AP Science Exam
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Part 1 - how do you calculate the number of Neutrons?
Atomic number minus Atomic mass
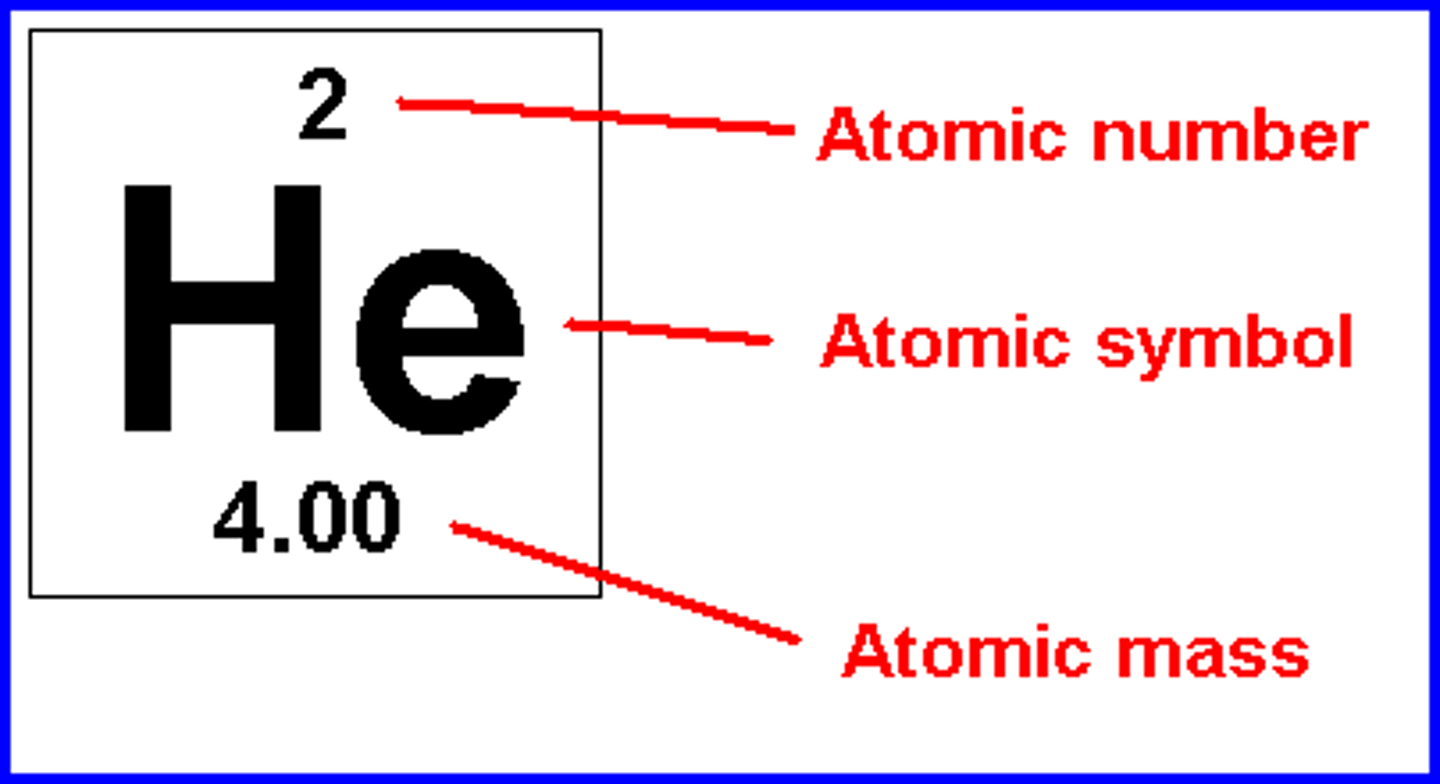
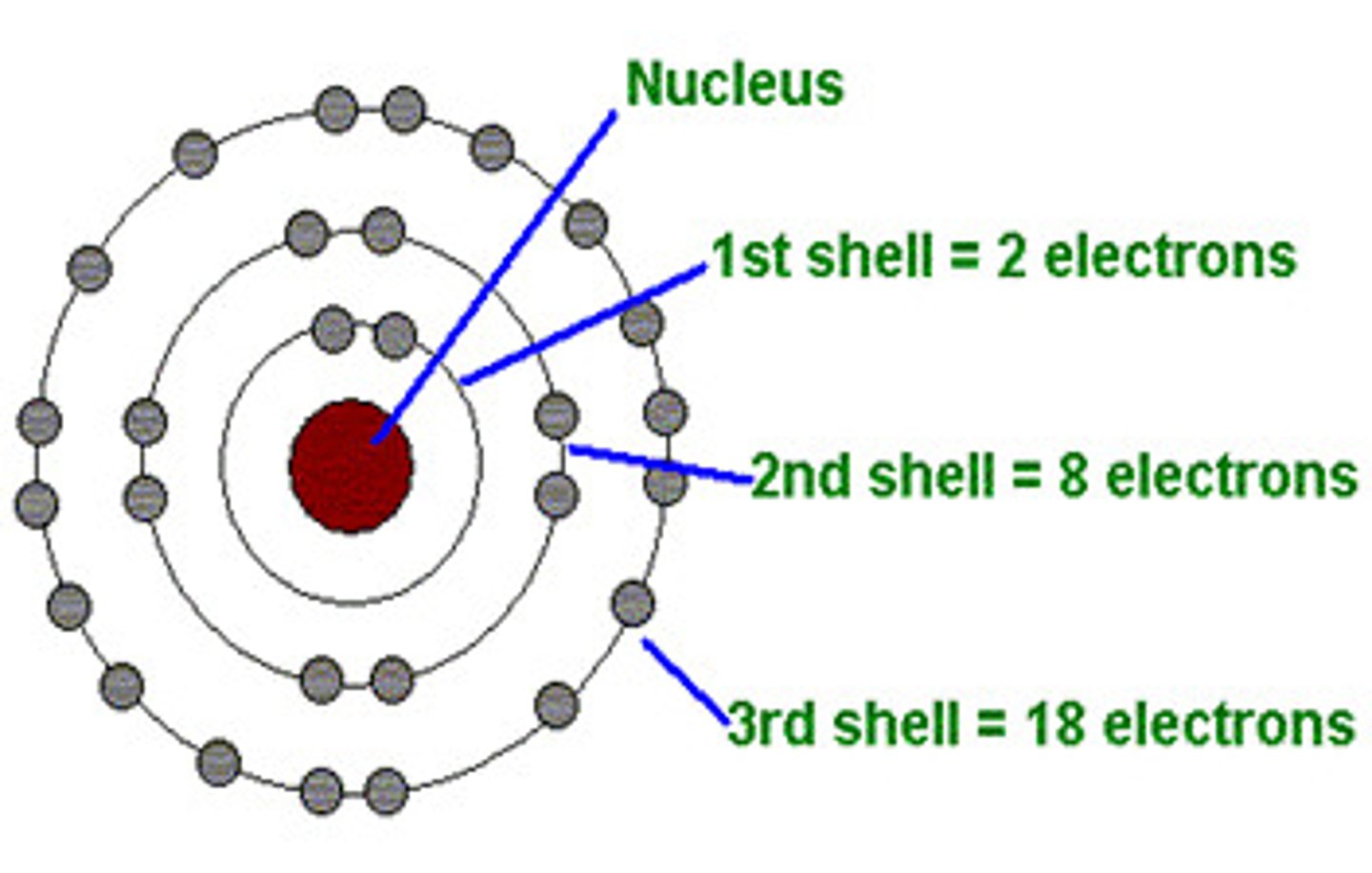
Part 1 - what does the bohr diagram show us? ( first 18 elements)
The diagram shows us the elements electrons, protons, neutrons, nucleus and shells
