Digital Marketing Exam 2
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
convert
final step where the user completes an action (purchase, sign up) affected by landing page quality
barriers to seeing an ad
user scrolls past
slow page load
poor placement
barriers to processing an ad
too much text
vague message
user distracted by page content
barriers to investigating an ad
weak value proposition
bad design
irrelevant offer
no CTA
Barriers to conversion
poor landing page
slow load times
technical issues
not ready to buy
importance of consistent messaging
matching ads and landing pages increases conversions
Interest-based targeting
Uses browsing history and online behavior to show relevant ads.
Limitation of interest-based targeting
Shared devices reduce targeting accuracy.
Keyword targeting
Ads appear on pages containing chosen keywords.
CPC (Cost Per Click)
Advertiser pays only when a user clicks the ad.
CPM (Cost Per Mille)
Advertiser pays per 1,000 impressions.
CPA (Cost Per Action)
Advertiser pays only when a conversion occurs.
Mobile ad issues
High bounce rates from accidental "fat-finger" clicks.
Three goals of banner design
Grab attention, show value proposition, include CTA.
Retargeting definition
Ads shown to users who previously visited your website.
Why retargeting works
Audience is already interested, so conversion rates are higher.
A/B testing definition
Comparing two ad versions to determine which performs better.
Metrics for A/B testing
CTR and conversion rate.
Why is email capture important?
Email marketing only works if a company has valid, permission-based email addresses.
What is the trade-off in email capture forms?
Short forms = higher conversion
long forms = more customer data.
What is double opt-in?
A sign-up method requiring email confirmation before being added to the list.
What is single opt-in?
An email is added immediately after entering the address without confirmation.
Why should customers know they're signing up for marketing emails?
To avoid spam complaints that damage email deliverability.
How often should companies send emails?
As often as they can create valuable content.
What is the most reliable segmentation variable?
Past purchases.
What is a broadcast email?
A scheduled email sent to all or part of a list.
What is a transactional email?
An email related to a purchase (order confirmation, shipping updates).
What is a triggered email?
An email sent based on user behavior (ex: abandoned cart).
What are onboarding emails?
A welcome series sent to new subscribers.
What is the most important part of an email?
The subject line.
What is list churn?
The rate of unsubscribing or inactive members leaving the list.
What is a hard bounce?
A fake or invalid email address.
What is a soft bounce?
An inbox that is full.
Three purposes of posting on social media
Create first-time customers; increase loyalty; supplement SEO.
Why paid ads outperform organic posting
Better targeting, higher engagement, more ad formats.
Reputation management purpose
Respond to conversations to build trust and avoid crises.
Five steps of a social media plan
Determine objective, choose platforms, plan content, distribute/promote, measure success.
Platforms for increasing loyalty
Instagram, Pinterest, Snapchat.
Best platforms for SEO posting
Facebook and X.
Best advertising platform
Facebook and Instagram due to targeting and reach.
Keywords to monitor
Company name, products, trademarks, executives, competitors, industry terms.
ORM (Online Reputation Management)
Managing how a brand is perceived online; PR for the internet.
Negative content locations
Review sites, scam sites, forums, press, activist pages, social media, blogs, info sites.
Emergency response 3 T's
Timeliness, transparency, and training.
Timeliness (crisis)
Respond quickly to influence media framing.
Transparency (crisis)
Admit mistakes and explain corrective actions.
Training (crisis)
Employees follow set protocols for complaints.
Creating positive content
Publishing useful brand-owned content to dominate search results.
Social media plan
Determine the objective
Plan the content
Distribute and promote content
Measure success
Why should brands use social media?
1) stimulate demand
2) shorten the sales cycle
3) create 2 way value
4) establishing a relationship
Why are mobile users considered more impatient than desktop users?
They prefer short, concise answers,
focus on top search results,
and want information that fits on their screens.
What is the difference between mobile "snacking" and desktop "feasting"?
Mobile users check their phones in many short sessions
desktop users have fewer, longer sessions.
Why are videos equally effective on mobile and desktop?
Videos are rich in information and easy to consume on both devices.
What are fat-finger clicks?
Accidental ad clicks on mobile apps, especially games, causing low-value traffic.
What are the three factors for choosing mobile bid modifiers?
Directed attention,
direct mobile purchasing,
and fat-finger clicks.
What is geo-fencing?
Targeting ads to mobile users within a specific radius of a location.
What role do mobile apps play in digital marketing?
They support customer service,
enhance loyalty,
and reduce service costs.
What is browser Bluetooth used for?
Indoor location tracking for navigation and in-store targeting.
Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO)
Testing website changes to increase conversion rates.
Affiliate Marketing
Affiliates earn commission for driving sales.
What are the three customer influence efforts?
Demand generation,
demand harvesting,
loyalty building.
What is demand harvesting?
Secure purchases from customers already wanting the product.
Product-Centric Demand Generation
Focuses on desire for the product category.
Brand-Centric Demand Generation
Focuses on features unique to the brand.
