Neuro Tracts and Spinal Cord Lesions Foundations
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Tracts: Ascending
Posterior Column-Medial Lemniscal: ______ ______, __________ and ______
FC
FG
Spinothalamic (also called the ______ _______)
_____ and _____
_______ Tracts (Data only ascends to the ____)
Sensory receptors are specific to their ______
Sensory neuron cells bodies → _____
Dermatome: Peripheral region innervated by sensory fibers from a…
Posterior Column-Medial Lemniscal: Light touch (called ”fine, discriminative touch” in the book), proprioception and vibration
Fasciculus Cuneatus
Fasciculus Gracilis
Spinothalamic (also called the anterolateral system)
Pain and temp
Spinocerebellar Tracts (Data only ascends to the CB)
Sensory receptors are specific to their modality
Sensory neuron cells bodies → DRG
Dermatome: Peripheral region innervated by sensory fibers from a single nerve root level
Posterior Column-Medial Lemniscal
Dorsal Column: Fasciculi _____ (T6 and below) and ______ (Above T6)
Carries:
3 Neuron pathway
1. Begins at the _____ ______ (____ _____, ______ _____, ______ ____)
2. Ascends the ____ in the Fasciculus _____ or _____ and synapses in the _____ or _____ N of the Lower _____. _____ here to ascend via the _____ ______
Ends in the _____ _____ ______
Dorsal Column: Fasciculi Gracile (T6 and below) and Cuneate (Above T6)
Carries light touch, proprioception and vibration
3 Neuron pathway
1. Begins at the nerve endings (muscle spindle, Pacinian Corpuscle, Ruffini Ending)
2. Ascends the SC in the Fasciculus Cuneate or Gracile and synapses in the Gracile or Cuneate N of the Lower Medulla. CROSSES here to ascend via the MEDIAL LEMNISCUS
Ends in the Post central Gyrus (Sensory association area, 3,1,2)
Spinothalamic (AKA: anterolateral)
Carries
3 Neuron pathway
Begins at the nerve endings (____ _____, ______ _____ _____)
ALL axons enter the central ____ matter and CROSS over via the ____ _____ _____.
These axons ascend via the ____ pathway
Continues to the
Carries pain, temp and gross or crude touch
3 Neuron pathway
Begins at the nerve endings (Merkel’s Receptor, Bare nerve ending)
ALL axons enter the central gray mater and CROSS over via the Anterior Gray Commissure. So they cross at the level they enter.
These axons ascend via the Spinothalamic pathway
Continues to the Post central Gyrus (Sensory association area, 3,1,2)
Incoming sensory data from the external world enters the CNS via receptors
There are (5) functional types of receptors:
Mechanoreceptors: Respond to ….
Thermoreceptors: Respond to changes in ….
Nociceptors: Respond to any stimulus that might cause ____ _____ → usually referred to as ____ ______
Electromagnetic Receptors: ____ and ____ of the eyes
Chemoreceptors: Responsible for chemical changes associated with …
Incoming sensory data from the external world enters the CNS via receptors
There are (5) functional types of receptors:
Mechanoreceptors: Respond to mechanical deformation **
Thermoreceptors: Respond to changes in temperature
Nociceptors: Respond to any stimulus that might cause tissue damage → usually referred to as pain receptors **
Electromagnetic Receptors: Rods and cones of the eyes
Chemoreceptors: Responsible for chemical changes associated with taste and smell AND O2/Co2 changes in the blood
Lateral Corticospinal Tract (LCST)
Most clinically important ____ pathway
Controls movements of the _____
Approx 70% originates in the _____ _____ _____ (Area _)
Remainder originates in ___-___ area (Area _)
85% of descending motor fibers come from the ______
The LCST is ______, crossing at the level of the ____ (Known as the ______ _______)
Most clinically important motor pathway
Controls movements of the extremities
Approx 70% originates in the primary motor cortex (Area 4)
Remainder originates in pre-motor area (Area 6)
85% of descending motor fibers come from the LCST
The LCST is CONTRALATERAL, crossing at the level of the medulla (Known as the medullary pyramids)
Lateral Corticospinal Tract (LCST): Path
Arises from _______ (______ _____)
Exit via ____ root to form the ____ portion of the Spinal Nerve
Somatotopic organization: ____ more Lateral than ____
Arises from cortex (internal capsule)
Exit via ventral root to form the motor portion of the Spinal Nerve
Somatotopic organization: LE more Lateral than UE
Anterior Corticospinal (ACST)
Controls ______ movement
15% of descending motor fibers come from the _____
The ACST is ______ – fibers never _____
arises from _______
Exit via _____ root to form the ____ portion of the Spinal Nerve
Controls proximal movement
15% of descending motor fibers come from the ACST
The ACST is IPSILATERAL – fibers never cross
arises from cortex (internal capsule)
Exit via ventral root to form the motor portion of the Spinal Nerve
New cards
Lesion Game: Is weakness ipsilateral or contralateral?
Cortex
Internal Capsule
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla
S Cord
Cortex- contralateral
Internal Capsule- contralateral
Midbrain- contralateral
Pons- contralateral
Medulla-
superior- contralateral
inferior- ipsilateral after crossing
S Cord- ipsilateral
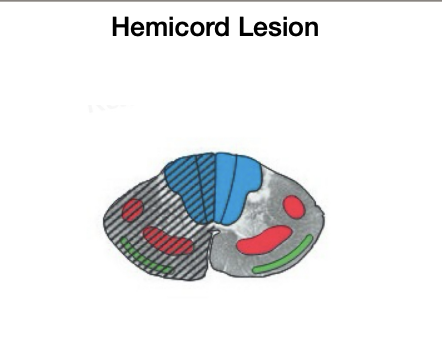
Hemicord lesion
_______ ______ loss of proprioception, light touch, and vibration + motor
________ _______ loss of pain, temp, crude touch
SAME SIDE loss of proprioception, light touch, and vibration + motor
OPPOSITE SIDE loss of pain, temp, crude touch
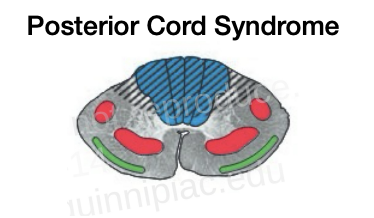
Posterior cord syndrome
______ _____ of proprioception, light touch, and vibration _______
Total loss of proprioception, light touch, and vibration bilaterally
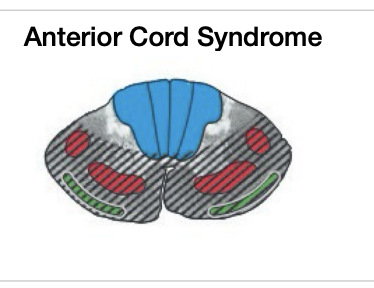
Anterior cord syndrome
total loss of
total loss of motor and pain, temp, crude touch bilaterally