Part 1 - what does the lewis dot notation show us? ( first 18 elements )
The diagram shows us the number of (valence) electrons in the outermost shell
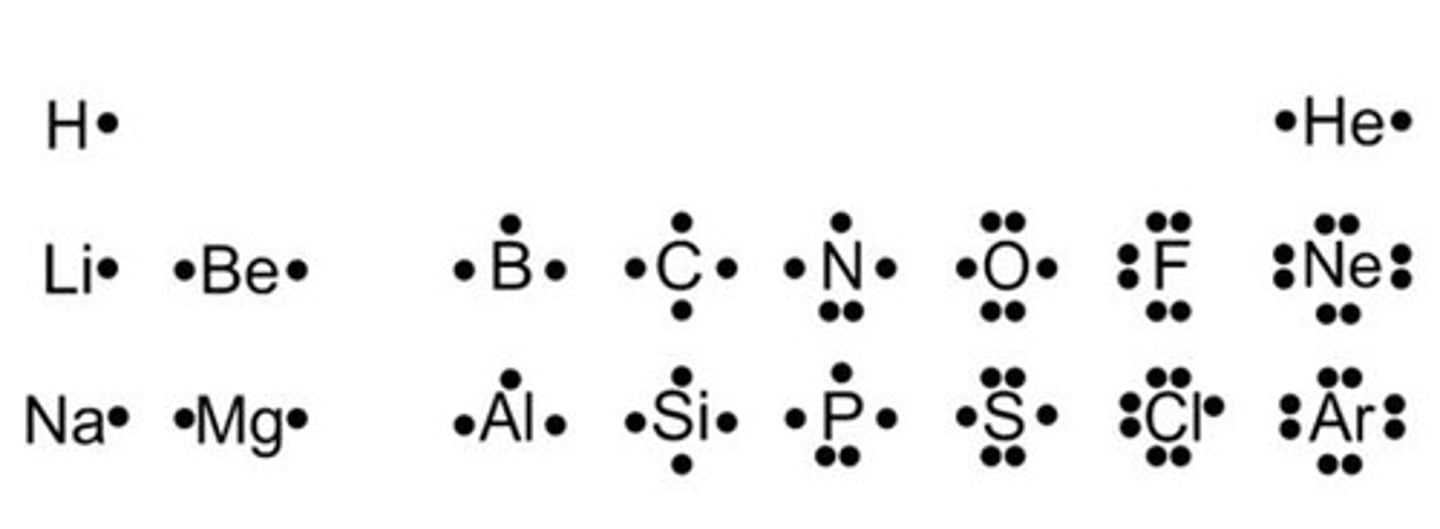
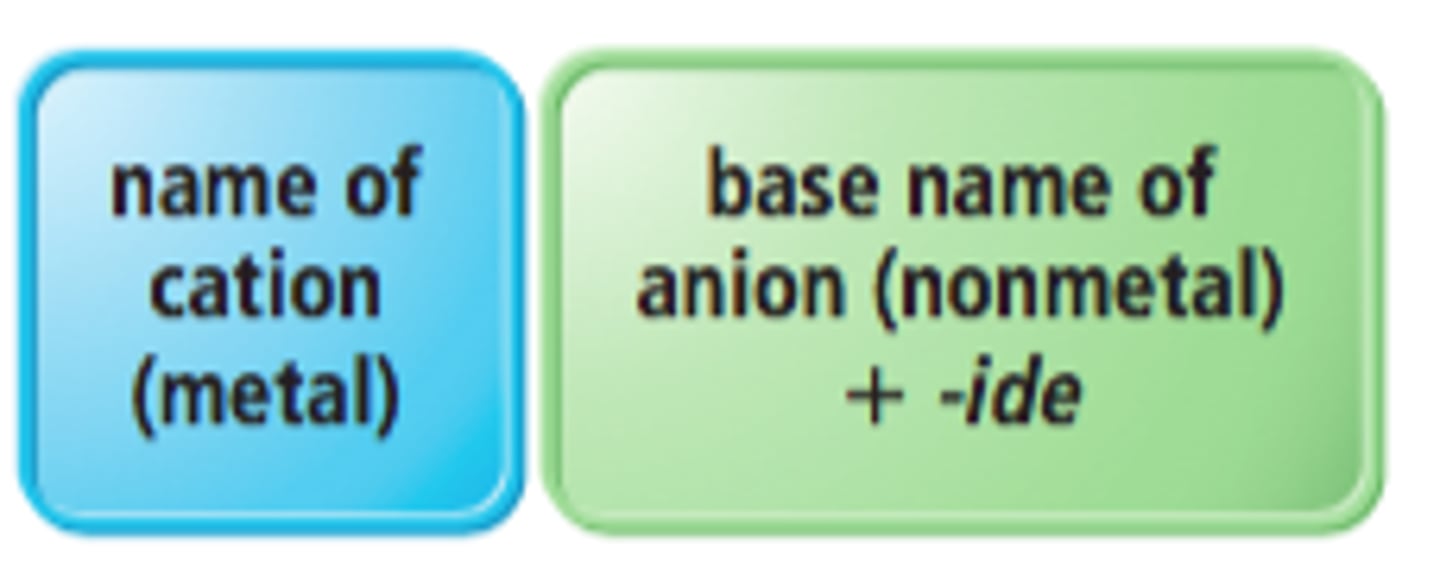
Part 1 - How do you name Ionic compounds?
The first element stays the same while the second one ends in ide