Why do returns diminish as spending increases?
Channels become saturated.
AI in Digital Advertising
Use of machine learning to allocate ad impressions for higher conversions and clicks.
AI Data Requirement
AI needs large amounts of data (impressions/clicks) to learn effectively.
Assigning Conversion Values for AI
Giving dollar values to conversions so AI prioritizes higher-value sales instead of simply more sales.
AI Attribution Problem
Difficulty determining which ad or channel actually caused a sale, worsened by AI optimization.
Generative AI in Ads
AI tools (like ChatGPT) that create ad copy, images, and ideas based on prompts.
Prompt Engineering
Crafting effective prompts to get better AI output by providing examples, context, and clarity.
SEO and AI
Using AI to draft content but requiring human editing to avoid penalties and improve quality.
One-to-One Personalization
Highly targeted messaging to individuals enabled by AI but limited by available customer data.
AI Bias
Unintentional replication of societal biases (racial, gender, etc.) found in the model's training data.
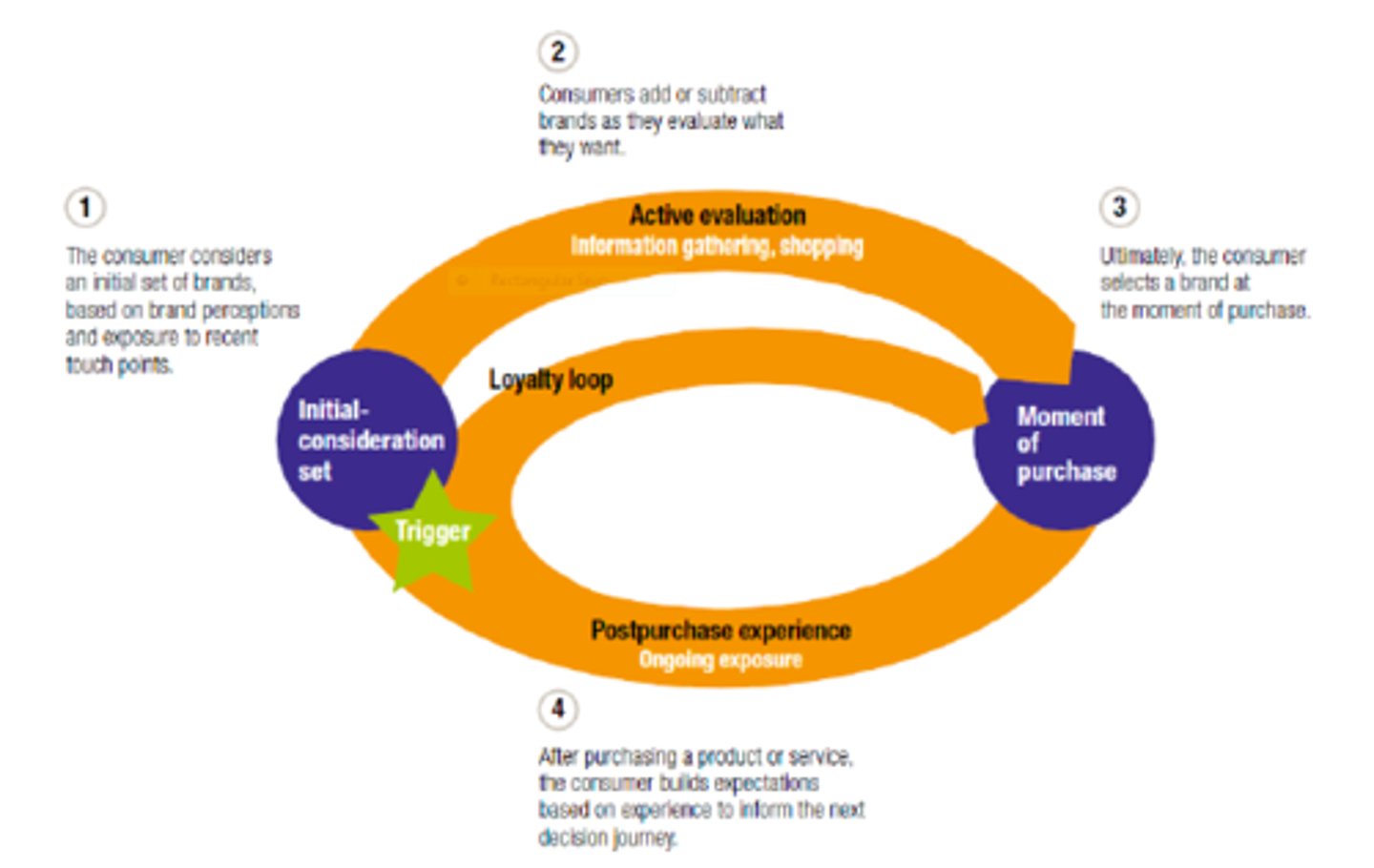
What are the steps of the consumer decision journey?
initial consideration set
active evaluation
moment of purchase
post-purchase experience
(loyalty loop)