the other
-Yields a different prismatic effect to correct the vertical imbalance
(looks werid)