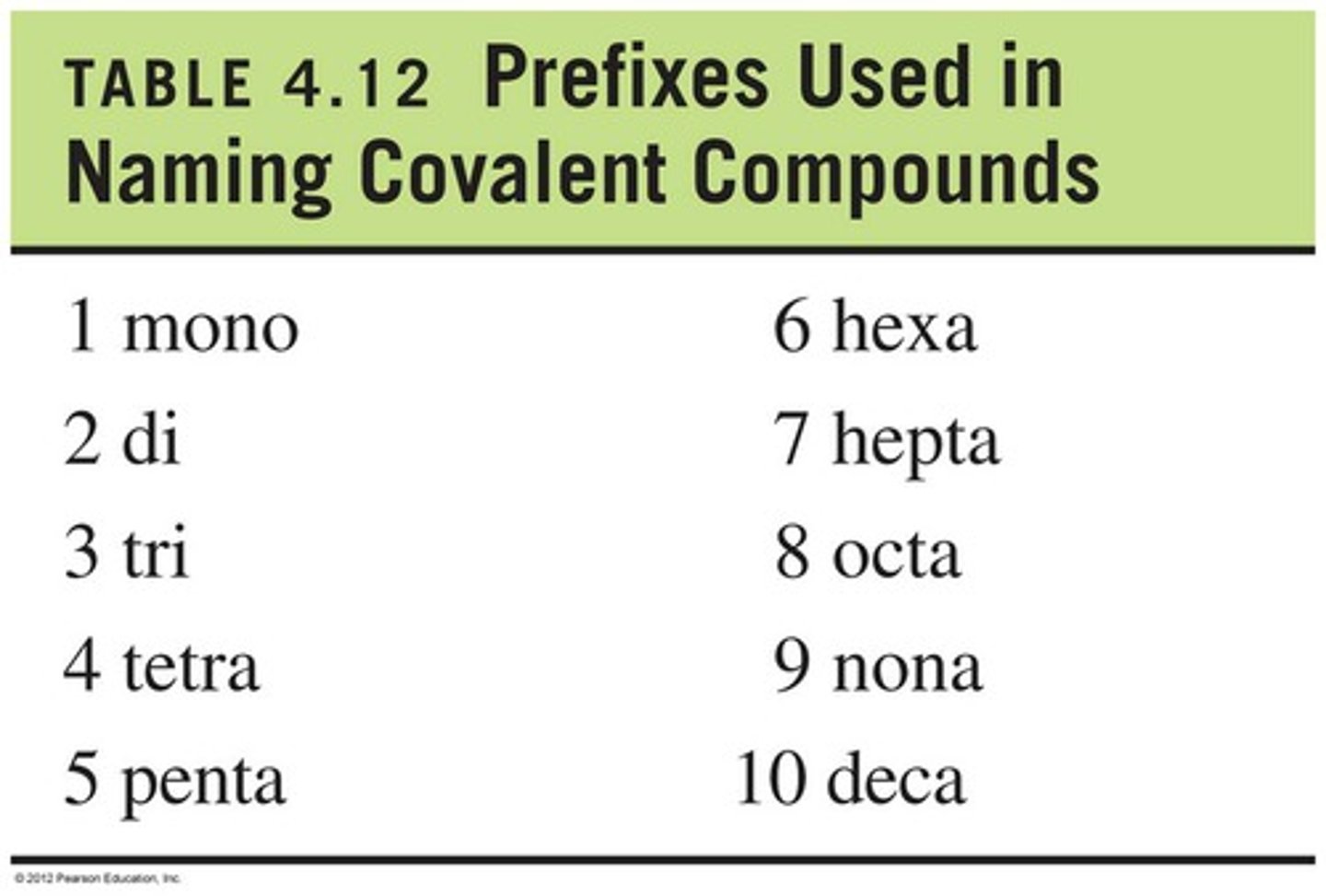
Part 1 - How do you name covalent ( molecular) compounds
Use the Latin numbers on both elements except when the first element has a one you do not use mono and the second element ends in ide
Part 1 - Types of reactions
Synthesis, Decomposition, Single Replacement, Double Replacement, Combustion
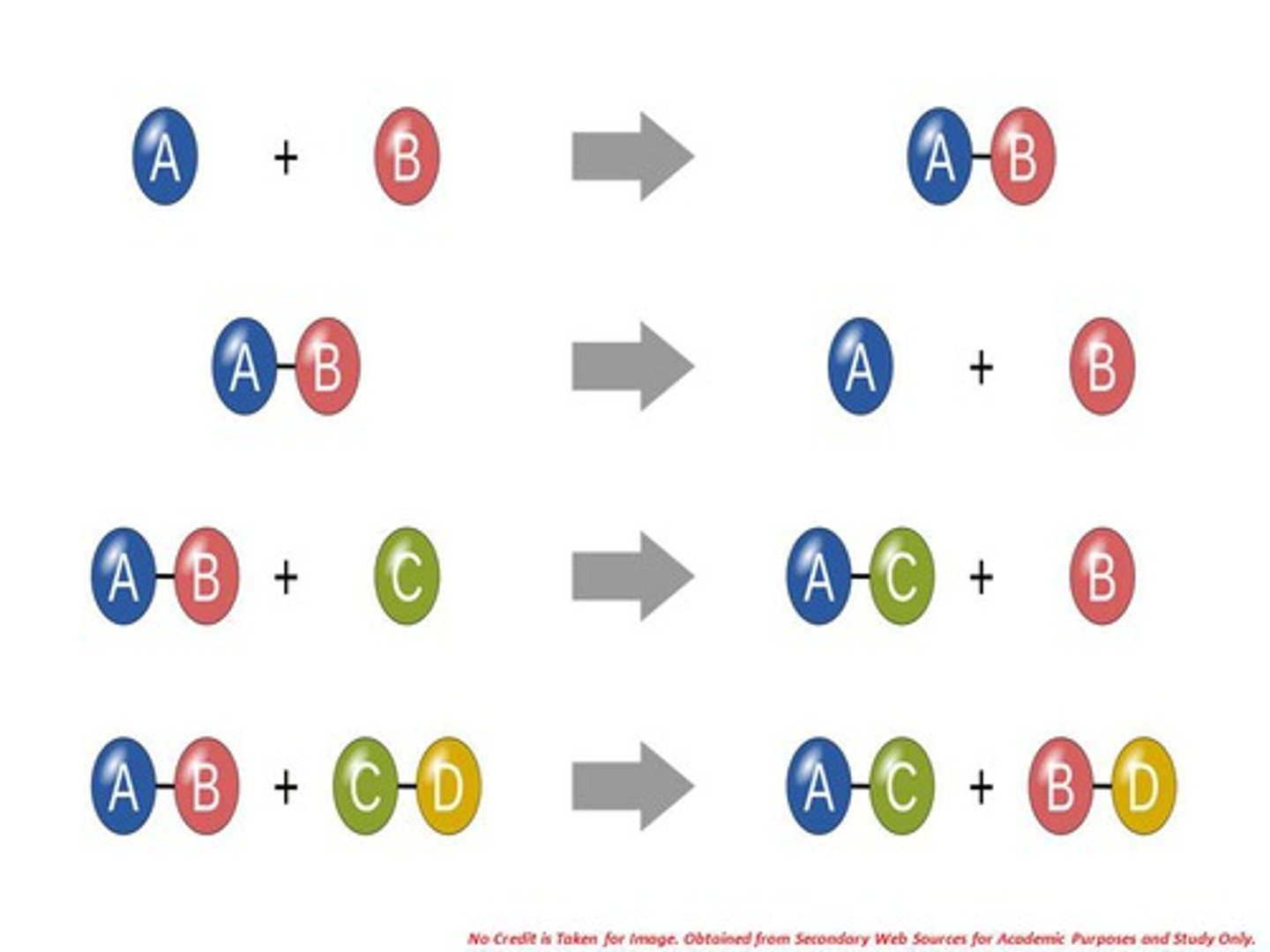
Part 1 - What happens during Synthesis?
making something new from two seperate thing (A + B = AB)
Part 1 -What happens during decomposition?
breaking down one thing into two (AB = A + B)
Part 1 - What happens during single replacement?
will edit
Part 1 - What happens during double placement?
will edit
Part 1 - What happens during combustion?
will edit
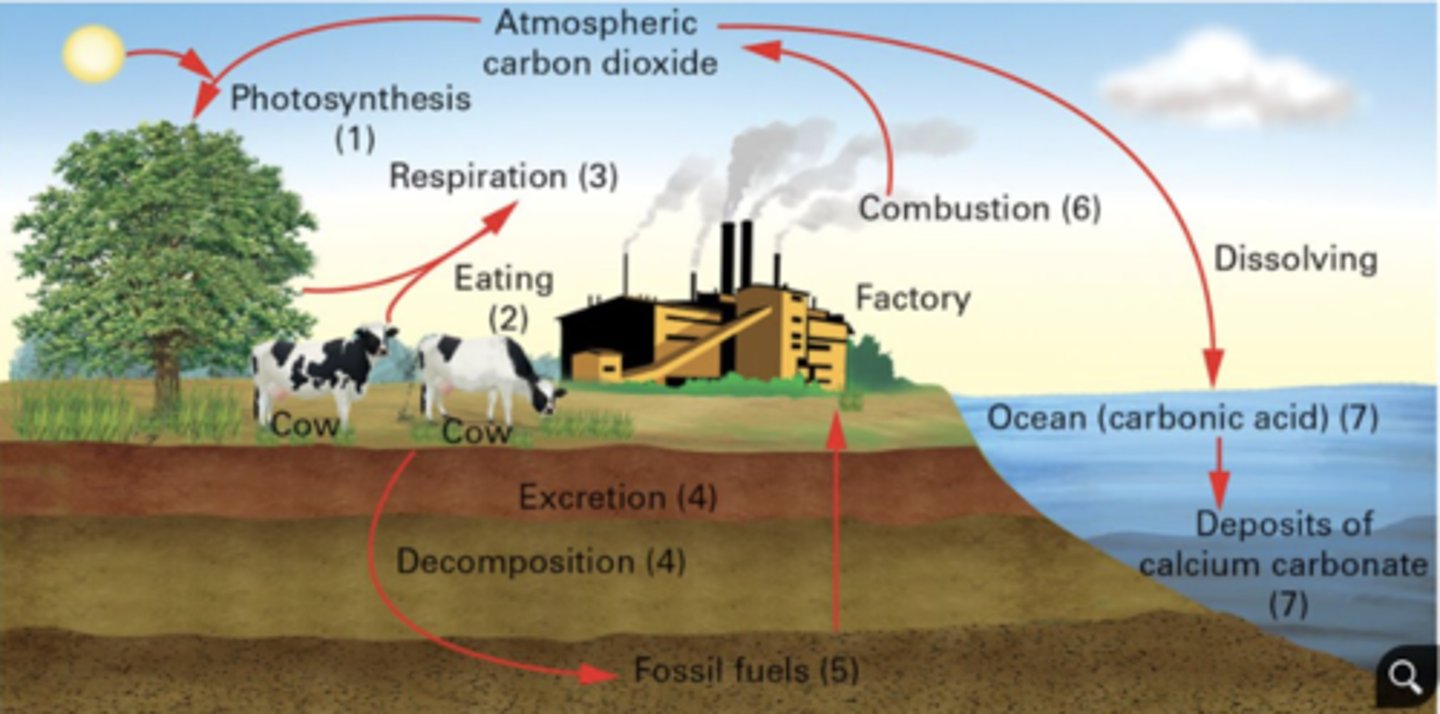
Part 2 - The cycle of the Carbon cycle
combustion( Burning of wood and fossil fuels by factory and auto emissions transfers carbon to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.), metabolism (Autotrophs convert carbon into organic molecules like fats, carbohydrates and proteins, which animals can eat.), cellular respiration (Animals eat plants for food, taking up the organic carbon (carbohydrates).
Plants and animals break down these organic molecules during the process of cellular respiration and release energy, water and carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is returned to the atmosphere during gaseous exchange. ), precipitate (Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere can also precipitate as carbonate in ocean sediments. ), decay (Carbon dioxide gas is also released into the atmosphere during the decay of all organisms.)
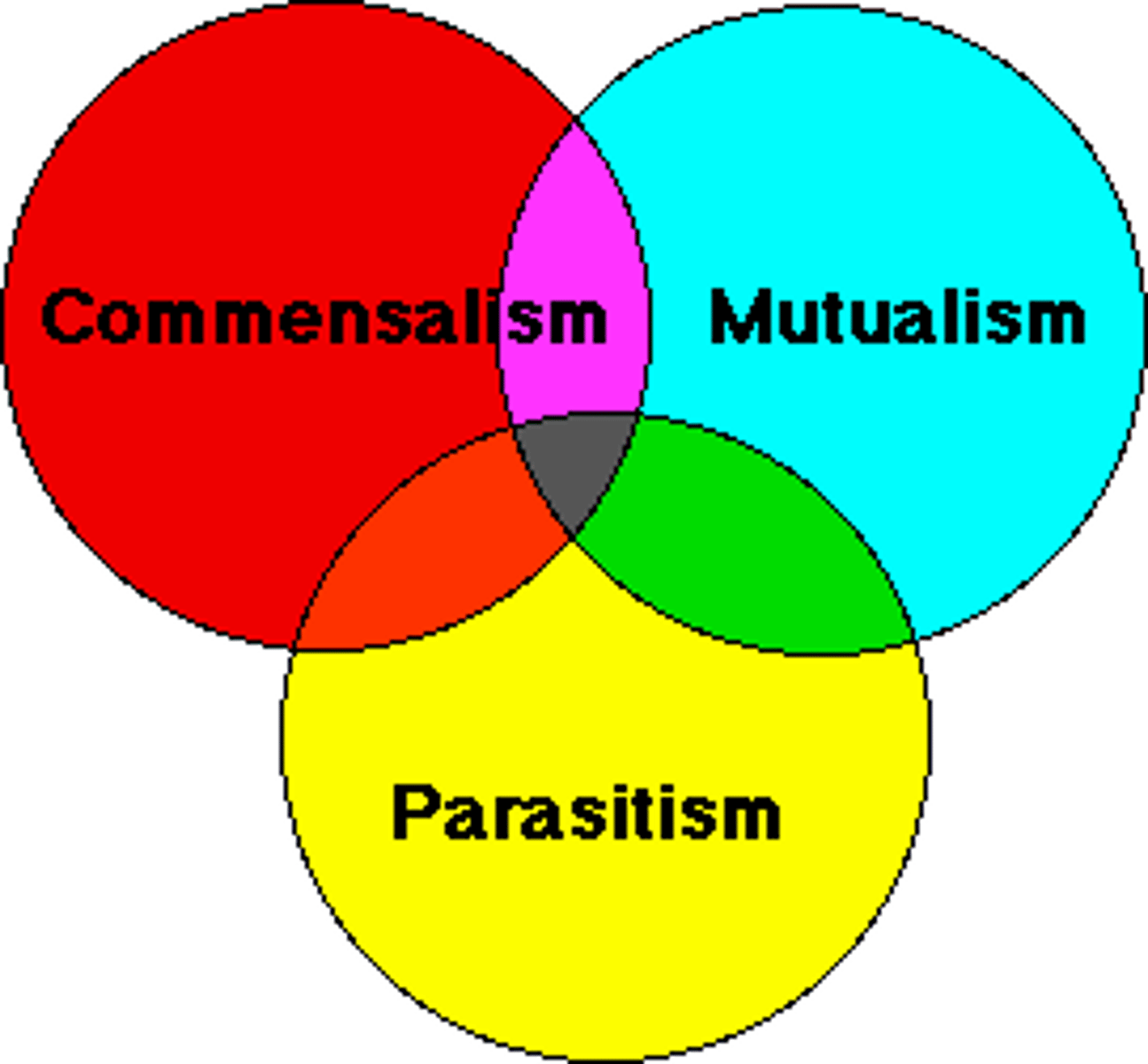
Part 2 - what are the 5 parts of symbiosis?
mutualism +/+ , commensalism +/0 and parasitism +/-, competition-/- or +/- and predation +/-
Part 2 - what are all three types of pyramids in ecosystems?
Pyramid of biomass, numbers and energy
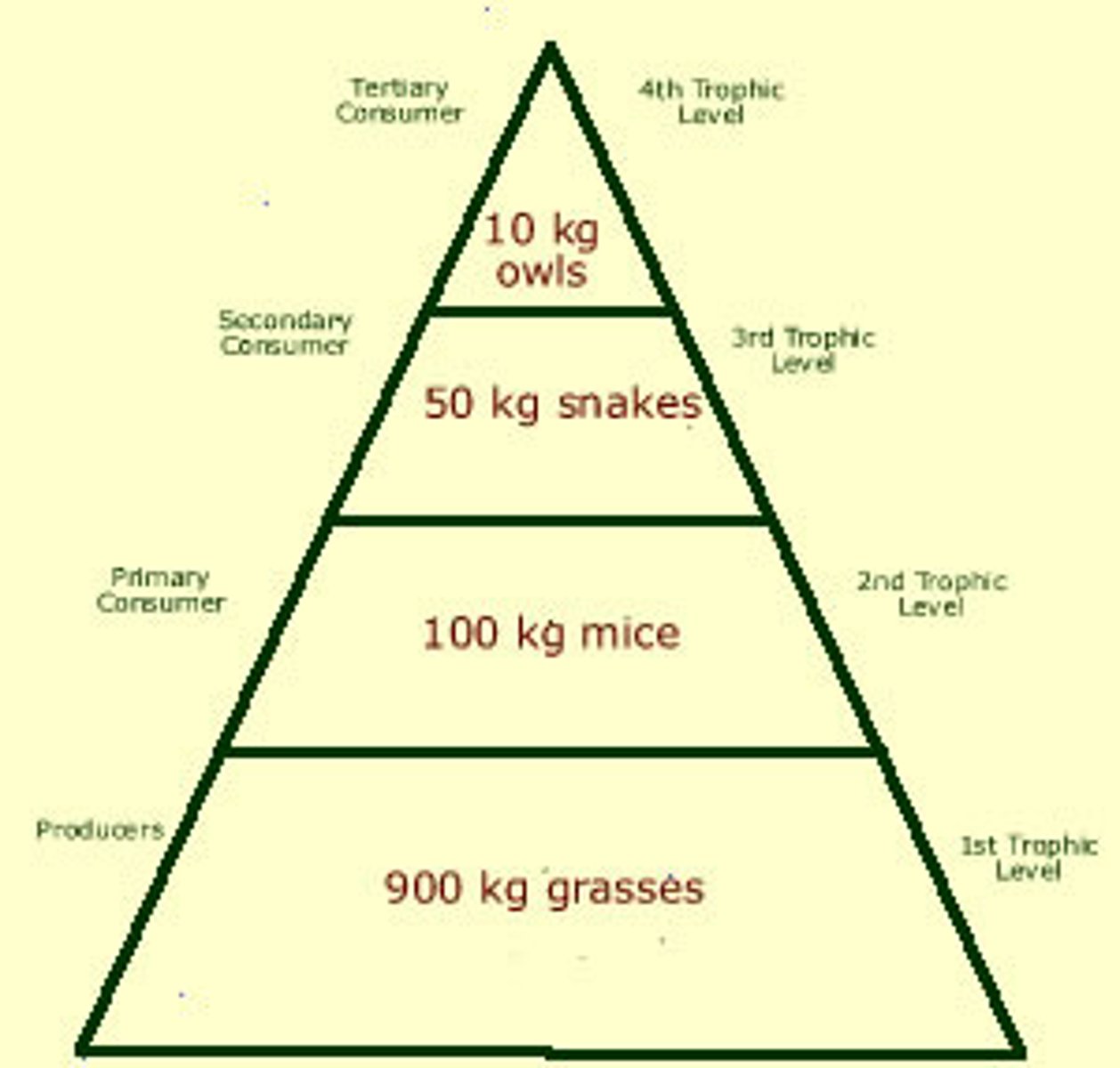
Part 2 - what does the pyramid of biomass show us?
the mass or weight of an animal or species without water in them
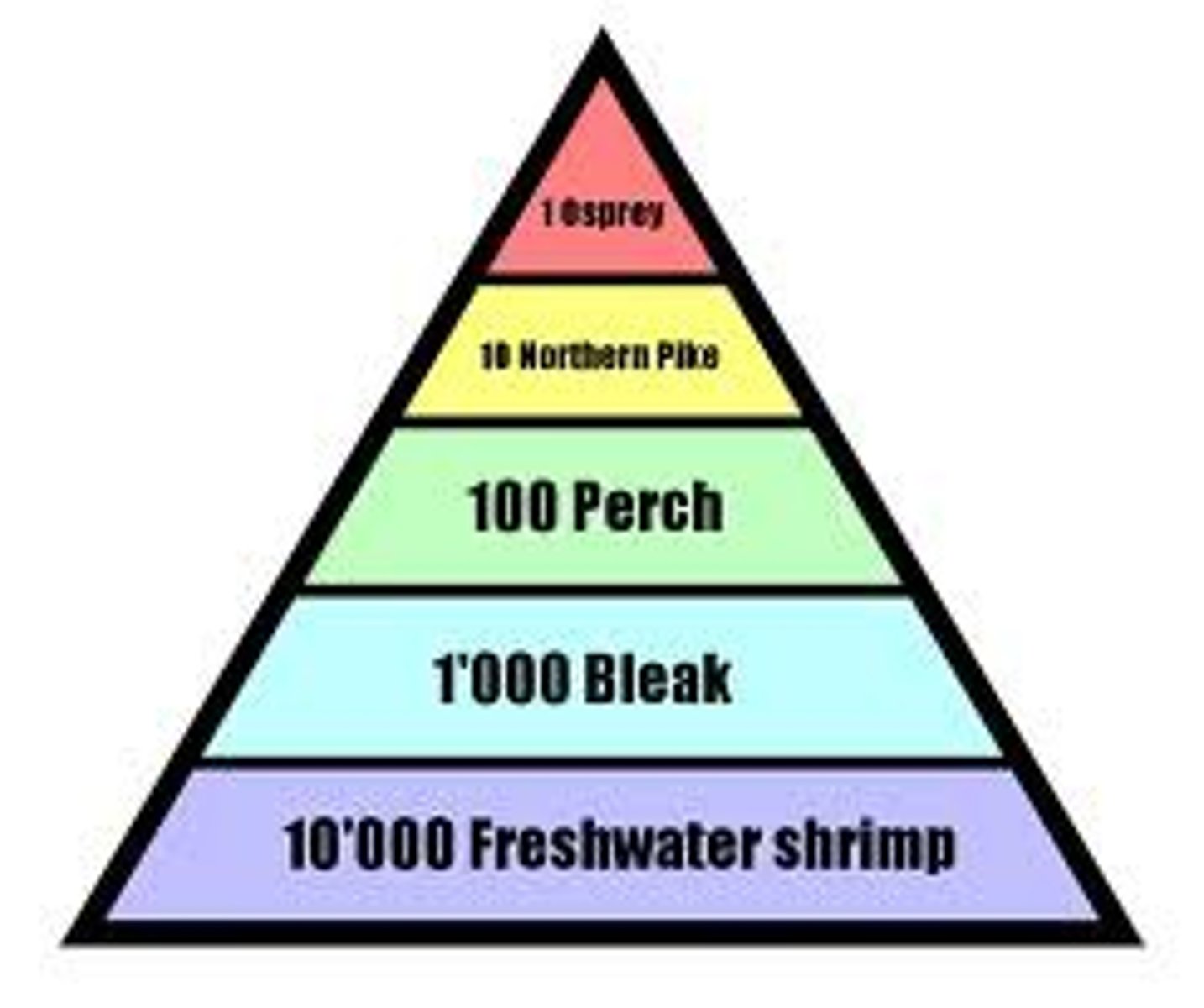
Part 2 - what does the pyramid of numbers show us?
representation of the number of individual organisms in each trophic level of an ecosystem
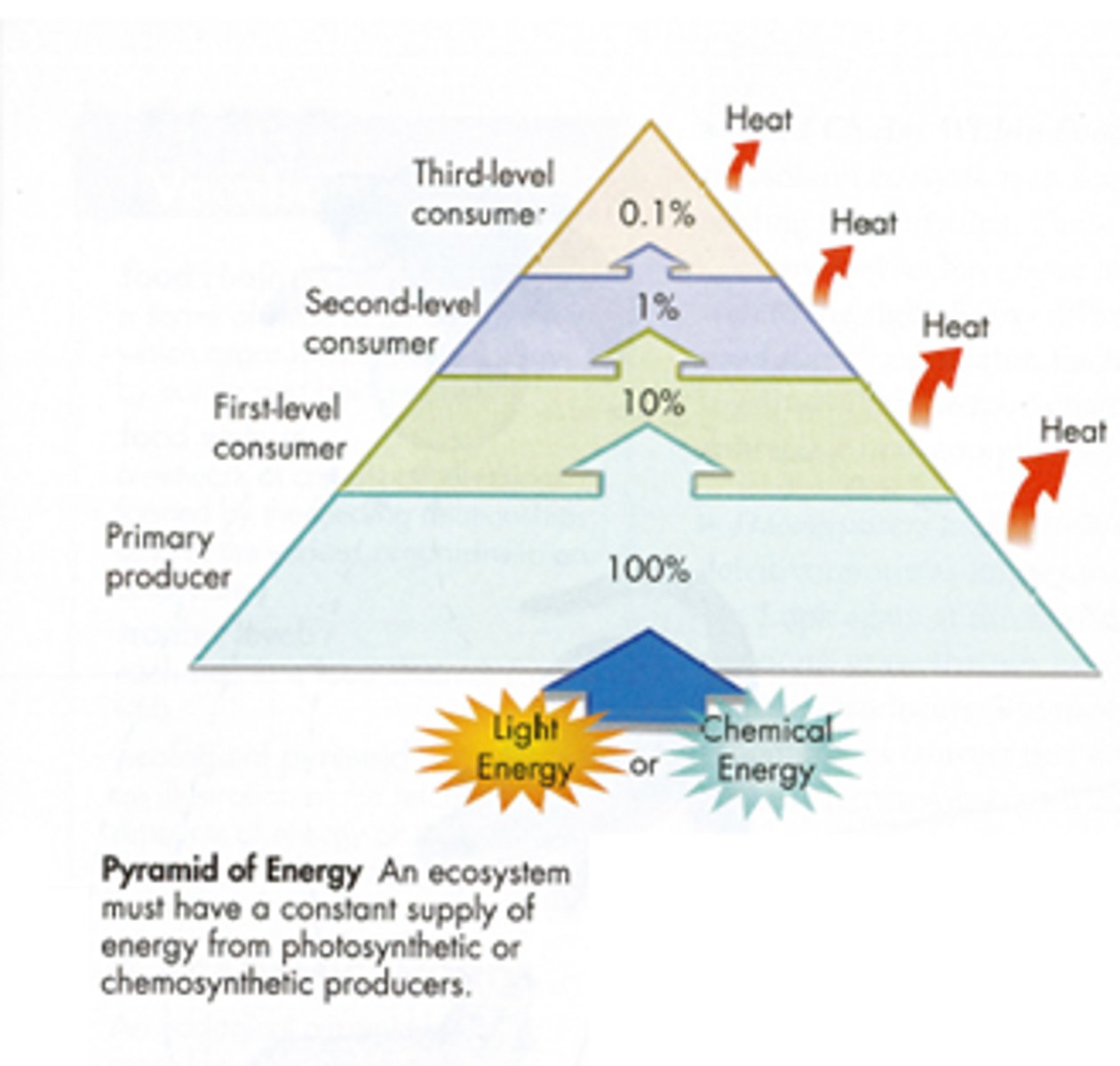
Part 2 - what does the pyramid of energy show us?
shows the total amount of energy available at each trophic level. 90% of all energy is lost between trophic levels.
Part 2 - What are the two categories of adaptation of animals and plants?
behavioural and structural
Part 2 - why does behavioural adaption happen?
this adaptation happens because of moving to a new environment, diurnally (animal behaviour characterized by the daytime) nocturnality ( animal behaviour characterized by the nighttime) or migration
Part 2 -examples of behavioural adaptation.
bears hibernation during winter, birds lining up in a pattern to fly some where during the winter ( migration)
Part 2 -why does structural adaption happen?
this happens because of protection for an animal or plant. over time an animal or plant change their looks to fit in or hide in there ecosystem.
Part 2 - examples and types of structural adaption.
polar bears white fur camouflage in the white snow, mimicry - butterflies mimic owl eyes so prey can't recognize them. for plants there are three types xerophytes, hydrophytes, and mesophytes
Part 2 - what are xerophytes?
means dry plant, they hold water in for a long time because the environment they live in is dry and rarely rains, they have Thick cuticle (prevent water loss) Modified leaves - spines, Fewer stomata, and Deep taproots or wide spreading fibrous roots near the soil surface(cacti, evergreen trees and succulent plant)
Part 2 - what are hydrophytes?
means water plants, live in aquatic environments and learnt how to grow in a place with alot of water with drowning, they have Thin cuticle, Large flat leaves on surface plants for flotation, Increased number of stomata, and Reduction in roots (H2O can diffuse directly into leaves) ( water lily)
Part 2 - what are mesophytes?
means middle/moderate plants, live in environments such as a garden, they have no specific morphological adaptations, Broad, flat, green leaves and Extensive fibrous root system ( clover)
Part 2 - what are biomes?
a specific ecosystem with a specific, climate, precipitation and temperature( tundra, grassland, savanna)